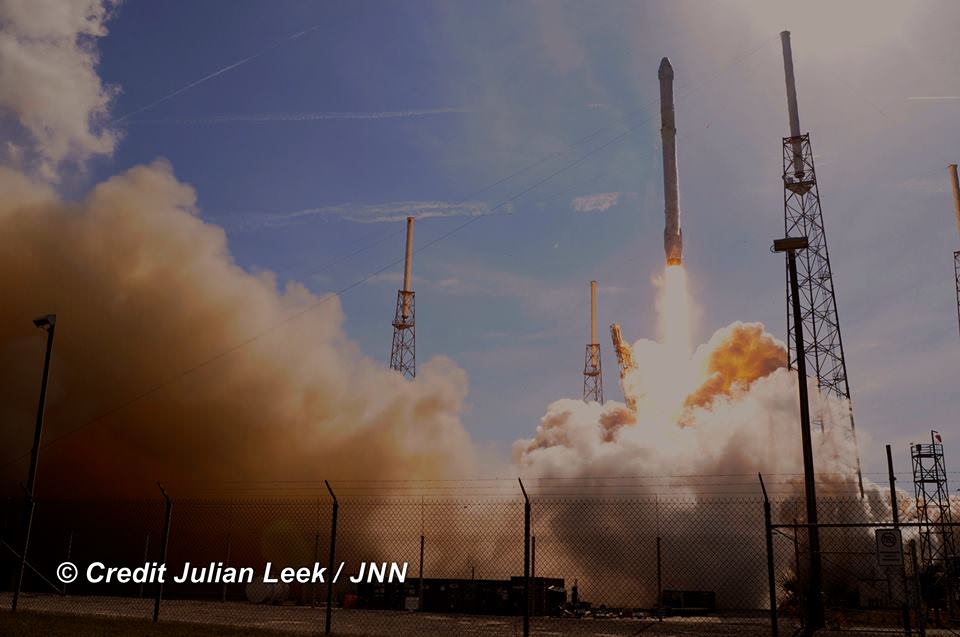
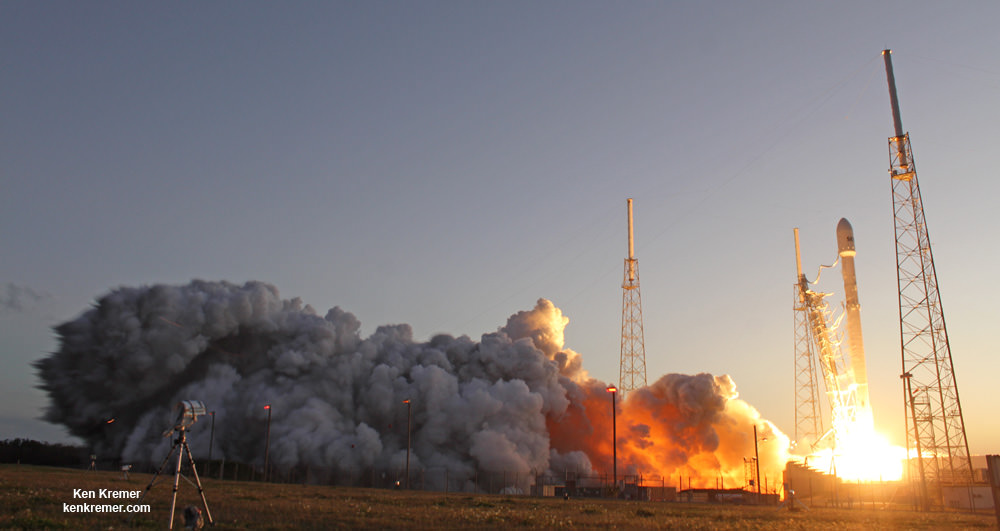