Getting to the International Space Station is no easy task. Generally speaking, it involves loading up a space capsule with several tons of cargo and then expending millions of liters of fuel to get it into orbit. This process is time consuming and very expensive. And what if astronauts want to send some things back? Currently, their only option for return capability is provided by the same cargo capsules that are sent up to them.
SpaceX Dragon Departs Space Station after Delivering Slew of Science and Returns with Ocean Splashdown

Concluding a busy five week mission, the SpaceX Dragon CRS-4 commercial cargo ship departed the International Space Station (ISS) this morning, Oct. 25, after delivering a slew of some 2.5 tons of ground breaking science experiments and critical supplies that also inaugurated a new era in Earth science at the massive orbiting outpost following installation of the ISS-RapidScat payload.
Dragon was released from the snares of the station’s robotic arm at 9: 57 a.m. EDT while soaring some 250 mi (400 km) over the northwest coast of Australia.
It returned safely to Earth with a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean some six hours later, capping the fourth of SpaceX’s twelve contracted station resupply missions for NASA through 2016.
“The Dragon is free!” exclaimed NASA commentator Rob Navias during a live broadcast on NASA TV following the ungrappling this morning. “The release was very clean.”

The private resupply ship was loaded for return to Earth with more than 3,276 pounds of NASA cargo and science samples from the station crew’s investigations on “human research, biology and biotechnology studies, physical science investigations, and education activities sponsored by NASA and the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, the nonprofit organization responsible for managing research aboard the U.S. national laboratory portion of the space station,” said NASA.
The release set up a quick series of three burns by the ship’s Draco thrusters designed to carry Dragon safely away from the station.
NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman and Butch Wilmore quickly retracted the arm working from their robotics workstation in the domed Cupola module.
“Thanks for the help down there,” the astronauts radioed. “It was a great day.”

The first burn took place a minute later at about 9:58 a.m. EDT and the second at about 10:00 a.m. A yaw maneuver at 10:05 a.m. set up the orientation required for the third burn at about 10:08 a.m.
Dragon moved away quickly during the nighttime release and was already outside the Keep Out Sphere (KOS), an imaginary bubble surrounding the station at a distance of 200 m. It disappeared quickly in the dark and was barely visible within minutes.
“The propulsion systems are in good shape,” said Navias. “All systems on Dragon are functioning perfectly.”
With Dragon safely gone following the trio of burns, the next major event was the deorbit burn at 2:43 p.m. EDT at a distance of about 90 statute miles from the station.
Dragon slipped out of orbit. After surviving the scorching heat of reentry through the Earth’s atmosphere, the ship sequentially deployed its drogue chutes and three main parachutes at about 3:30 p.m.
Splashdown in the Pacific Ocean occurred as expected at about 3:39 p.m., approximately 265 miles west of the Baja peninsula.
Dragon is the only vehicle that can return intact from the ISS with a substantial load of cargo and is carrying critical science samples for distribution to researchers.
Today’s Dragon departure starts a week of heavy traffic of comings and goings to the ISS involving a series of US and Russian unmanned cargo ships.

The Orbital Sciences Antares rocket with the commercial Cygnus cargo freighter is set to launch on Monday, Oct. 27, from NASA Wallops, VA. It will dock at the ISS on Nov. 2 at the Earth-facing port on the Harmony module just vacated by Dragon.
Russia’s Progress 56 unmanned cargo ship will also undock on Oct. 27. And Progress 57 will launch from Baikonur on Wednesday, Oct 29.
The SpaceX Dragon CRS-4 cargo resupply mission thundered to space on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Sept. 21.

Dragon was successfully berthed at the Harmony module on Sept. 23, 2014.
Among the nearly 5000 pounds of cargo hauled up by Dragon was as an Earth observation platform named ISS-RapidScat loaded in the unpressurized trunk section.
Also loaded aboard were a slew of science experiments, spare parts, crew provisions, food, clothing and supplies to the six person crews living and working aboard the ISS soaring in low Earth orbit under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.
It also carried the first 3-D printer to space for the first such space based studies ever attempted by the astronaut crews. The printer will remain at the station for at least the next two years.
20 mice housed in a special rodent habitat were also aboard, as well as fruit flies.
The ISS Rapid Scatterometer, or ISS-RapidScat, is NASA’s first research payload aimed at conducting near global Earth science from the station’s exterior and will be augmented with others in coming years.

The successful installation and activation of the ISS-RapidScat science instrument on the exterior of Europe’s Columbus module in late September and early October inaugurated a new era in space station science.
RapidScat is designed to monitor ocean winds for climate research, weather predictions, and hurricane monitoring.
The 1280 pound (580 kilogram) experimental instrument is already collecting its first science data following its recent power-on and activation at the station.

