Hunting for satellites from your backyard can be positively addicting. Sure, the Orion Nebula or the Andromeda Galaxy appear grand… and they’ll also look exactly the same throughout the short span of our fleeting human lifetimes. Since the launch of Sputnik in 1957, humans also have added their own ephemeral ‘stars’ to the sky. It’s fun to sleuth out just what these might be, as they photobomb the sky overhead. In the coming week, we’d like to turn your attention towards a unique opportunity to watch a high profile space launch approach a well-known orbiting space laboratory.
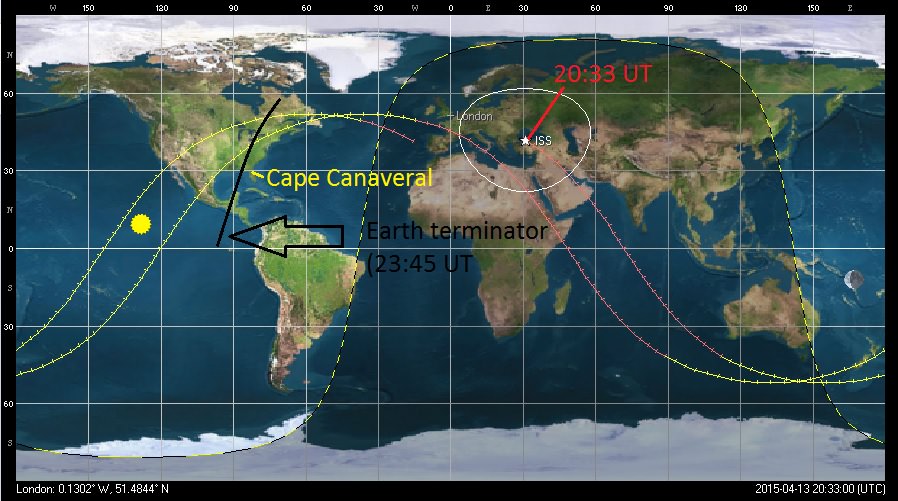
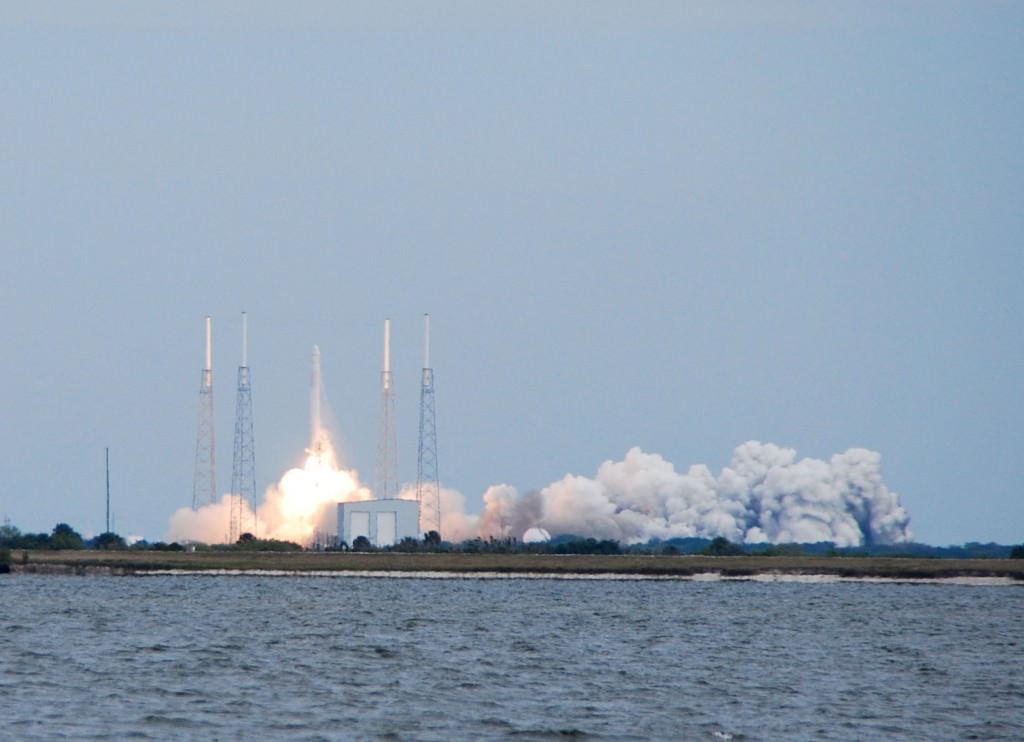
On Monday, April 13th 2015, SpaceX will launch its CRS-6 resupply mission headed towards the International Space Station. As of this writing, the launch is set for 20:33 Universal Time (UT) or 4:33 PM EDT. This is just over three hours prior to local sunset. The launch window to catch the ISS is instantaneous, and Tuesday April 14th at 4:10 PM EDT is the backup date if the launch does not occur on Monday.

