The Whitewater-Baldy fire is the largest wildfire in New Mexico’s history and has charred more than 465 square miles of the Gila National Forest since it started back on May 16, 2012 after several lightning strikes in the area. This wildfire produced so much smoke that it was visible even at night to the astronaut photographers on the International Space Station. This image was taken on June 2, 2012 by the crew of Expedition 31 on the ISS, with a Nikon D3S digital camera. A Russian spacecraft docked to the station is visible on the left side of the image.
Credit: NASA Earth Observatory website.
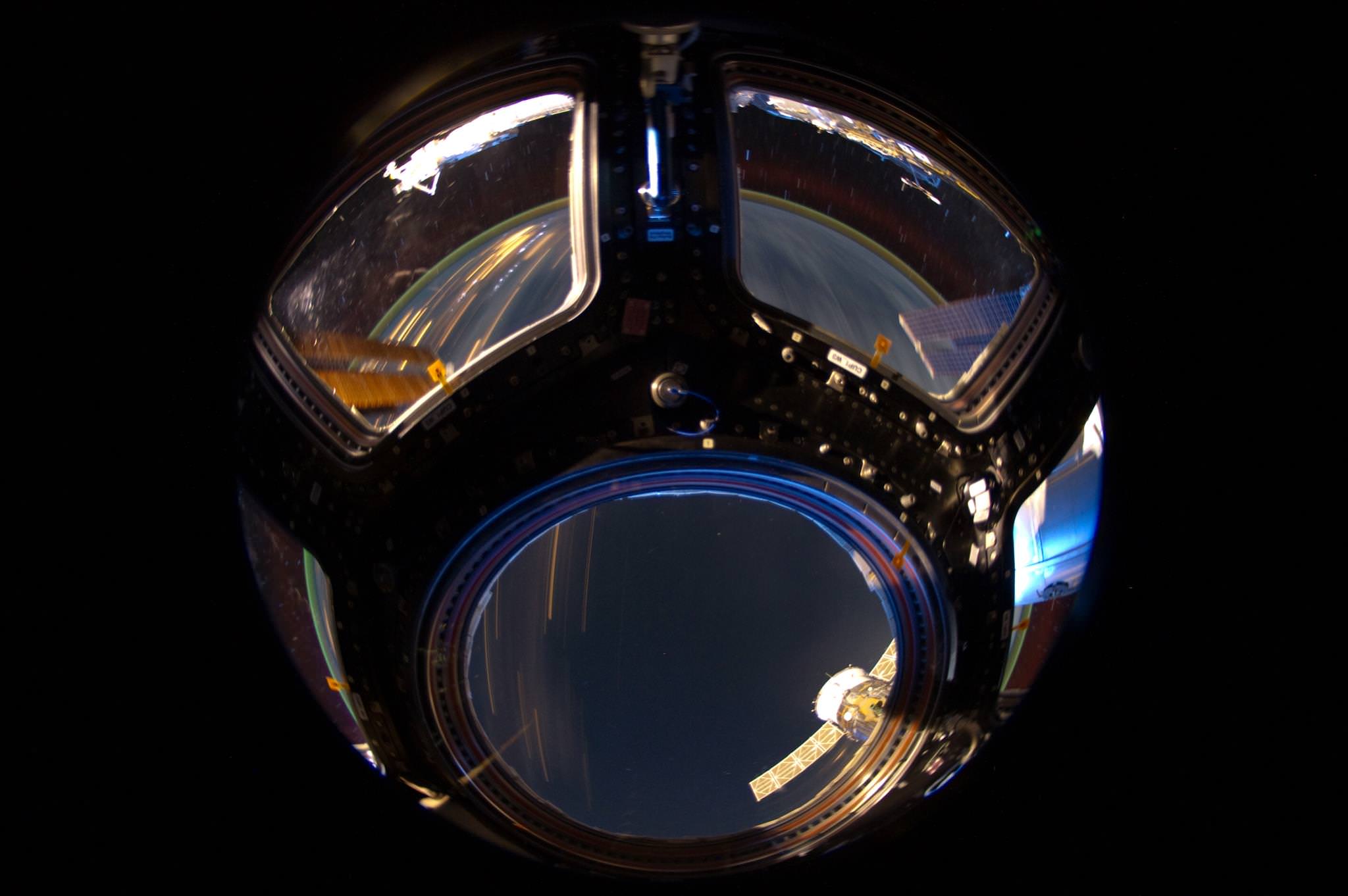
A Sci-Fi View from the ISS
What an awesome image of the Cupola on the International Space Station, with a view of Earth whizzing by! But, is the astronaut-photographer on the outside looking in, or on the inside looking out of the Cupola? We know it is taken from the inside, with a view of the Pacific Ocean near Mexico’s Baja Peninsula, but it offers a stunning and futuristic — if not somewhat perplexing — perspective. It was captured at 04:59 GMT June 26, 2012. Credit: NASA
ISS Expedition 31 Crew Returns Safely to Earth
We’re sure going to miss Don Pettit’s and Andre Kuipers’ reports and images from the International Space Station. Pettit, Kuipers and Russian Commander Oleg Kononenko undocked from the International Space Station and returned safely to Earth on July 1, wrapping up their six-and-a-half-month mission in orbit.
