[/caption]
Opportunity, the Princess of Martian Robots, phoned home dusty new self portraits – above and below – of her beautiful bod basking in the utterly frigid sunshine during her 5th winter on the Red Planet whilst overlooking a humongous crater offering bountiful science.
NASA’s endearing robot is simultaneously carrying out an ambitious array of ground breaking science experiments this winter – providing insight into the mysterious nature of the Martian core – while sitting stationary until the energy augmenting rays of the springtime Sun shower down on Mars from the heavens above.
Opportunity’s current winter worksite is located at the rim of the vast crater named Endeavour, some 14 miles (22 kilometers) in diameter. The robot will remain parked for the winter on a slope at the north end of the crater rim segment called Cape York with an approximate 15-degree northerly tilt towards the life-giving sun to maximize solar energy production. The park-site is at an outcrop dubbed “Greeley Haven”, named in honor of Ronald Greeley, a beloved and recently deceased science team member.
The power killing dust buildup is readily apparent on the solar arrays and High Gain Antenna pictured in the new panoramic self-portraits of Opportunity’s wing-like deck. The red Martian dust also functions as a rather effective camouflage agent, sometimes blending the rover to near invisibility with the surface.
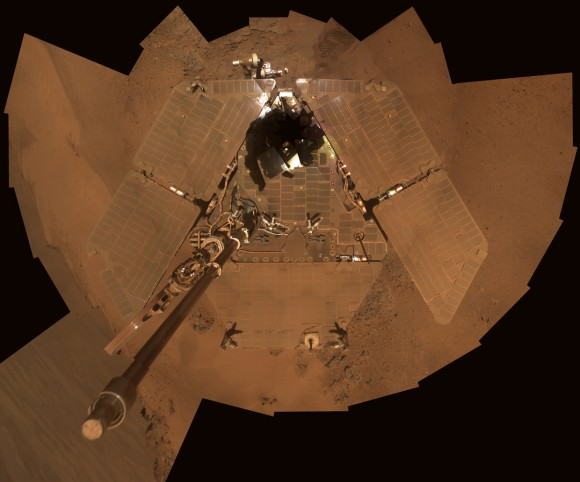

NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows dust accumulation on the rover's solar panels as the mission approached its fifth Martian winter at the rim of Endeavour Crater. Opportunity is located on the north-facing slope of a site called "Greeley Haven." This is a mosaic of images taken by Opportunity's panoramic camera (Pancam) during the 2,811th to 2,814th Martian days, or sols, of the rover's mission (Dec. 21 to Dec. 24, 2011). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/Arizona State Univ.
Indeed because Opportunity is covered with a thicker film of dust compared to her prior four Martian winters, the rover team was forced to employ the same “tilting” strategy they successfully used to keep her twin sister Spirit alive during her trio of Antarctic-like winters. This is the first winter that Opportunity did not have sufficient power to continue roving across the surface.
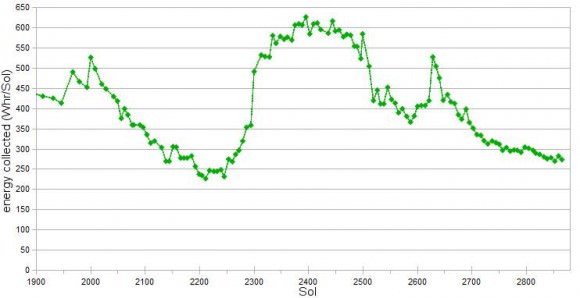
Since Opportunity is located just south of the Martian equator, the daylight hours for solar power generation are growing shorter until the southern Mars winter solstice occurs on March 30, 2012. As of mid- February 2012, the latest measure of solar array energy production was 274 watt-hours, compared to about 900 watt-hours at the start of the mission. See Solar Power energy graph below.
Power generation from the solar arrays has fluctuated up and down throughout Opportunity’s lifetime depending on when the completely unpredictable and fortuitous Martian wind storms chance by and miraculously clean the arrays of the rusty red dust.
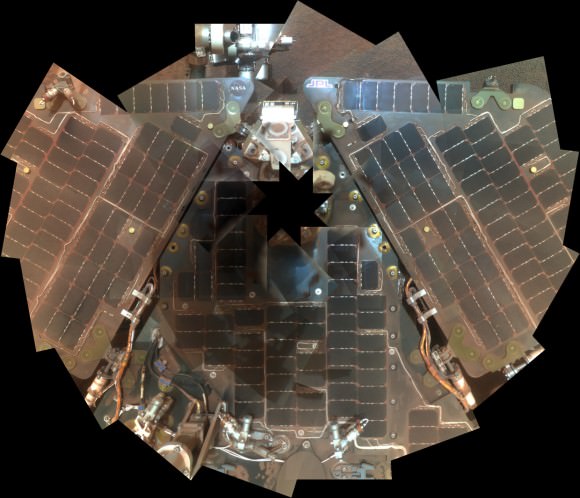

