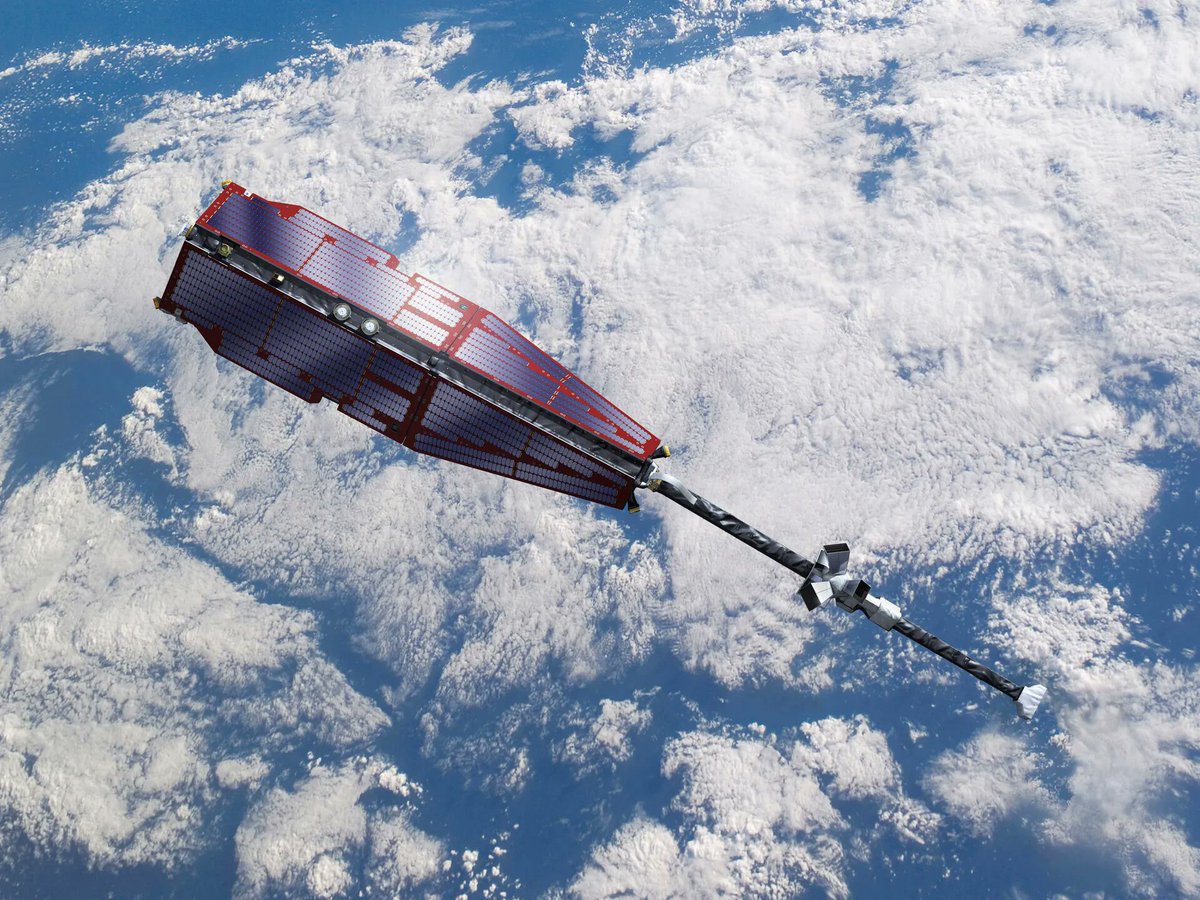
The phrase “when it rains, it pours” is commonly used in the US to denote that bad things usually happen simultaneously. And it doesn’t only have to apply to things that happen where it can physically rain. Recently an ESA satellite had a series of bad things happen that could potentially have happened to it, but quick action from the team responsible for the satellite avoided two what could have been catastrophic events.