They landed in their Soyuz TMA-03M spacecraft in Kazakhstan at 08:14 a.m. UT (2:14 p.m. local time) after undocking from the space station’s Rassvet module at 04:47 UT. This video shows a great view of the Soyuz slowly drifting down (it’s interesting to see the parachute undulate, looking almost like a jellyfish!) and then visible are the breaking thrusters firing just a second before the hard landing.
The trio originally arrived at the station back on Dec. 23, 2011, and during this mission spent a total of 193 days in space, 191 of which were aboard the station.
During their expedition, the crew supported more than 200 scientific investigations involving more than 400 researchers around the world. The studies ranged from integrated investigations of the human cardiovascular and immune systems to fluid, flame and robotic research. They also were part of the team that successfully berthed the first commercial spacecraft to visit the ISS, the SpaceX Dragon capsule.
Before leaving the station, Kononenko handed over command of Expedition 32 to the Russian Federal Space Agency’s Gennady Padalka, who remains aboard the station with NASA astronaut Joe Acaba and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Revin. NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Akihiko Hoshide will join them July 17. Williams, Malenchenko and Hoshide are scheduled to launch July 14 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
During Expedition 31, Pettit used household objects aboard the station to perform a variety of unusual physics experiments for the video series “Science Off the Sphere,” like his recent video showing water balloons in space. Through these demonstrations, Pettit showed more than a million Internet viewers how space affects scientific principles.
On June 25, Pettit reached a milestone: spending one cumulative year in space, combining his time in orbit on Expedition 6, Expedition 30/31 and the STS-126 space shuttle Endeavour flight to the station in November 2008. Pettit now has 370 days in space, placing him fourth among U.S. space fliers for the longest time in space.
Kuipers conducted over 50 scientific experiments for ESA, and shared, almost daily, images and reports of his stay in space. The next ESA astronaut to board the Space Station is Luca Parmitano of Italy, who will fly on Soyuz TMA-09M in 2013 as member of Expedition 36/37.
Water Balloons in Space
As part of his ongoing (and always entertaining) “Science Off the Sphere” series, Expedition 31 flight engineer Don Pettit experiments in orbit with a classic bit of summertime fun: water balloons.
Captured in real-time and slow-motion, we get to see how water behaves when suddenly freed from the restraints of an inflated latex balloon… and gravity. With Don NASA doesn’t only get a flight engineer, it gets its very own Mr. Wizard in space — check it out!
