[/caption]
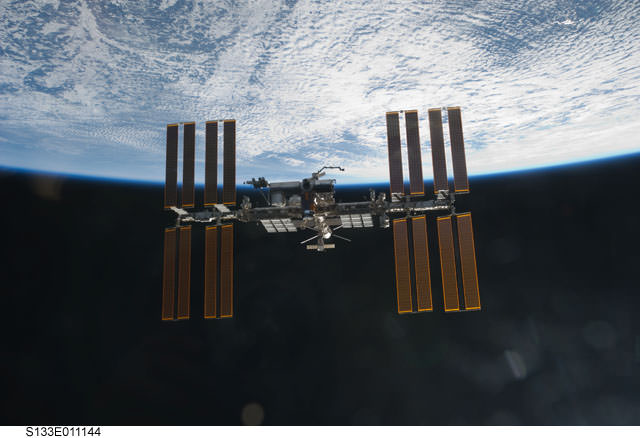
Today’s loss of a Russian Progress re-supply ship to the International Space Station will likely have implications to the ISS and crew, said NASA’s Mike Suffredini, who is the space station program manager. But, just how the entire program will be affected is yet to be determined. “We are in a good position, and can go several months without a re-supply vehicle if necessary, due to the supplies delivered by the last shuttle flight,” said Suffredini.
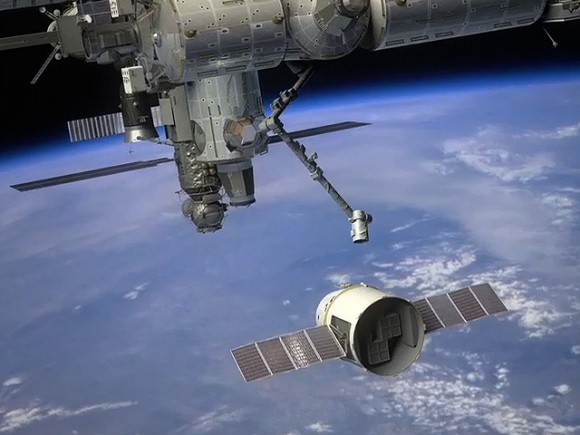
This first post-shuttle era launch of a Progress cargo abruptly ended at about six minutes into the flight when an engine anomaly prompted an engine shutdown, just before the third stage of the Soyuz rocket ignited. The rocket and ship crashed to Earth in eastern Russia, in a sparsely populated area in the Choisk region of the Republic of Altai. No injuries have been reported so far.
“Our Russian colleagues have immediately begun the process of assessing implications of the program and ISS crew, and to assess the data that’s available to try to determine root cause,” Suffredini said at a press briefing shortly after the malfunction. He added everyone is now trying hard “to give our Russian colleagues time to gather data and sort it out and find important details.”
Suffredini said they normally have 30 days of contingency supplies on board, and with the latest (and final) shuttle resupply, they have at least 40-50 extra days of supplies for the current crew. “We’re in a good position logistically to withstand this loss of supplies,” Suffredini said. “And in fact, I would tell you we can go several months without a resupply vehicle if that becomes necessary.”
Since the Russian Soyuz crew module also flies on a Soyuz rocket, albeit a different version, the implications for crew rotation are not yet known, and Russian teams are gathering data to sort out the cause of the malfunction to the normally reliable spacecraft.
Suffredini said the current crew can stay on board extra time if necessary; if a delay for next Soyuz crew goes longer than anticipated, they will bring part of crew home and operate the ISS with crew of three.
Another Progress cargo ship is scheduled to fly in October; Suffredini said if the problem is figured out rather soon, it could probably fly earlier to make up for the loss of this current ship. Additionally, a European ATV supply ship is scheduled to launch in March 2012 and a Japanese HTV cargo ship will likely launch in May 2012.
“There are things we can do to extend our current supplies, but we have no concerns in that area even if nothing flies before ATV in March 2012,” Suffredini said.
The Progress was carrying 2.9 tons of supplies, mainly fuel for a planned station re-boost, water, hygiene supplies, food and other various supplies. Suffredini said no science experiments were on board the Progress, and that there should be enough fuel on board the ISS to do a re-boost, as well as any space debris avoidance maneuvers that might become necessary.
The biggest problem might be a shortage of what Suffredini called “potty supplies,” extra parts and equipment for the bathroom on the station. The specialized toilet includes hardware designed to recycle urine into drinking water.
Currently, Expedition 29 is scheduled to launch for the ISS on Sept. 22, 2011 with a crew of Anton Shkaplerov, Anatoly Ivanishin and Dan Burbank, launching aboard the Soyuz TMA-22 spacecraft. But that launch schedule will be assessed in light of today’s launch failure.
This was the second launch failure in a row — and within a week — for the Russian space program. The Breeze-M upper stage of a Proton rocket malfunctioned last Thursday, putting a communications satellite in the wrong orbit.