“This mission enabled research critical to achieving NASA’s goal of long-duration human spaceflight in deep space,” said Sam Scimemi, director of the International Space Station division at NASA Headquarters.
“The delivery of the ISS RapidScatterometer advances our understanding of Earth science, and the 3-D printer will enable a critical technology demonstration. Investigations in the returned cargo could aid in the development of more efficient solar cells and semiconductor-based electronics, the development of plants better suited for space, and improvements in sustainable agriculture.”
The next SpacX cargo Dragon on the CRS-5 mission is slated for launch no earlier then Dec. 9.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
…………….
Learn more about Commercial Space, Orion and NASA Human and Robotic Spaceflight at Ken’s upcoming presentations:
Oct 26/27: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA
Videos: From Space, Lightning Looks Like Creepy White Blobs
Standing on the ground, we’re used to seeing the bolts and flashes of lightning during epic thunderstorms. But how would it look like from space? These three Vine videos from orbiting NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman provide a glimpse.
As you can see in these videos he uploaded to his Twitter account a few days ago, flashes and pools of light appear in this lightning storm over Kansas that he spotted from the International Space Station. Check out more below the jump. Continue reading “Videos: From Space, Lightning Looks Like Creepy White Blobs”
Gallery: NASA Astronauts Spacewalk Boldly Into The Void, Finishing Vital Repairs
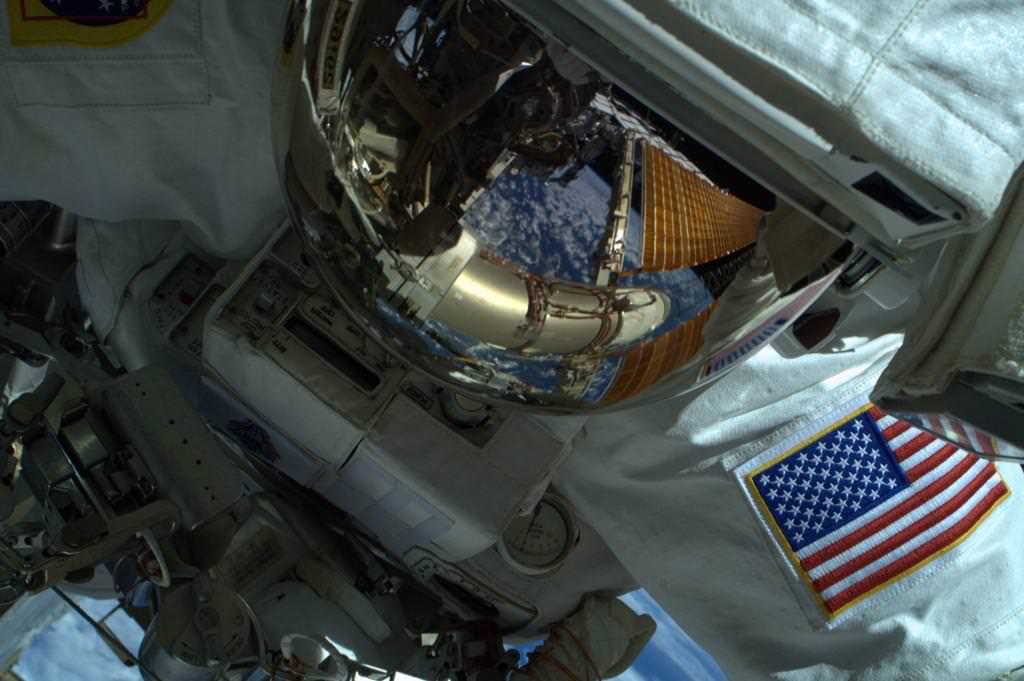
What a view! NASA’s Reid Wiseman and Butch Wilmore spacewalked successfully yesterday (Oct. 15) for more than 6.5 hours, replacing a faulty camera as well as a broken power regulator that was reducing the amount of power available on the International Space Station. The astronauts also shifted equipment to get ready for some bigger upgrades on station to prepare for commercial spacecraft arriving in 2017.
Check out the stunning pictures from the spacewalk below.
Here’s a quick rundown of tasks for today’s #ISS #spacewalk by @astro_reid & #AstroButch: http://t.co/JB95jSoYdz
— Intl. Space Station (@Space_Station) October 15, 2014
Unique perspective of an #ISS solar array from today’s #spacewalk pic.twitter.com/yXSrO1YG1B
— Reid Wiseman (@astro_reid) October 15, 2014
What’s through the tiny window? Today’s #spacewalk duo is on the other side of the airlock hatch. pic.twitter.com/TgTdiF4axp
— NASA (@NASA) October 15, 2014
.@Space_Station spacewalk continues to go well as @astro_reid (left) joins #AstroButch atop the #ISS Harmony node. pic.twitter.com/tsapufeWPI
— Intl. Space Station (@Space_Station) October 15, 2014
Mission Control – Houston is a windowless room…with a view that is out of this world! cc: @astro_reid @astro_ricky pic.twitter.com/ey1YDNuDc7
— Douglas H. Wheelock (@Astro_Wheels) October 15, 2014
#AstroButch cinches up cables of wireless antenna system that provides helmet cam views of #ISS #spacewalks. pic.twitter.com/TdEPPE3KBh
— Intl. Space Station (@Space_Station) October 15, 2014
Welcome back! @Astro_Alex pulls #AstroButch into equipment lock of #ISS Quest airlock after successful #spacewalk. pic.twitter.com/Q1qjY0FJZv
— Intl. Space Station (@Space_Station) October 15, 2014
“;) – this was after the EVA…” #AstroButch @astro_reid pic.twitter.com/UzBDVQWP24
— NASA Astronauts (@NASA_Astronauts) October 15, 2014
Bigelow Inflatable Module to be Added to Space Station in 2015
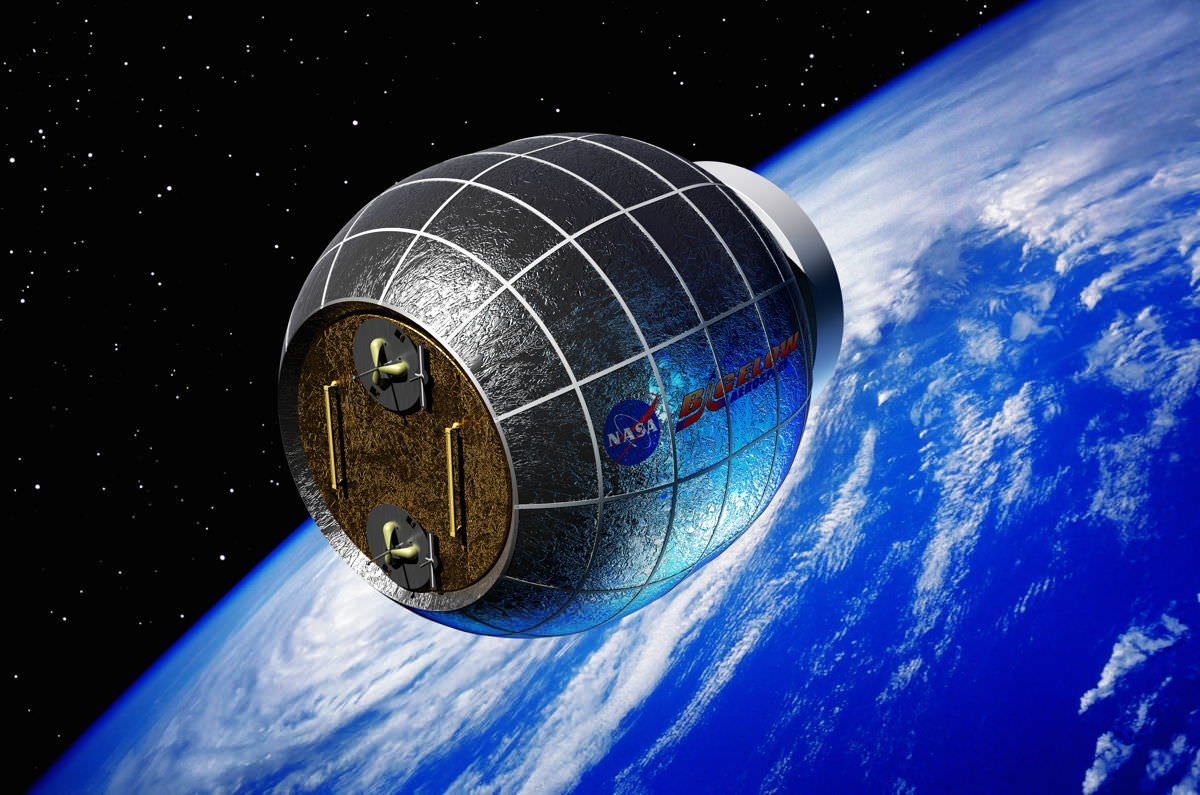

