Video Caption: Live Video of Shenzhou-8 and Tiangong-1 docking in Earth orbit. Photos below. Credit: CCTV commentary/CMSE
China’s technological capabilities took a major surge forward with the successful docking in space today for the first time ever of two Chinese built and launched spaceships – orbiting some 343 kilometers in the heavens above at 1:37 a.m. Beijing time Nov. 3(1:37 p.m. EDT, Nov. 2). China’s goal is to build a fully operational space station in Earth orbit by 2020 – about the time when the ISS may be retired.
Today’s space spectacular joining together the Shenzhou-8 unmanned spacecraft and the Tiangong-1 prototype space station was an historic feat for China, which now becomes only the 3rd country to accomplish a rendezvous and docking of spacecraft in Earth orbit.
Shenzhou is China’s manned spaceflight capsule but is flying without a crew for this particular test flight. The prowess demonstrated with this triumph paves the way for further manned Shenzhou’s launches soon.
[/caption]
The remarkable space milestone follows in the footsteps of what the United States and Russia accomplished decades ago but this was carried out with 21st century science, technology and manufacturing abilities developed by China during the nation’s rapid rise over the past few decades to become the world’s 2nd most powerful economy.

Shenzhou 8 has been chasing Tiangong-1 in orbit for two days since it was launched on Nov. 1 atop a Long March 2F booster rocket from the Gobi desert in northwest China.
The Commander-in-chief of China´s manned space program Gen. Chang Wanquan, announced “China’s first rendezvous and docking in space joining together the spacecraft Shenzhou-8 and Tiangong-1 space lab module was a complete success.” Chang leads the China Manned Space Engineering (CMSE) Project and pronounced the achievement at the Beijing Aerospace Control Center.
Chinese President Hu Jintao sent a congratulatory message from the G-20 summit in Cannes, France. “I am very pleased to hear the news and I send congratulations to all who made this possible. This will push China’s manned space program forward.”
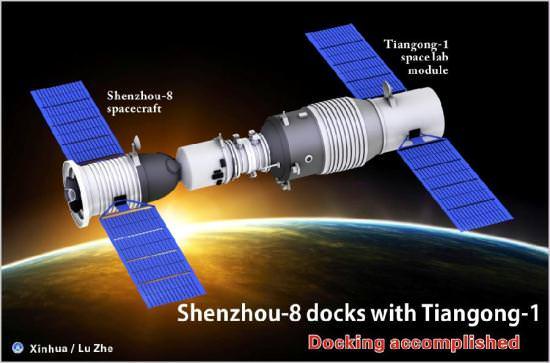
The landmark rendezvous and docking was carried live by state run CCTV for all the world to watch. The impressive 2 hour long TV broadcast showed simultaneous and breathtaking camera videos from both the unpiloted Shenzhou-8 capsule and the Tiangong-1 space station module as they viewed one another in the cameras field of view and slowly approached together with the lovely Earth as a backdrop.
Mission controllers carefully monitored all spacecraft systems on both Shenzhou-8 and Tiangong-1 as they sped closer at about 20 cm/sec and stopped at several parking points along the way (400 m, 140 m, 30 m) to confirm everything was nominal.
Chinese engineers and on board systems precisely guided the two spaceships and watched for any deviations. In case of any failures they had the capability to radio the vehicles to separate. But no deviations occurred and the autonomous docking proceeded to completion.
The two vehicles will remain docked for 12 days, then unhook and back off about 150 meters and then conduct another practice docking. The second practice docking is being done to gain more expertise and confidence and will be carried out under different conditions and in daylight.
The combined Shenzhou-8/Tiangong-1 orbiting complex weighs about 16 tons, some 8 tons each. Tiangong-1 is 10.4 m in length and 3.3. m in diameter. Shenzhou 8 is 9.2 m in length.
China plans two crewed flights to Tiangong-1 starting in 2012. The multi-person crews aboard Shenzhou 9 & Shenzhou 10 are almost certain to include China’s first female astronaut. The astronauts would float into Tiangong 1 from their Shenzhou capsules and remain on board for a few days or weeks. They will check out the spacecraft systems and conduct medical, space science and technology tests and experiments.
Meanwhile, since the premature retirement of the space shuttle with no successor in place, the US has absolutely no capability to launch astronauts to earth orbit. Therefore the ISS is totally reliant on Russian Soyuz rockets and capsules. US astronauts must hitch a ride to space with the Russians.
The US Senate just passed a NASA budget for 2012 that cuts NASA funding and will delay a replacement manned vehicle even further, likely into 2017. The US House seeks even deeper NASA budget cuts.
Thus China surges powerfully forward in space and science while the US political establishment has directed NASA to delay and retrench and layoff still more workers.

Read Ken’s related features about China’s Shenzhou-8, Tiangong-1 and Yinghou-1
China launches Shenzhou-8 bound for Historic 1st Docking in Space
Shenzhou-8 rolled out for Blastoff to China’s 1st Space Station on November 1
Bizarre Video: China’s Tiangong 1 Space Lab Animation set to ‘America the Beautiful’ Soundtrack
China Blasts First Space Lab Tiangong 1 to Orbit
China set to ‘Leap Forward in Space’ as Tiangong 1 Rolls to Launch Pad
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline