KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – Spectacular 4th of July fireworks are coming tonight, July 3,[reset to July5] to the Florida Space Coast courtesy of SpaceX and Intelsat with the planned near dusk launch of the commercial Epic 35e next-generation high throughput satellite to geostationary orbit for copious customers in the Americas, Europe and Africa. UPDATE: After a 2nd abort launch is now NET July 5.
JULY 5 UPDATE: GO for launch attempt tonight at 7:37 PM. Weather looks good at this time.
“SpaceX, confirms that we are ‘Go’ for a launch tonight, 5 July, at approximately 23:37:00 UTC (7:37pm EDT), GO INTELSAT 35E!!” Intelsat announced.
If all goes well, SpaceX will have demonstrated an amazing launch pace with 3 rockets propelled aloft in the span of just 10 days from both US coasts.
Originally slated for Sunday evening, July 2, the launch was automatically aborted by the computer control systems literally in the final moments before the scheduled liftoff due to a guidance issue, and under picture perfect weather conditions – which would have resulted in 3 launches in 9 days.
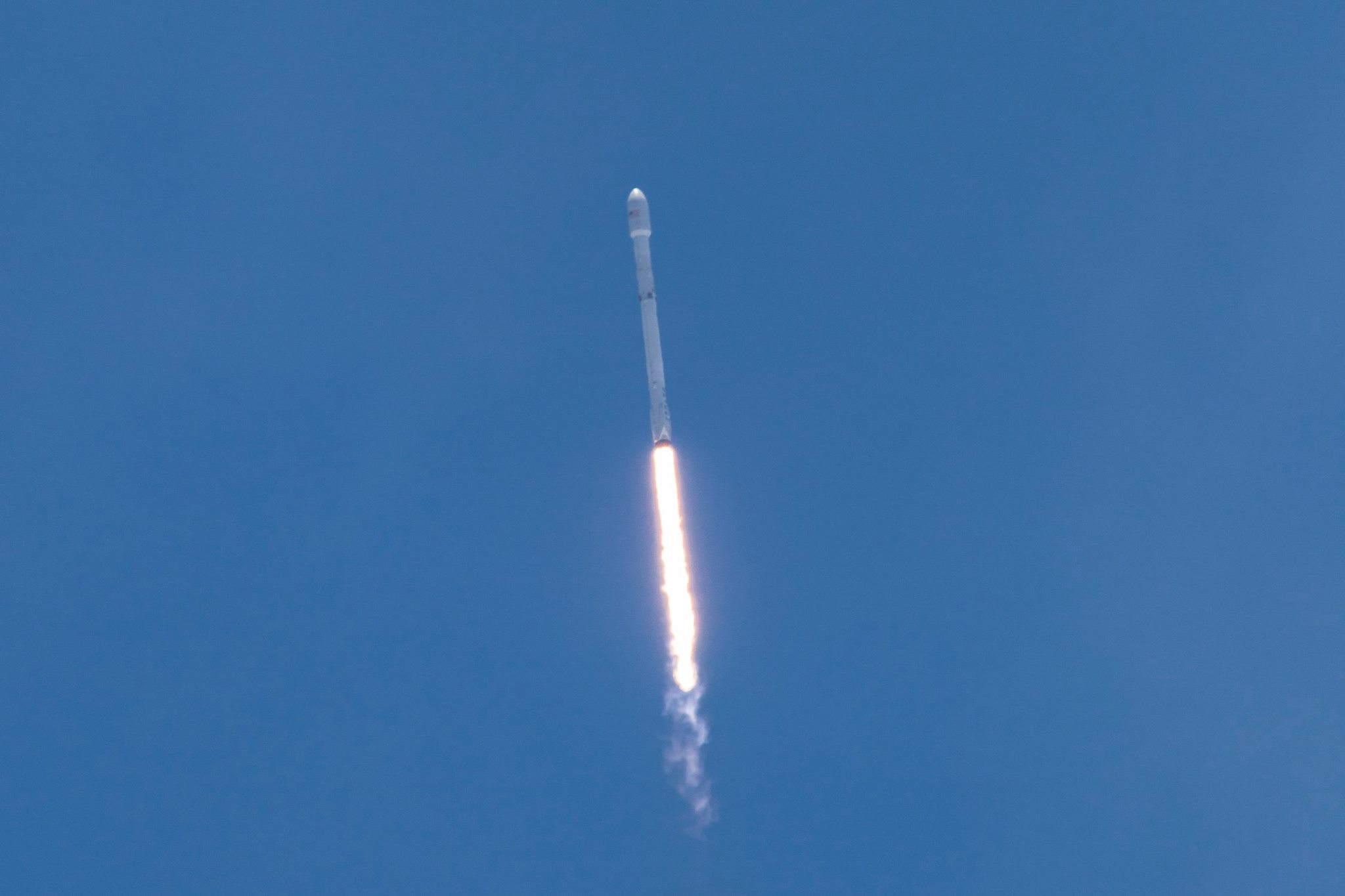
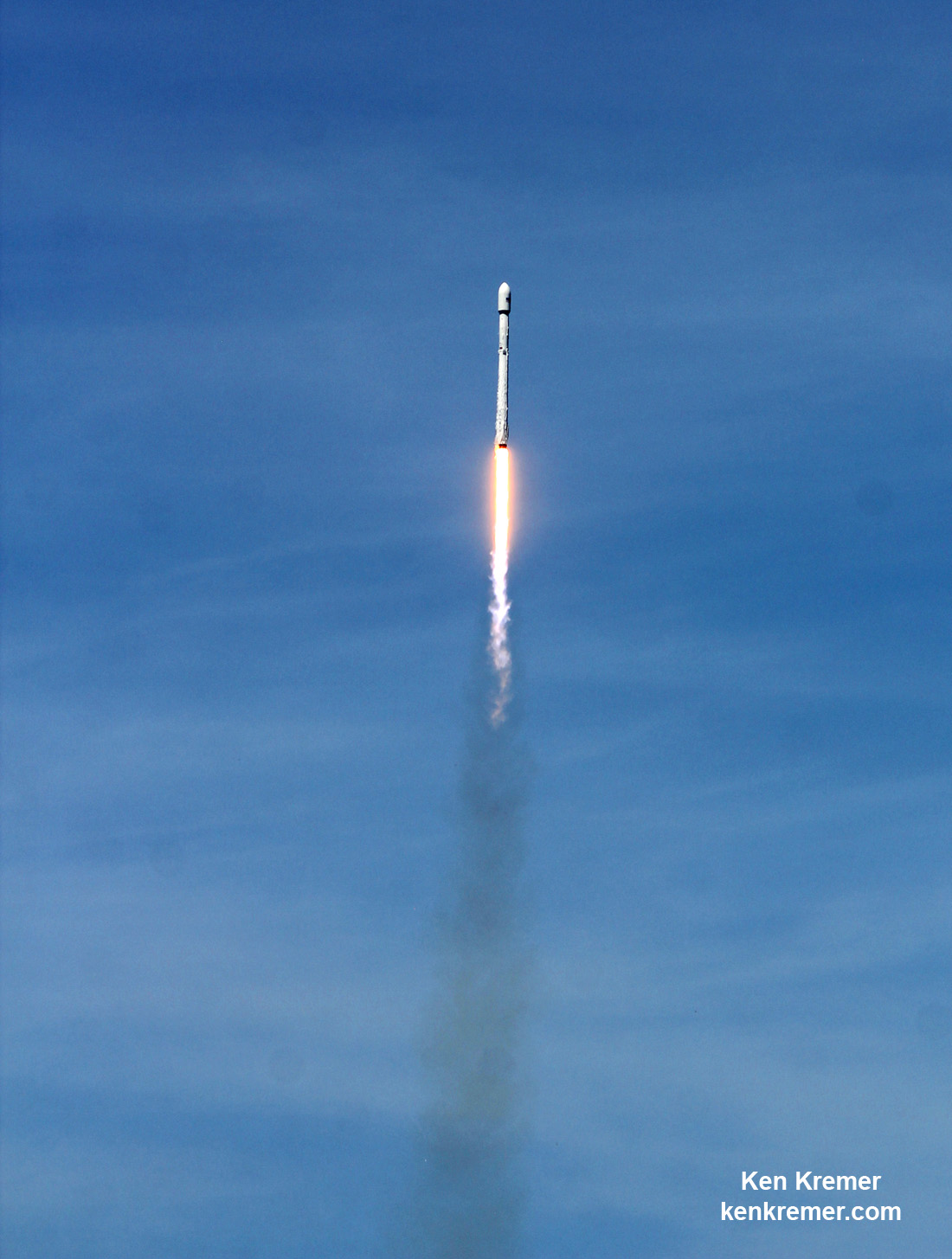
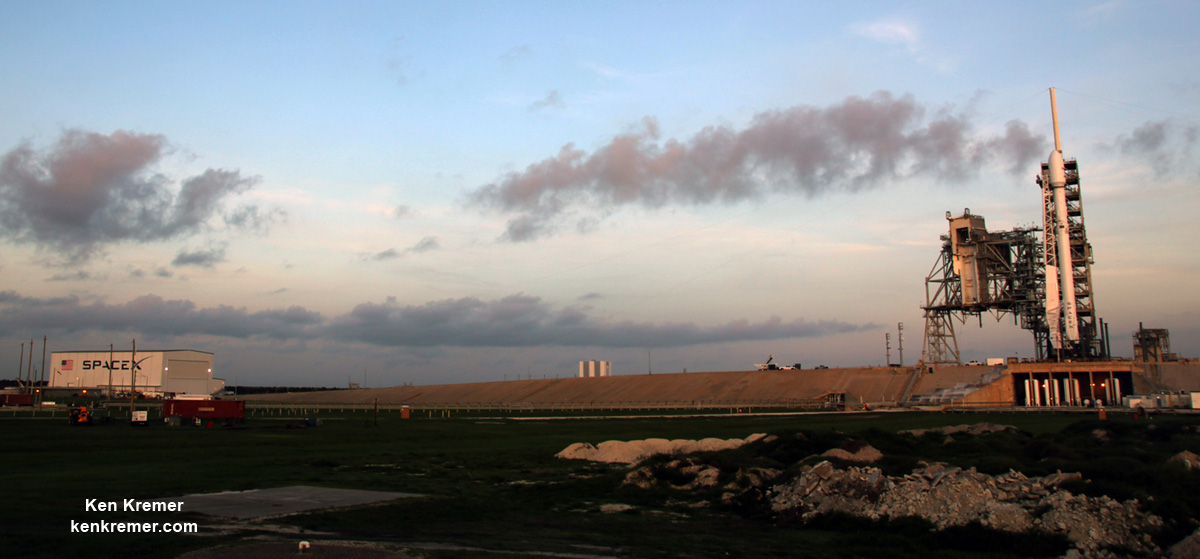
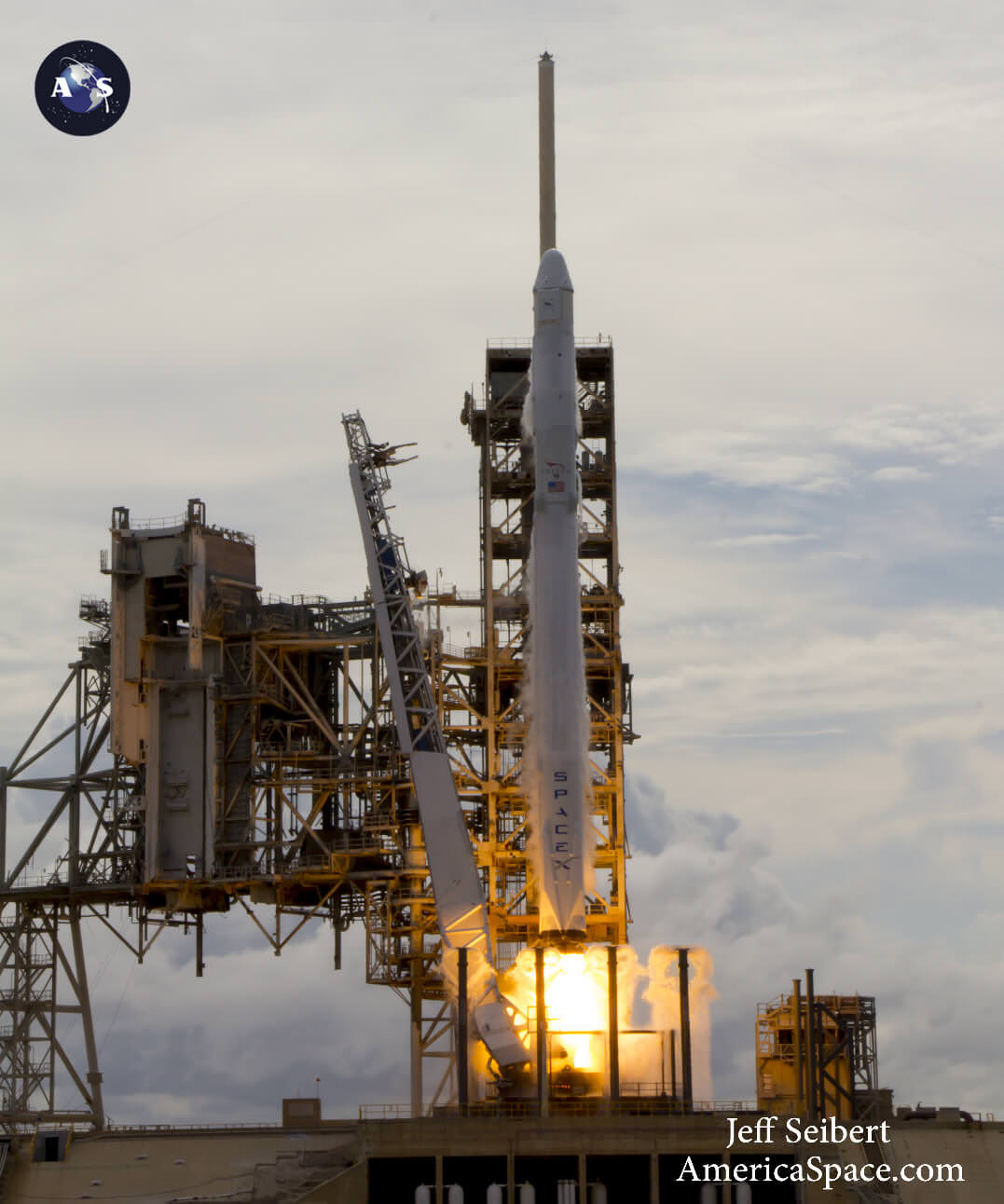
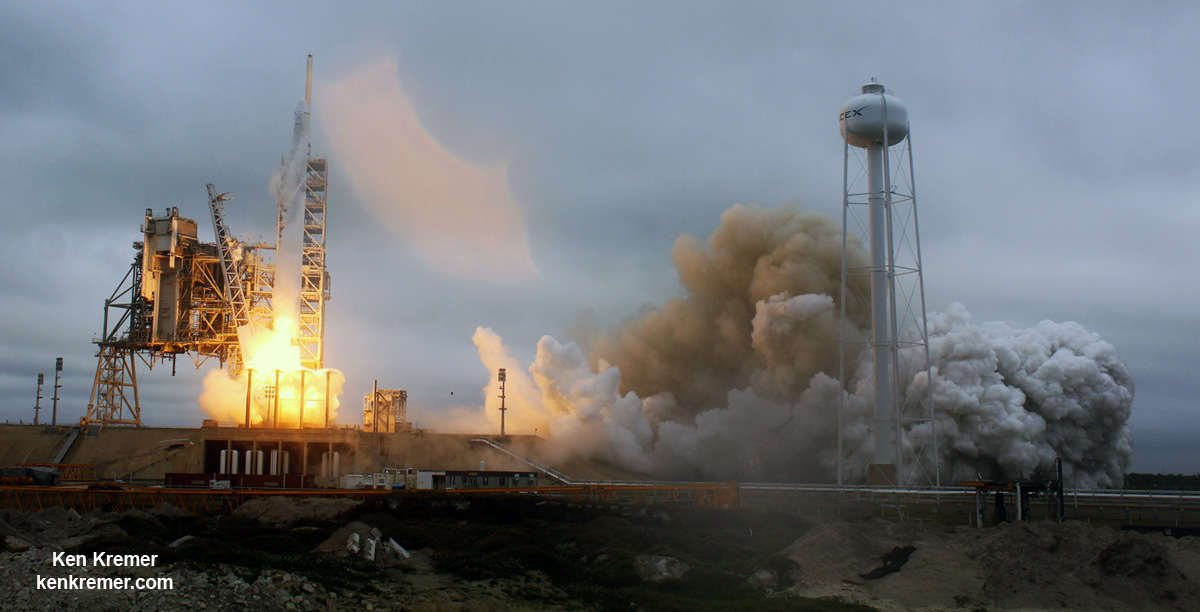
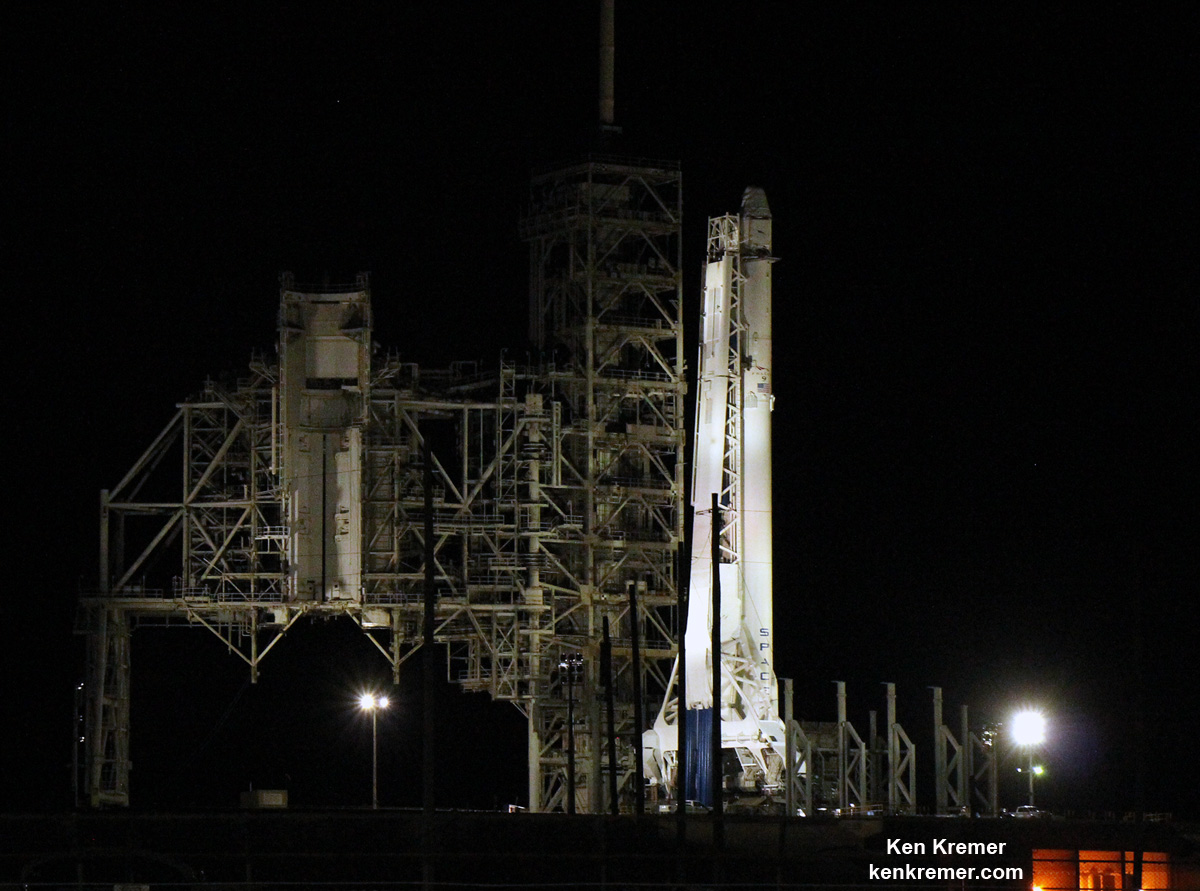
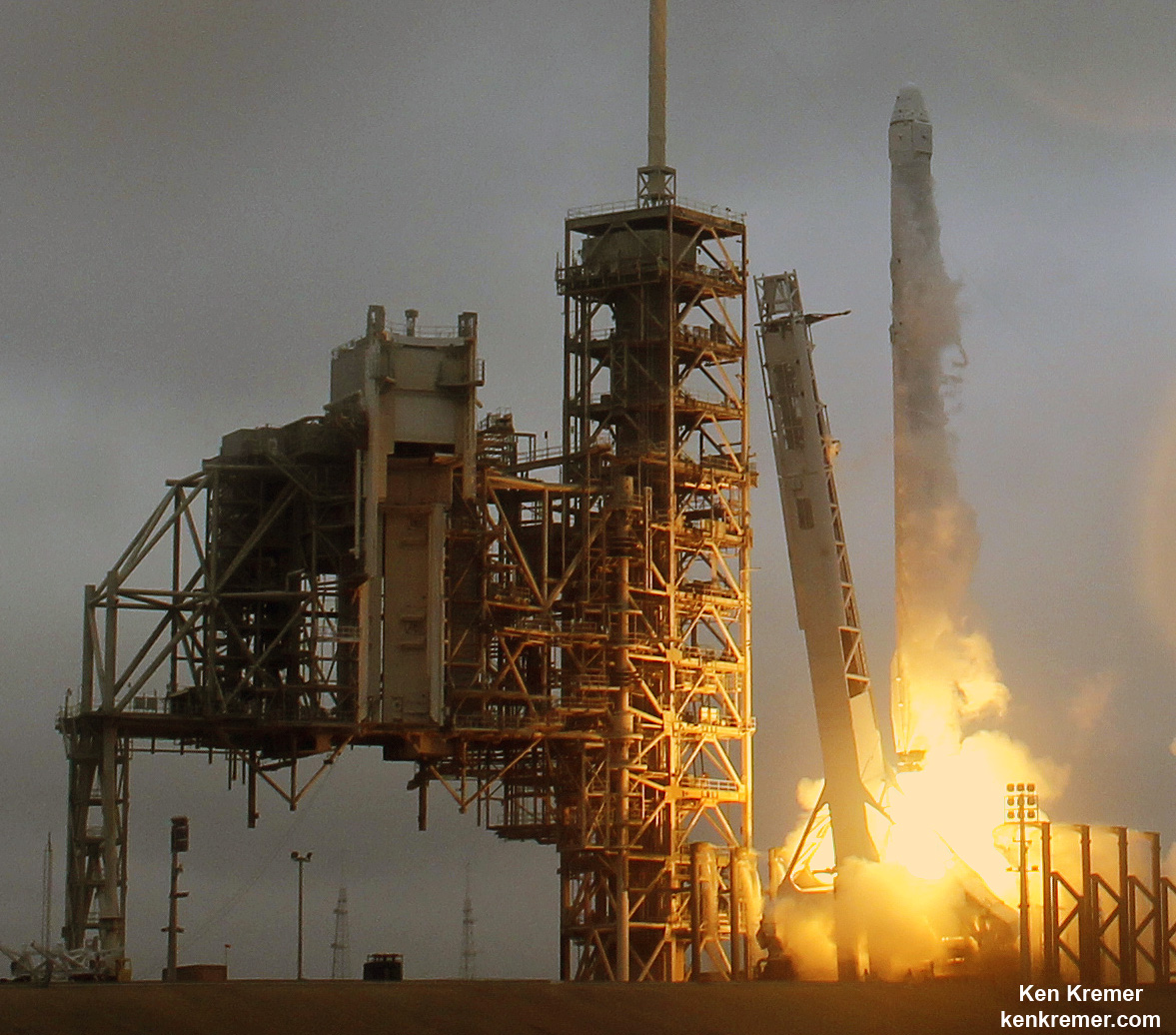
Following the 24 hour scrub turnaround, blastoff of the Intelsat 35e communications satellite for commercial broadband provider Intelsat is now slated for dinnertime early Monday evening, July 3 at 7:37 p.m. EDT, or 2337 UTC from SpaceX’s seaside Launch Complex 39A on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