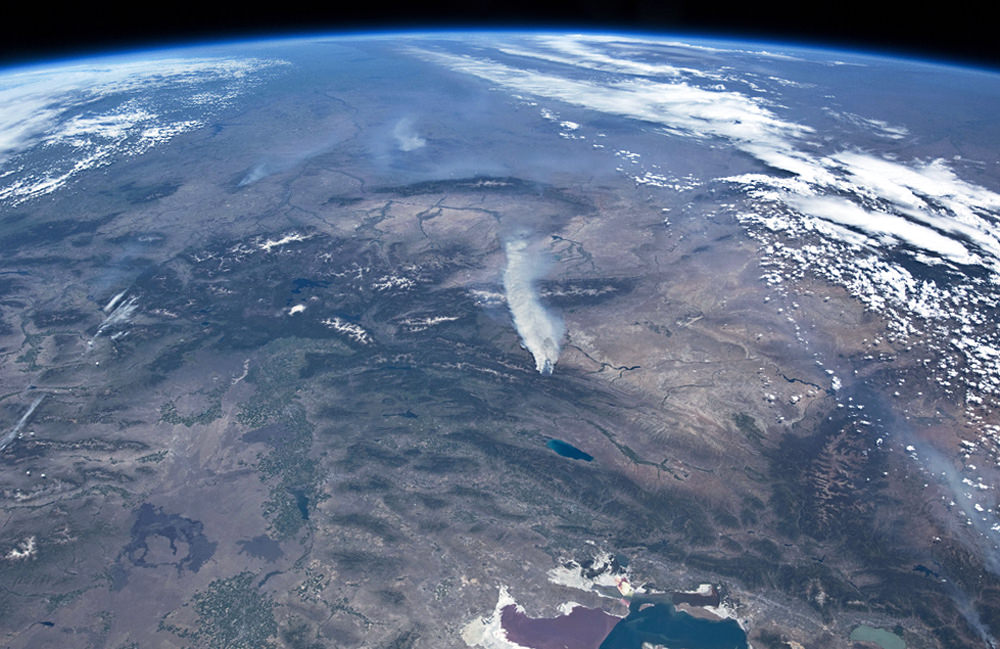
Smoking Wildfires Seen From Space
Wildfires continue to rage across the western United States, burning forests and property alike, and even the most remote have sent up enormous plumes of smoke that are plainly visible to astronauts aboard the Space Station.
The photo above was taken by an Expedition 31 crew member on June 27, showing thick smoke drifting northeast from the Fontenelle fire currently burning in Wyoming. More plumes can be seen to the north.
Utah’s Great Salt Lake can be seen at the bottom right of the image. Its two-tone coloration is due to different species of algae that live in the lake, which is split by the physical barrier of a railroad causeway.
You can watch a video of the wildfires in the west taken from the ISS here, and see more “fire and smoke” news and images from space here.
Image: NASA
Don Pettit’s Guide to Space Etiquette: Having Guests for Dinner
If you haven’t been reading astronaut Don Pettit’s “Letters to Earth” – a diary of his 6-month stay in space – it’s a great look at living on board the International Space Station. He talks about everything from the big events to the minutia of daily life. His latest entry about being a gracious host in space is classic Pettit: detailed, precise, with just a hint of snark. We present it in its entirety here:
It does not matter that you’ve seen the same faces every day for months on end; you’d still like to invite everyone over to “your module” for dinner. With invitations accepted, you prepare for the occasion. But what is the expected etiquette for entertaining in orbit? How do you arrange things so your guests will not think you are gauche? Here are a few space-tested guidelines to help in the preparations.
Have plenty of food, and serve your very best. Now is the time to break out those thermal-stabilized pouches of beef steak that you have been hoarding. Bring out any specialty item from your personal crew allotment (these items arrive on the periodic unmanned resupply spacecraft that visit us). Perhaps you can share a can of smoked anchovies, New Mexico green chili, or a piece of Old Amsterdam cheese. Always serve something special that is not repeatedly eaten on the standard nine-day menu. Being generous now will reap more benefits than eating these delicacies in solitude.
The choice of beverage is rather limited. You can serve the standard ones: coffee, tea, and artificially flavored, artificially colored, sugar-loaded, fruit-replica drinks. All, of course, are served in a bag, and you sip the fluid through a straw. The image of an insect sucking the juices from some lower insect may come to mind, but in space it is considered impolite to give voice to such imagery.
You can provide a special treat if you have access to one of the research refrigerators. In space, all your food is either hot or at room temperature. When you live in an isothermal environment, it can be a real treat to serve your guests a bag of cold water.
For special occasions—perhaps after a space walk or the docking of a resupply vehicle—you can serve your beverages in a “zero-g” cup. This is something you will have to make from scrap plastic sheeting (instructions are in Appendix C). These cups allow you to sip beverages from an open container, like we do on Earth. Zero-g cups, unlike bags with straws, are better for social rituals like toasting, and will bring a smile to the faces of your guests.
It is important to dress up your galley. Have full packets of wet and dry wipes within easy reach on the galley table. Take any partial packets and save them for another time. Empty the trash bins. A full trash bin is problematic; a handful of small things typically float out when new items are added. This rudely interrupts conversation while everyone scatters to collect the floating debris. It is good to have two trash bins; the standard-sized one for largish items, and an old wet wipe container for small ones. This separation of smaller trash—cutoff pouch corners, food crumbs, and wrappers—helps prevents their release when the lid is opened. Be sure to label this wet wipe container “trash”. Newly arrived crew may not be aware of this trash protocol, so it is best to politely demonstrate by example. They will learn quickly enough.
Clean the food scissors. Scissors are needed to open food pouches, as tearing them along the built-in perforations usually results in liberating hot droplets of fatty ooze and other asteroid-like particles. That’s why, if the scissors aren’t kept clean, they become caked in solidified gravy to the point where they become glued shut (not to mention being slightly repulsive). Such a state is considered rude, so clean your scissors before the guests arrive.
Always have a loaner spoon available. In weightlessness, it is easy to lose things. It is not unusual in a group of six for someone’s spoon to have floated off. Having a clean loaner spoon allows for the evening to continue and the conversation to flow. It is rude to give your guest a loaner spoon caked in crud from the last time it was used. The lost spoon is usually found by morning, stuck to a ventilator inlet screen, and your guest will appreciate it being returned.
Always put out new tape. The galley table has multiple spots of Velcro to park packets of food. However, not all packets and pouches have mating spots of Velcro, which means they can’t be set down on the table. Several strips of duct tape, carefully folded so the adhesive side is out (see Appendix D for instructions), allows such containers to be parked on the table. Tape left over from the previous week, while perfectly functional, collects errant crumbs, hairs, lint, and other unsightly things. Displaying dirty tape is exceedingly rude to your guests; always put out new, clean tape.
In space, catching food in your mouth is considered polite. Opening wide and making a clean catch will most always bring cheers from your guests. In one impressive gulp, you can leave them with the image of some sea creature inhaling another. Catching food in your mouth, like belching at the table (considered impolite in most cultures, but a compliment to the chef in others) is rude on Earth but de rigueur in space.
By following these simple rules, you will ensure a delightful evening with your guests. And remember, on the space frontier, the etiquette book is still being written. I encourage you to invent new ways of conducting everyday life, including entertaining. It is one of the reasons we find ourselves here in the first place.
Source: NASA Blogs
Image captions:
Astronauts eats gummy worms in space. Credit: NASA
Don Pettit displays his favorite snack in space. Credit: NASA
NASA astronaut Don Pettit (left) and European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, both Expedition 31 flight engineers, eat a snack in the Unity node of the International Space Station. Credit: NASA
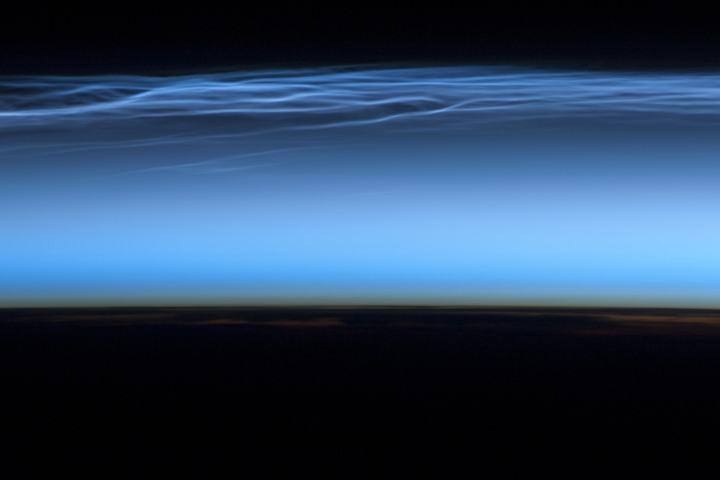
Mysterious Noctilucent Clouds as Seen from the International Space Station
Mysterious “night shining” or noctilucent clouds are beautiful to behold, and this stunning image offers an unusual view of these clouds as seen by astronauts on board the International Space Station. Also called polar mesospheric clouds, these clouds are puzzling scientists with their recent dramatic changes. They used to be considered rare, but now the clouds are growing brighter, are seen more frequently, are visible at lower and lower latitudes than ever before, and sometimes they are even appearing during the day.