Astronauts aboard the International Space Station are going to be getting an addition in the near future, and in the form of an inflatable room no less. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is the first privately-built space habitat that will added to the ISS, and it will be transported into orbit aboard a Space X Falcon 9 rocket sometime next year.
“The BEAM is one small step for Bigelow Aerospace,” Bigelow representative Michael Gold told Universe Today, “but is also one giant leap for private sector space activities since the BEAM will be the first privately owned and developed module ever to be part of a crewed system in space.”
Continue reading “Bigelow Inflatable Module to be Added to Space Station in 2015”
NASA Inaugurates New Space Station Era as Earth Science Observation Platform with RapidScat Instrument
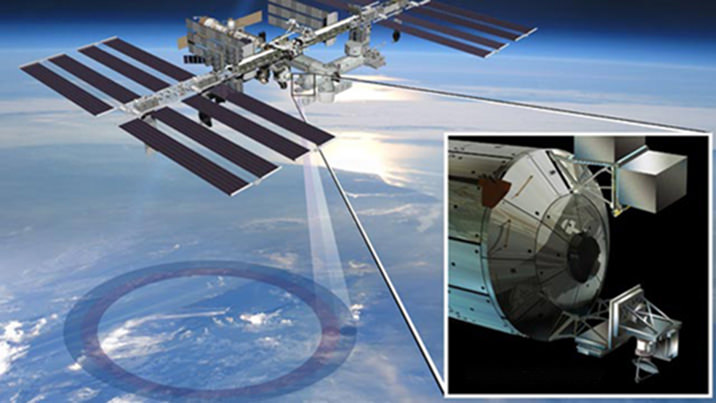