Continue reading “A Satellite had to Dodge Space Junk as it was Raising its Orbit to Avoid Solar Activity”Engineers Build a gun That can Fire Projectiles at 10 km/s, Simulating High-Speed Space Debris Impacts
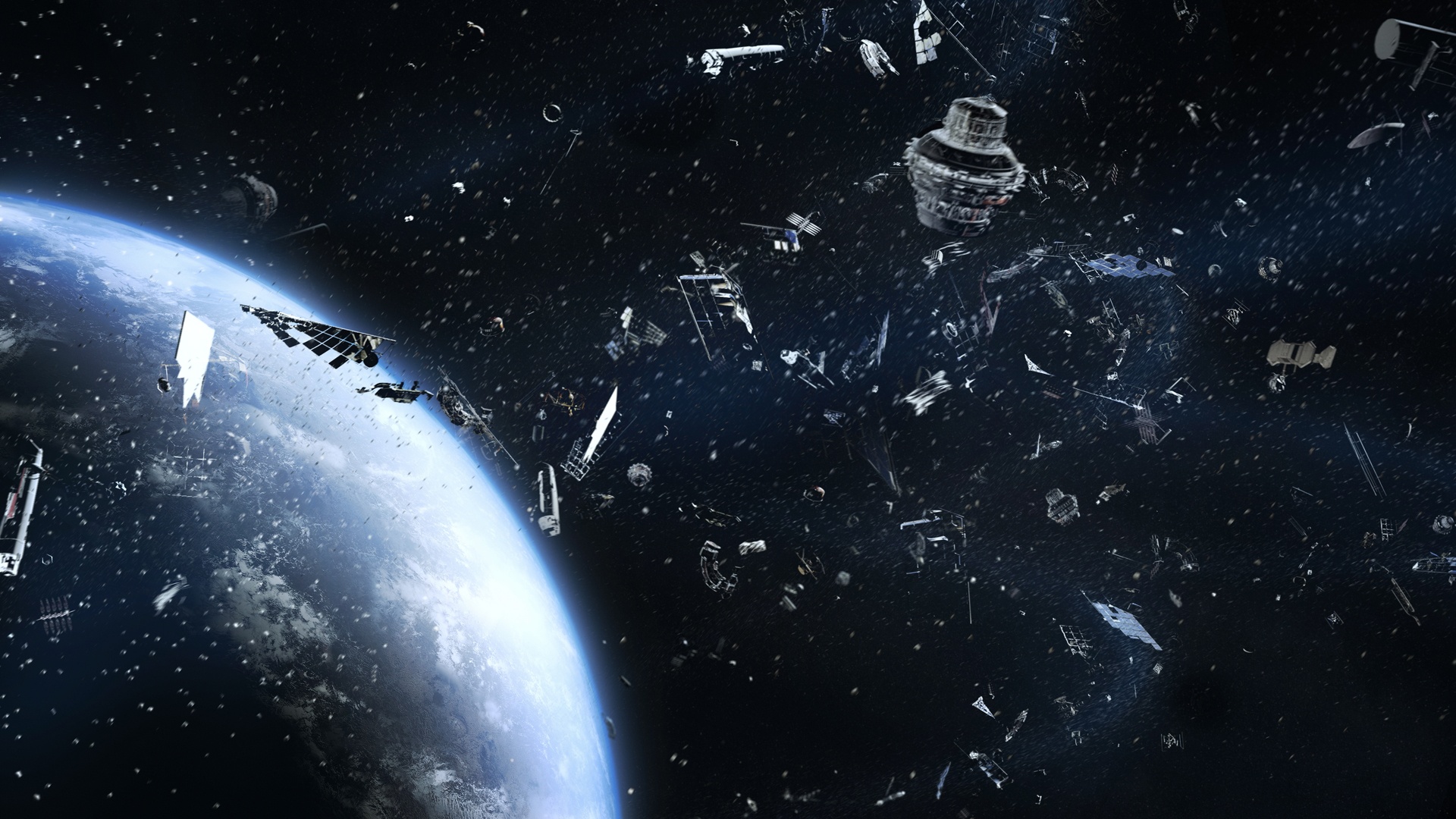
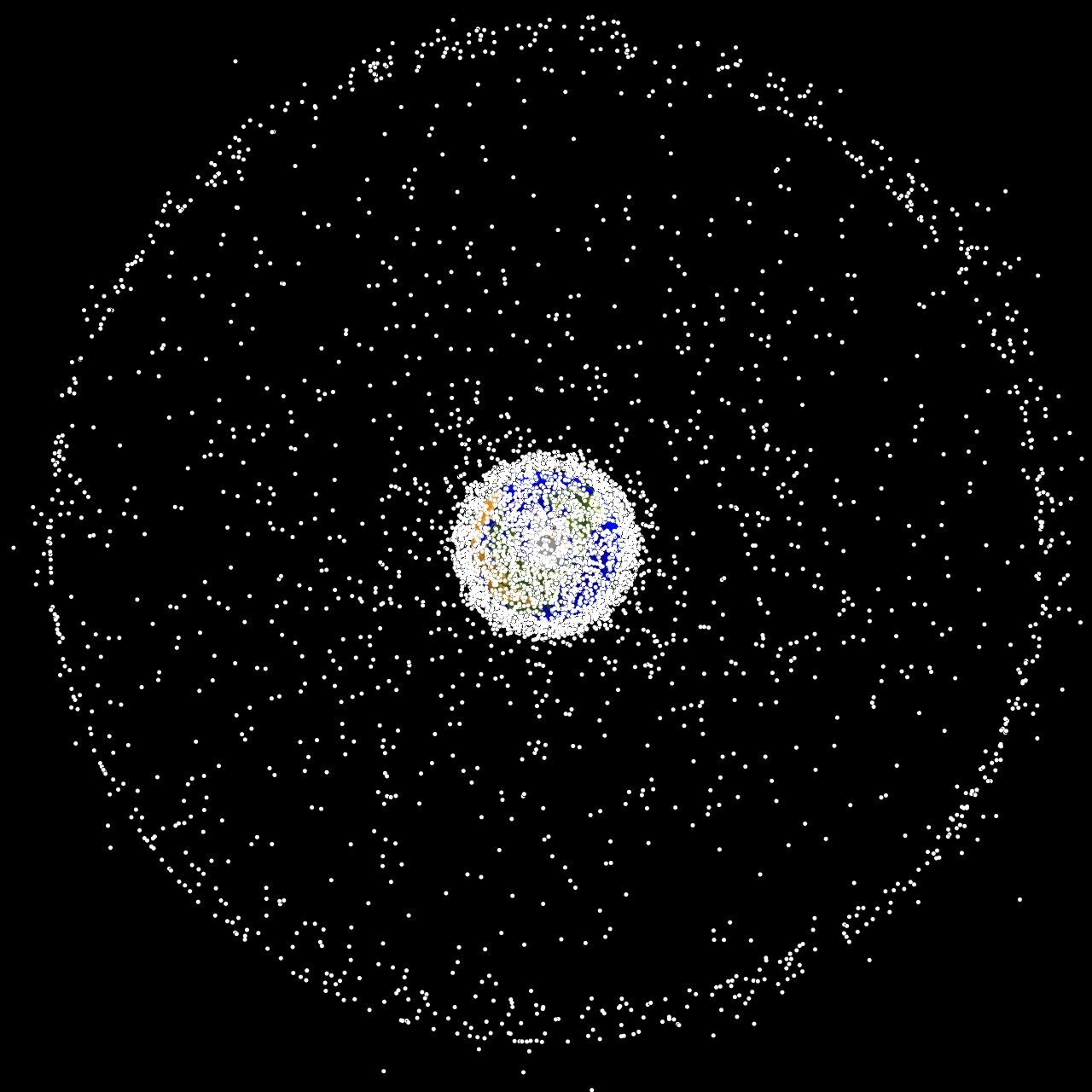
According to the ESA’s Space Debris Office (SDO), there are about 31,630 debris objects in orbit that are regularly tracked by space surveillance networks. However, this only accounts for the larger objects and doesn’t include the (literally) millions of tiny bits of “space junk” that pollute Low Earth Orbit (LEO). According to the SDO, this includes an estimated 36,500 objects greater than 10 cm in diameter (~4 inches), 1 million space debris objects measuring between 1 cm to 10 cm (0.4 to 4 inches), and 130 million space debris objects measuring between 1 mm to 1 cm.
These objects pose a regular threat to the International Space Station (ISS) and will only worsen as satellite “mega-constellations” are deployed to LEO and humanity’s presence there grows. To simulate the dangers these impacts will pose to future missions, a team of Canadian engineers developed an Implosion-Driven Launcher (IDL) that would accelerate magnesium projectiles to hypervelocity – up to 10 kilometers a second (36,000 km/h; 22,370 mph). This gun will effectively simulate the damage micro-objects could inflict on future space stations, spacecraft, and satellites.