Of course, launches are fun to watch up-close from the Kennedy Space Center. To date, we’ve seen two shuttle launches, one Falcon launch, and the MAVEN and MSL liftoffs headed to Mars from up close, and dozens more from our backyard about 100 miles to the west of KSC. We can typically follow a given night launch right through to fairing and stage one separation with binoculars, and we once even had a serendipitous launch occur during a local school star party! We really get jaded along the Florida Space Coast, where space launches are as common as three day weekend traffic jams elsewhere.
And it’s true that you can actually tell when a launch is headed ISS-ward, as it follows the station up the US eastern seaboard along its steep 52 degree inclination orbit.
On Monday, Dragon launches 23 minutes behind the ISS in its orbit. Viewers up should be able to follow CRS-6 up the U.S. East Coast in the late afternoon sky if it’s clear.
And of course, SpaceX will make another attempt Monday at landing its Falcon Stage 1 engine on a floating sea platform, known as the ‘autonomous spaceport drone ship’ (don’t call it a barge) after liftoff.
About 15-20 minutes after liftoff, Europe and the United Kingdom may catch the Dragon and Falcon S2 booster shortly after the ISS pass on the evening of April 13th. Observers ‘across the pond’ used to frequently catch sight of the Space Shuttle and the external fuel tank shortly after launch; such a sight is not to be missed!
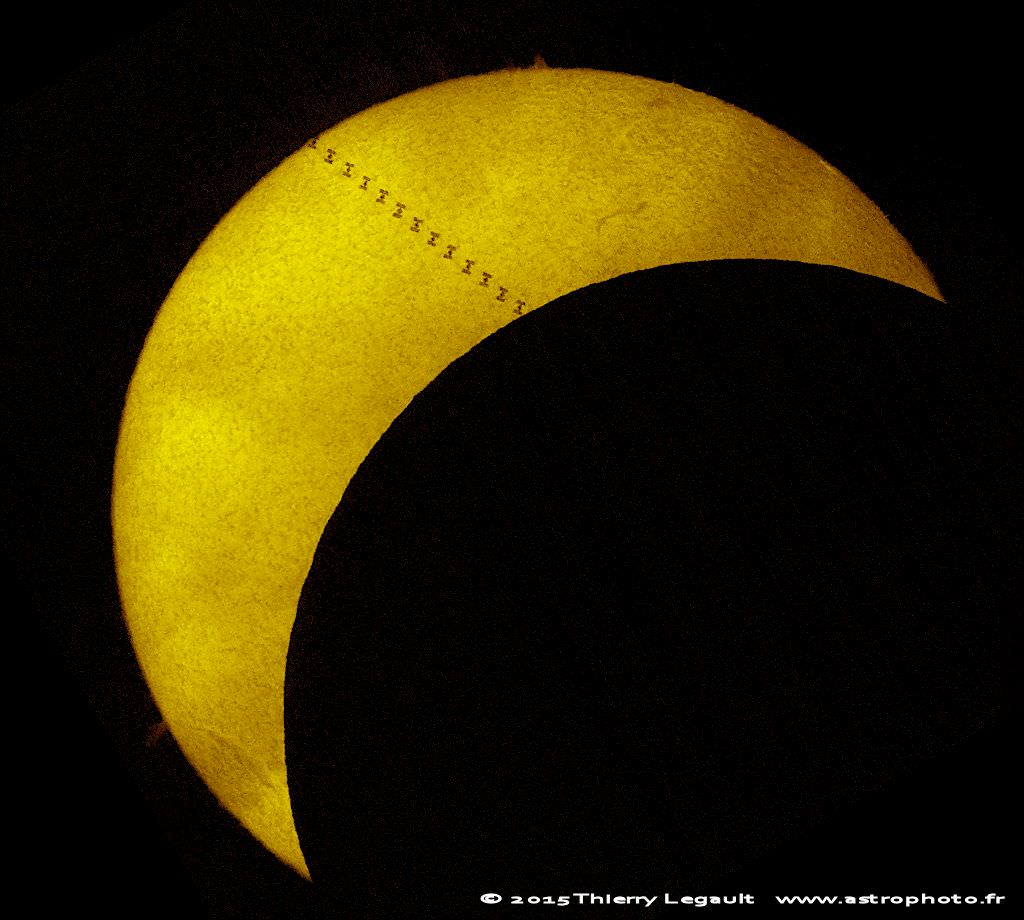
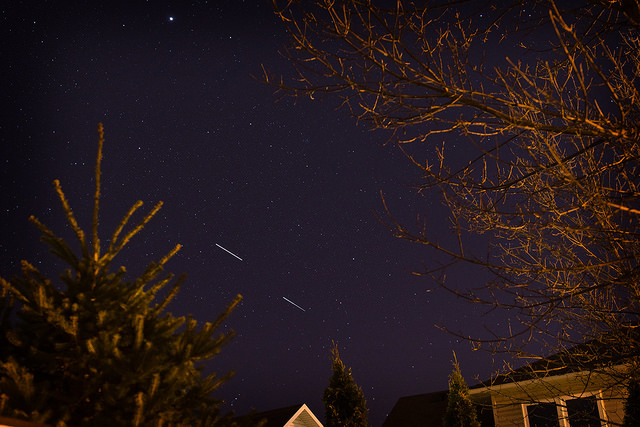
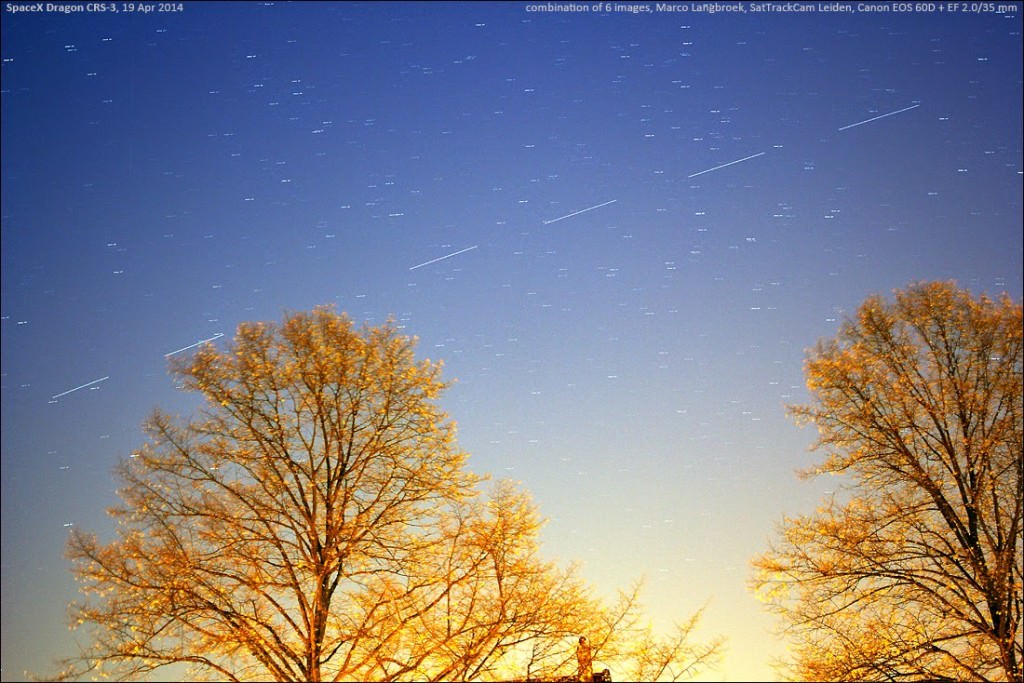
Spotting Dragon ‘and friends’ on early orbits may provide for a fascinating show in the evenings leading up to capture and berthing. Typically, a Dragon launch generates four objects in orbit: the Dragon spacecraft, the Falcon Stage 2 booster, and the two solar panel covers. These were very prominent to us as they passed over Northern Maine on first orbit in the pre-dawn sky on the morning of January 10th, 2015. Universe Today science writer Bob King also noted that observers spotted what was probably a venting maneuver over Minnesota on the 2nd pass on the same date.