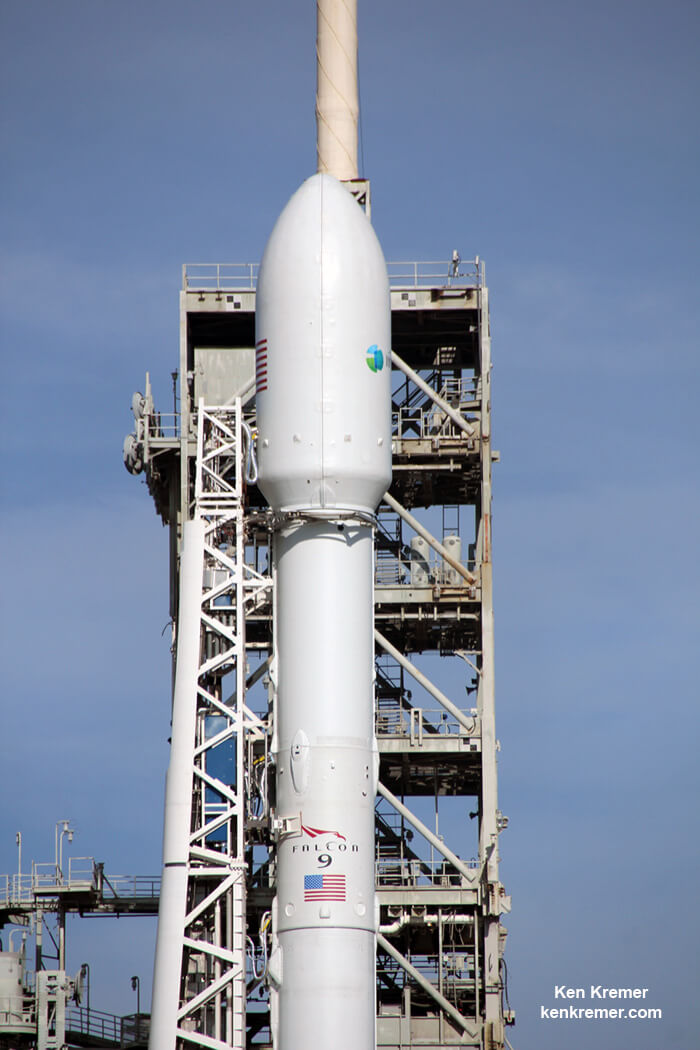

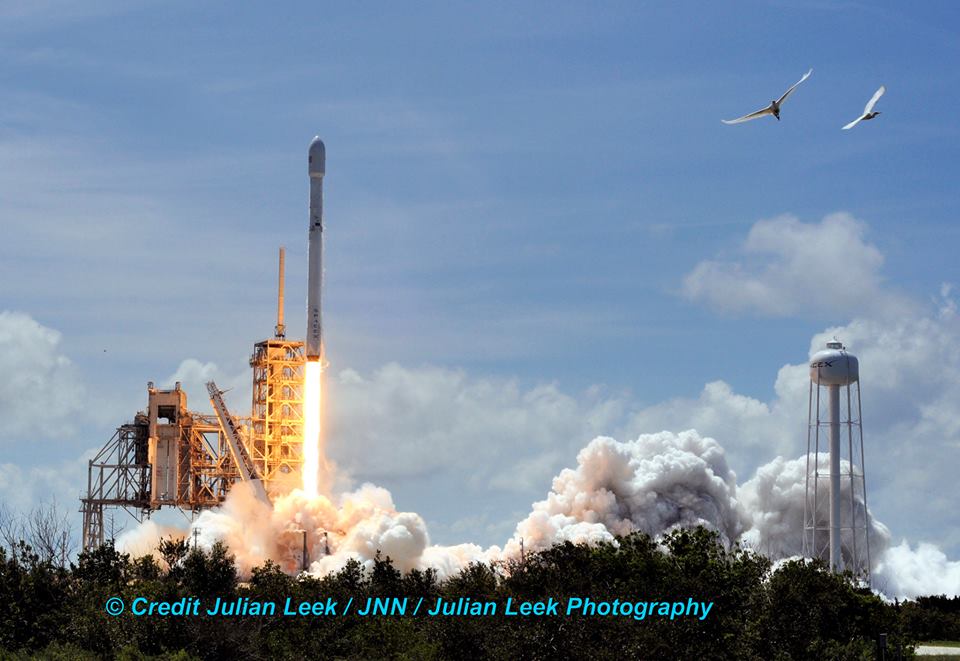
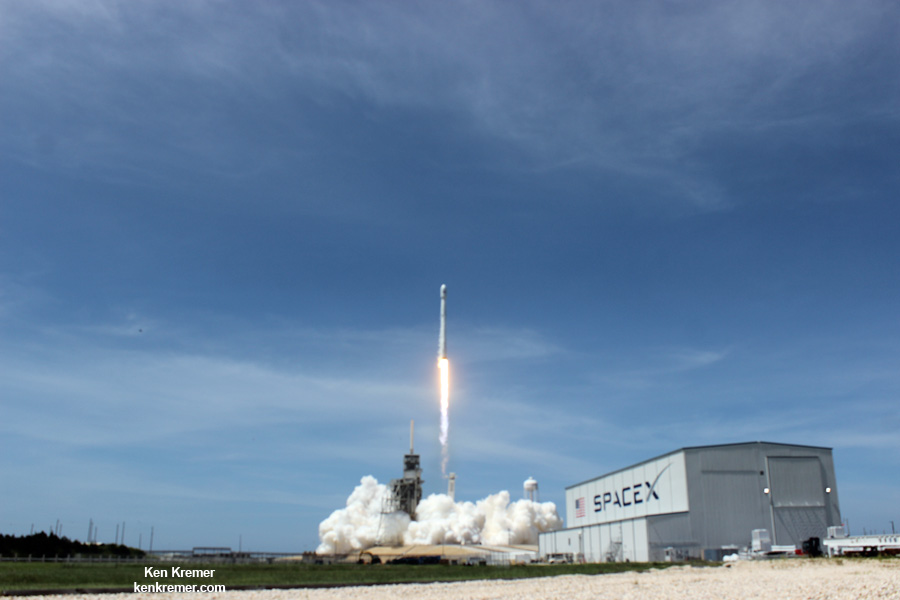
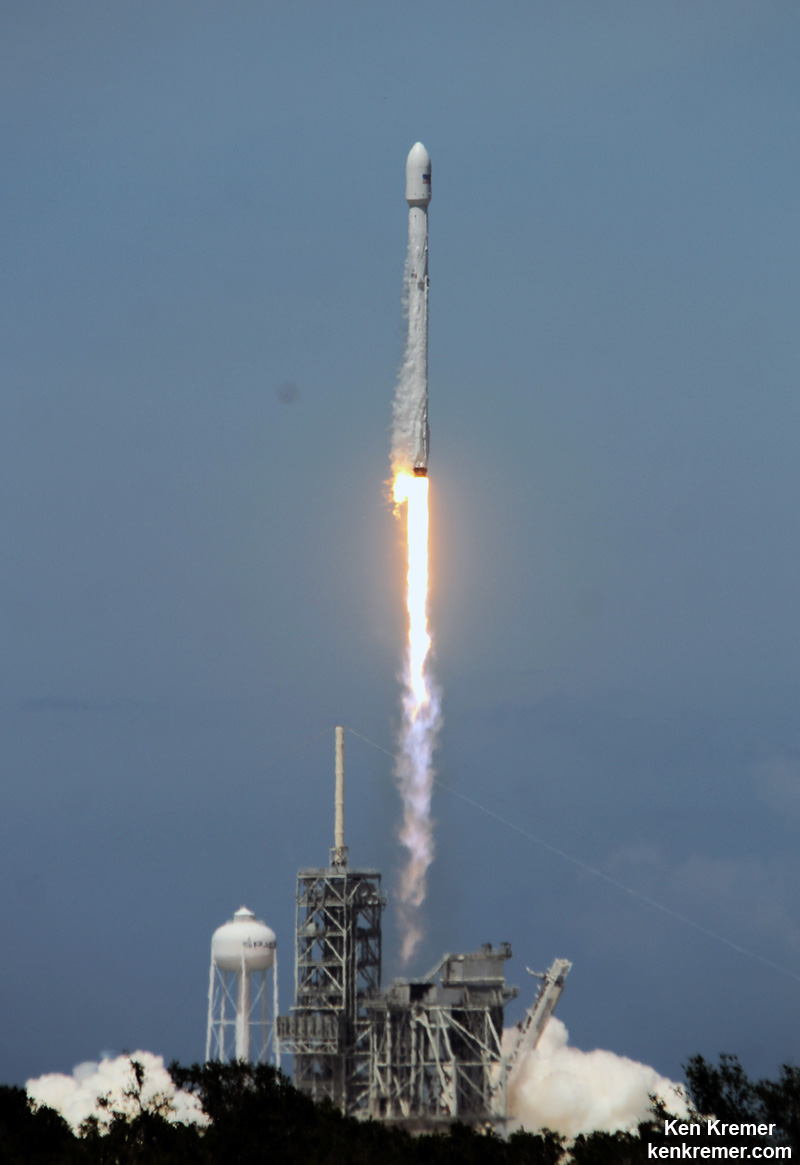
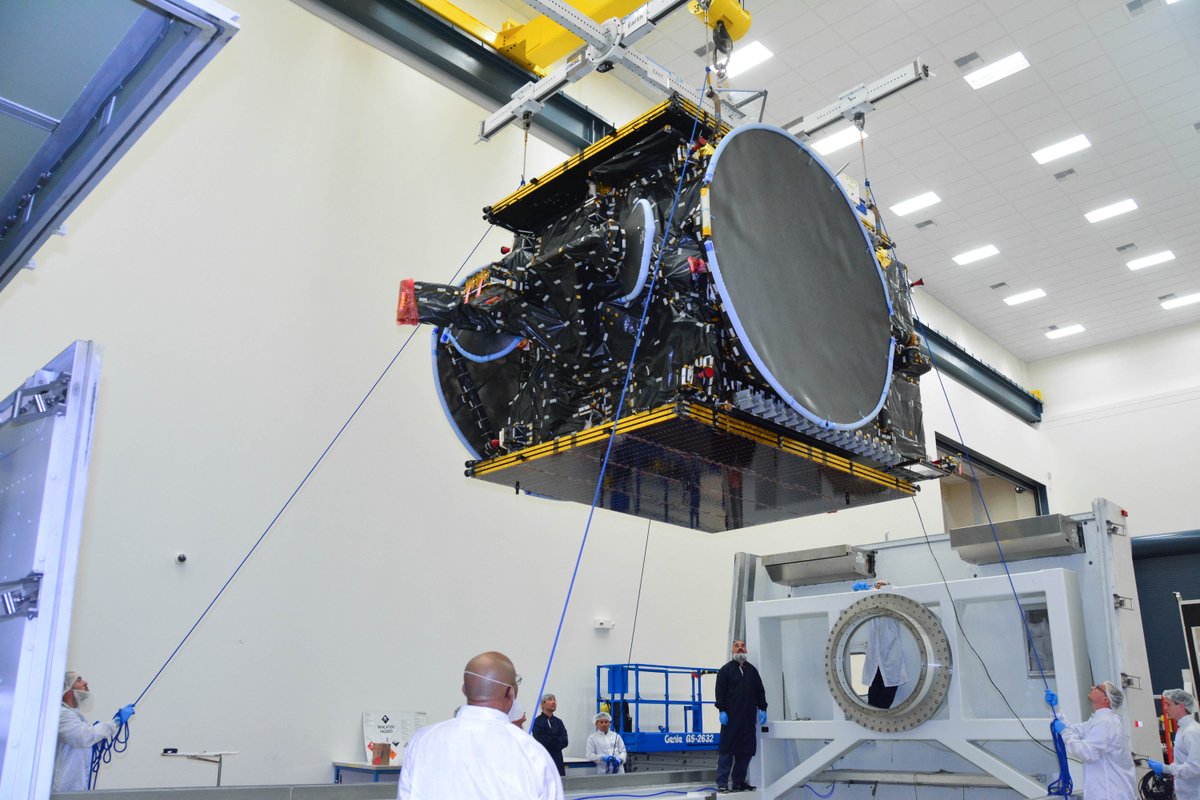
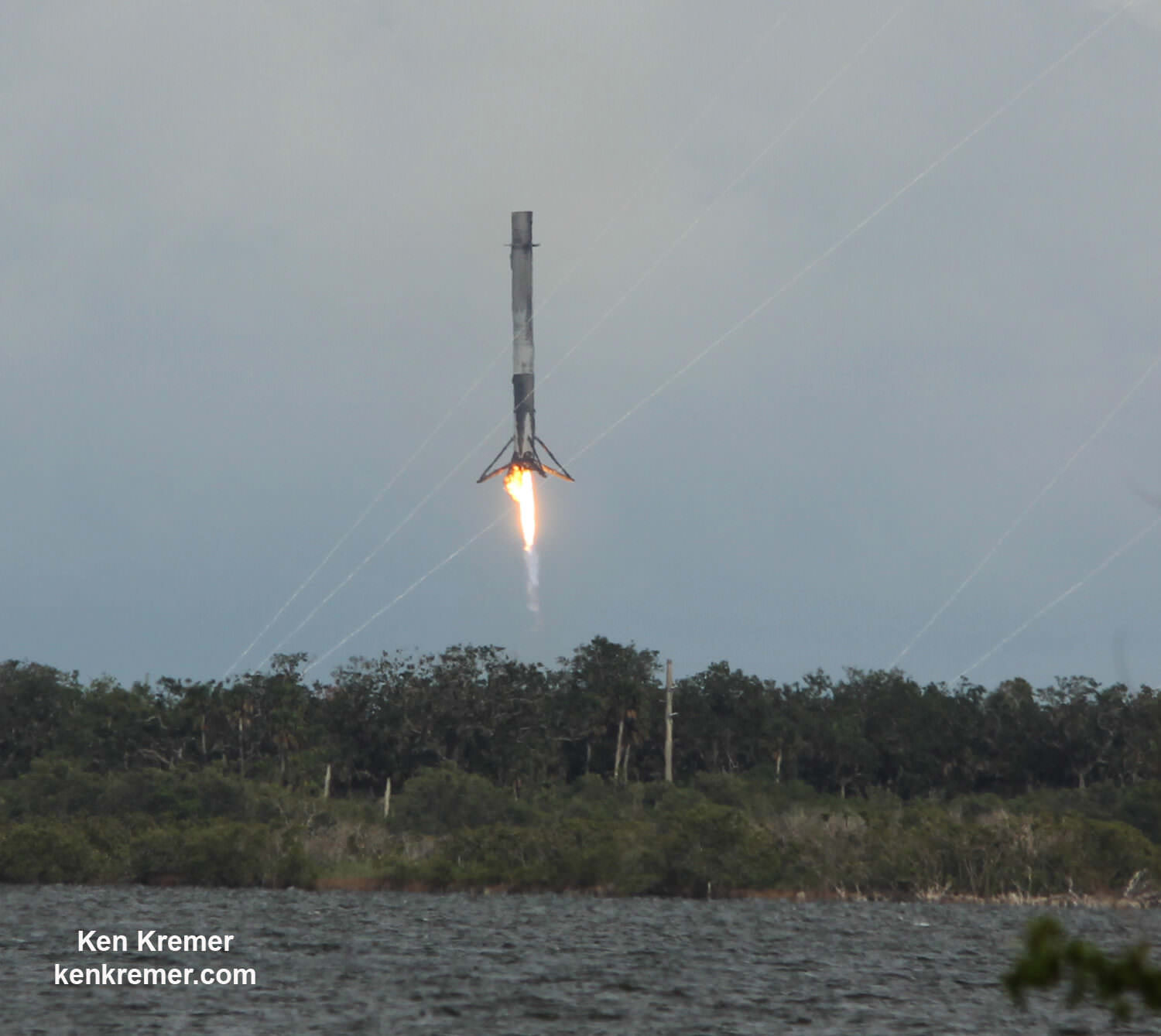
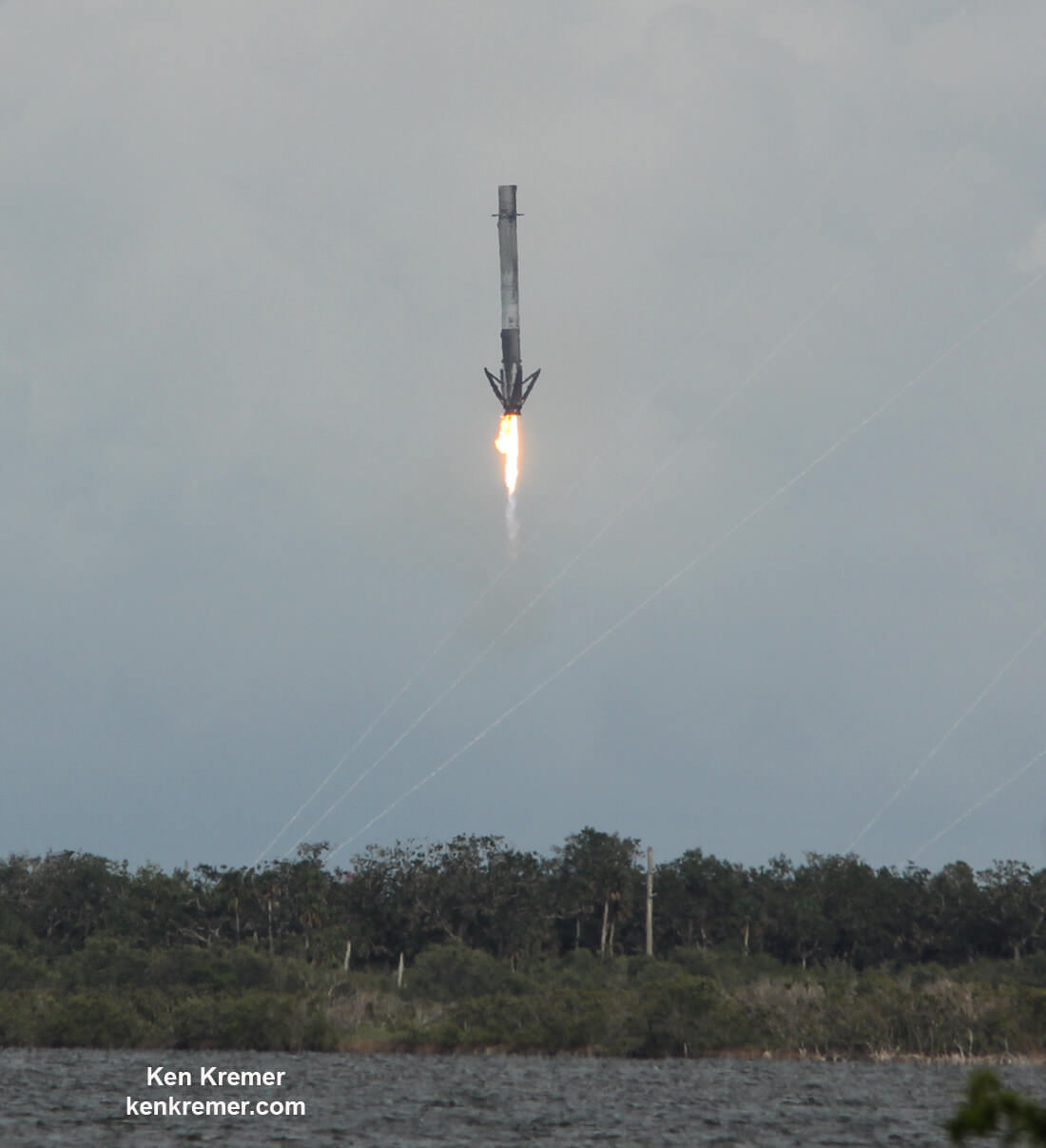
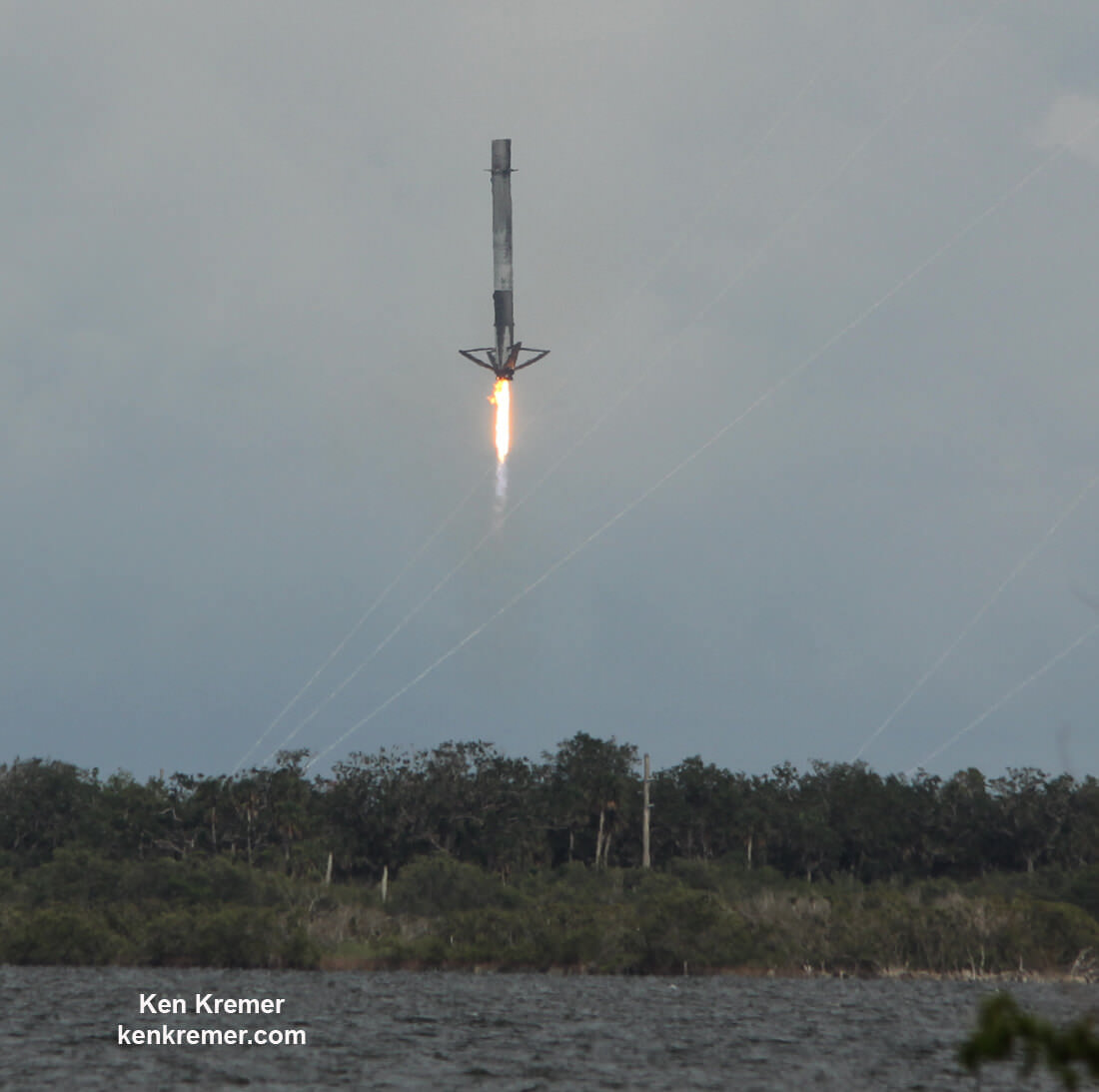
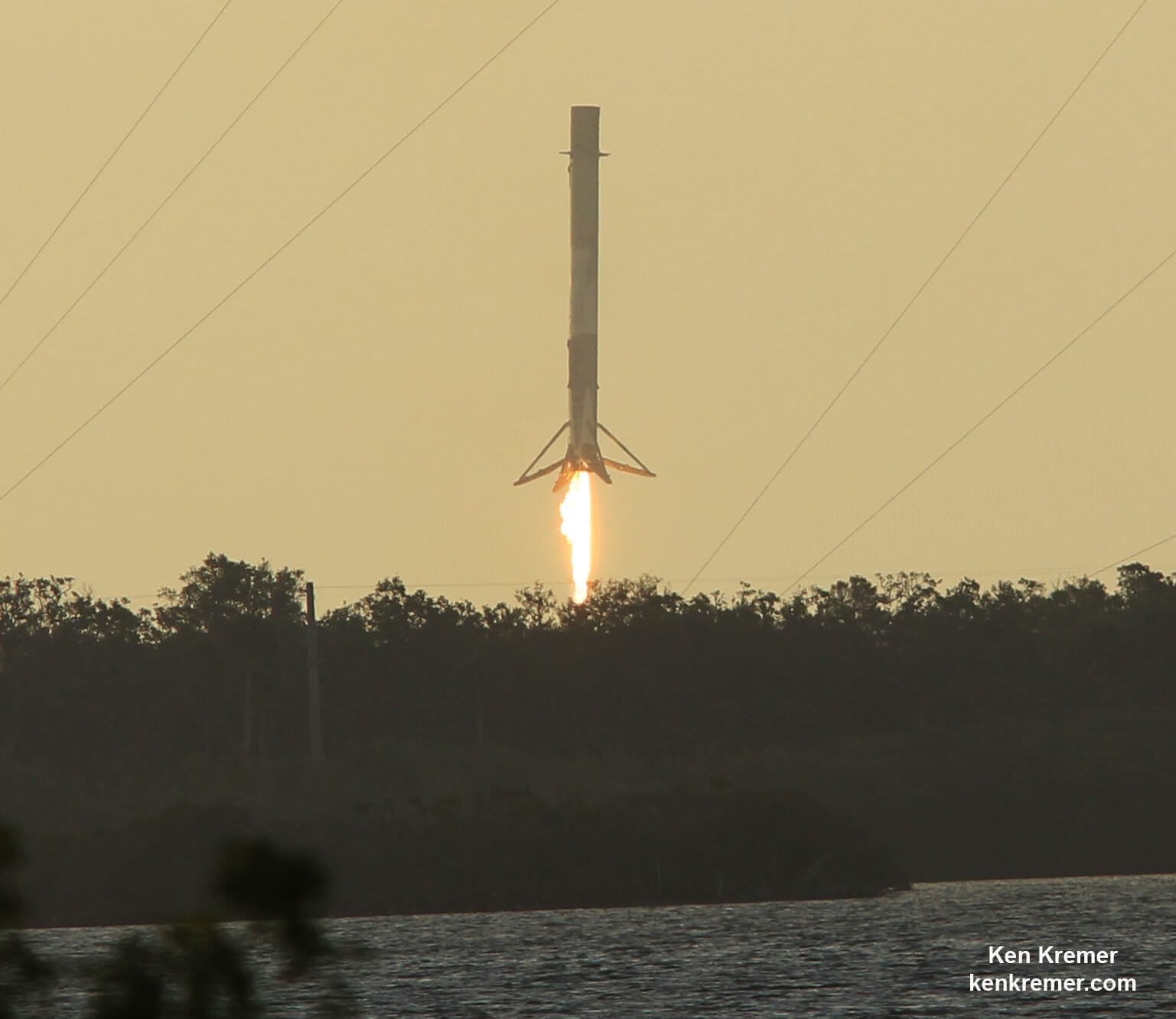
The first stage will not be recovered for this launch because the massive 6800 kg Intelsat 35e comsat requires every drop of fuel to get to the desired orbit.