NASA inaugurated a new era of research for the International Space Station (ISS) as an Earth observation platform following the successful installation and activation of the ISS-RapidScat science instrument on the outposts exterior at Europe’s Columbus module.
The ISS Rapid Scatterometer, or ISS-RapidScat, is NASA’s first research payload aimed at conducting near global Earth science from the station’s exterior and will be augmented with others in coming years.
RapidScat is designed to monitor ocean winds for climate research, weather predictions, and hurricane monitoring.
The 1280 pound (580 kilogram) experimental instrument is already collecting its first science data following its recent power-on and activation at the station.
“Its antenna began spinning and it started transmitting and receiving its first winds data on Oct.1,” according to a NASA statement.
The first image from RapidScat was released by NASA on Oct. 6, shown below, and depicts preliminary measurements of global ocean near-surface wind speeds and directions.
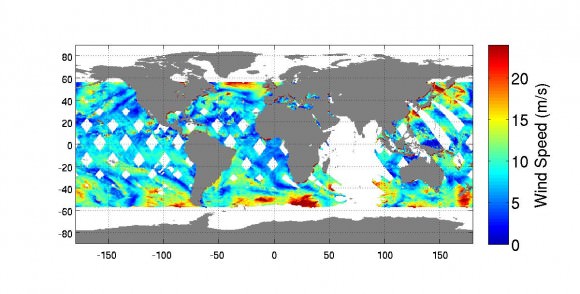
The $26 million remote sensing instrument uses radar pulses to observe the speed and direction of winds over the ocean for the improvement of weather forecasting.
“Most satellite missions require weeks or even months to produce data of the quality that we seem to be getting from the first few days of RapidScat,” said RapidScat Project Scientist Ernesto Rodriguez of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, which built and manages the mission.
“We have been very lucky that within the first days of operations we have already been able to observe a developing tropical cyclone.
“The quality of these data reflect the level of testing and preparation that the team has put in prior to launch,” Rodriguez said in a NASA statement. “It also reflects the quality of the spare QuikScat hardware from which RapidScat was partially assembled.”
RapidScat, payload was hauled up to the station as part of the science cargo launched aboard the commercial SpaceX Dragon CRS-4 cargo resupply mission that thundered to space on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Sept. 21.
Dragon was successfully berthed at the Earth-facing port on the station’s Harmony module on Sept 23, as detailed here.
It was robotically assembled and attached to the exterior of the station’s Columbus module using the station’s robotic arm and DEXTRE manipulator over a two day period on Sept 29 and 30.
Ground controllers at Johnson Space Center intricately maneuvered DEXTRE to pluck RapidScat and its nadir adapter from the unpressurized trunk section of the Dragon cargo ship and attached it to a vacant external mounting platform on the Columbus module holding mechanical and electrical connections.

The nadir adapter orients the instrument to point at Earth.
The couch sized instrument and adapter together measure about 49 x 46 x 83 inches (124 x 117 x 211 centimeters).
Engineers are in the midst of a two week check out process that is proceeding normally so far. Another two weeks of calibration work will follow.
Thereafter RapidScat will begin a mission expected to last at least two years, said Steve Volz, associate director for flight programs in the Earth Science Division, NASA Headquarters, Washington, at a prelaunch media briefing at the Kennedy Space Center.
RapidScat is the forerunner of at least five more Earth science observing instruments that will be added to the station by the end of the decade, Volz explained.
The second Earth science instrument, dubbed CATS, could be added by year’s end.
The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) is a laser instrument that will measure clouds and the location and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, and other particulates in the atmosphere.
CATS is slated to launch on the next SpaceX resupply mission, CRS-5, currently targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral, FL, on Dec. 9.