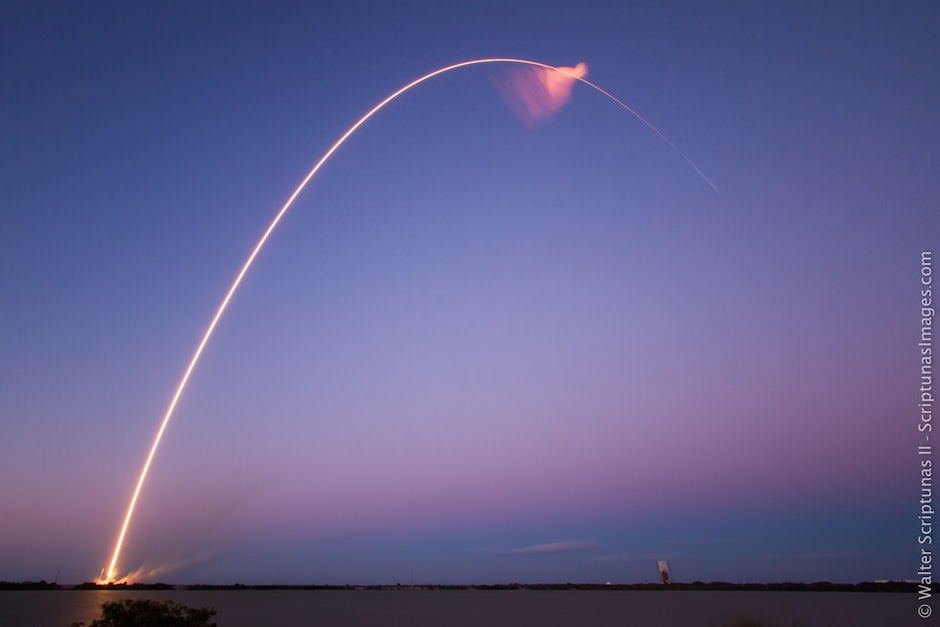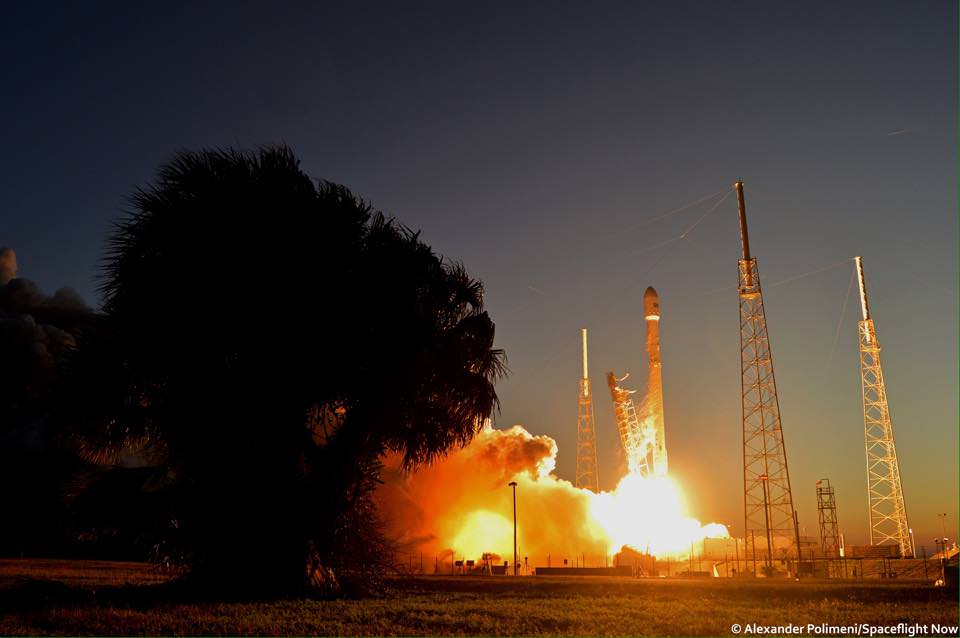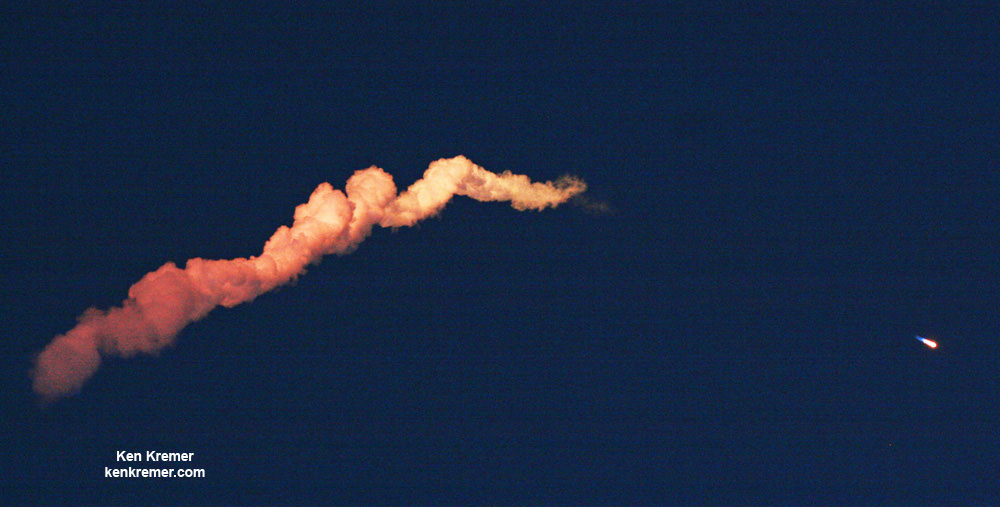