“There will be no return of the booster for this mission, “ Ken Lee, Intelsat’s senior vice president of space systems, told Universe Today in a prelaunch interview on Sunday.
“We [Intelsat] need all the fuel to get to orbit.”
By using all available fuel on board the Falcon 9, Intelsat 35e will be delivered to a higher orbit.
“This will enable us to use less fuel for orbit raising maneuvers and make more available for station keeping maneuvers,” Lee told me.
“We hope this will potentially extend the satellites lifetime by 1 or 2 years.”
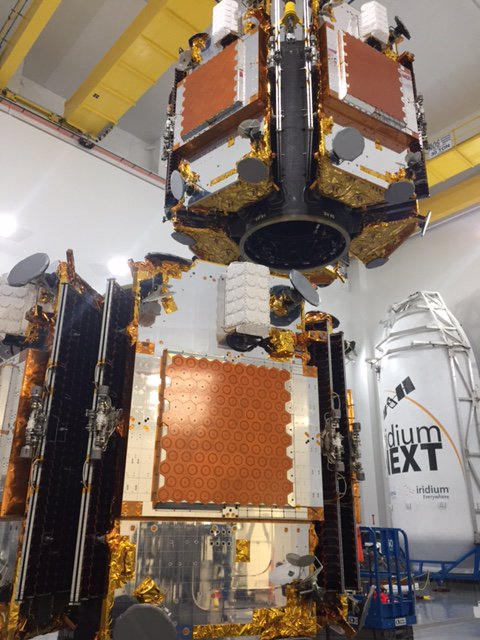
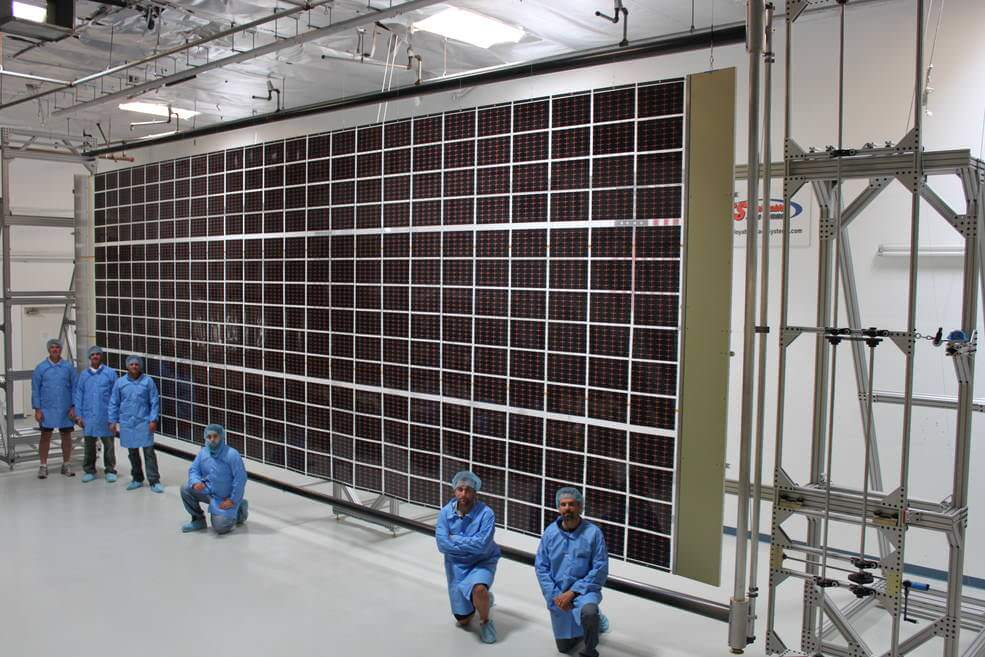
“Intelsat 35e is the fourth in the series of our ‘Epic’ satellites. It will provide the most advanced digital services ever and a global footprint.”
You can watch the launch live on a SpaceX dedicated webcast starting about 15 minutes prior to the opening of the launch window at 7:37 p.m. EDT, or 2337 UTC
Watch the SpaceX broadcast live at: SpaceX.com/webcast
The never before used Falcon 9’s launch window extends for nearly an hour – 58 minutes – until 8:35 p.m. EDT, July 5, or 0035 UTC
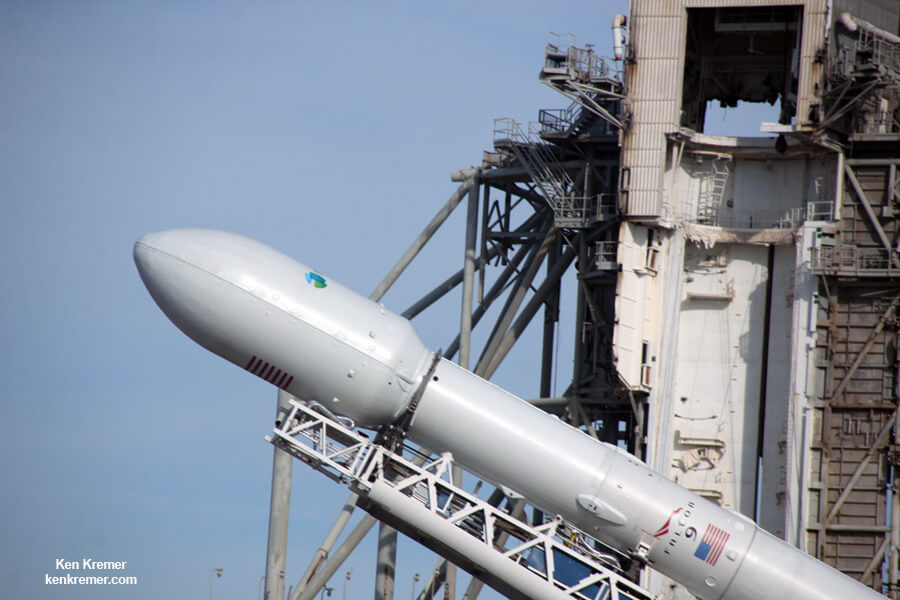

“Our whole team had to activate quickly to get Intelsat 35e into this window and ready for launch. The good news is we partnered with SpaceX and Boeing, the satellite builder,” said Kurt Riegel Sr VP Intelsat Sales & Markenting, in an interview with Universe Today at the countdown clock at the KSC Press Site.
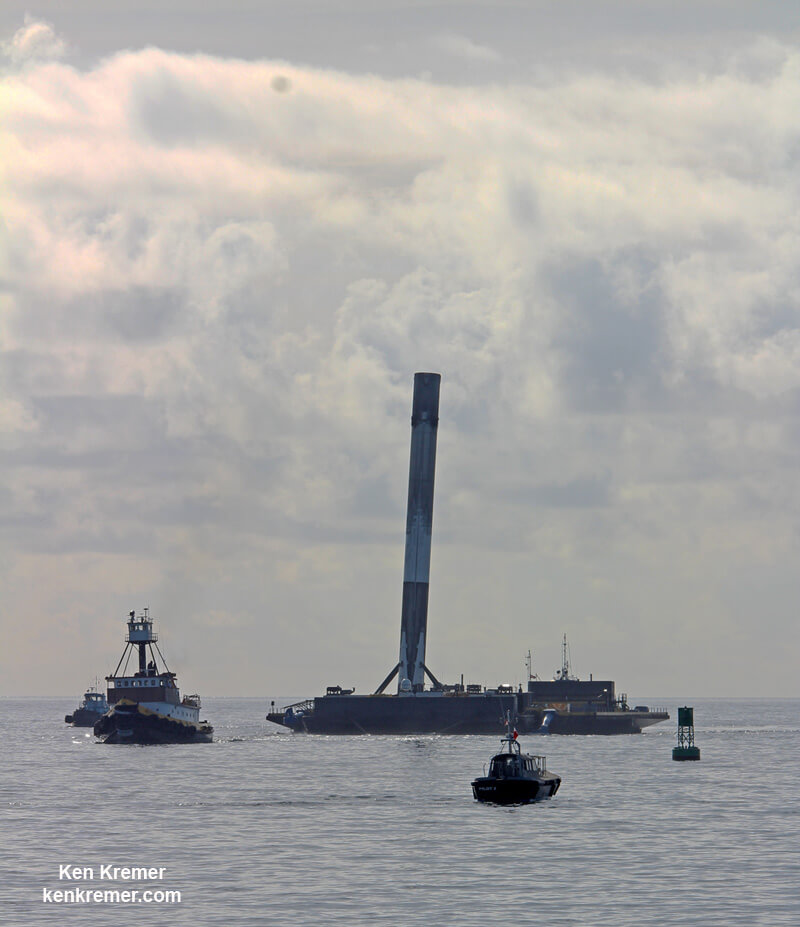
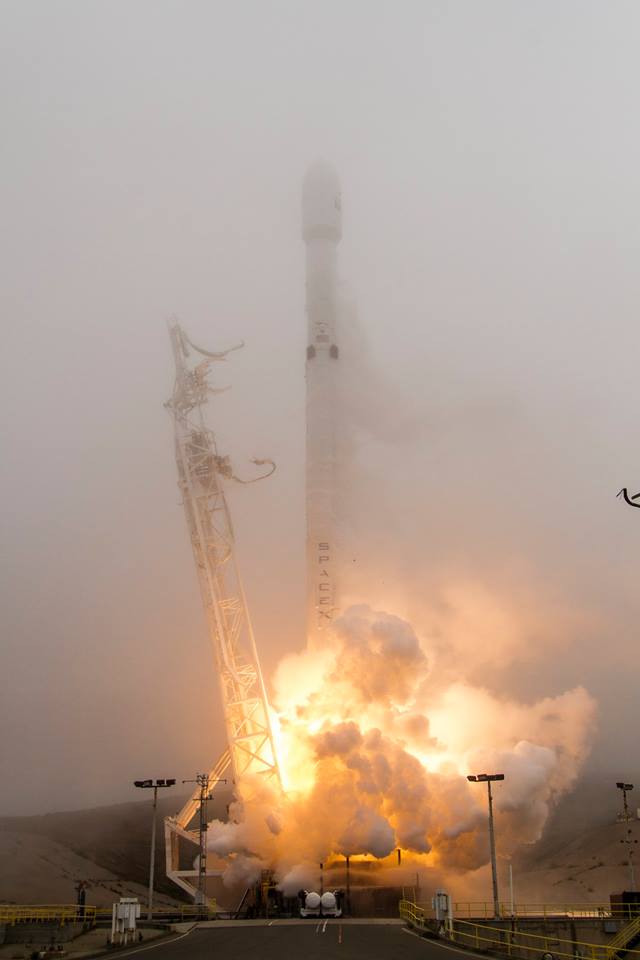
There was barely a week to turn around the Falcon 9 rocket and launch pad sinevc the blastoff of BulgariaSat-1.
