The Soyuz TMA-19 vehicle blasted off from Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan today to bring three new crew members to the International Space Station. This was the 100th launch of missions in support of space station assembly, resupply and crew exchanges. The rocket lit up the early morning sky in Kazakhstan at 3:35 a.m. Wednesday local time, (5:35:19 p.m. EDT and 9:35 pm GMT on Tuesday). The Soyuz took eight and a half minutes to reach orbit, but it will take about 2 days to catch up to the ISS.
Continue reading “100th Launch to the International Space Station”
Unusual Views of the Soyuz Rocket

[/caption]
Two NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut will launch to the International Space Station later today, and astronauts Douglas Wheelock has been able to get up close and personal with the Soyuz rocket that will take them there. He’s taken a few pictures of his rocket from unusual vantage points and posted them on Twitter, and is sharing his prelaunch experiences, too (@Astro_Wheels). Wheelock has big shoes to fill in the Twitter and picture-taking department, as JAXA astronaut Soichi Noguchi set a new standard in making his time on board the ISS a shared experience through images and social media. More pics below, plus a newly released video by NASA of the landing of the Soyuz that brought the Noguchi, Soyuz Commander Oleg Kotov and TJ Creamer back home. It’s a view of the landing not normally seen.

For the next crew heading to the ISS, which will bring the crew size back to six at the space station, veteran cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin, Wheelock and Shannon Walker are scheduled for liftoff aboard the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 5:35:19 p.m. EDT (9:35 pm GMT) (3:35:19 a.m. June 16 local time Kazakhstan).
Including manned and unmanned missions, this will be the 100th launch supporting space station operations since assembly began in 1998.
Space Station Twitter Crew Returns Home
The Expedition 23 crew from the International Space Station landed safely in their Soyuz-17 spacecraft, concluding their five-and-a-half-month stay in space. Commander Oleg Kotov and Flight Engineers T.J. Creamer and Soichi Noguchi were welcomed by sunshine on Wednesday morning in Kazakhstan (11:25 pm EDT Tuesday). This crew may well be remembered as the ‘Twitter Crew’: Creamer posted the first “live” Tweet from space on Twitter from the now functioning internet on the ISS, which he helped to get up and running. Noguchi’s use of Twitter to post hundreds of images from space documented and shared his experiences in space like no previous astronaut, as he garnered over 250,000 Twitter “followers,” and his images were featured on many blogs and news sites.
Continue reading “Space Station Twitter Crew Returns Home”
The Last Train to KSC: Final Set of Solid Rocket Boosters Arrive
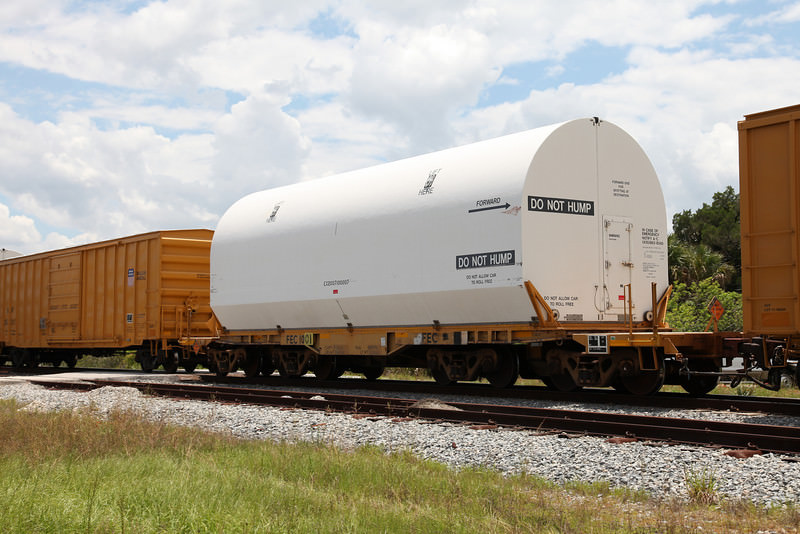