This has been a banner year for NASA’s Earth science missions. At least five missions will be launched to space within a 12 month period, the most new Earth-observing mission launches in one year in more than a decade.
ISS-RapidScat is the third of five NASA Earth science missions scheduled to launch over a year.
NASA has already launched the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, a joint mission with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency in February, and the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) carbon observatory in July 2014.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
…………….
Learn more about Commercial Space Taxis, Orion and NASA Human and Robotic Spaceflight at Ken’s upcoming presentations:
Oct 14: “What’s the Future of America’s Human Spaceflight Program with Orion and Commercial Astronaut Taxis” & “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Princeton University, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton (AAAP), Princeton, NJ, 7:30 PM
Oct 23/24: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA
Earth Shines In Space Pictures In Glory You’ve Rarely Seen Before
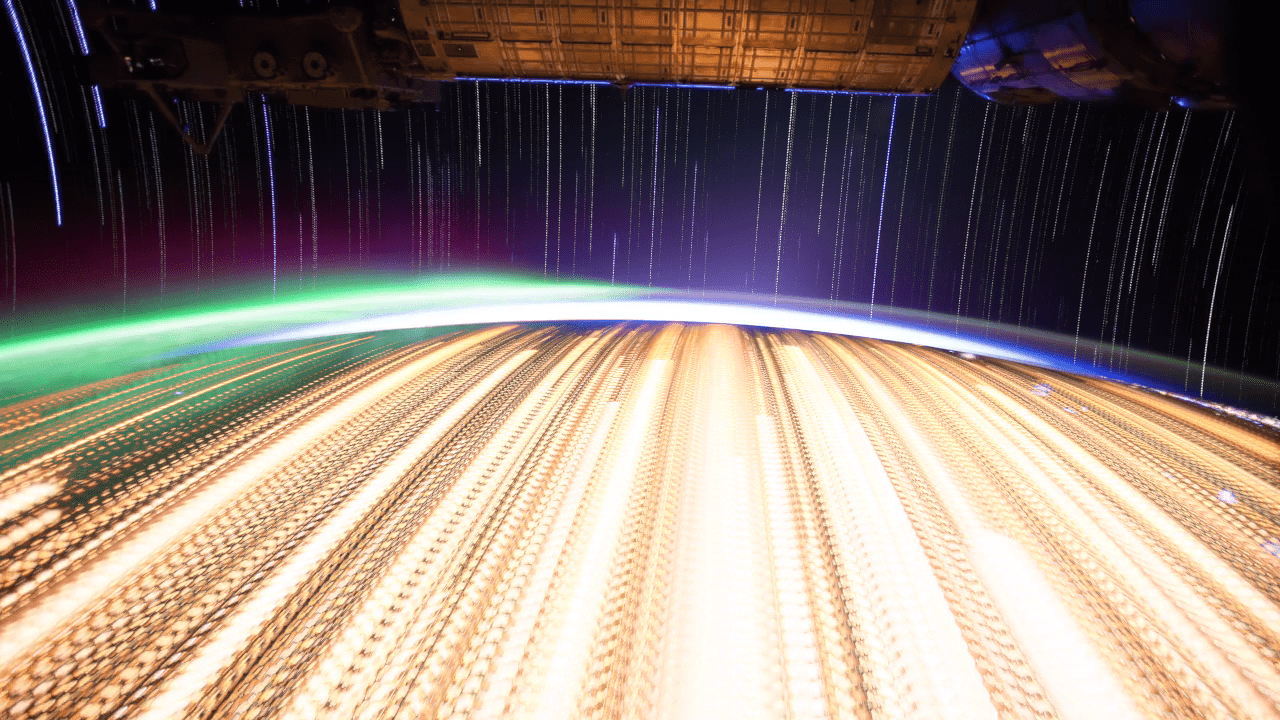

