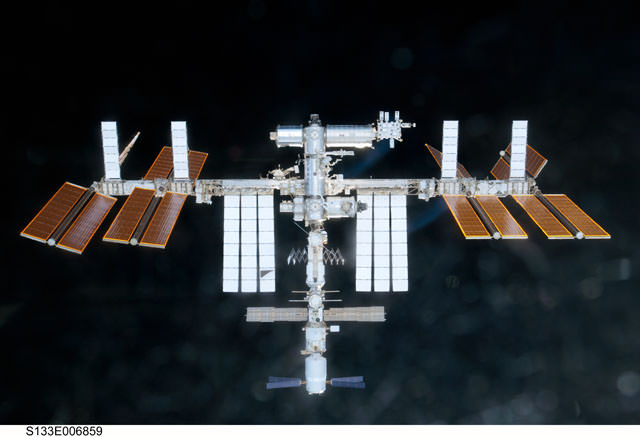
ISS Crew May Be Forced to Take Shelter from Space Debris
[/caption]
Nov. 23 update: NASA reports that flight controllers have downgraded conjunction threat, and there is now no need for the crew to shelter in place on the space station.
What a fine welcome for the new crew on board the ISS: The three astronauts/cosmonauts on the space station may have to take shelter in their Soyuz spacecraft early Wednesday morning (Nov. 23), due to a close flyby or even a possible collision with a piece of space debris. Mission Control called up to the Expedition 30 at 2:06 pm EST today (Nov. 22), saying it was too late to do a debris avoidance maneuver with the entire station, and the crew should be ready to “shelter in place” in the Soyuz vehicle.
Reports are that the object is a piece of debris about 4 inches (10 centimeters) in diameter from the Chinese Fengyun 1C weather satellite that was destroyed in 2007. Current tracking indicates the object may come within 850 meters (2,800 feet) of the station.
An approach of debris is considered close only when it enters an imaginary “pizza box” shaped region around the station, measuring 0.75 kilometers above and below the station and 25 kilometers on each side (2,460 feet above and below and 15.6 by 15.6 miles). The undocking of the Expedition 29 crew yesterday altered the orbit of the ISS enough so that this object –which had previously not been a threat – is now on its way for a very close pass with the station.
Commander Dan Burbank and Flight Engineers Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin will awake early and confer with Mission Control on the latest tracking data of the object, and decide by 4:30 a.m. EST (0930 UTC) on Nov. 23 if they should take shelter in the Soyuz.
NASA’s Chief Scientist for Orbital Debris Nicholas Johnson told Universe Today during a previous close conjunction of space debris and the ISS that on average, close approaches to ISS occur about three times a month.
Johnson said that small pieces of debris have already collided with ISS on many occasions, but these debris to date have not affected the safety of the crew or the operation of the mission. “The dedicated debris shields on ISS can withstand particles as large as 1 cm in diameter,” he said.
The crew has taken shelter in the Soyuz vehicles only twice during the 11 years of continual human presence on the ISS.
Video Shows Rare View of Soyuz Capsule Returning to Earth
The three Expedition 29 astronauts have safely returned to Earth after spending nearly six months on the International Space Station. They landed to a cold and snowy Kazakhstan at 8:26 p.m. CST Nov. 21 (8:26 a.m. Kazakhstan time, Nov. 22). Video cameras on the space station captured the dramatic re-entry of the Soyuz capsule, and the fiery show was also visible to bystanders on the ground on the Russian central steppe.
Continue reading “Video Shows Rare View of Soyuz Capsule Returning to Earth”
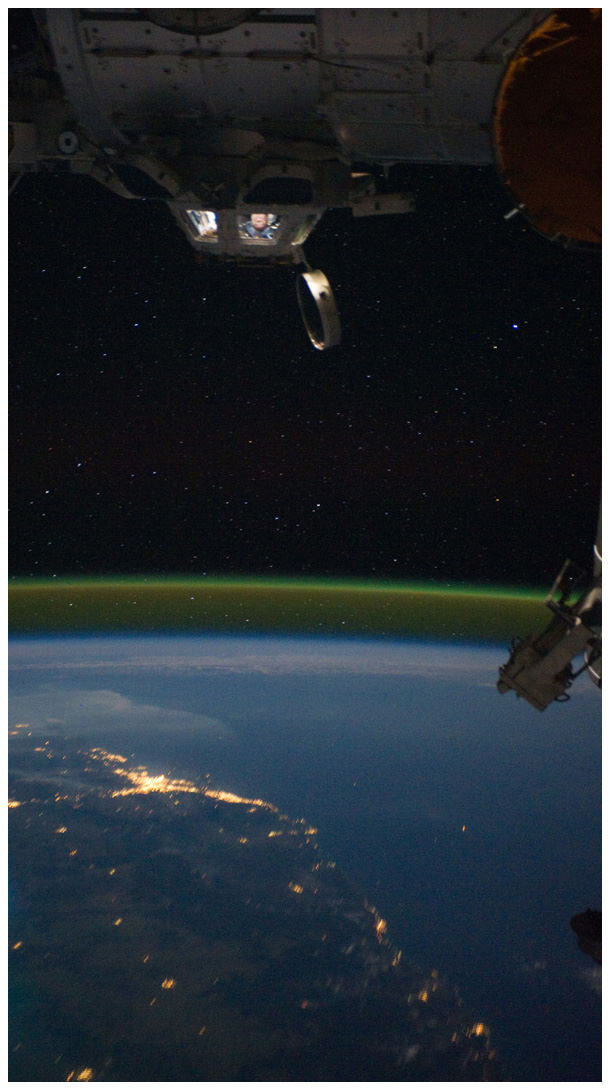
Ron Garan’s Incredible ISS Timelapse: Coming Back Home

