[/caption]
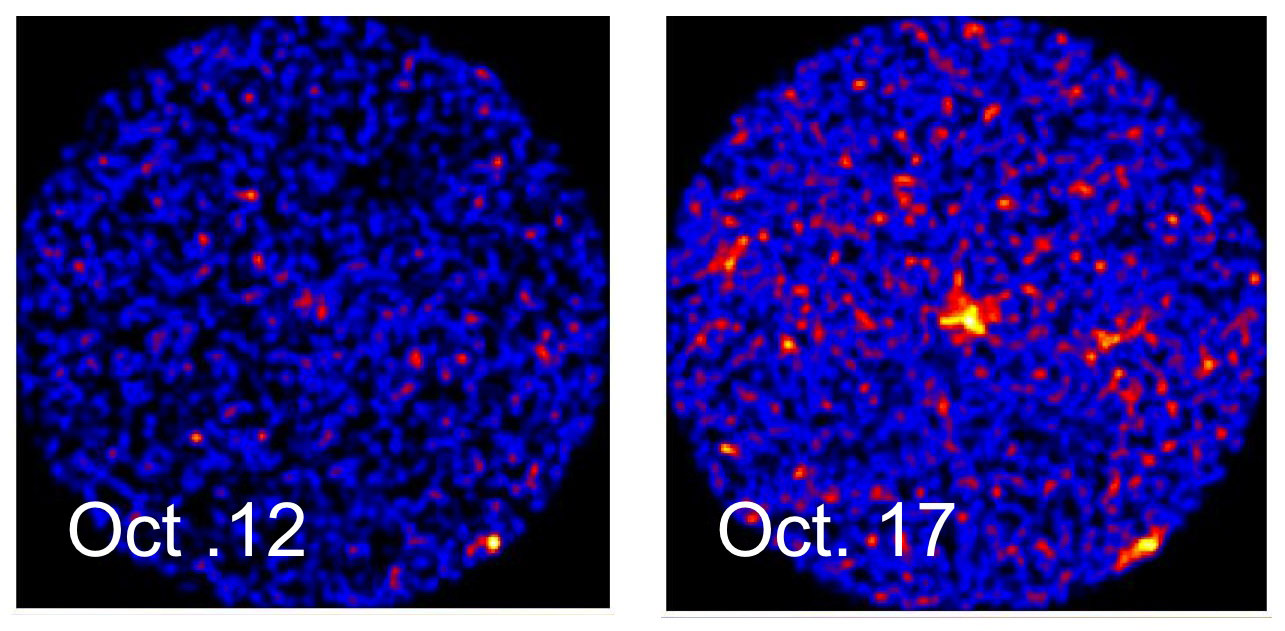
A new X-ray emitting object in the Milky Way has been recently announced by the Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image (MAXI) team and the Swift satellite astronomers. MAXI, a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency supported instrument, monitors the entire sky in the X-ray portion of the spectrum from its perch on the International Space Station module “Kibo”. On October 12th, MAXI noticed nothing out of the ordinary in a portion of the sky in the constellation Centaurus.
On October 17th, however, things started to brighten up in the region but were still dark enough that the team wanted to analyze their observations before announcing it to the world. By the 20th, they were able to confirm the X-ray source as something more unusual, and sent out an Astronomer’s Telegram (ATel No.2959) at 2:00 a.m. EDT alerting other astronomers to the object.
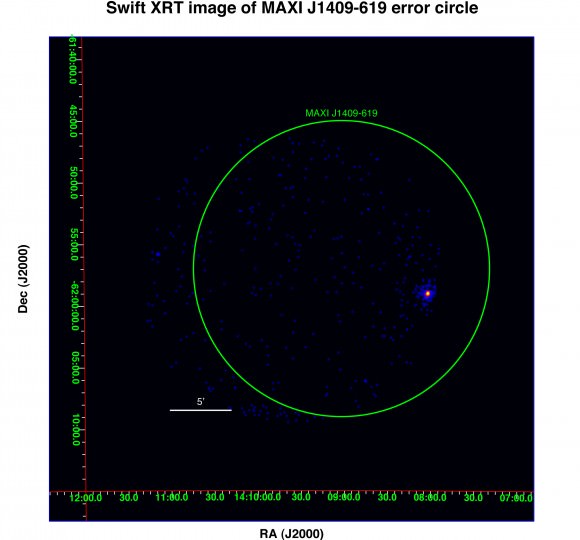
The Swift satellite – in keeping with its name – began taking observations a mere nine hours later. Swift is equipped with an X-ray telescope, as well as an optical/ultraviolet telescope, and is designed to maneuver quickly to home in on gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)
David Burrows, professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State and the lead scientist for Swift’s X-ray Telescope said in a press release, “The Swift observation suggests that this source is probably a neutron star or a black hole with a massive companion star located at a distance of a few tens of thousands of light years from Earth in the Milky Way…The contribution of Swift’s X-ray Telescope to this discovery is that it can swing into position rapidly to focus on a particular point in the sky and it can image the sky with high sensitivity and high spatial resolution.”
The object has been named MAXI J1409-619. The area of the sky that it was discovered in is not a known source of bright X-rays, though there were two dimmer objects located in the same area detected by the BeppoSAX X-ray survey on January 29th, 2000. One of the objects is consistent with the Swift observation, though this most recent flare-up made it almost 52 times brighter in the X-ray than previously observed.

X-ray novae are short-lived events, with an initial bright burst that falls off over a period of weeks or months. Their source is generally understood to be material falling into a black hole or accreting onto a neutron star.
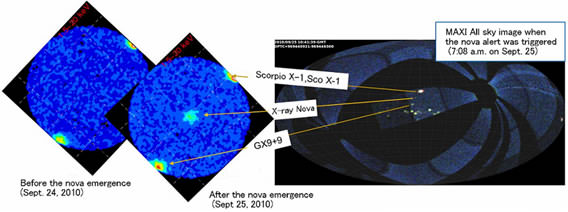
This is not the first discovery made by the MAXI instrument. It detected another X-ray source on the 25th of September in the constellation Ophiuchus – named MAXI J1659-152 – which we wrote about here.
Further observations of the new object are likely in the works, so we’ll keep you posted.
Sources: Eurekalert, JAXA, ATel 2965, Penn State Press Release