The astronauts were also able to take a time-lapse sequence of these clouds on June 5, 2012, as seen below. According to NASA, it is first such sequence of images of the phenomena taken from orbit.
The sequence in this video was taken while the ISS was passing over western Asia. By focusing on the limb of the Earth at night with the Sun illuminating it, the crew was able to capture some movement to these mysterious clouds.
There is quite a bit of debate for the cause of noctilucent clouds. Dust from meteors, global warming, and rocket exhaust have all been tagged as contributors, but the latest research suggests that changes in atmospheric gas composition or temperature has caused the clouds to become brighter over time.
Noctilucent clouds are usually seen during the summertime, appearing at sunset. They are thin, wavy ice clouds that form at very high altitudes (between 76 to 85 kilometers (47 to 53 miles) above Earth’s surface and reflect sunlight long after the Sun has dropped below the horizon. They appear in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere and appear as delicate, shining wispy clouds against the dark sky.
The top image from the ISS was taken on June 13, 2012, as the space station passed over the Tibetan Plateau. At the same time, polar mesospheric clouds were also visible to aircraft flying over Canada. In addition to the noctilucent/polar mesospheric clouds trending across the center of the image, lower layers of the atmosphere are also illuminated. The lowest layer of the atmosphere visible in this image—the stratosphere—is indicated by dim orange and red tones near the horizon.
Lead image caption: Noctilucent or Polar Mesospheric clouds captured by the crew of the ISS on June 13, 2012. Credit: NASA
Source: NASA Earth Observatory
Shenzhou-9 Crew Docks and Enters Chinese Spacelab
The crew of the Chinese Shenzhou-9 spacecraft docked today with the Tiangong-1 mini-spacelab and the three taikonauts entered the small spacelab for the first time. China becomes only the third nation to have a manned craft rendezvous and dock with another spacecraft, behind the U.S. and Russia. Commander Jing Haipeng led the crew into the lab, followed by Liu Wang and then later Liu Yang, China’s first female taikonaut. The Shenzhou capsule completed the docking maneuvers shortly after 0600 UTC (2 am EDT). The two spacecraft are about 343 kilometers (213 miles) above Earth. The docking was shown live on national television.
This docking was automated and monitored by China’s mission control. A manual docking by the crew will be done later in the mission.
The docking video is below.