Time Lapse From Space – Literally. The Journey Home. from Fragile Oasis on Vimeo.
We’ve seen lots of timelapse videos lately from the International Space Station, as the astronauts have just recently started shooting long sequences of images enabling the creation of these stunning videos made from still photos. This video was put together by one of the photographers himself — Ron Garan — who returned home on September 16, 2011 after spending about six months in space. Today on his blog, Fragile Oasis, Garan explained how the genesis of time-lapse photography on the ISS came from a suggestion from Katrina Willoughby, a photography instructor for the astronauts.
“I hadn’t tried time-lapse yet because I overestimated how hard it would be to capture great images, and the time-lapse photography I had seen to date didn’t seem as impressive as the still imagery we had been taking with some of the new equipment onboard,” Garan said.
But he set up a Nikon D3S camera in the Cupola on the space station (see an awesome picture of him, below, working in the Cupola), took some practice shots, and worked on getting the right settings, then set up the camera to take about 500 pictures at 3-second intervals.
“When I saw the results, I was so excited that I couldn’t sleep!” Garan said, adding that these videos really do give a great representation of what the view is like from space.
[/caption]
Following Garan’s lead, the other astronauts have since joined in taking time-lapse imager, and astronaut Mike Fossum has “since elevated time-lapse photography from space to an art form,” Garan said.
You can see a collection of ISS time-lapse videos here, and read Garan’s post on Fragile Oasis for more information on the cameras, settings, etc for their time-lapse photography.
Also, check out the Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth to see the latest images and videos from space.
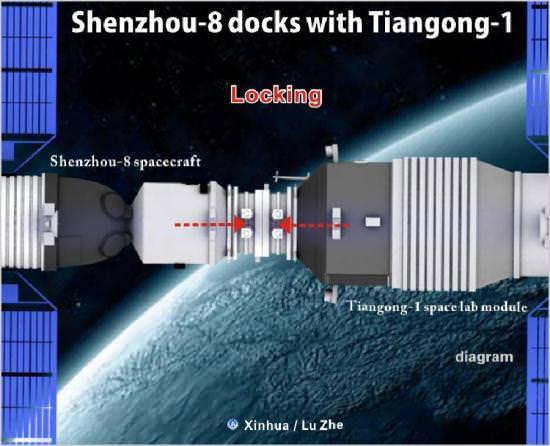
Shenzhou-8 lands after China’s 1st Space Docking propelling Ambitious Human Spaceflight Agenda
[/caption]
China’s historic first docking mission in space ended in a complete success today (Nov. 17) following the safe landing of the unmanned Shenzhou-8 in Inner Mongolia. Today’s landing will robustly propel China’s space program forward and sets the stage for an ambitious agenda of human spaceflight missions in 2012 to the Tiangong-1 Space Lab and eventually to a hefty 100 ton Earth orbiting Space Station to be assembled by 2020.
Shenzhou-8 was launched to low Earth orbit on Nov. 1 atop a Long March 2F booster from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert and successfully conducted China’s first ever rendezvous and docking mission in space with the nation’s Tiangong-1 Space Lab module on Nov. 3 while orbiting some 343 kilometers in altitude above Earth.
Gen. Chang Wanquan, the Commander in Chief of China’s human spaceflight program said, “The Shenzhou-8 capsule has safely returned to the main landing site at Inner Mongolia and the Tiangong-1/Shenzhou-8 rendezvous and docking mission has achieved full success!”

Chang leads the China Manned Space Engineering (CMSE) Project, the nation’s human spaceflight program. He is the Commanding Officer of the Tiangong-1/Shenzhou-8 Rendezvous and Docking Mission Headquarters, and director of the PLA (Peoples Liberation Army) General Armaments Department. The People Liberation Army directs China’s human spaceflight program.
Shenzhou-8 landed today at 7:30 pm. Beijing time in central Asia after flying nearly 17 days in earth orbit. Recovery crews reached the capsule within a few minutes of the parachute assisted touchdown.
Most of the flight was spent linked up to the Tiangong-1 Space Lab module – China’s first prototype space station.

