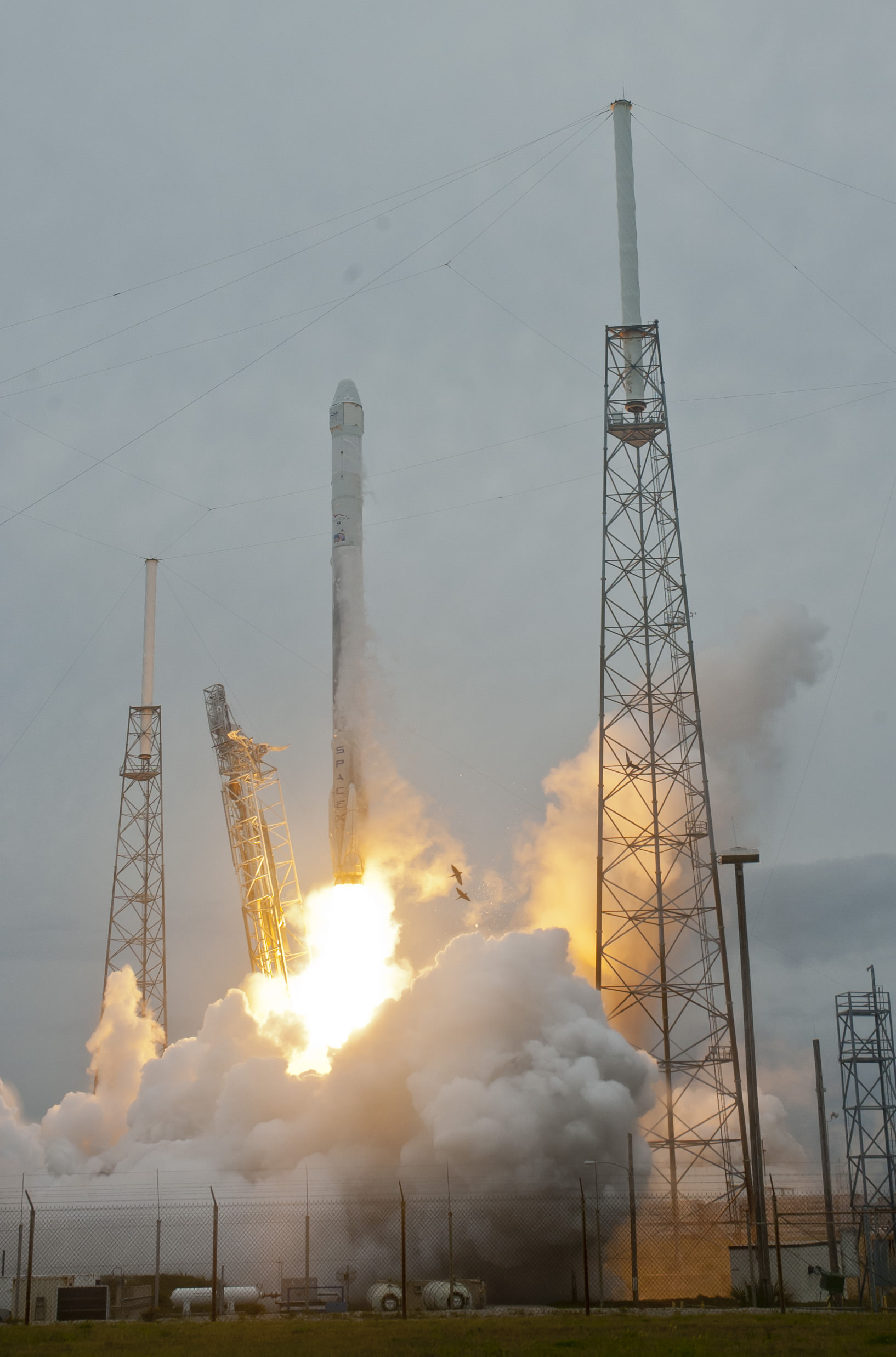
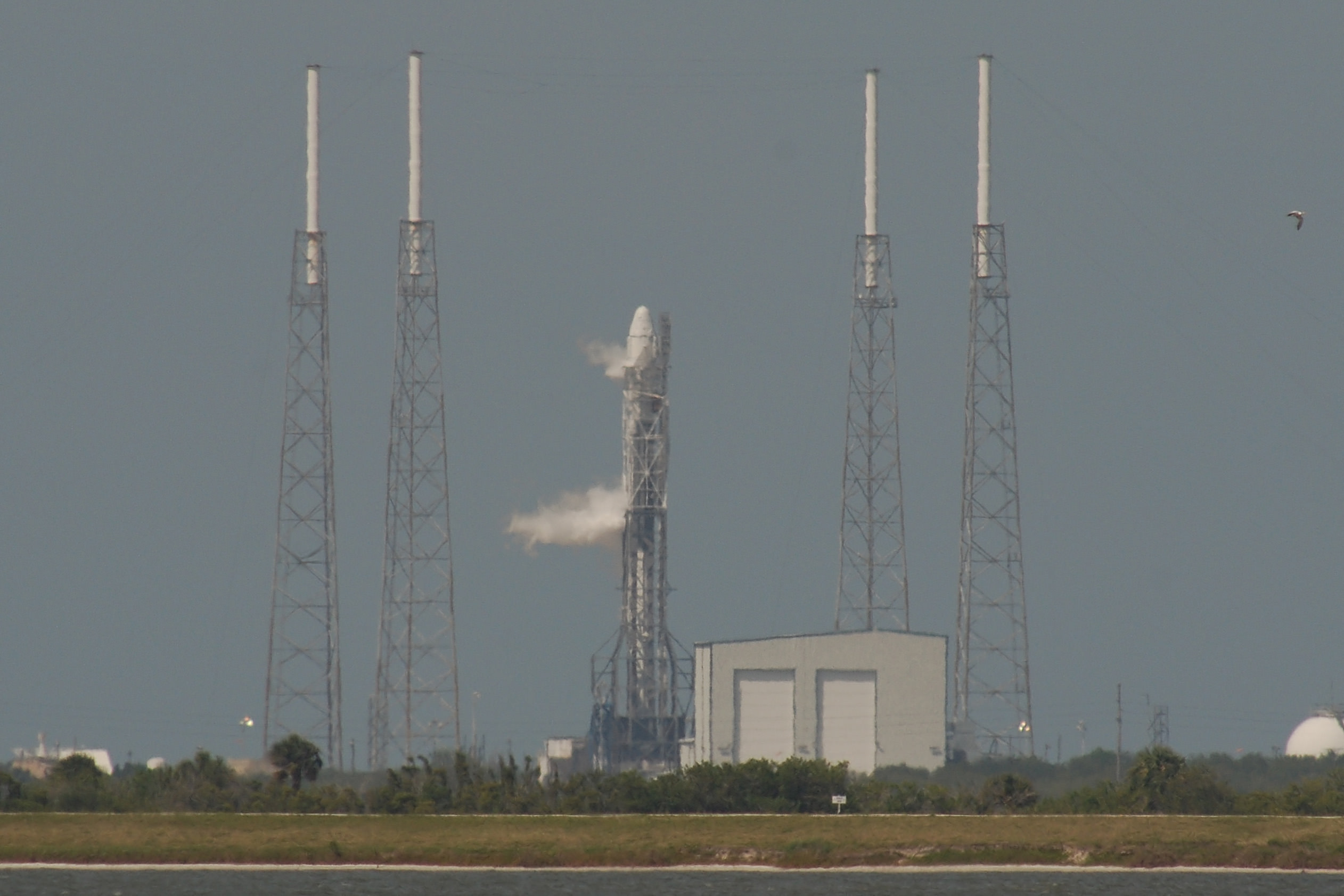
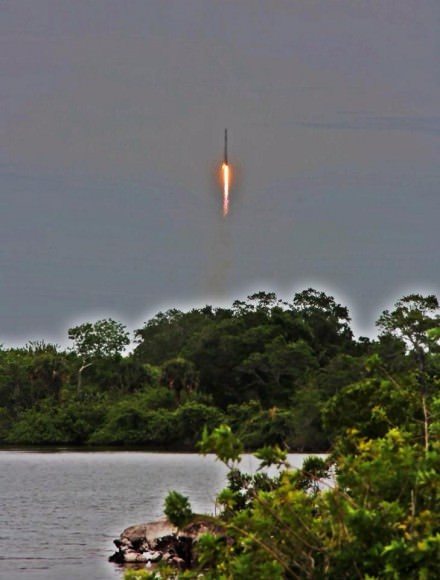
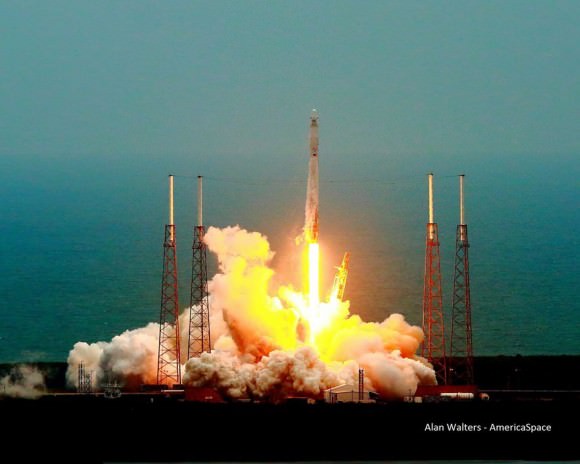
SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon resupply ship launch from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 18, 2014. Credit: Jeff Seibert/Wired4Space
See expanding launch gallery below[/caption]
A mighty SpaceX rocket carrying the firms commercial Dragon resupply ship loaded with nearly 2.5 tons of NASA science instruments and critical supplies thundered to space this afternoon on a two day journey bound for the International Space Station.
The Dragon vessel launched atop the 20 story tall, upgraded Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida precisely on time at 3:25 p.m. EDT (1925 GMT), Friday, April 18.
“I want to congratulate SpaceX. Everyone did a great job” said William Gerstenmaier, NASA associate administrator for human exploration and operations, at a post launch briefing at the Kennedy Space Center press site.
“The SpaceX team went the extra mile to get everything ready for an on time launch.”
The spectacular blastoff went off without a hitch despite a poor weather prognosis in the morning that brightened considerably in the final hours leading up to the afternnon liftoff.
“Everything went well with the ascent,” said SpaceX CEO and founder Elon Muck at the briefing.