Continue reading “Shenzhou-9 Crew Docks and Enters Chinese Spacelab”
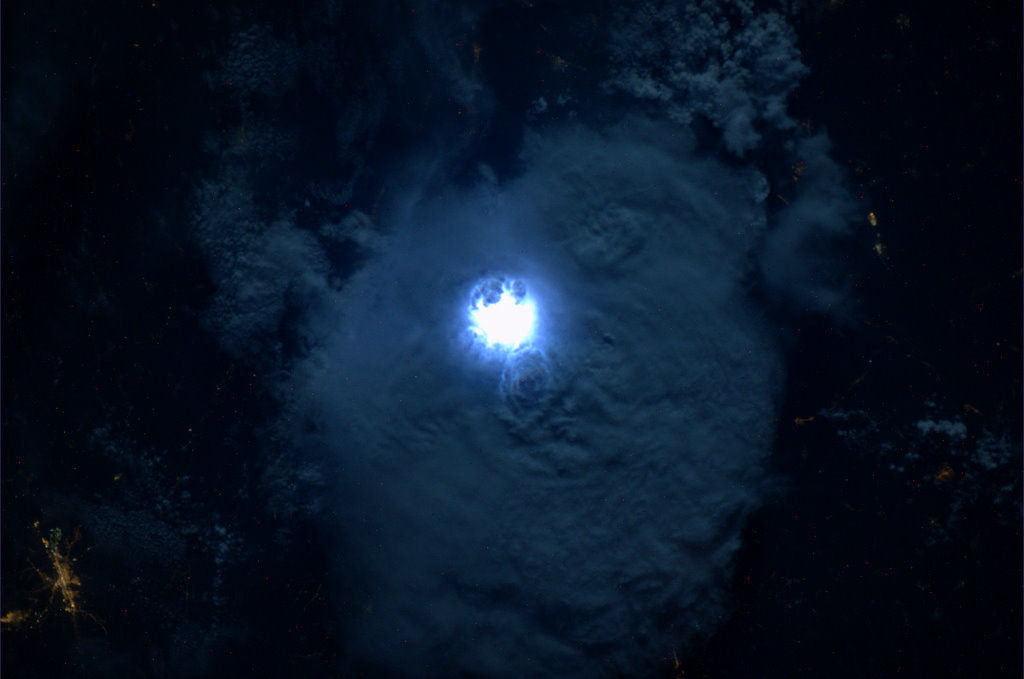
Lightning From Space!
[/caption]
Here’s an amazing shot of a flash of lightning within storm clouds over west Africa, captured from orbit by ESA astronaut André Kuipers aboard the ISS.
Lightning is a common sight from Space Station, creating a constant light show for the astronaut and cosmonaut crew members. On average, lightning strikes the ground somewhere on Earth 100 times each second, and there are 5 to 10 times as many cloud-to-cloud flashes as there are ground strikes. That adds up to about 40 to 80 million flashes of lightning every day around the world! Considering that the ISS orbits Earth 16 times a day — and from quite a high viewpoint — it stands to reason that lightning is spotted quite often.
So although it may not be rare, lightning still makes for dramatic photos — especially to those of us here on the ground!
For more information on André and his ongoing long-duration PromISSe mission, visit the ESA site here.
Image credit: ESA/NASA
Shuttle Enterprise Lands on the Deck of Intrepid in Manhattan

[/caption]
NASA’s Space Shuttle Enterprise magnificently completed her final mission by making a historic landing on the deck of a retired aircraft carrier berthed in Manhattan- the Intrepid – as the first and only space shuttle to ever do so on a once-in-history spectacle befitting the Big Apple.
But instead of a piloted landing by air, Enterprise arrived afloat, atop a seagoing barge and was then hoisted and gently lowered for touch down on top of the Intrepid’s flight deck by a humongous seagoing crane accompanying the shuttle on a second barge at 4 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, June 6.
The Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum is the permanent new home of the Enterprise, NASA’s prototype shuttle – built in 1976 – that was used for a series of critical atmospheric approach and landing tests in the late 1970’s and that paved the way for building all the five shuttle orbiters that followed and the first launch by the Columbia in April 1981.

Enterprise embarked on a long and winding road to reach the Intrepid which I witnessed at points along the way. First she flew piggyback on top of NASA’s specially modified 747 Jumbo Jet from Dulles International Airport for a triumphant fly over tour of the New York Metropolitan region on April 27 before touching down at John F. Kennedy (JFK) International Airport.
Enterprise had been on public display at the Smithsonian’s National Air & Space Museum Annex in Virginia since 2003.
Then the shuttle took a two day cruise on June 3 and June 6, towed by a tugboat; departing from JFK on June 3 and voyaging through New York Harbor to the Statue of Liberty before making an intermediate stop at a port in Bayonne, New Jersey to switch to another larger barge. Along the way the orbiter suffered some minor damage to the right wing tip when wind gusts caused her to scrape against a railroad bridge.
After a 24 hour postponement due to poor weather, a repaired shuttle Enterprise at last put out to sea again on Wednesday morning, June 6, at about 9:45 a.m. for the very last time on the final leg of her thrilling final voyage.