After 12 days of joint orbital operations, Shenzhou-8 carried out a 2nd docking test to enable Chinese space engineers and mission controllers to gain further practice and experience in mastering the complex techniques involved in rendezvous and docking in space.
Shenzhou-8 disengaged from Tiangong-1 on Nov. 14, backed off to a distance of 140 meters (460 ft) and then carried out a re-docking about 30 minutes later. Controllers at the Beijing Aerospace Control Center monitored systems as Shenzhou-8 automatically re-approached Tiangong-1 for the second link up.
The main purpose of the second docking test was to confirm the performance of the rendezvous and docking procedures and hardware on Shenzhou-8 and Tiangong-1 under conditions of the glare of sunlight which are different compared to nighttime conditions of the first docking attempt.
Although the Shenzhou-8 flew unmanned during this flight, the capsule was fully human rated – even food and water are stored on board to simulate the presence of a human crew.
Today’s success sets the stage for possibly two Chinese manned missions to follow in 2012, namely Shenzhou-9 and Shenzhou-10.
Each Shenzhou can carry two or three astronauts. One of the missions is highly likely to include the first female Chinese astronaut.
Read Ken’s features about Shenzhou-8 & Tiangong-1
China completes 2nd Docking to Space Lab and sets Path to Manned flights in 2012
China Technology Surges Forward with Spectacular First Docking in Space
China launches Shenzhou-8 bound for Historic 1st Docking in Space
Shenzhou-8 rolled out for Blastoff to China’s 1st Space Station on November 1
Bizarre Video: China’s Tiangong 1 Space Lab Animation set to ‘America the Beautiful’ Soundtrack
China Blasts First Space Lab Tiangong 1 to Orbit
China set to ‘Leap Forward in Space’ as Tiangong 1 Rolls to Launch Pad
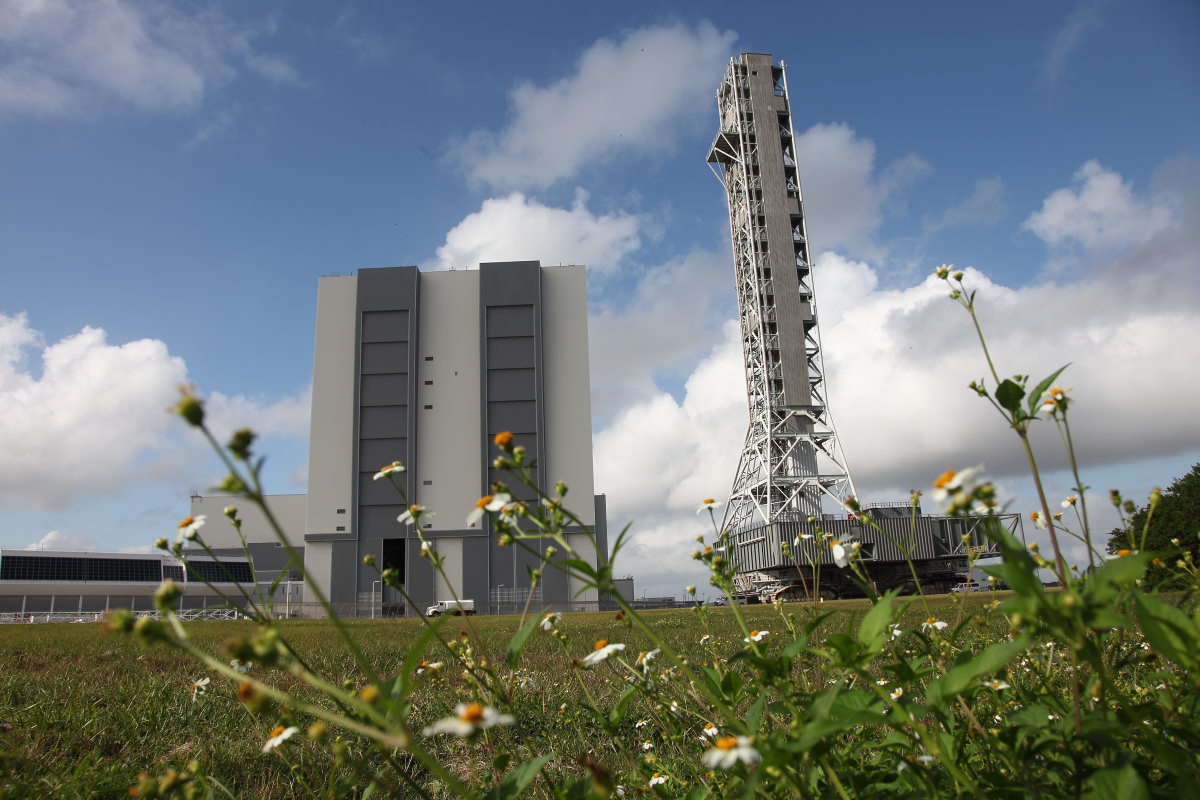
Massive Motion – NASA’s Mobile Launcher Moves to Launch Pad

Video of Mobile Launcher on its move out to Launch Complex 39B courtesy of Alan Walters/awaltersphoto.com
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla – NASA decided that its Mobile Launcher (ML) needed a bit of a shakedown cruise – so it took it on a trip to Launch Complex – 39B (LC-39B). Along the way it stopped and reviewed data as to how the massive tower fared as it lumbered along at the blistering pace of a mile-an-hour. This does not make for riveting must-see video – unless you speed it up.
In the roughly minute-long video the ML moves along at a (somewhat) faster pace. The ML is part of the space agency’s plans to return NASA to the business of space exploration once again. If all goes according to plan, the ML will be the platform used to launch NASA’s Space Launch System or SLS.
[/caption]
As with so many aspects of space exploration, there is a type of art that flows from even the least aesthetic blocky components that are used to lift Heaven and Earth. For those with the right eye, even a metallic tower has a beauty all its own.
That is exactly what aerospace photographer Alan Walters does – find the path to let an object’s inner beauty shine through. The burly photographer has an artist’s eye and loves sharing the awe of all manners of space flight and spacecraft processing.
On Wednesday one of the most emotional aspects of the journey to the launch pad – was the resemblance of some of the images – to those shot during the Apollo era. This imagery could well be prescient as NASA is passing the responsibility of delivering crew and cargo to the International Space Station to commercial space firms as it turns its focus on launching crews to points beyond low-Earth-orbit.