“I’m pretty excited. We did a good gob for our NASA customer and that’s very important,” Musk added.
The on time blastoff sets the stage for an Easter Sunday, April 20, rendezvous and berthing of the Dragon resupply spacecraft at the massive orbiting outpost packed with a striking variety of science experiments and needed supplies for the six person crew.
Station crew members Rick Mastracchio and Steven Swanson will grapple the Dragon cargo freighter with the 57 foot long Canadarm2 on Easter Sunday at about 7:14 a.m. if all goes well and then berth it at the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module.
The SpaceX-3 mission marks the company’s third resupply mission to the ISS under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the ISS during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016.
There are over 150 science experiments loaded aboard the Dragon capsule for research to be conducted by the crews of ISS Expeditions 39 and 40.
“SpaceX is delivering important research experiments and cargo to the space station,” said Gerstenmaier.

“The diversity and number of new experiments is phenomenal. The investigations aboard Dragon will help us improve our understanding of how humans adapt to living in space for long periods of time and help us develop technologies that will enable deep space exploration.”
This unmanned SpaceX mission dubbed CRS-3 mission will deliver some 5000 pounds of science experiments, a pair of hi tech legs for Robonaut 2, a high definition imaging camera suite, an optical communications experiment (OPALS) and essential gear, the VEGGIE lettuce growing experiment, spare parts, crew provisions, food, clothing and supplies to the six person crews living and working aboard the ISS soaring in low Earth orbit under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.

To date SpaceX had completed two operational cargo resupply missions and a test flight. The last flight dubbed CRS-2 blasted off a year ago on March 1, 2013 atop the initial version of the Falcon 9 rocket.
The next launch of Orbital Sciences Antares/Cygnus commercial rocket to the ISS from NASA Wallops, VA, was tentatively slated for May 6. But the target date will now slip to into mid-June since it can’t arrive until the Dragon departs.

Both the Dragon and Antares dock at the same port on the Harmony module at the end of the station.
This extra powerful new version of the Falcon 9 dubbed v1.1 is powered by a cluster of nine of SpaceX’s new Merlin 1D engines that are about 50% more powerful compared to the standard Merlin 1C engines. The nine Merlin 1D engines 1.3 million pounds of thrust at sea level rises to 1.5 million pounds as the rocket climbs to orbit
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Orion, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.