[/caption]
Another end-of-an-era event heralding the conclusion of the space shuttle program: the final set of space shuttle solid rocket booster segments arrived at the Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, May 27, 2010. The segments were carried on railway cars from the ATK factory in Utah where the boosters are built. The last part of the trip from Jacksonville, Florida included passenger cars carrying NASA personnel and ATK officials, including astronaut Mike Massimino, shuttle launch director Mike Leinbach, and the “voice” of NASA TV, George Diller. The train stopped across the Indian River from KSC where the tracks lead to the Vehicle Assembly Building.
The boosters will be stacked in the VAB for a possible rescue mission, or perhaps, even one last add-on flight for space shuttle Atlantis.
The SRB segments are designated for STS-335, the Launch-On-Need mission that would be flown if the last scheduled shuttle flight — STS-134, now scheduled for launch in late November — would encounter a problem. Or, if Congress allows, another shuttle mission using the ready-to-go shuttle could be added. U.S. Sen. Bill Nelson told President Obama in a letter this week that he intended to request funding for the extra mission. NASA hopes to get a go-ahead for the flight, which would become the STS-135 mission, by late June. If approved, the likely launch date would be sometime in the summer of 2011.
NASA’s Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier said at a news conference this week that if the additional flight were approved, a Soyuz would be readied as a rescue vehicle, and the shuttle crew would be smaller, probably 4 crew members. The crew could take safe harbor at the International Space Station, if needed, until the rescue Soyuz arrived. The shuttle could bring extra supplies and hardware to the ISS.

Veteran astronaut Mike Massimino told a Florida television station crew that he hopes for an additional shuttle mission. “I think we have to be optimistic,” Massimino said. “There are just too many people around the country and the world who are so supportive of our program.”
ATK laid off 1,300 of their 5,000 person workforce because of shutting down production of the boosters, but the company is hoping to be part of NASA’s future spaceflight plans.
“There’s quite a bit of uncertainty,” said ATK KSC Deputy Director Ted Shaffner. “The direction is very cloudy from our politicians and NASA is struggling with what direction we do take.”
More images from the event:




And I know someone is going to comment on the “Do Not Hump” sign on the railcar. What it means is that the contents of the railcar are delicate enough that the car should not be ‘humped,’ which is a method to sort freight cars by rolling them down a hill instead of using a locomotive engine to move the cars. Obviously, NASA and ATK don’t want the SRB segments to go rolling down a hill. Find out more about humping here.
Sources: Florida Today, CFNews 13
Atlantis Crew ‘Riding Inside a Fireball’

[/caption]
At a post-landing news conference, STS-132 commander Ken Ham described the incredible visual effects the crew of Atlantis witnessed as they returned to Earth today. As the shuttle was engulfed in plasma during the hottest part of their re-entry through Earth’s atmosphere, they were in orbital darkness, which highlighted the orange, fiery glow around the shuttle. “We were clearly riding inside of a fireball, and we flew right into the sunrise from inside this fireball, so we could see the blue color of the Earth’s horizon coming through the orange. It was amazing and just visually overwhelming.”
As evidence, ISS astronaut Soichi Noguchi captured Atlantis as that fireball, streaking though atmosphere, just as dawn approached. “Dawn, and Space Shuttle re-entered atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. 32 years of service, 32nd beautiful landing. Forever, Atlantis!” Noguchi wrote on Twitter, posting a link to the image.
Amazing.
Asked about his thoughts after landing, Ham said, “Walking around Atlantis after the flight I realized I probably just did the most fun and amazing thing I’ll do in my life.”
As for Atlantis, and whether she’ll fly one more time, the latest word is that the NASA authorization bill — as it stand now –will include language authorizing an additional shuttle mission.
As for Noguchi, take in all the images you can now from him on his Twitter feed, He, along with Expedition 23 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kotov, and astronaut T.J. Creamer are scheduled to leave the ISS on the Soyuz spacecraft on June 1 and land on the southern region steppe of Kazakhstan, completing almost six months on the station.
Here’s an image Noguchi took of Atlantis just after it undocked from the ISS last weekend.

Atlantis Returns Home — For the Last Time?
A bittersweet moment in space history as Atlantis and her six-member crew landed at Florida’s Kennedy Space Center on Wednesday morning. Very likely, this was Atlantis’ final landing, returning home after 25 years of service. The rich history of the Atlantis space shuttle includes 294 days in space, 4,648 orbits and 120,650,907 miles during 32 flights. There’s a chance this orbiter could fly again – she’ll be readied as a rescue ship for the last scheduled shuttle mission –and many shuttle supporters feel that since Atlantis will be fully geared up, she should fly one last time. But only time (and funding and Congress) will tell if Atlantis will fly again.
Continue reading “Atlantis Returns Home — For the Last Time?”
It Takes Six Minutes to Fly From One End of ISS to the Other
How long does it take you to walk from one end of your house to the other? The ISS is now so large that it takes astronauts about six minutes to go between the two farthest points inside the space station — and that is by ‘flying,’ not walking. Enjoy this very cool video tour of the interior of the ISS, filmed earlier this year.
Picture Gallery: STS-132, Atlantis’ Last Mission
[/caption]
Is this Atlantis’ last mission to space? STS-132 is the last scheduled flight for space shuttle Atlantis, and it remains to be seen whether any additional shuttle flights will be added. But the imagery from this mission is incredibly rich with wonderful images of the orbiter. So, while previous shuttle mission galleries we have here on Universe Today normally feature images from the EVAs, this gallery will mainly showcase images of Atlantis. And there are some really great photos — not sure whether the astronauts/photographers are consciously focusing on the shuttle or these images are just marvelously serendipitous. We’ll do a second gallery as more images come in from the later part of the mission. Enjoy!