Enterprise took one last beauty ride past the Statue of Liberty, Ground Zero and the Freedom Tower before sailing North up the Hudson River and past the Empire State Building on Manhattan’s West Side; enjoyed by throngs of onlookers and space enthusiasts lining the shores of New York and New Jersey.
She arrived at the Intrepid, located at Pier 86 at 46th Street and 12th Avenue, at about 1 p.m. accompanied by a flotillia of police and water spraying fire boats, ferries , sailboats and pleasure craft.
The giant lifting crane was maneuvered into position in between the Intrepid and Enterprise.
Over the next three hours, technicians carefully attached a yellow steel harness sling to the 150,000 pound orbiter at four points, two in the front and two in the rear. This was the same sling used to lift Enterprise onto and off the back of the 747 jet.
The 240 foot crane used to hoist Enterprise is the same one used to lift the US Airways jet piloted by hero captain Chesley “Sully” Sullenberger out of the Hudson after an emergency water landing near the same exact spot in January 2009 – where all the passengers and crew on board miraculously survived.
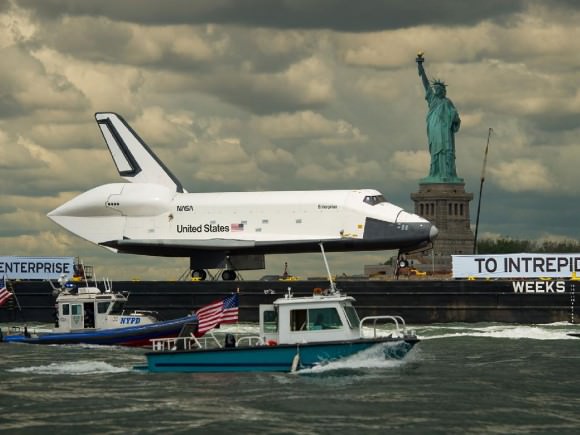

The dramatic pluck of the 75 ton Enterprise off the Weeks Marine barge started around 3:45 p.m. as the winds were gently gusting. Enterprise was raised some 75 feet and rotated nearly 180 degrees so her nose faced directly towards the Hudson River and the beautiful city and cliffs of Weehauken, in Hudson County, New Jersey, where I was watching and photographing from. Enterprise came to rest with wheels down around 4:02 p.m., pretty much exactly on time.
Finally the yellow sling was detached around 6 p.m. and Enterprise was dramatically exposed on the deck of the Intrepid in a beautiful sight for all to see.
But that gorgeous deck view didn’t last long because the museum quickly covered Enterprise with an inflatable pavilion to protect the delicate and precious orbiter from the weather and flying debris – and gawkers looking for free.
To see the Enterprise in all her glory now, you’ll have to pay $22 for admission to the museum and an extra $6 for the shuttle – or check my deck top photo below.
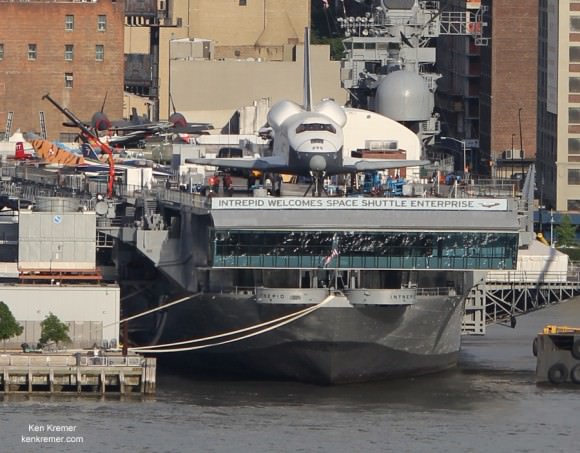

The museum is hastily constructing a temporary, climate controlled “Space Shuttle Pavilion” to house Enterprise. She will be open for public display starting on July 19.
Enterprise is named after the fictional starship in the world renowned and beloved TV science fiction series – “Star Trek”.