The ML moved from next to Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC) Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to LC-39B to collect data from structural and functional engineering tests. Any relevant data that is gleaned from the journey will be used to modify the ML. The 355-foot-tall ML is being developed to support NASA’s exploration objectives.
“To be honest, I wasn’t expecting much from the move,” Walters said. “After the thing got moving, I began having Apollo flashbacks and I got more and more into photographing and getting video of this event. It made me hopeful about what we might be seeing fly out of Kennedy (Space Center) in the years to come.”

Want To Fly In Space? NASA Looking For More of the “Right Stuff”
[/caption]
NASA is looking for folks with the “right stuff.” The space agency is seeking qualified individuals for when the space agency once again travels into space – and beyond low-Earth-orbit. The announcement of NASA’s process for selecting its next class of astronauts was made at an event held at the Webb auditorium at NASA Headquarters located in Washington D.C. on Tuesday, Nov. 15.
At this event was NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, Assistant Administrator for Human Capital Jeri Buchholz, Flight Crew Operations Director Janet Kavandi as well as five members of the 2009 astronaut class. They were Serena Aunon, Kjell Lindgren, Kathleen Rubins, Scott Tingle and Mark Vande Hei.

“For 50 years, American astronauts have led the exploration of our solar system,” Bolden said. “Today we are getting a glimpse of why that will remain true for the next half-century. Make no mistake about it, human space flight is alive and well at NASA.”
Bolden is a former shuttle astronaut himself, having flown into space four times.
The 2009 class of astronauts – was the first to graduate in a new era of space flight – one which would eventually see the retirement of NASA’s fleet of space shuttle orbiters. NASA is currently working to develop not only a new spacecraft – but a new launch vehicle as well. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV may one day ferry astronauts to points beyond LEO.

To get the Orion MPCV to orbit the space agency is developing the Space Launch System or SLS. This launch vehicle, resembling a cross between the space transportation system (STS) that comprised the shuttle – and the Saturn V moon rocket was recently unveiled by the space agency.
As far as access to LEO is concerned, NASA is working to hand those responsibilities over to commercial space firms such as SpaceX, Sierra Nevada Corporation and Boeing. These companies will also work to deliver crew and cargo to the orbiting International Space Station (ISS). If it all works out these new astronauts could well be among the first to return the U.S. to the Moon or be the first person to visit an asteroid or even Mars.

The Astronaut Candidate Program is open to any person that meets the agency’s qualifications. They can submit their applications online through the USAJobs.gov website. For those considering a career in the astronaut corps, here are some of the requirements:
• Bachelor’s Degree in either science, engineering or math
• Three years of relevant professional experience
• Experience in flying high-performance jet aircraft is considered a plus
• Educators that have taught grades kindergarten through the 12 are highly encouraged to apply
NASA will be accepting applications through January 27, 2012. The agency will bring in applicants to be interviewed and evaluated. NASA plans to make their final decision in 2013 – with training of these new astronauts starting that summer.

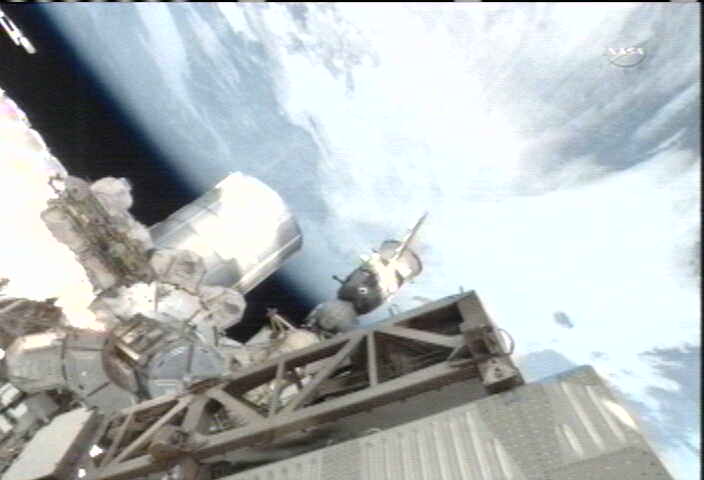
Dramatic Soyuz Docking Averts Potential Station Abandonment

[/caption]
A Russian Soyuz capsule carrying the first crew of humans to fly to space in the post Space Shuttle Era has successfully docked at the International Space Station early this morning, Nov. 16 at 12:24 a.m. EST, averting the potential of having to at least temporarily abandon the massive Earth orbiting research complex.
After an 11 year stretch of continuous human occupation, the future residency of humans aboard the ISS swung in the balance in the wake of a Russian Soyuz rocket failure in August that temporarily grounded all Soyuz launches – manned and unmanned – until the root cause was determined and satisfactorily rectified with NASA’s consent.
The very survival of the ISS hinged on the successful launch of a trio of Russian and American space flyers just 2 days ago from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazahkstan aboard the Soyuz TMA-22 capsule, which took place amidst an unprecedented blizzard and white out conditions with near zero visibility.
The three man crew of Russian rookie cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin along with veteran NASA astronaut Dan Burbank arrived at the Poisk module of the orbiting outpost just in the nick of time – before the last three ISS crewmembers still aboard would have been forced to depart just 5 days from today leaving no humans aboard.

