It seems an unlikely scenario: a teenager from Minnesota helping Italy’s next astronaut talk to the public about spaceflight. But for Luca Parmitano, who has mentored Abigail “Abby” Harrison for two years, it’s a way to reach out to a young audience. For Abby, it brings her closer to her dream of becoming an astronaut herself.
Parmitano does have the official outreach team available through the Italian Space Agency (which is part of the European Space Agency) and NASA, he acknowledged. Official mission reports will proceed as usual through those agencies’ press releases and social media accounts.
He’s pursuing this partnership with Abby, however, to have an additional “channel” targeted directly at children and teenagers, Parmitano told Universe Today:
It’s very simple. I thought one of the most important things that I can do in my job is talking to young people, youngsters, and try to inspire them try to guide them towards choosing a career path that goes towards science, technology, exploration of all sorts.
My message is to try to find something that you like, and to pursue it, and don’t wait for things to happe, but make it happen yourself. At one point, talking to Abby — this fantastic young girl who is so enthusiastic — I thought maybe she would be much better at communicating with kids than I could. I’m 36 years old. Maybe I don’t realize it, but I may be disconnected from the age group.
Parmitano is no social media pushover himself, though. The first-time flyer has a “landing page” website at LucaParmitano.com giving one-stop shopping for his Twitter, Facebook and Google pages. And just last week, he did a Google+ hangout with his protégé. (You can watch the whole thing below.)
Abby, at the tender age of 15, has amassed qualifications of her own. The Minnesota teenager is a Space Camp alumnus. She’s planning to learn Russian — an important language for the space program — and is already taking lessons in Mandarin. Her Twitter account has about 6,500 followers. And she’s raising money on Rockethub to see Parmitano’s launch in Kazakhstan next month and do outreach afterwards. With 19 days left, Abby’s approaching half of her $35,000 goal.
The aspiring Mars astronaut has a huge list of activities planned during Parmitano’s mission. She’ll share daily updates from the astronaut on her blog (AstronautAbby.com) and various social media profiles. She proposes an “Ask Luca” series where readers will be able to send questions to the Italian astronaut.
There also will be articles to write, Skype classroom chats to do, and a conference tour — including the International Mars Society Convention in August. Besides the social media updates, Abby is in the midst of booking appearances at conferences and scheduling chats with classrooms. There are more than 20 schools who have signed up for her to be a speaker, either in-person or by Skype.
“That is great, because I won’t be able to be there,” Parmitano said with a laugh.
It was two chance connections that brought him together with Abby. In 2011, Abby and her mother flew to Florida to see the penultimate launch of the space shuttle, mission STS-134. Abby’s mother, Nicole, briefly talked to Parmitano at a tweetup. Then Abby herself met Parmitano at the airport while waiting for the flight home.
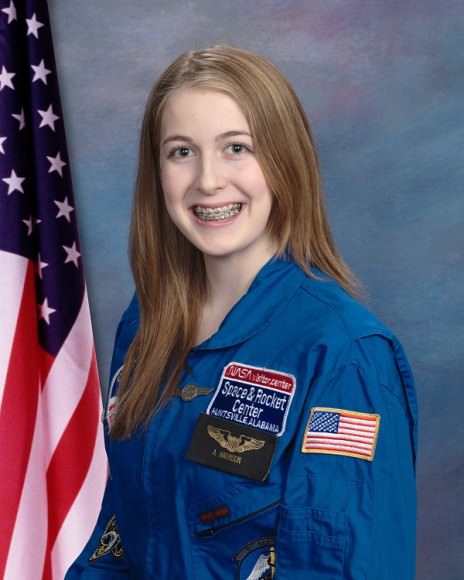

The teenager and astronaut, who both had space dreams from young childhood, made a professional connection. Parmitano agreed to be Abby’s mentor. The two kept in touch in the years following, then Abby proposed her outreach program to compliment ESA’s activities.
“The main difference [over ESA’s outreach] is when it’s my program, it’s kid to kid. I’m trying to show that by working hard, you can do great things, and I’m an example of that,” Harrison said. “As an aspiring astronaut, you can meet amazing people and have amazing experiences.”
As a rookie, Parmitano said he is looking forward to the experiences his first spaceflight will bring, no matter who is watching. He joked that Italy does not really pay attention to him as an astronaut — the media flock to Samantha Cristoforetti, Italy’s first female astronaut, who is expected to reach station on Expedition 42/43.
“From Day 1, since we were selected, every news magazine went crazy for the female astronaut — and by the way, there’s another guy. I started introducing myself as ‘the other guy.’ ”
But the mission is still a notable one for Italy. Parmitano is the first assigned to a flight from the European Space Agency’s latest class of six astronauts, who call themselves The Shenanigans. The Italian Space Agency got this chance due to a substantial hardware contribution to the station program: a modified multipurpose logistics module (Leonardo) that was adapted for use as a laboratory on station. It and two other MPLMs (Raffaello and Donatello) ferried cargo on shuttle flights to use on station, too.