Continue reading “Engineers Build a gun That can Fire Projectiles at 10 km/s, Simulating High-Speed Space Debris Impacts”What Would a Sustainable Space Environment Look Like?
October 4th, 2022, will be an auspicious day as humanity celebrates the 65th anniversary of the beginning of the Space Age. It all began in 1957 with the launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik-1, the first artificial satellite ever sent to orbit. Since that time, about 8,900 satellites have been launched from more than 40 countries worldwide. This has led to growing concerns about space debris and the hazard it represents to future constellations, spacecraft, and even habitats in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
This has led to many proposed solutions for cleaning up “space junk,” as well as satellite designs that would allow them to deorbit and burn up. Alas, there are still questions about whether a planet surrounded by mega-constellations is sustainable over the long term. A recent study by James A. Blake, a research fellow with the University of Warwick, examined the evolution of the debris environment in LEO and assessed if future space operations can be conducted sustainably.
Continue reading “What Would a Sustainable Space Environment Look Like?”A Chunk of Space Junk Just Hit the Far Side of the Moon
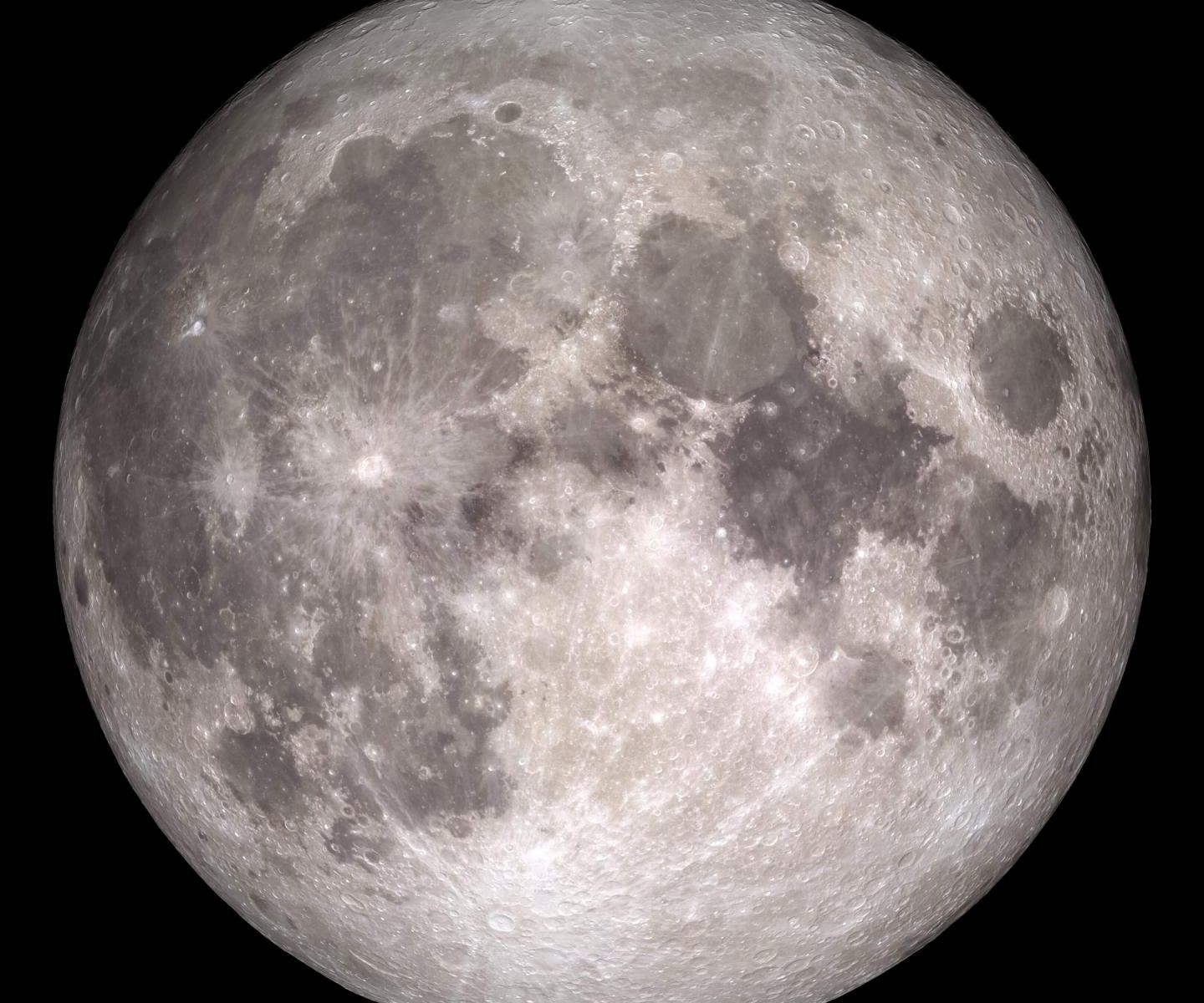

Observers have been tracking a chunk of space junk, waiting for it to strike the Moon. It should’ve hit the far side of the Moon, and hopefully, orbiters will have images of the impact site, though that might take a while.