“Boeing got everything accomplished on time and not give an inch on our test schedule or our quality which is so important to us.”
Monday’s [now Wednesday July] weather forecast is currently 70% GO for favorable conditions at launch time.
The weather odds have changed dramatically all week – trending more favorable.
The concern is for the Cumulus Cumulus Cloud Rule according to Air Force meteorologists with the 45th Space Wing at Patrick Air Force Base.
Monday’s abort took place 10 seconds before liftoff but was called at T-Zero by the SpaceX launch director. A problem was detected with the GNC system, which stands for guidance, navigation and control.
“We had a vehicle abort criteria violated at T-minus 10 seconds, a GNC criteria,” the launch director announced on the SpaceX webcast soon after the abort was called.
“We’re still looking into what that is at this time.
He then announced a scrub for the day.
“We’re not going to be able to get a recycle in today without going past the end of the window, so we’re officially scrubbed,” he stated on the webcast.
“Go ahead and put a 24-hour recycle into work.”

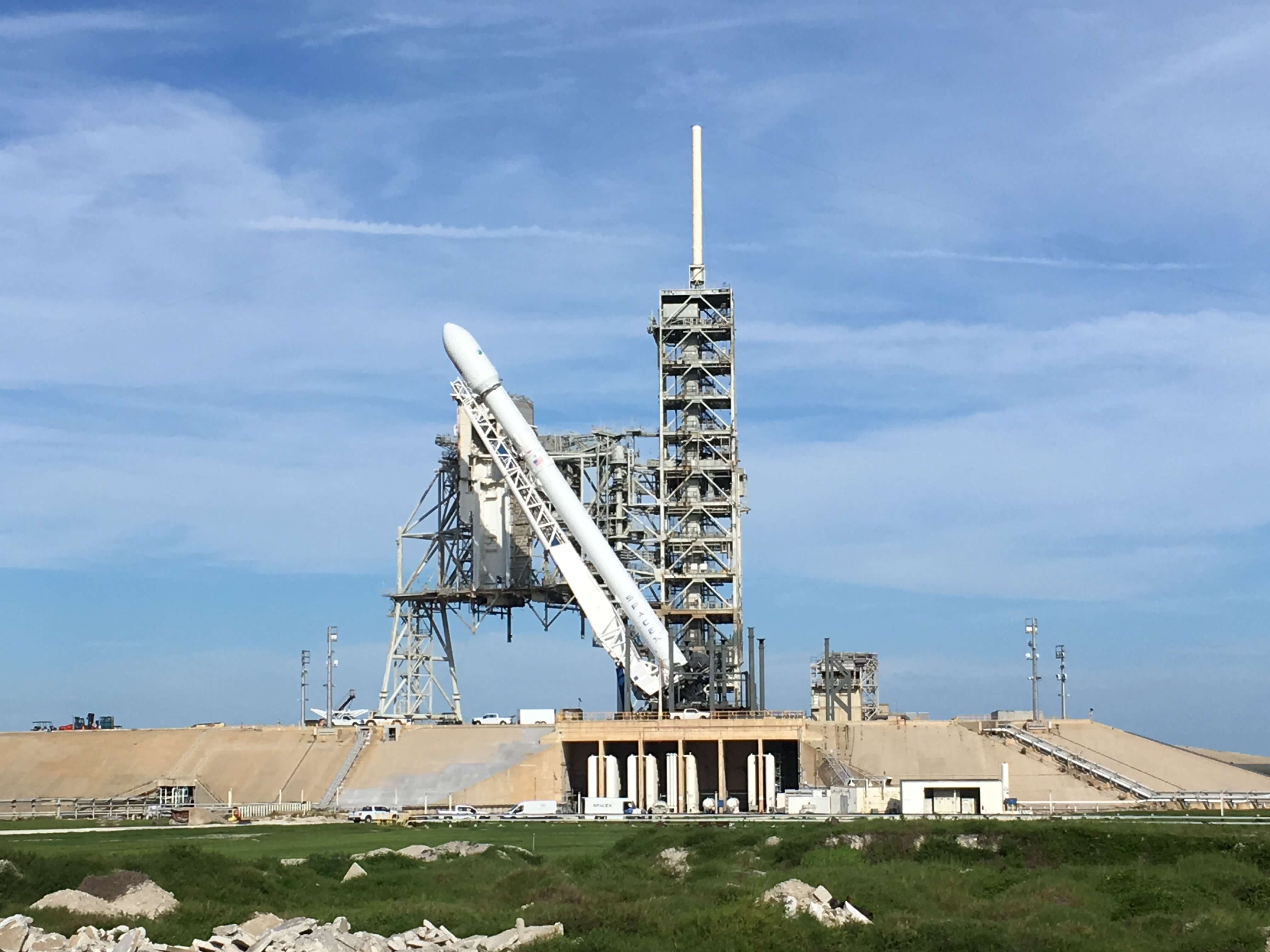
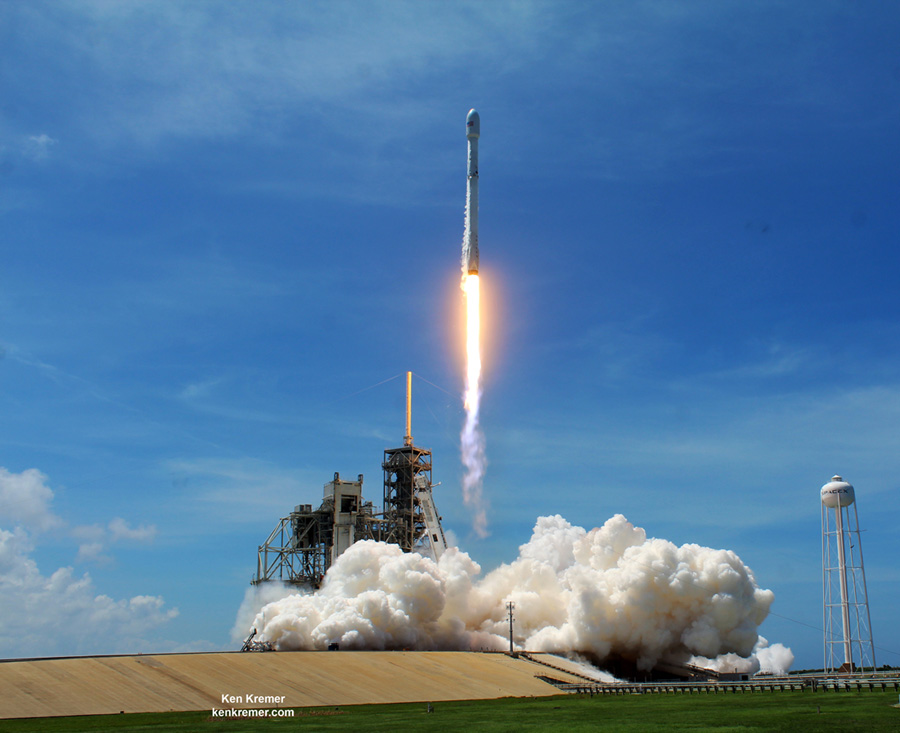
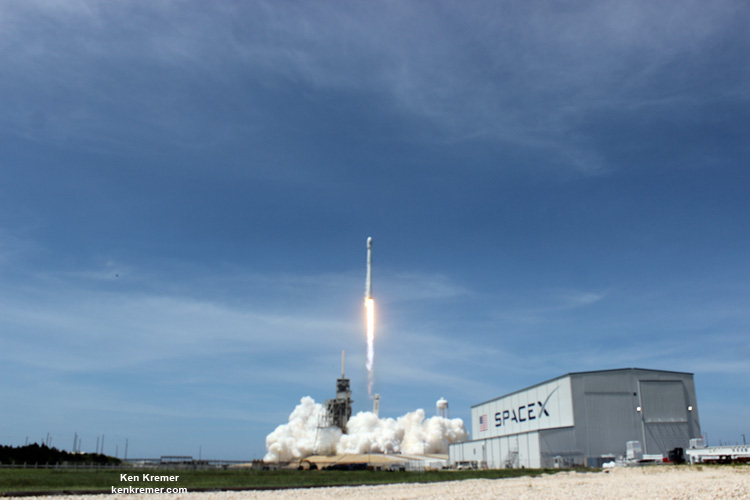
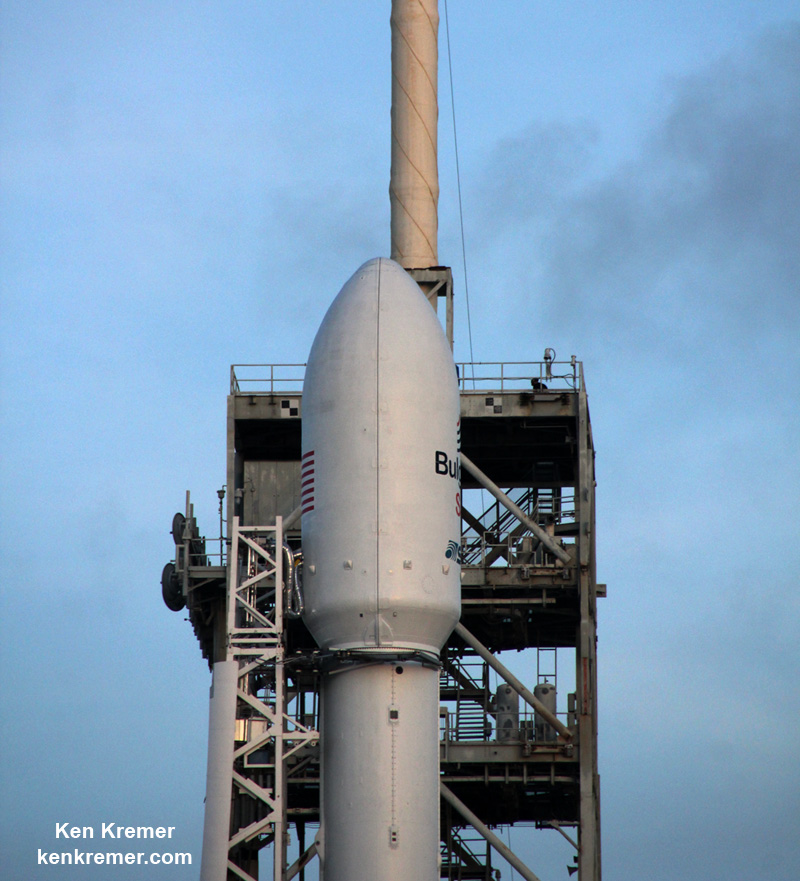
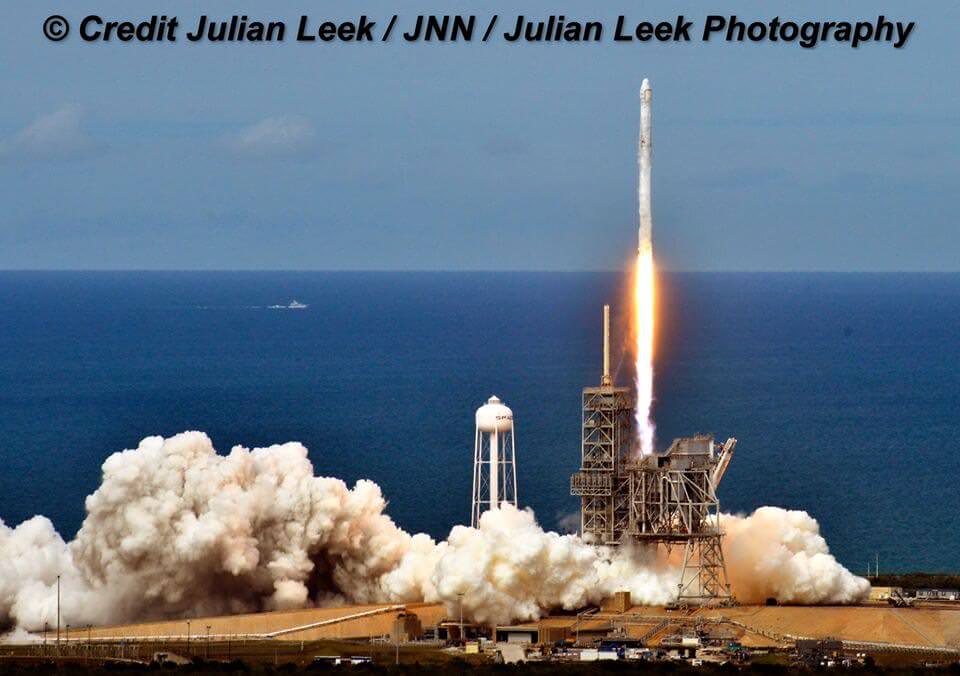
The brand new 29 story tall SpaceX Falcon 9 will deliver Intelsat 35e to a Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO).