And even after berthing, the Falcon S2 booster and solar panel covers will stay up in orbit, either following or leading the ISS for several weeks before destructive reentry.
Orbits on Monday and Tuesday leading up to capture for Dragon on Wednesday April 15th at 7:14 AM EDT/11:14 UT will be the key times to sight the pair. Capture by the CanadaArm2 will take place over the central Pacific, and the Dragon will be berthed to the nadir Harmony node of the ISS. Dragon will remain attached to the station until May 17th for a subsequent return to Earth. With the end of the U.S. Space Shuttle program in 2011, SpaceX’s Dragon is currently the only vessel with a ‘down-mass’ cargo capability, handy for returning experiments to Earth.
The first few orbits on the night of the 13th for North America include a key pass for the US northeast at 1:04UT (on the 14th)/9:04 PM EDT, and subsequent passes at dusk westward about 90 minutes later. NASA’s Spot the Station App usually lists Dragon passes shortly after launch, as does Heavens-Above and numerous other tracking applications. We’ll also be publishing sighting opportunities for Dragon and the ISS, along with maps on Twitter as @Astroguyz as the info becomes available.
Pre-berthing passes next week favor 40-50 degrees north for evening passes, and 40-50 degrees south for morning viewing.

The International Space Station has become a busy place since its completion in 2009. To date, the station has been a port of call for the U.S. Space Shuttles, the Soyuz spacecraft with crews, and Progress, HTV, ATV and Dragon resupply craft.
The current expedition features astronaut Scott Kelly and cosmonaut Mikhail Korniyenko conducting a nearly yearlong stay on the ISS to study the effects that long duration spaceflight has on the human body. Kelley will also break the U.S. duration record by 126 days during his 342 stay aboard the station. The future may see Dragon ferrying crews to the ISS as early as 2017.

And you can always watch the launch live via NASA TV starting at 3:30 PM EDT/19:30 UT.
Don’t miss a chance to catch the drama of the Dragon spacecraft approaching the International Space Station, coming to a sky near you!