The origins of the junk are in dispute. Some say it’s a spent booster from a Chinese rocket. Others say it’s from a SpaceX rocket. So far, nobody is claiming it.
Continue reading “A Chunk of Space Junk Just Hit the Far Side of the Moon”“Irresponsible” Russian Anti-Satellite Test Creates Orbital Debris Field, Endangering the Space Station and Crew
Early Monday, November 15, 2021, the International Space Station Flight Control team in Houston told the crew that due to a to satellite breakup, a debris field was created near the station’s orbital path. The astronauts and cosmonauts were told to “shelter in place” on board the Soyuz and SpaceX capsules attached to the ISS.
What became apparent as the day wore on is that the debris field was the result of a “destructive” test by Russia of an anti-satellite missile system against one of their own satellites. Experts from the US Space Command say the test resulted in “over fifteen hundred pieces of trackable orbital debris” which could stay in orbit for several years.
Continue reading ““Irresponsible” Russian Anti-Satellite Test Creates Orbital Debris Field, Endangering the Space Station and Crew”We Need to Fix Space Junk Before It’s Too Late
As of 2020, there were over 19,000 pieces of individually tracked space junk in orbit above the Earth. Of those, a mere 2,200 were operational satellites. As more and more satellites go up, the risk of collisions increases. And what are governments doing to stop it? Basically, nothing.
Continue reading “We Need to Fix Space Junk Before It’s Too Late”Nooo! Canadarm2 Hit by a Piece of Space Debris

The International Space Station’s robotic arm, Canadarm2, was struck by a piece of space debris. But luckily, it appears to be only a flesh wound, and the arm has been cleared for nominal operations while analysis on the strike continues.
Continue reading “Nooo! Canadarm2 Hit by a Piece of Space Debris”A Solution to Space Junk: Satellites Made of Mushrooms?
According to the latest numbers from the ESA’s Space Debris Office (SDO), there are roughly 6,900 artificial satellites in orbit. The situation is going to become exponentially crowded in the coming years, thanks to the many telecommunications, internet, and small satellites that are expected to be launched. This creates all kinds of worries for collision risks and space debris, not to mention environmental concerns.
For this reason, engineers, designers, and satellite manufacturers are looking for ways to redesign their satellites. Enter Max Justice, a cybersecurity expert, former Marine, and “Cyber Farmer” who spent many years working in the space industry. Currently, he is working towards a new type of satellite that is made out of mycelium fibers. This tough, heat-resistant, and environmentally friendly material could trigger a revolution in the booming satellite industry.