The geostationary comsat will provide high performance services in the C- And Ku-bands to customers in North and South America, the Caribbean, as well as the continents of Europe and Africa.

The Ku band service includes a customized high power beam for direct-to-home television (DTH) and data communications services in the Caribbean as well as mobility services in Europe and Africa.
Hordes of spectators lined local area beaches and causeways north and south of the launch pad in anticipation of Sunday’s launch.
Many are expected to return given the promising weather forecast and July 4th holiday weekend.
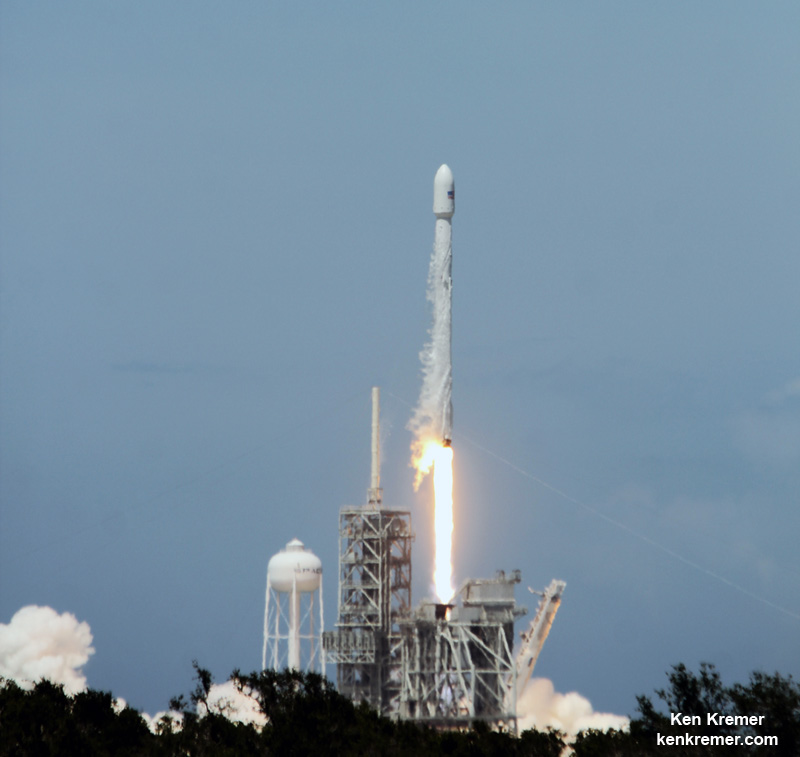
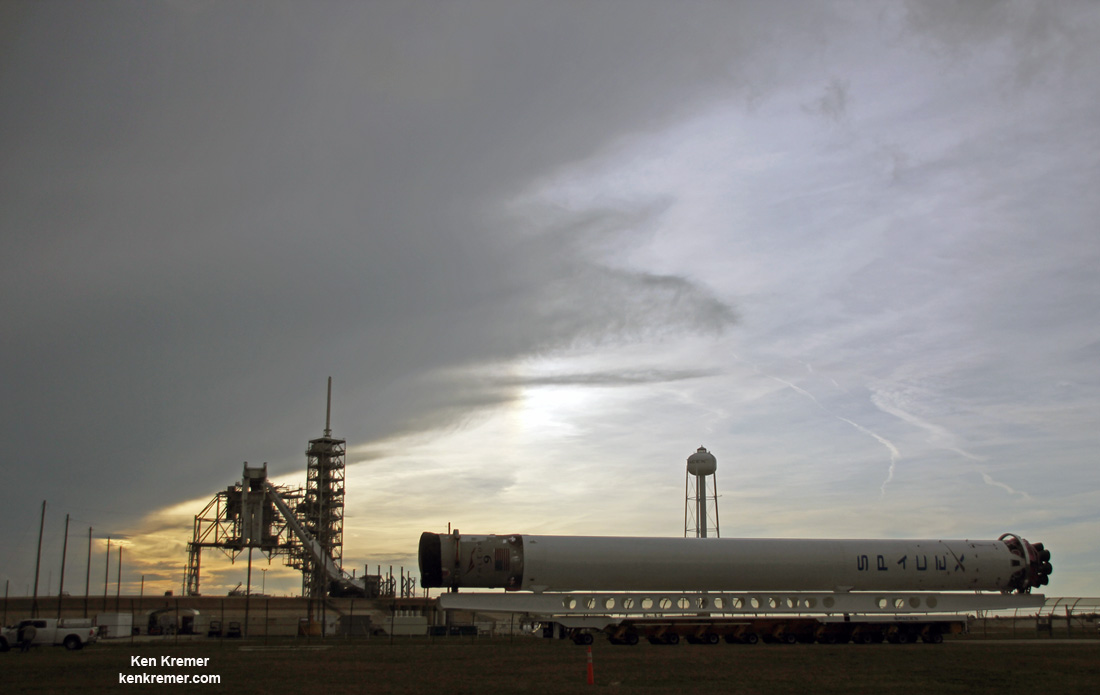
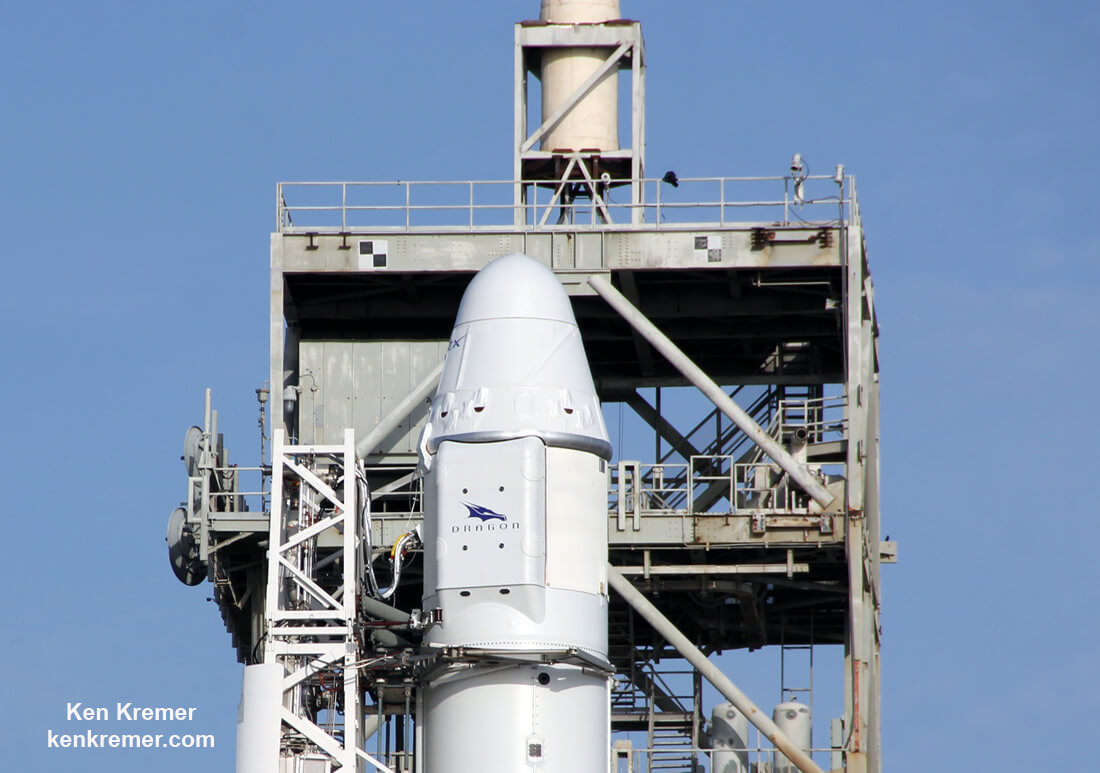
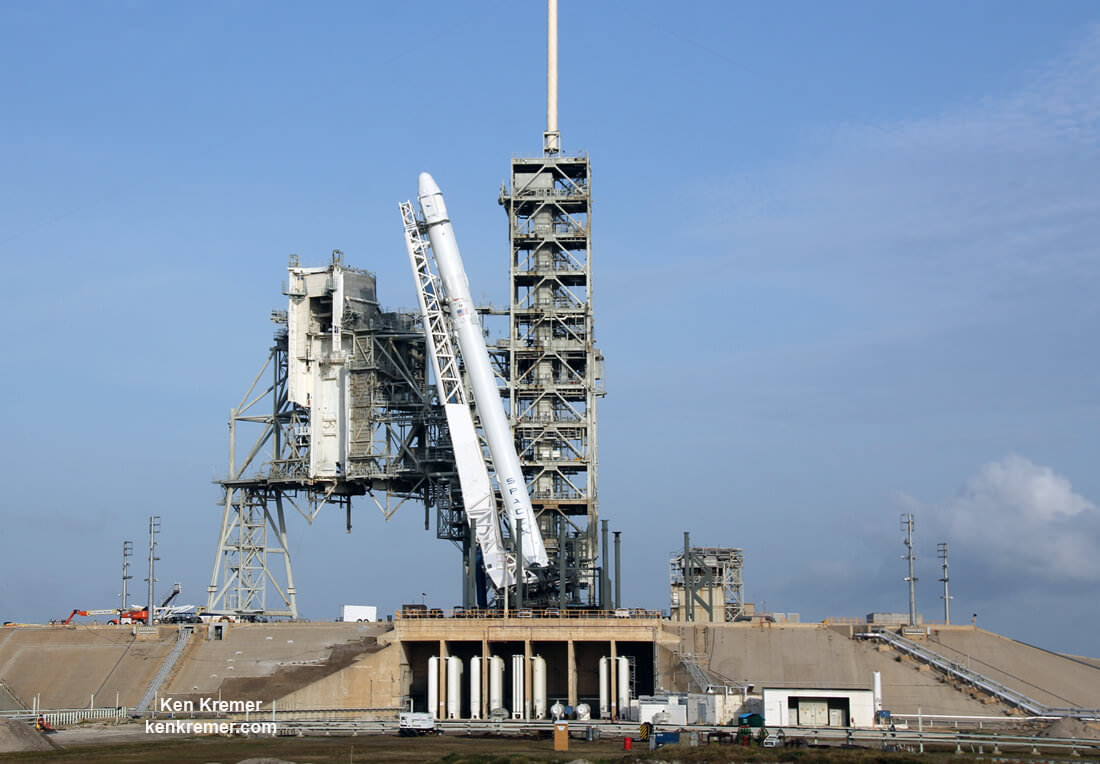
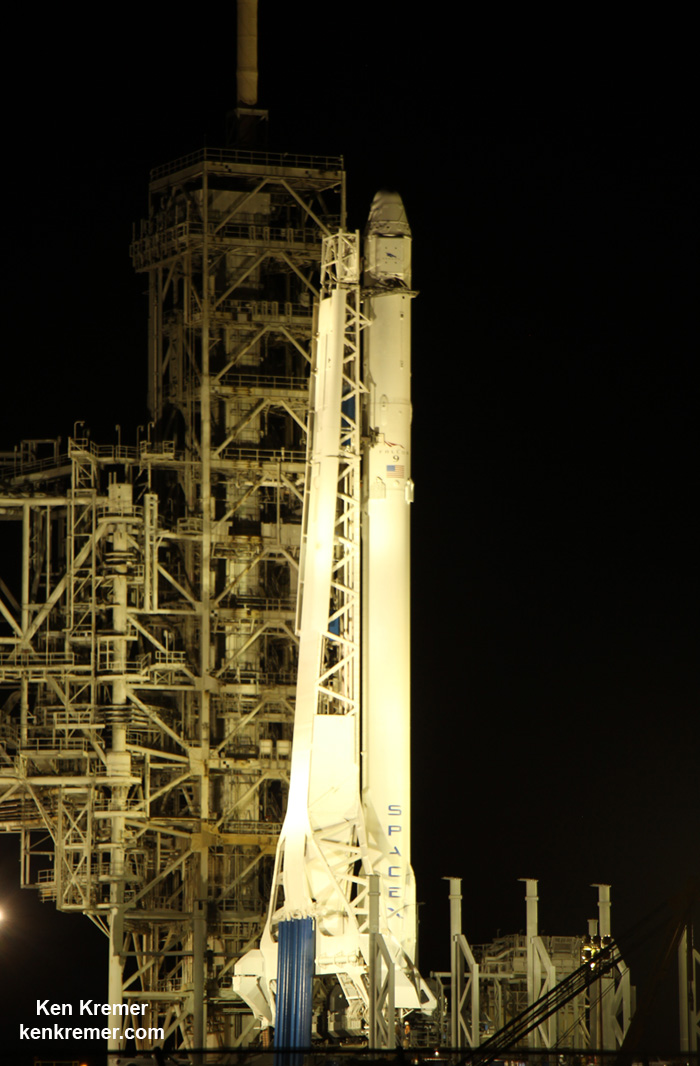
The 229-foot-tall (70-meter) Falcon 9/Intelsat 353e rocket was raised erect Sunday morning, July 2 and is poised for liftoff and undergoing final prelaunch preparations.