We truly live on a beautiful planet, and sometimes it just takes a bit of an unusual picture to remind us of that fact. An intrepid amateur took time lapse pictures from the Expedition 28 and 29 crews (filmed in 2011) and combined the shots to create some incredible composite pictures of our planet.
The pictures below are the result of blending 9 different timelapse sequences in two different ways,” wrote a user dubbed zqyogl on Imgur. “The first in each set of two was made by finding the brightest colour for each pixel, and the second by averaging every frame of the timelapse.”
Anyone else out there reminded of Don Pettit’s stunning pictures from space a few years ago? To check out the entire gallery, visit this website to download everything in high-resolution glory. The source video is below the jump.
Earth from Michael König on Vimeo.
h/t Reddit
Magical Images From Two Prolific Astronaut Tweeters Doing Their First Spacewalk
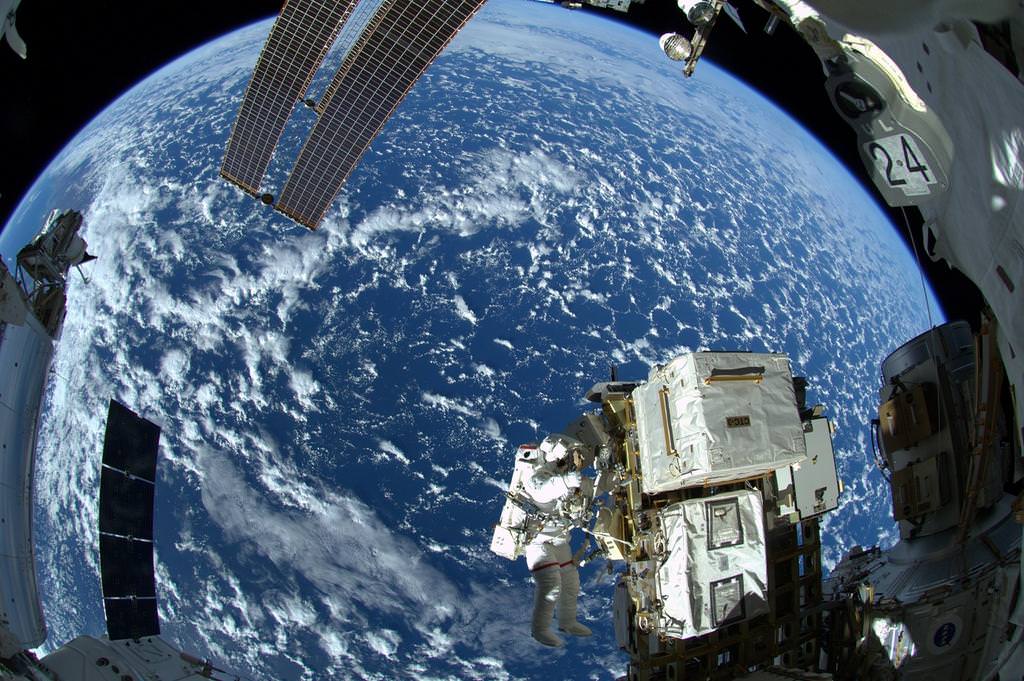