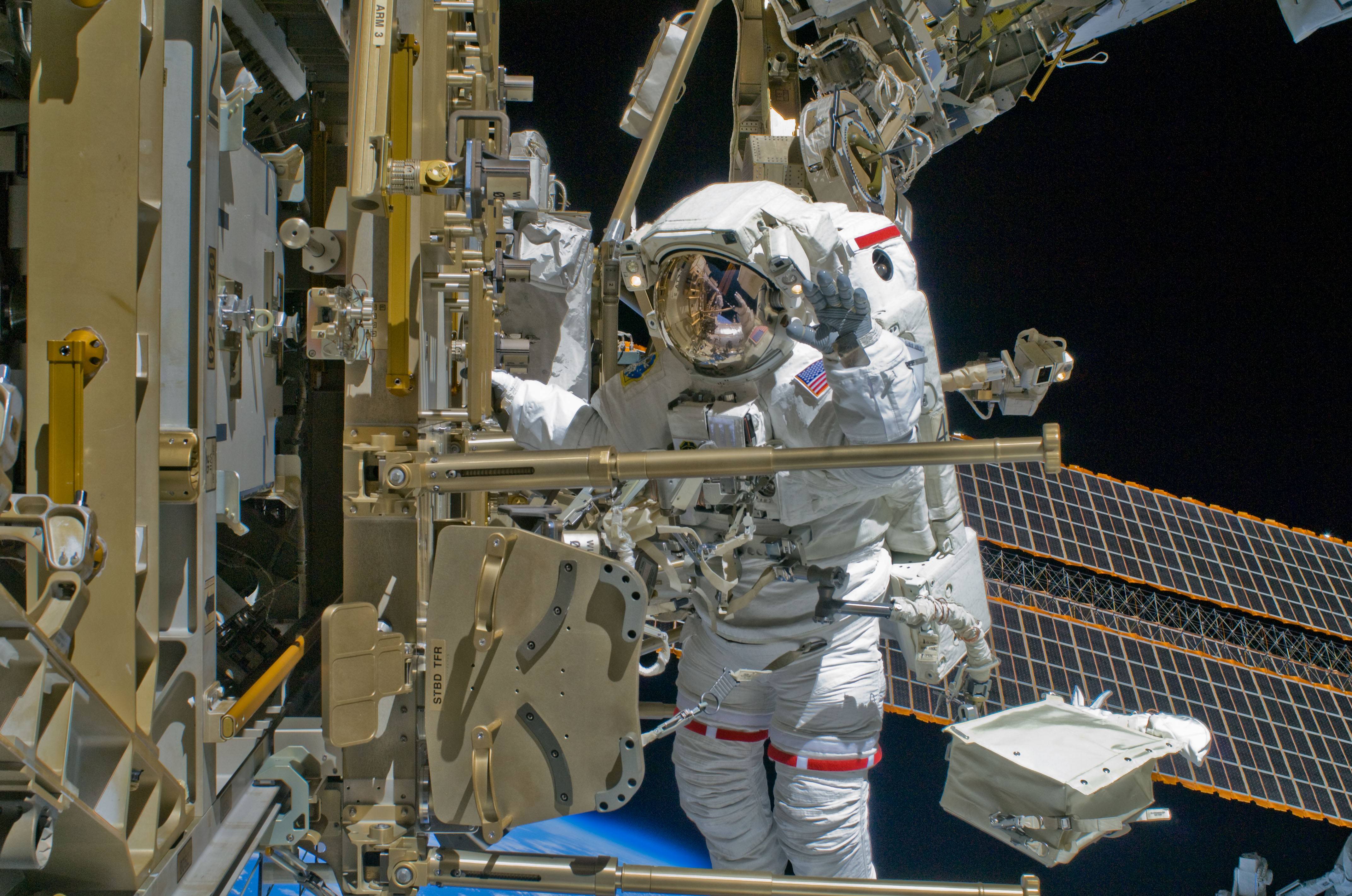
Parmitano will perform the first Italian spacewalk — two of them are planned, in fact. He and crewmate Chris Cassidy (a former Navy SEAL who spoke with Universe Today last month) are scheduled to go outside in July to swap out experiments, put up a blanket to shield part of the station from space exposure, and install new orbital replacement units to upgrade certain ISS functions.

In between, of course, Parmitano has dozens of experiments to work through — contributions from various station partners ranging from Japan to Canada.
An Italian one he speaks of frequently involves him deliberately setting controlled fires on station. Called ICE-GA (Italian Combustion Experiment for Green Air), it’s intended to seek renewable fuels that are less polluting than what we use today. Results will be used for future space fuels, and also on the ground to reduce toxic emissions.
Despite his high-flying duties, Parmitano plays down any adulation from Abby.
“She’s a tremendous young lady, and she has enthusiasm to sell, and maturity way beyond her age,” he said. “It’s really an honor for me to be called her mentor. I learn from her more than she learned from me.”
As for how Abby plans to get to Mars, first she is figuring out what interests her to narrow down her university choices.
Abby, who is entering her junior year in high school next year, is conscious that time away from school is hard to do when starting to think about university applications. She’s working out alternative scheduling arrangements with her teachers and keeping them apprised of what could be a busy speaking schedule in the coming months.
She’s still mulling her options for university — perhaps the United States Air Force Academy, or maybe studying geology at the University of Colorado. Along the way, she’ll keep in contact with Parmitano.
“How important it is to work hard was really the main subject of our discussion [at the airport],” Abby said, “and how if you have a dream and you set a goal, you can achieve it with hard work.”