Atlantis is backdropped by Earth as the shuttle approaches the International Space Station during STS-132 rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 9:28 a.m. (CDT) on May 16, 2010.

Just a very neat image of Atlantis, as seen from the ISS, backdropped by a cloudy area on Earth.
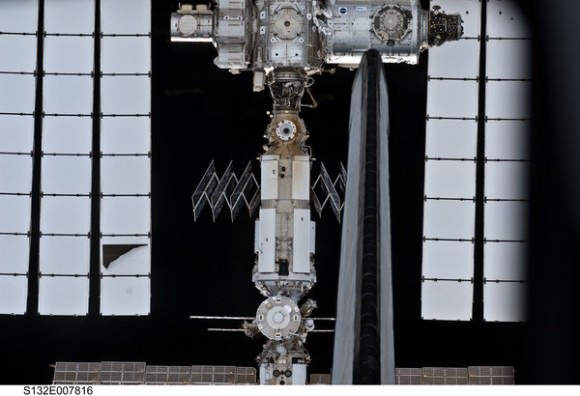
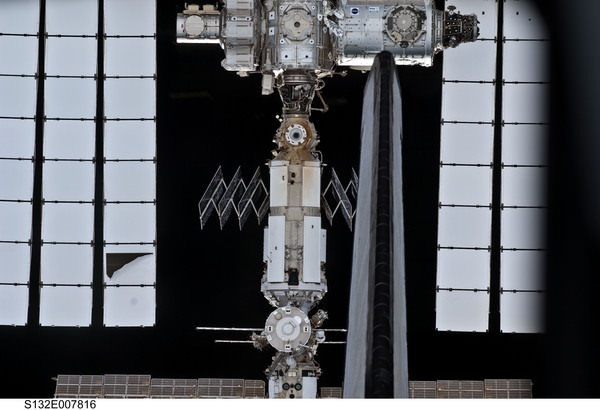
Amazing shot of the Russian Segment behind Atlantis’s tail on FD 4 prior to docking.

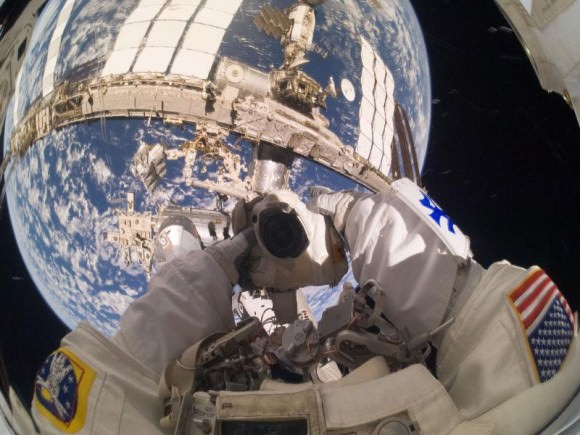
Anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint, NASA astronaut Garrett Reisman works during the STS-132 mission’s first EVA. Dextre, a two-armed extension for the station’s robotic arm is also visible.

This image might win the award for most futuristic looking image of the mission, and some have compared it to a scene from the movie “2001” — um, wait, is that considered a history movie now?


In the grasp of the Canadarm2, the Russian-built Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM-1) is transferred from space shuttle Atlantis’ payload bay to be permanently attached to the Earth-facing port of the Zarya Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the International Space Station.

Obligatory image of a waving astronaut during an EVA. But it never gets old, so keep it up, guys!