Continue reading “A Solution to Space Junk: Satellites Made of Mushrooms?”Ground-Based Lasers Could Push Space Debris off Collision-Course Orbits
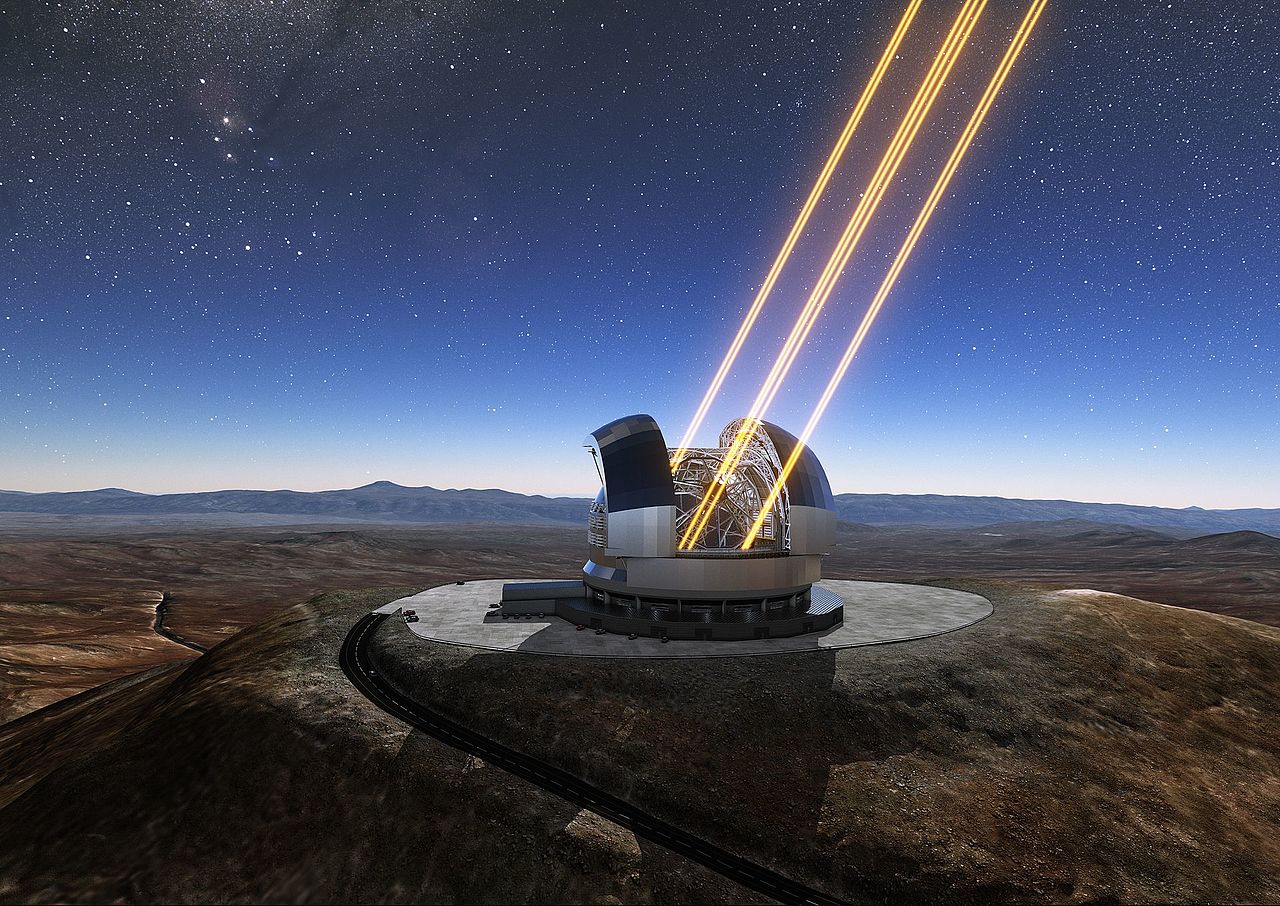
Researchers at the Australian National University (ANU) are finding new uses for the laser-based technology that sharpens telescope imagery – called adaptive optics – and it just might help mitigate the world’s growing space debris problem. Purpose-built lasers could give derelict satellites a slight ‘push’ of photons, imparting just enough energy to change the debris’s orbit and prevent an impending collision.
Continue reading “Ground-Based Lasers Could Push Space Debris off Collision-Course Orbits”How Long Will Space Junk Take to Burn Up? Here’s a Handy Chart

If the Roman Empire had been able to launch a satellite in a relatively high Low Earth Orbit – say about 1,200 km (750 miles) in altitude – only now would that satellite be close to falling back to Earth. And if the dinosaurs had launched a satellite into the furthest geostationary orbit – 36,000 km (23,000 miles) or higher — it might still be up there today.
Continue reading “How Long Will Space Junk Take to Burn Up? Here’s a Handy Chart”