Luckily the Soyuz launch and automated rendezvous and linkup with the ISS flying some 400 km (248 miles) above the South Pacific proceeded flawlessly, announced Russian space officials at Mission Control in Moscow shortly after the successful docking. The event was carried live on NASA TV.
A full complement of 6 crew members was thus restored to the ISS, but the handover period will be exceedingly short because the Soyuz TMA-22 launch was postponed from September 22 due to the Soyuz rocket failure in August carrying the unmanned Progress cargo resupply vessel.
The new trio joins the current Expedition 29 residents comprising ISS Commander Mike Fossum (NASA) and Flight Engineers Satoshi Furukawa (Japan) and Sergei Volkov (Russia). But Fossum, Furukawa and Volkov will depart on Monday, Nov. 21, and thereby reduce the station crew population back down to three.
“The crew will have a very busy time during the short handover period,” said William Gerstenmaier, NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operation Directorate, who was present in Moscow.
“I want to thank our Russian colleagues for a tremendous job. It’s great to have six people back aboard the ISS,” Gerstenmaier said.
The newly arrived crew is expected to stay at the ISS for about five months and carry out a wide range of science experiments.
After closing the hooks and latches, removing the docking probe and conducting extensive pressure and leak checks, Shkaplerov, Ivanishin and Burbank opened the hatches and floated into the ISS to join their awaiting friends friends with a big round of bear hugs and greetings at about 2:39 a.m. EST today, Nov 16.
“Its great to see all six of you together up there,” radioed Gerstenmaier after the hatch opening.
“It’s was a great ride uphill and it will be a great stay up here,” Burbank replied.
The cosmonauts children exuberantly said “Hi , how are you. Kisses to you Daddy !” to their dads in space moments later !

The next three man Soyuz crew of US astronaut Don Pettit, Dutch astronaut André Kuipers, and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko, is set to arrive on December 23 and again restore the crew to a full complement of six.

Read Ken’s continuing features about Russian Space Programs including Soyuz, Progress, Phobos-Grunt and Soyuz in South America starting here:
Soyuz Launches to Station amid Swirling Snowy Spectacular
Soyuz Poised for High Stakes November 13 Blastoff – Space Stations Fate Hinges on Success
Success ! Launch Video of Crucial Russian Rocket to ISS puts Human Flights back on Track
Russians Race against Time to Save Ambitious Phobos-Grunt Mars Probe from Earthly Demise
Russia’s Bold Sample Return Mission to Mars and Phobos Blasts Off
Video Duet – Soyuz Debut Blast off from the Amazon Jungle and Rockin’ Russian Rollout !
Historic 1st Launch of Legendary Soyuz from South America
Russian Soyuz Poised for 1st Blastoff from Europe’s New South American Spaceport
Nov 16: Ken Kremer lectures about Mars and Vesta exploration at Gloucester County College, NJ
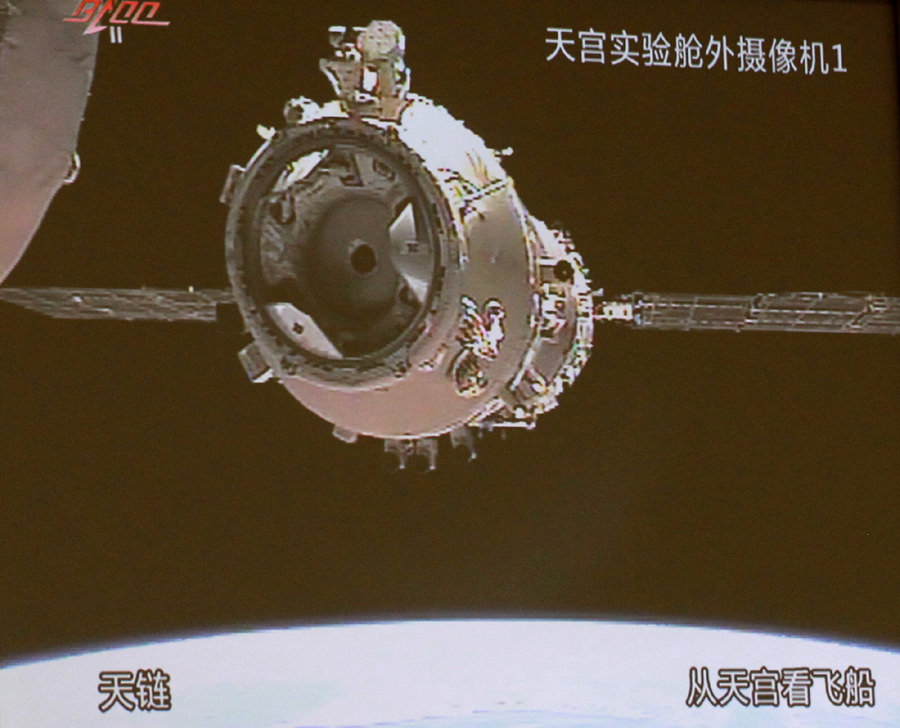
China completes 2nd Docking to Space Lab and sets Path to Manned flights in 2012
[/caption]
Chinese space prowess took another major leap forward today (Nov. 14) when the unmanned Shenzhou-8 capsule successfully re-docked with China’s Tiangong-1 space lab while speeding through space and orbiting some 343 km above Earth. Today’s events pave the way for China to rapidly ramp up their human space program and loft up to two manned flights to the space lab module in 2012.
The re-docking marked only the 2nd time that China had accomplished a successful space docking, a critical technical milestone that opens the door to China’s real ambition of assembling a 100 ton operational Space Station in low Earth orbit by 2020 – about the time when the ISS might be decommissioned.
China made space history on Nov. 3 by becoming only the 3rd country on Earth – after the US and the Russia – to accomplish a space link up when Shenzhou- 8 and Tiangong-1 rendezvoused and docked in earth orbit.
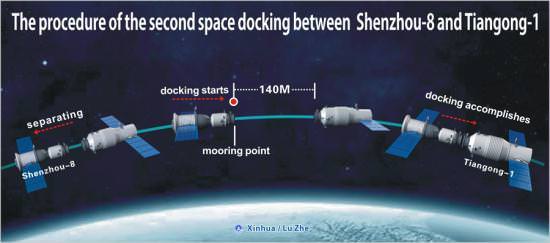
Shenzhou-8 was launched to orbit on Nov. 1 atop a Long March 2F booster rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert in northwest China. The two Chinese built spacecraft have been joined together for 12 days.
China’s space re-docking exercise today came just hours after Russia successfully launched their Soyuz capsule with two Russians and one American bound for the ISS.