What happens when you send two prolific social media astronauts out on a spacewalk? The best photos ever. Reid Wiseman (NASA) and Alexander Gerst (European Space Agency) both participated in their first extra-vehicular activity yesterday, and sent back amazing pictures of what the view looked like outside their visors.
Their comments are also fun: “reasonably INSANE” and “learning to fly” are among the phrases they put on Twitter, which you can see in the photo gallery below. The spacewalkers accomplished the major task of yesterday’s spacewalk, placing a failed International Space Station pump module in a permanent location, and doing a couple of minor maintenance tasks.
The view was reasonably INSANE during the #spacewalk pic.twitter.com/V8PbaPo2Rg
— Reid Wiseman (@astro_reid) October 7, 2014
Learning to fly. #EVA27 #selfie pic.twitter.com/LmoYKLaIJt — Alexander Gerst (@Astro_Alex) October 8, 2014
What an experience and an honor to share it with @Astro_Alex pic.twitter.com/3WACwhCPOQ
— Reid Wiseman (@astro_reid) October 7, 2014
Safe to say, this was the most amazing thing I have done in my life. #spacewalk #EVA27 pic.twitter.com/HiX6ZrN0U7 — Alexander Gerst (@Astro_Alex) October 8, 2014
Guilty pleasure to turn the camera upon thyself during a #spacealk pic.twitter.com/ivCZ4rxNyF
— Reid Wiseman (@astro_reid) October 7, 2014
My friend @astro_reid doing what he’s good at. #EVA27 #spacewalk https://t.co/iYXV91FvXi pic.twitter.com/8SzrIJUwRm — Alexander Gerst (@Astro_Alex) October 8, 2014
And here’s a bonus for those who scrolled to the end of this post — the first Vine video posted real-time during a spacewalk! This comes courtesy of NASA’s account. Click on the video to access the audio, which is Reid Wiseman exclaiming on the view over southern South America.
Watch the Space Station Zip Across the Sun: Incredible New Views from Thierry Legault
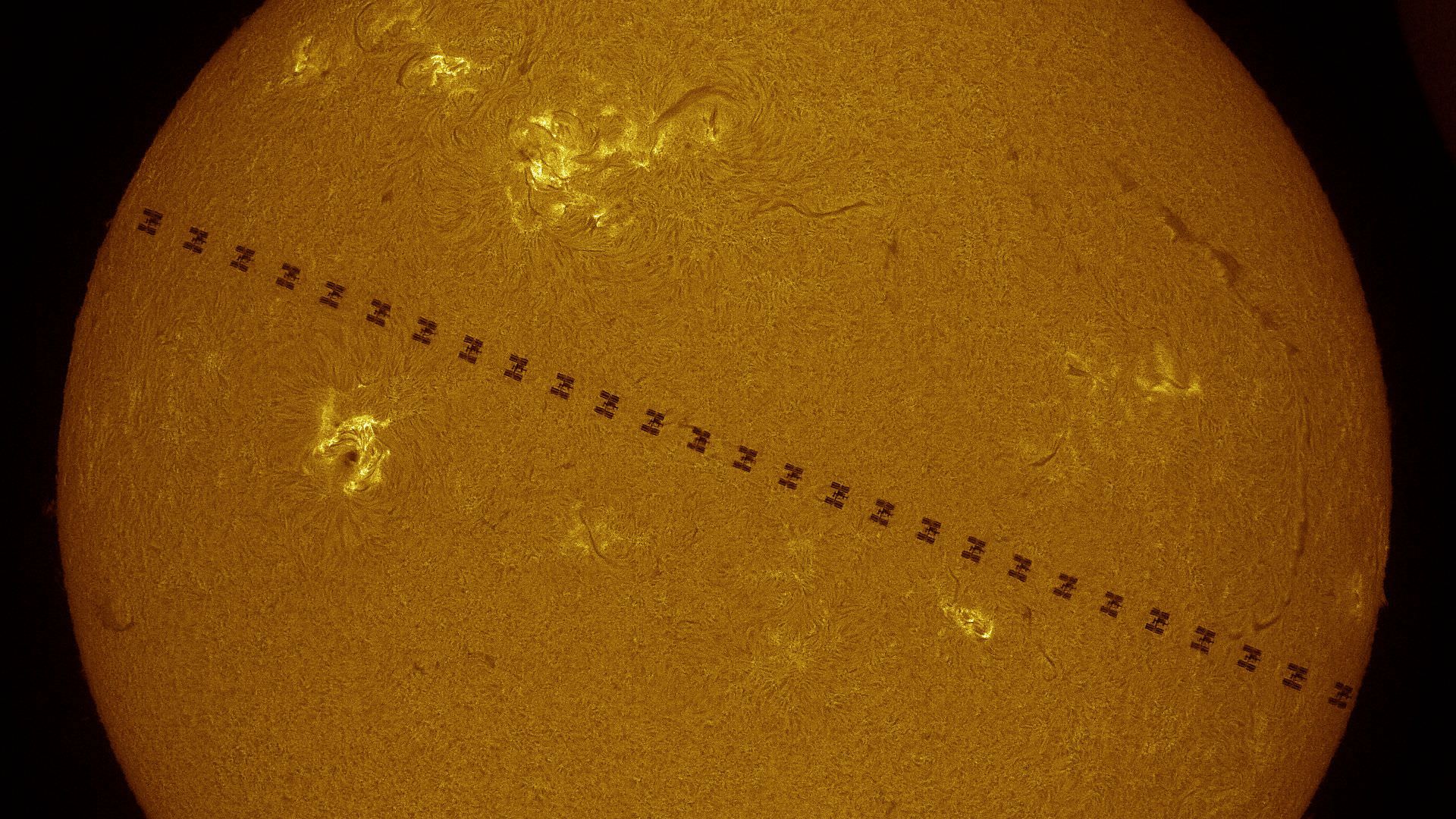
Take a look at the incredible detail in the latest work from astrophotographer extraordinaire Thierry Legault. He captured images of the International Space Station transiting in front of the Sun in September 2014, and visible in the images are several of the visiting docked spacecraft (at one point in September there were 5 ships parked at the Station). Clearly visible are the ATV-5 ‘Georges Lemaitre,’ the Soyuz 39 and the Progress 56.
Wow!
Keep in mind, an ISS transit lasts less than a second (.7 seconds to be exact — and is shown in real time in the video above) and capturing the event in images must be timed with ultimate precision. Legault has captured a detailed night passage of the ISS, as well. See images below.
Legault used his Celestron C14 EdgeHD to capture these images, and for the solar transit of ISS, he used both both H-alpha and white light filters.
In a previous Universe Today article, Legault explained how he studies maps, and will travel thousands of kilometers to be in the right place to capture such a transit. He uses a radio synchronized watch to know very accurately when the transit event will happen.
His camera has a continuous shuttering for 4 seconds, and he begins the imaging sequence 2 seconds before the calculated time.
“For transits I have to calculate the place, and considering the width of the visibility path is usually between 5-10 kilometers, but I have to be close to the center of this path,” Legault explained, “because if I am at the edge, it is just like a solar eclipse where the transit is shorter and shorter. And the edge of visibility line of the transit lasts very short. So the precision of where I have to be is within one kilometer.”

See more images and information at Thierry’s website, and we thank him for sharing his work with Universe Today.