The first and second stages will again be fueled with liquid oxygen and RP-1 propellants starting about one hour before liftoff.
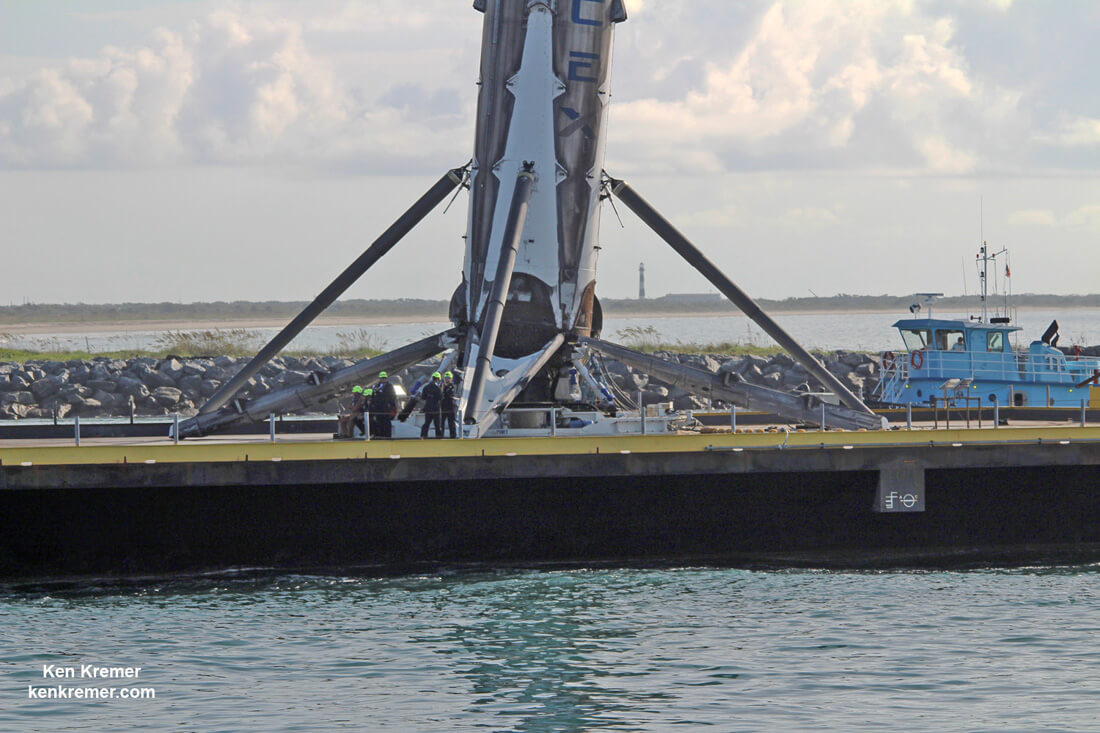
Intelsat 35e marks the tenth SpaceX launch of 2017 – establishing a new single year launch record for SpaceX.
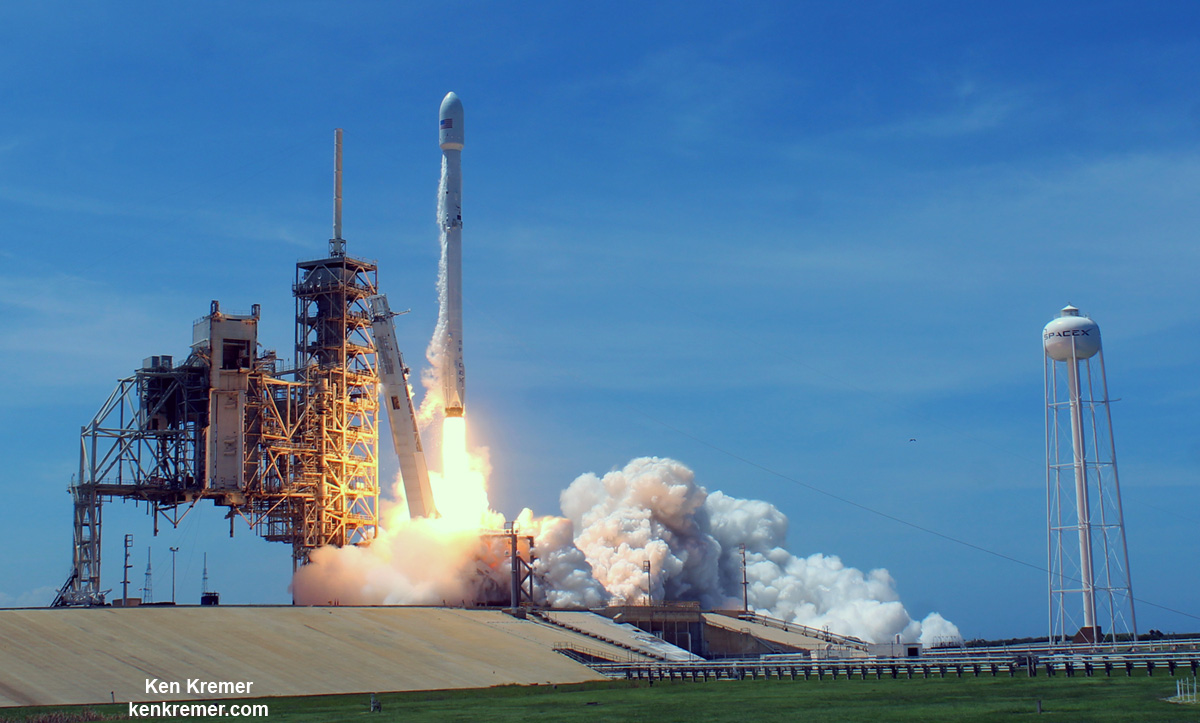

The recent BulgariaSat-1 and Iridium-2 missions counted as the eighth and ninth SpaceX launches of 2017.


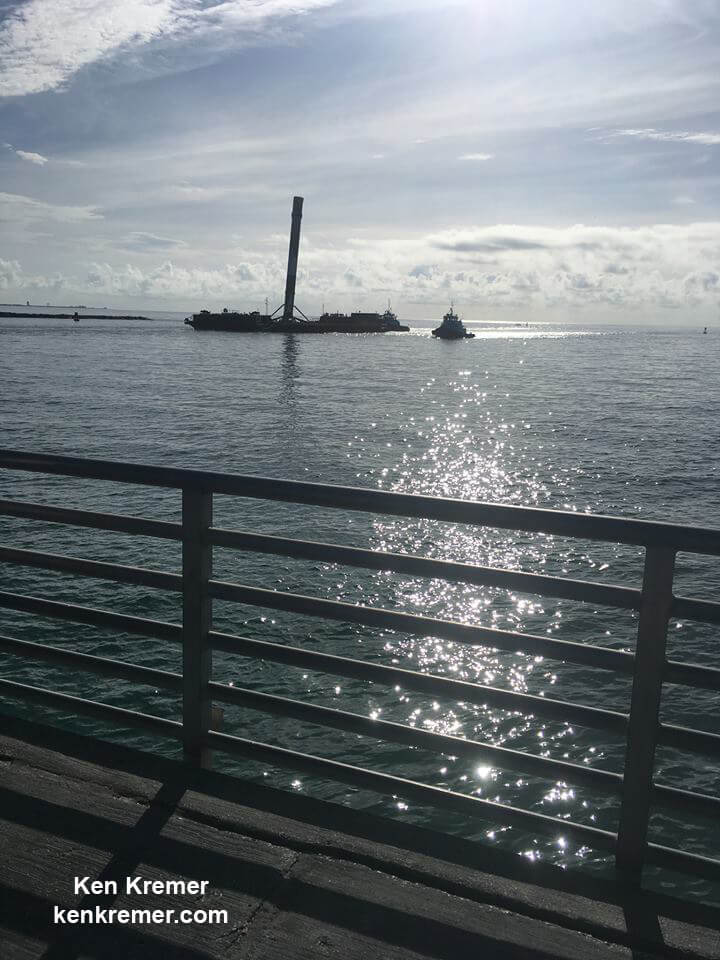
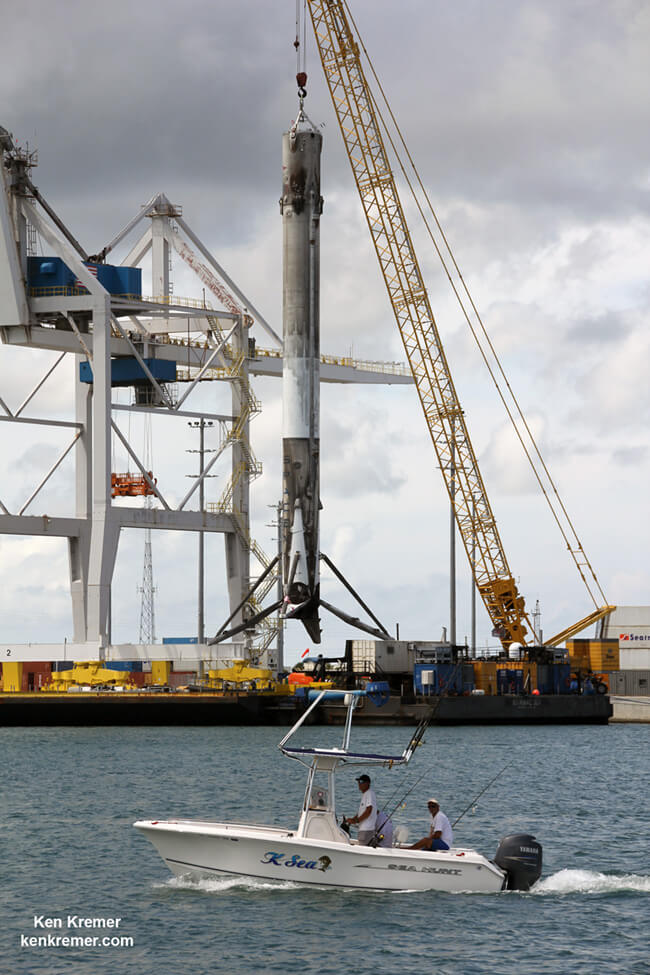
Including those last two ocean platform landings, SpaceX has now successfully recovered 13 boosters; 5 by land and 8 by sea, over the past 18 months.
Watch for Ken’s onsite Intelsat 35e and space mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.