Today’s goal was to give Chinese engineers more practice and confidence in mastering the complex maneuvers required for rendezvous and docking two vehicles in space. It was carried out in daylight conditions as opposed to the nighttime conditions for the initial docking to expand the testing envelope under different scenarios.
Shenzhou-8 first disengaged from the prototype space station at about 6:37 a.m. EST and then withdrew to a distance of about 140 meters (460 ft). About 30 minutes later, mission controllers at the Beijing Aerospace Control Center monitored Shenzhou-8 as it automatically approached Tiangong-1 and completed the second docking – or “Space Kiss” as the Chinese media fondly say – at about 6:53 a.m. EST.

The combined Shenzhou-8/Tiangong-1 orbiting complex is some 20 meter in length and weighs about 16 tons. Each vehicle weighs some 8 tons. Tiangong-1 is 10.4 m in length and 3.3. m in diameter. Shenzhou-8 is 9.2 m in length
Shenzhou is China’s manned space capsule but flew this flight with no humans aboard because Chinese space officials felt it was safer and prudent and did not want to expose astronauts to excessive risk during the unprecedented docking attempts.
Following today’s complete success, the China Manned Space Engineering (CMSE) Project is pushing ahead with plans to launch up to two manned missions to Tiangong-1 in 2012 – namely Shenzhou-9 and Shenzhou-10 which are already under construction.
Both 2012 missions would be short duration flights of a few days or weeks since the Tiangong-1 module is a prototype space station module and not outfitted for long duration flights.
CMSE is evaluating a pool of Chinese astronauts already in training – including two women – for the two flights. Both women candidates are married and about 30 years of age but have not been publically identified.
It seems highly likely that one of the Shenzhou missions will include the first female Chinese astronaut.
So far China has launched six astronauts on three manned Shenzhou capsules between 2003 and 2008.
The docking mechanism on Shenzhou-8 was developed and manufactured in China, says Wu Ping, spokeswoman for the CMSE.
In two days, Shenzhou-8 is due to undock from Tiangong-1 for the final time and initiate the fiery re-entry to Earth on Nov. 17. The descent capsule will land by parachute.
These historic feats prove that China’s manufacturing and technological capabilities are surging forward and rapidly matching the Western powers and Japan in a broad swath of scientific and technical fields.
Since the forced retirement of NASA’s functioning space shuttle orbiters, only China and Russia can launch people into space.
Video animation caption: Chinese spacecraft to ‘kiss’ in space. Credit: NMANewsDirect
Read Ken’s features about Shenzhou-8 & Tiangong-1
China Technology Surges Forward with Spectacular First Docking in Space
China launches Shenzhou-8 bound for Historic 1st Docking in Space
Shenzhou-8 rolled out for Blastoff to China’s 1st Space Station on November 1
Bizarre Video: China’s Tiangong 1 Space Lab Animation set to ‘America the Beautiful’ Soundtrack
China Blasts First Space Lab Tiangong 1 to Orbit
China set to ‘Leap Forward in Space’ as Tiangong 1 Rolls to Launch Pad
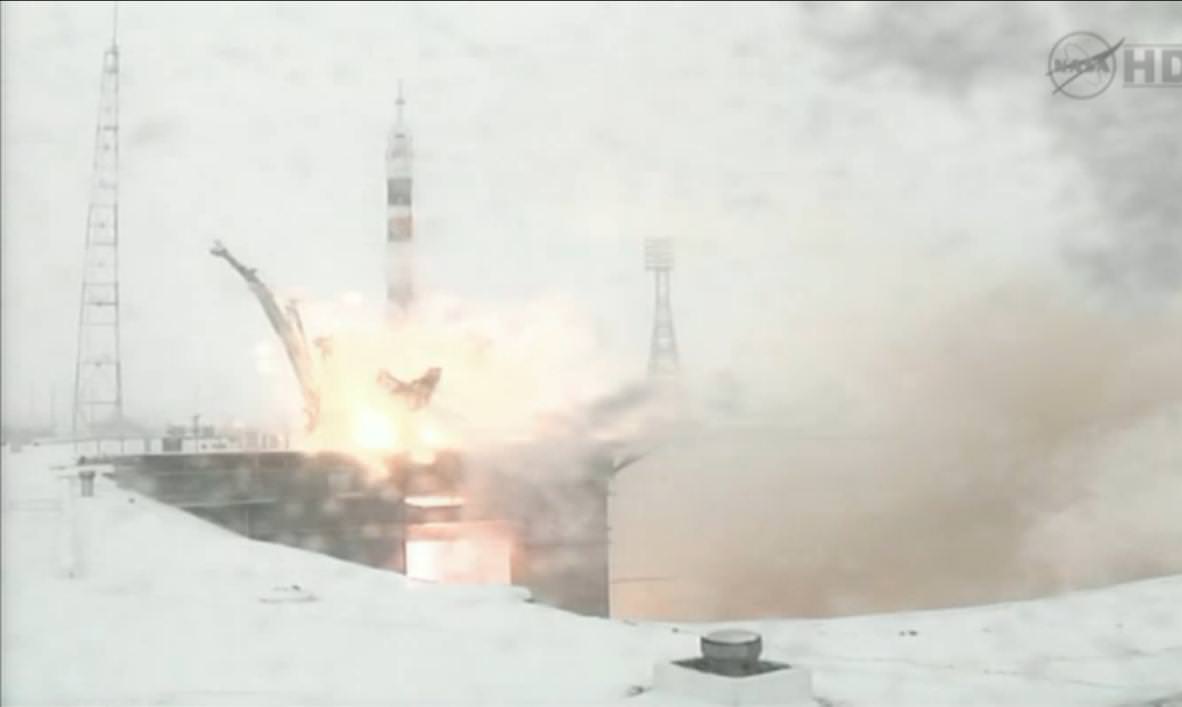
Soyuz Launches to Station amid Swirling Snowy Spectacular