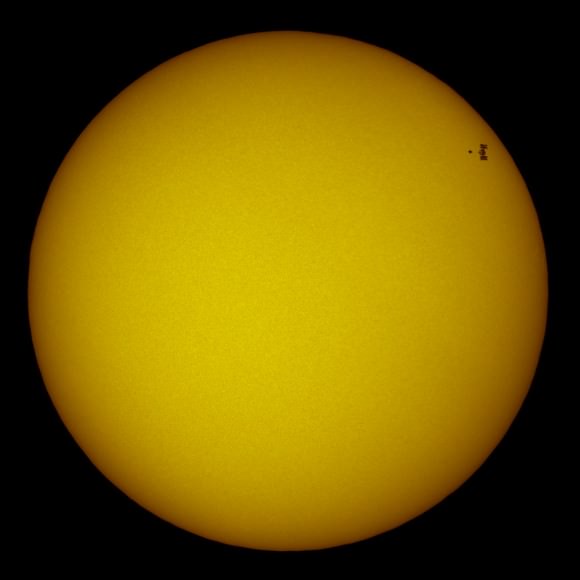
Incredible Image: Atlantis and ISS Transit the Sun
Here are some incredible images of Atlantis and the International Space Station captured as it transit the Sun.
You can also view space from where you are. You just need a good telescope for that. Take a look at these cool and amazing telescopes from Amazon.com.
French astrophotographer Thierry Legault has done it again. He captured a view of space shuttle Atlantis and the International Space Station crossing the face of the Sun on May 16, 2010 about 50 minutes before the shuttle docked with the space station. Legault took the image from Madrid, Spain at 13:28:55 UT. “Atlantis has just begun the ‘R-bar pitch maneuver,'” Legault wrote on his website, “as the shuttle performs a backflip that exposes its heat-shield to the crew of the ISS that makes photographs of it; since its approach trajectory is between the ISS and the Earth, this means that we are seeing Atlantis essentially from above, with the payload bay door opened.”
Since this may be Atlantis’ last flight to space, the image is especially poignant.
See below for the full image, and make sure you go to Legault’s website and watch the movie of how quickly the pair of spacecraft actually flew across the face of the Sun — like the blink of an eye! It’s amazing he was able to capture this incredible image at all, not to mention how clear and sharp the two spacecraft are in the photo, against the face of the otherwise spotless Sun. The shuttle’s tail is even visible!
Legault said he used a Takahashi TOA-150 refractor (diameter 150mm, final focal 2500mm), Baader Herschel prism and Canon 5D Mark II camera, at an exposure of 1/8000s at 100 ISO, extracted from a series of 16 images (4 images/s) started 2 seconds before the predicted transit time.

Take time to browse through Legault’s impressive collection of spacecraft photography, including an amazing 3-D movie of the ISS.
Space Station Gets a New Science Module
[/caption]
A 8,550 kg (17,760-pound) Russian Mini-Research Module, known as Rassvet or “Dawn,” was attached to the International Space Station today. This is the first (and last) Russian-built module to be delivered by a space shuttle, and the 8 meter long (20 ft) 2.5 meter (8 ft) diamater module will serve an area for scientific research, as well as for stowage and a docking port extension for future visiting spacecraft such as the Soyuz and Progress resupply vehicles.
“The ISS has grown by one more module,” Moscow mission control radioed up the crew. “We are really very grateful to you. And our congratulations to all of you for this new step in space research and thanks for all your effort and all your work.”
The MRM is packed full of 1,400 kg (3,086 pounds) of NASA equipment and supplies, plus an experiment airlock and European robot arm equipment that will be attached to other modules later.
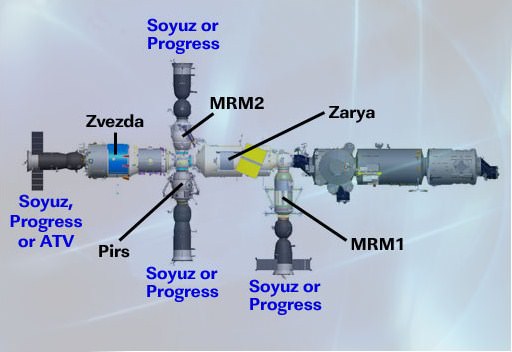
MRM was docked to the Earth-facing port of the central Zarya module, and will provide needed clearance between the forward Russian docking port and a US storage module, the Permanent Logistics Module, scheduled to arrive at the station later this year.
Operations began early this morning to install the MRM, with Atlantis commander Ken Ham and pilot Dominic Antonelli, operating the shuttle’s robot arm to take the new module from the shuttle’s cargo bay. Then astronauts Garrett Reisman and Piers Sellers installed the MRM-1 on Zarya, — appropriately waiting until orbital sunrise to attach the module with great precision. Controllers said Reisman maneuvered the module so precisely, he made a “hole in one.”

Now that the MRM is attached, the ISS and shuttle astronauts now turn their attention to the second spacewalk of the mission scheduled for Wednesday, May 19 to be conducted by Steven Bowen and Michael Good. The primary tasks are the removal and replacement of P6 truss batteries that store solar energy. These batteries have outlived their expected lifespan of 6 years, so the batteries will be swapped out with new ones.
Behind the scenes work has also been ongoing to develop a task to clear a cable that is pinched out on the end of the Atlantis’ boom and sensor system that prevented an inspection of the shuttle’s thermal protection system. NASA TV commentator Kyle Herring said the procedure appears to be a fairly straightforward task to clear the cable out of the way and secure it with a wire-tie. Mission planners are seeing where the procedure fits in best with the rest of the spacewalks tasks.