Opportunity used its panoramic camera (Pancam) during the mission's sols 1282 and 1284 (Sept. 2 and Sept. 4, 2007) to take the images combined into this mosaic view of the rover. The downward-looking view omits the mast on which the camera is mounted.The deck panorama is presented in approximate true color, the camera team's best estimate of what the scene would look like if humans were there and able to see it with their own eyes.Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell
The rover science team is ingeniously using the lack of movement to their advantage and Opportunity is still vigorously hard at work doing breakthrough research each and every day.
From her stationary position, Opportunity is conducting her first ever radio science Doppler tracking measurements to support geo-dynamic investigations and to elucidate the unknown structure of the Martian interior and core. The team was eager for the long awaited chance to carry out the radio tracking experiment with the High Gain Antenna (HGA) and determine if Mars core is liquid or solid. Months of data collection are required while the rover stays stationary.
“This winter science campaign will feature two way radio tracking with Earth to determine the Martian spin axis dynamics – thus the interior structure, a long-neglected aspect of Mars,” Ray Arvidson told Universe Today. Arvidson, of Washington University in St. Louis, is the deputy rover Principal Investigator.
Opportunity has nearly finished snapping the 13 filter, 360 degree stereo Greeley” panorama. The rover deployed the robotic arm onto the surface of the “Amboy” outcrop to collect multi-sol integrations with the Mössbauer Spectrometer and the largest ever mosaic campaign using the Microscopic Imager.
“We’ll do good science while we’re at Greeley Haven. But as soon as we catch a wind gust or the seasons change, we’ll be on our way again,” Steve Squyres told Universe Today. Squyres, of Cornell University is the rover Science Principal Investigator
“The Martian southern winter solstice occurs at the end of March. A few months after that date we will drive her off the outcrop and further explore Cape York,” Arvidson told me
The team will drive Opportunity in search of further evidence of the gypsum mineral veins like “Homestake” – indicative of ancient water flow – previously discovered at Cape York. Thereafter they’ll rove further south to investigate deposits of phyllosilicates, the clay minerals which stem from an earlier epoch when liquid water flowed on Mars eons ago and perhaps may have been more favorable to sustaining life.

Opportunity is now well into her 9th year exploring hitherto unknown terrain on Mars, far exceeding anyone’s expectation. She landed inside a tiny crater on Jan. 24. 2004 for what was expected to be a mission of merely 90 Martian days, or Sols.
Today is Martian Sol 2873, that’s 32 times beyond the rover designers “warranty” for NASA’s Opportunity rover.
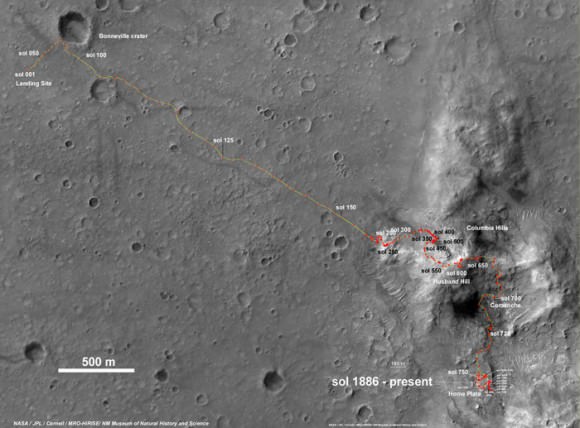
Altogether, Opportunity has journeyed more than 21 miles (34 kilometers) across the Red Planet’s surface, marking the first overland expedition on another Planet. See our route map below.
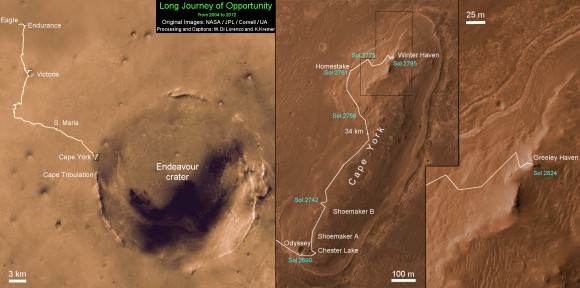
Traverse map shows the 8 Year Journey of Opportunity from Eagle Crater landing site on Sol 1- Jan. 24, 2004 - to 5th Winter Haven worksite at Greeley Haven at Endeavour Crater rim in January 2012. Opportunity embarked on a crater tour and discovered bountiful evidence for the flow of liquid water on Mars billions of years ago. Endeavour Crater is 14 miles 22 kilometers) in diameter. Opportunity has driven more than 21 miles (34 km). Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/UA/Marco Di Lorenzo/Kenneth Kremer
Meanwhile, NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory rover is rocketing through space and on course for a pinpoint touchdown inside the layered terrain of Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. Curiosity is now America’s last planned Mars rover following the cancellation of the joint NASA/ESA ExoMars rover mission in the Obama Administrations newly announced Fiscal 2013 NASA budget.