[/caption]
The future survival and fate of the International Space Station was on the line and is now firmly back on track following today’s (Nov. 13) successful, high stakes liftoff of a Russian Soyuz rocket carrying a three man crew of two Russians and one American bound for the orbiting research platform, amidst the backdrop of a spectacular snowstorm swirling about the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan – rare even by Russian standards.
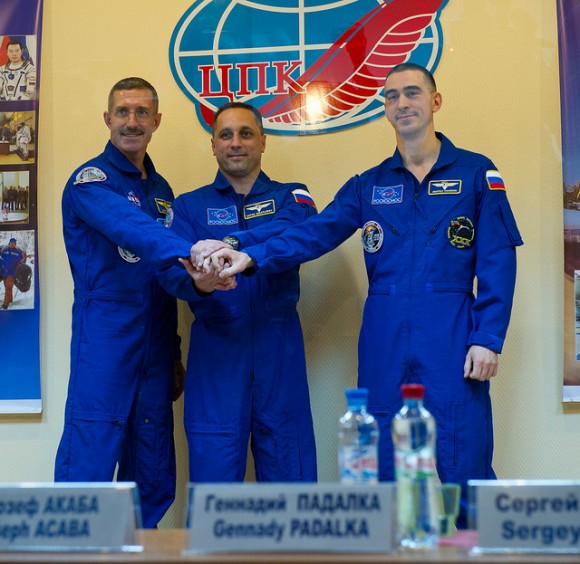
The international crew comprises Expedition 29 Flight Engineer Dan Burbank from NASA – veteran of two prior shuttle missions to the station in 2000 and 2006 – and Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin from Russia. It’s the rookie flight for both Russian cosmonauts.

This is the first flight of a manned Soyuz-FG rocket – and of humans to space – since NASA’s Space Shuttle was forcibly retired in July and the subsequent failure of a virtually identical unmanned Soyuz-U booster in August which grounded all Russian flights to the ISS and threatened to potentially leave the station with no human presence aboard.

The trio of space flyers soared to the heavens at 11:14:03 p.m. EST Sunday Nov. 13 (11:14:03 a.m. Baikonur time Monday, Nov. 14) abroad their Soyuz TMA-22 capsule which was mounted atop the 50 meter tall Soyuz rocket.
Blastoff occurred precisely on time at about the time when the frigid, snow bedecked launch pad rotated into the plane of the orbit of the ISS. The launch was carried live on NASA TV and the ship quickly disappeared from view behind the nearly blinging blizzard.
The Soyuz TMA-22 achieved orbital insertion some nine minutes later into an initial 143 by 118 mile orbit, inclined 51 degrees to the equator.
The vehicles antennae’s and solar arrays were quickly deployed per plan and all spacecraft systems were functioning perfectly according to Russian Ground Control in Moscow.

