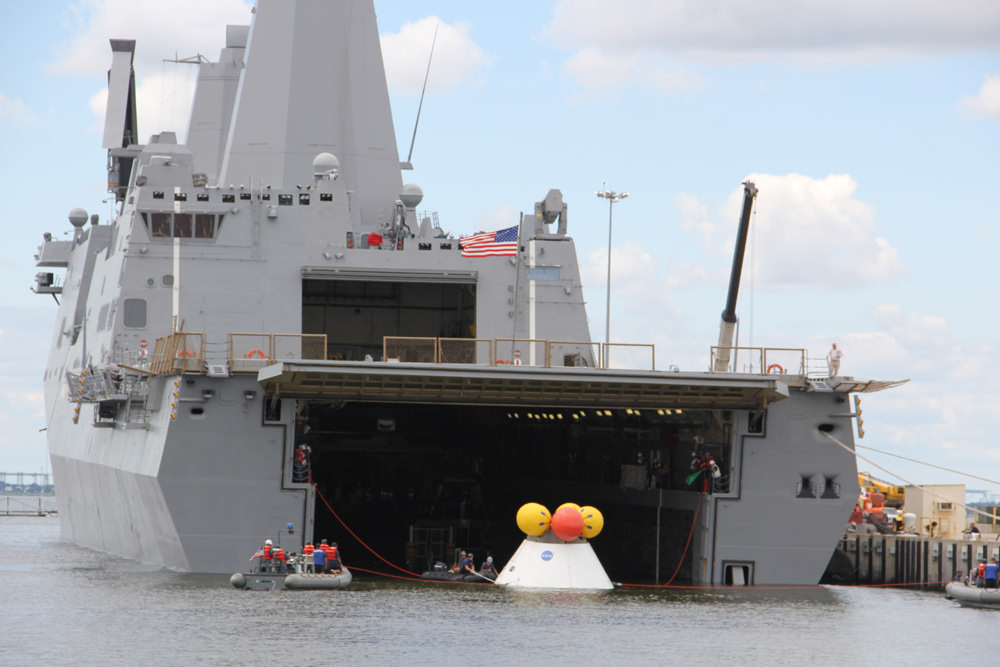
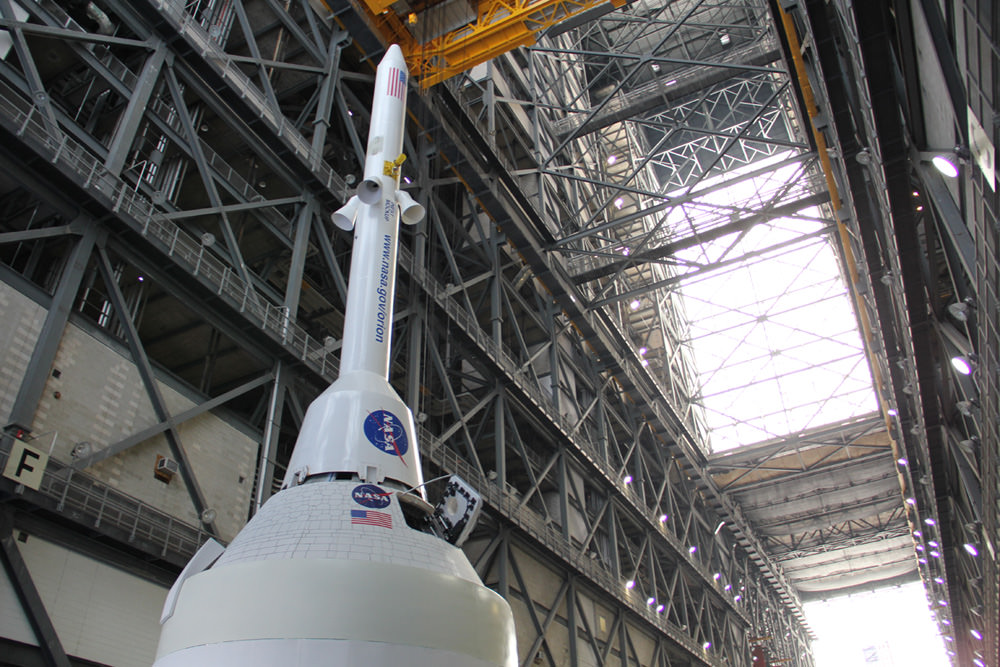
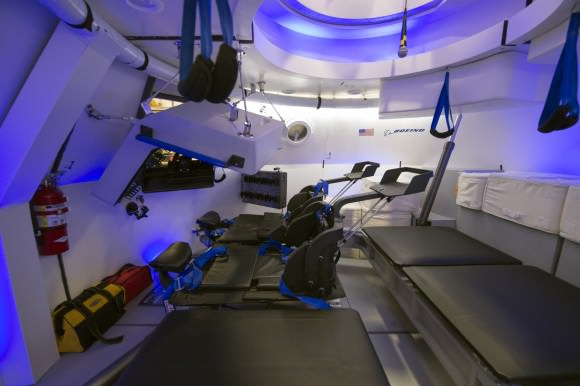
During the stationary recovery test of Orion at Norfolk Naval Base on Aug. 15, 2013, US Navy divers attached tow lines and led the test capsule to a flooded well deck on the USS Arlington. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com.
Story updated with additional test Video and images[/caption]
NAVAL STATION NORFOLK,VA – When American astronauts again venture into deep space sometime in the next decade, their return trip to Mother Earth will end with the splashdown of their Orion capsule in the Pacific Ocean – much like the Apollo lunar landing crews of four decades ago.
But before that can happen, Orion must first pass through a myriad of milestones to insure the safe return of our human crews.
A NASA and U.S. Navy test successfully demonstrated the water recovery of the Orion crew module today (Aug. 15) at Naval Station Norfolk in Virginia – and Universe Today witnessed the entire operation.
“Today’s test was terrific,” Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations, told Universe Today in a post test interview at Naval Station Norfolk.
“We got all the data we needed and the test was very successful. This was exactly what we wanted to do and we don’t like surprises.”

Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Today’s ‘Orion Stationary Recovery Test’ was conducted to support the upcoming first flight of Orion on the EFT-1 mission due to blastoff in September 2014 from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
“We completed all of our primary and secondary test objectives,” Wilson stated.
Teams of US Navy divers in a flotilla of amphibious boats launched from the USS Arlington approached a test version of the Orion capsule known as the boilerplate test article (BTA). The Arlington was docked against its pier during the test in a benign, controlled environment.

Divers attached several tow lines to the capsule, in a coordinated operation with the Arlington, and led the capsule into the ship’s flooded well deck.
The Orion capsule was carefully towed inside the well deck and positioned over the recovery cradle. The sea water was drained and the capsule was attached to the recovery cradle.

“During the test there is constant radio communications between the ship and the divers teams in the boats.”
“The operation within the well deck areas are also being controlled as well as the rope and winch handlers on the boat,” Wilson told me.
At the conclusion of the test, myself and the NASA social media participants boarded the USS Arlington and toured the Orion capsule for a thrilling up close look.
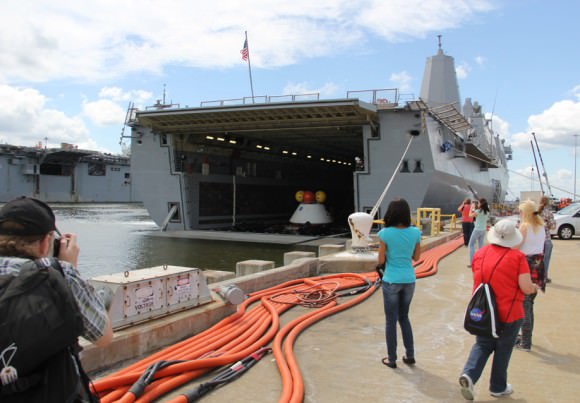

“Today marks a significant milestone in the Navy’s partnership with NASA and the Orion Human Space Flight Program,” said Navy Commander Brett Moyes, Future Plans Branch chief, U.S. Fleet in a statement.
“The Navy is excited to support NASA’s continuing mission of space exploration. Our unique capabilities make us an ideal partner for NASA in the recovery of astronauts in the 21st century — just as we did nearly a half century ago in support of America’s quest to put a man on the moon.”
The ocean recovery of Orion will be far different from the Apollo era where the crew’s were first hoisted out of the floating capsule and the capsule then hoisted on deck of a US Navy aircraft carrier.
The next Orion water recovery test will be conducted in the open waters of the Pacific Ocean in January 2014.

NASA’s Langley Research Center in nearby Hampton, VA is conducting an extensive drop test program in support of the Orion project.
“The Orion capsule tested today has the same mold line and dimensions as the Orion EFT-1 capsule.”
“The Orion hardware and the Delta IV Heavy booster for the EFT-1 launch are on target for launch in 2014,” Wilson told me.
Watch this NASA Video of the Orion test:
During the unmanned Orion EFT-1 mission, the capsule will fly on a two orbit test flight to an altitude of 3,600 miles above Earth’s surface, farther than any human spacecraft has gone in 40 years.
The EFT-1 mission will provide engineers with critical data about Orion’s heat shield, flight systems and capabilities to validate designs of the spacecraft before it begins carrying humans to new destinations in the solar system, including an asteroid and Mars.
It will return to Earth at a speed of approximately 20,000 mph for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
Right now its T Minus 1 Year and counting to liftoff of Orion EFT-1.
…………….
Learn more about Orion, Cygnus, Antares, LADEE, MAVEN, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Sep 5/6/16/17: LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM
Oct 3: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars – (3-D)”, STAR Astronomy Club, Brookdale Community College & Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ, 8 PM