One More Absolutely Amazing Timelapse from the International Space Station
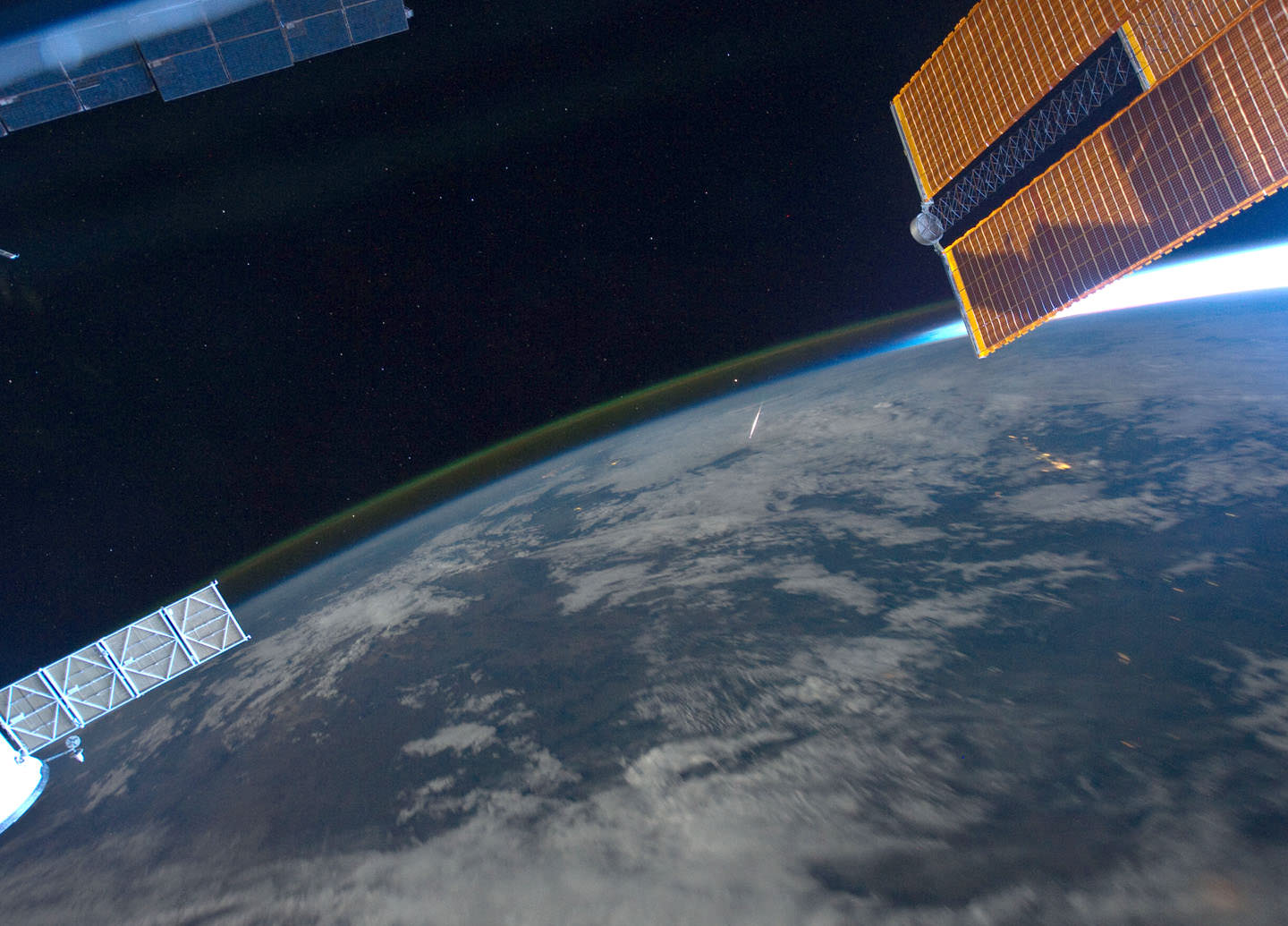

We’ve featured several timelapse compilations of footage and imagery taken from the International Space Station (like here, here and here) but this one put together by Phil Selmes is great in that it also includes footage *of* the ISS, as shot by the astronauts on the space shuttle as well as actual space to ground audio communications. Phil said he included the audio clips “to remind the audience of the humanity that inhabits the space station.”
There is just something about these videos from the ISS that speaks to your soul. Phil told Universe Today that while putting this together, he saw “how different our world looks just 370kms above our heads. I didn’t see politics, races, borders, countries, religions or differences,” he said via email. “I saw one planet, one world, one incredibly beautiful miracle in the absolute vastness of the universe. It gave me some perspective, ironically it brought me ‘back to earth.’”
The video and imagery is from the Johnson Space Center’s Gateway to Astronaut Photography of the Earth.
Look for more #TimelapseThursday videos in the weeks to come.