Following a two day orbital chase and three course correction burns the future ISS residents are due to dock at the Russian Poisk module at the complex at about 12:33 a.m. EST on Wednesday, Nov. 16.
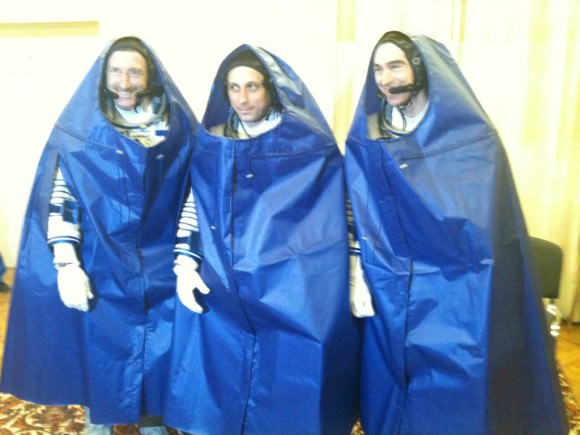
In the hours prior to launch the crew received a religious blessing from the Russian Orthodox Church, took the bus for the 25 mile trip to the Cosmodrome, donned their white Sokol launch and entry suits and headed to the pad.
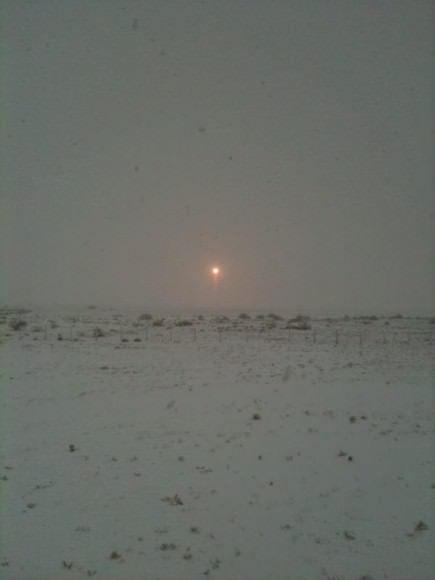
The crew boarded the capsule in the midst of an extremely heavy snow storm which struck the Baikonur region of Kazakhstan in the evening prior to launch. See photo from backup NASA astronaut Joe Acaba.
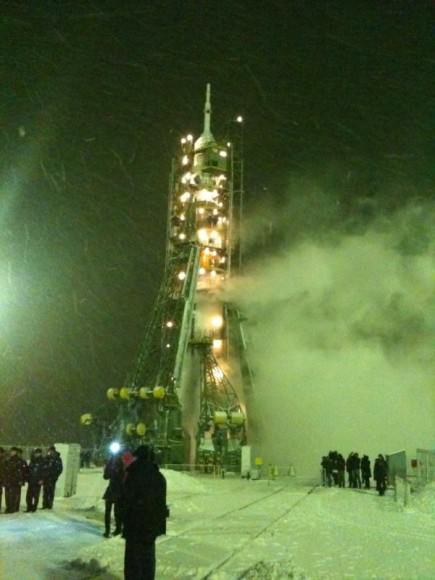

Although snow is quite common at this time of year, the blizzard conditions at launch time were actually quite rare according to NASA spokesman Rob Navias at Baikonur.
American rockets would never blast off in such severe weather conditions – but it’s nothing for the Russians!
The temperature was about 24 F, roughly 6 inches (15 cm) of snow had accumulated on the ground at launch time and moderate wind gusts partially obscured the view.
For the first time ever, a Soyuz crew was dressed in parkas – See Joe Acaba twitpic below !
Gantry towers were retracted from the three stage Soyuz booster at about T minus 25 minutes. The umbilical’s retracted in the final seconds.
The three stage Soyuz-FG rocket lifted off from Launch Pad 1 (LC-1), the same pad from which Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin flew as the first human to space 50 Years ago this year. The pad is named “Gagarin Start” in honor of Gagarin’s courageous achievement on April 12, 1961.
The rocket was fueled with kerosene (RP-1) and cryogenic liquid oxygen.
The ISS was flying some 248 miles above the Pacific Ocean and just west of Chile at launch time.

The importance of the TMA-22 mission cannot be overstated because it restored confidence in Russian rockets which now serve as the world’s only pathway for providing human access to the $100 Billion earth orbiting outpost.
The cramped Soyuz capsule measures just 2.2 m wide by 2.1 m high and weighs 2200 kg.
Today’s critical launch had been delayed be nearly two months from September 22, following the failure of a nearly identical Soyuz-U booster in August which was carrying the Progress 44 cargo resupply spacecraft and crashed ignominiously in Siberia after the third stage shut down unexpectedly.
The Progress 44 was loaded with nearly 3 tons of supplies and was bound for the ISS.
The third stage is nearly identical for both the manned and unmanned versions of the normally highly reliable Soyuz booster rocket.
The launch came only after a thorough review of the causes of the accident by a special State Commision- which was traced to a clogged fuel line – introduction of new quality control measures and careful inspection of all the engines.
“We have no doubt in our minds both the rocket and the vehicle are ready, all the activities have been done at the appropriate level of quality and reliability,” said Vladimir Popovkin, Head of Roscosmos, the Russian Federal Space Agency, prior to liftoff.

The new crew will join the other half of Expedition 29 already in residence aboard the ISS; Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum (NASA) and Flight Engineers Satoshi Furukawa (Japan) and Sergei Volkov (Russia). This will temporarily restore the ISS to a full complement of 6 crewmembers – but only for a few days.
Fossum will hand over command of the station to the new crew within four days. His crew departs the ISS for Earth reentry on Nov. 21.
The successful launch means that the ISS will not have to be left unmanned for the first time since continuous manned occupation began over 11 years ago and which would have placed the station at risk in case of failures requiring human intervention.
Burbank, Shkaplerov and Ivanishin will spend 5 months aboard the station. They will be joined in December by the next trio to round out Expedition 30


Read Ken’s continuing features about Russian Space Programs including Soyuz, Progress, Phobos-Grunt and Soyuz in South America starting here:
Soyuz Poised for High Stakes November 13 Blastoff – Space Stations Fate Hinges on Success
Success ! Launch Video of Crucial Russian Rocket to ISS puts Human Flights back on Track
Russians Race against Time to Save Ambitious Phobos-Grunt Mars Probe from Earthly Demise
Russia’s Bold Sample Return Mission to Mars and Phobos Blasts Off
Video Duet – Soyuz Debut Blast off from the Amazon Jungle and Rockin’ Russian Rollout !
Historic 1st Launch of Legendary Soyuz from South America
Russian Soyuz Poised for 1st Blastoff from Europe’s New South American Spaceport