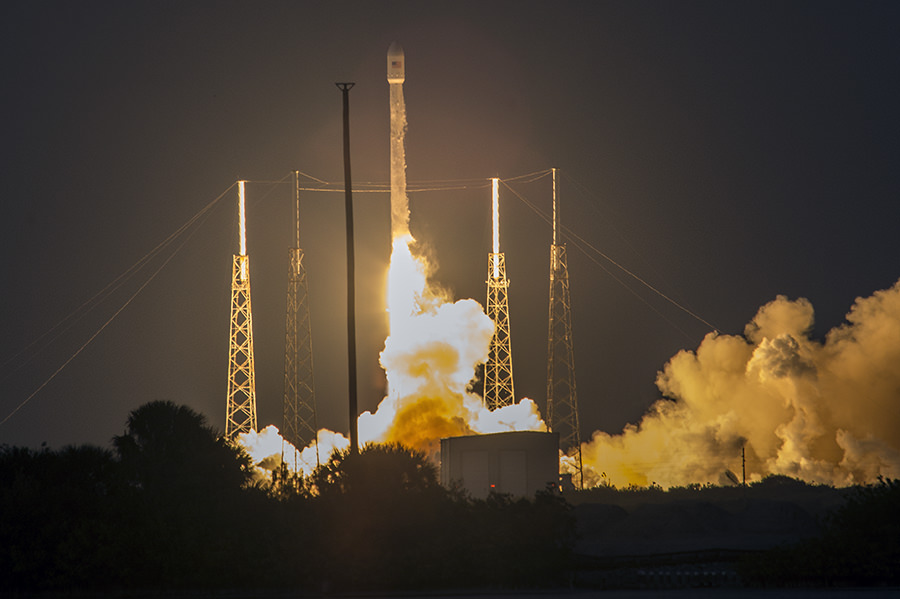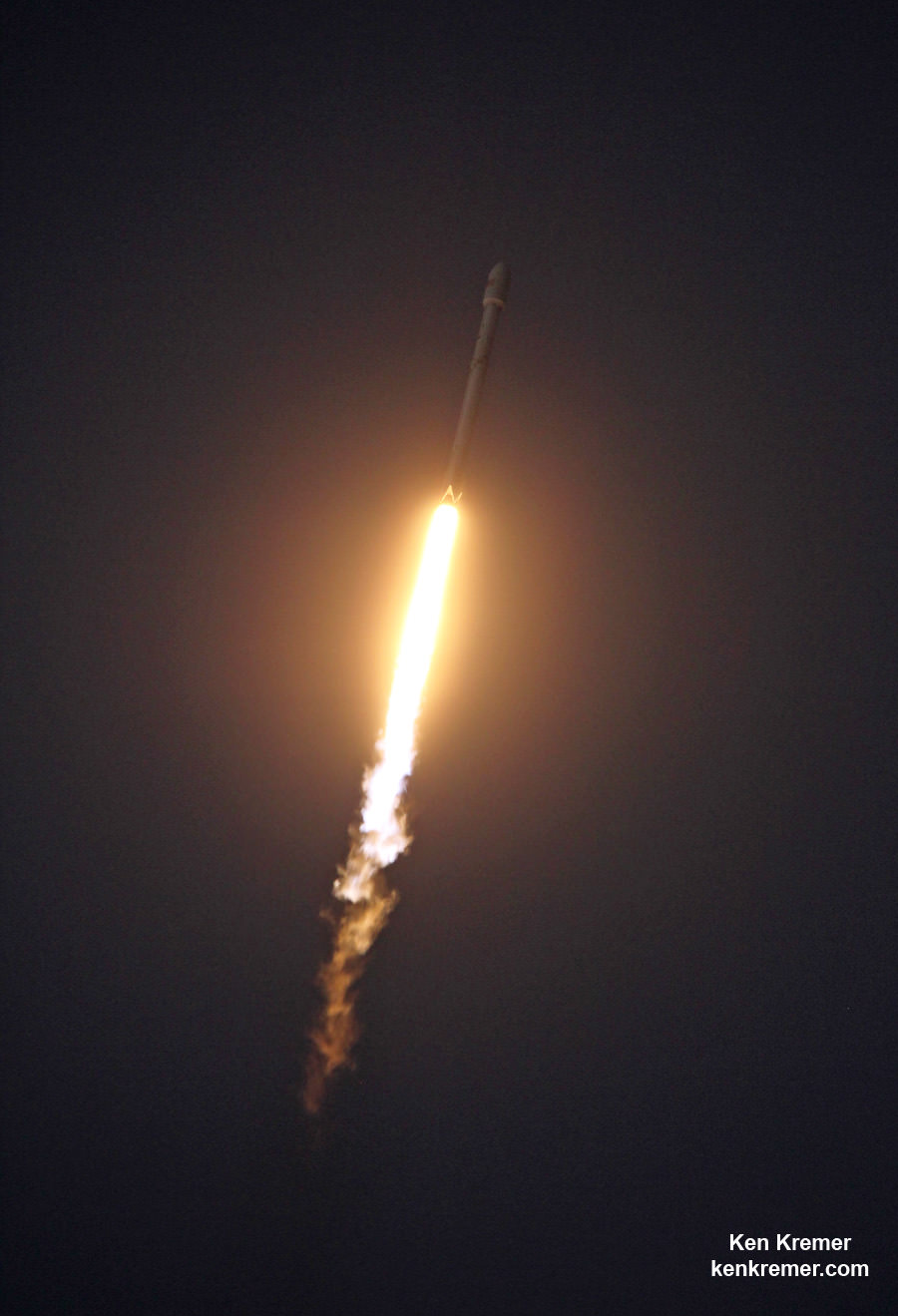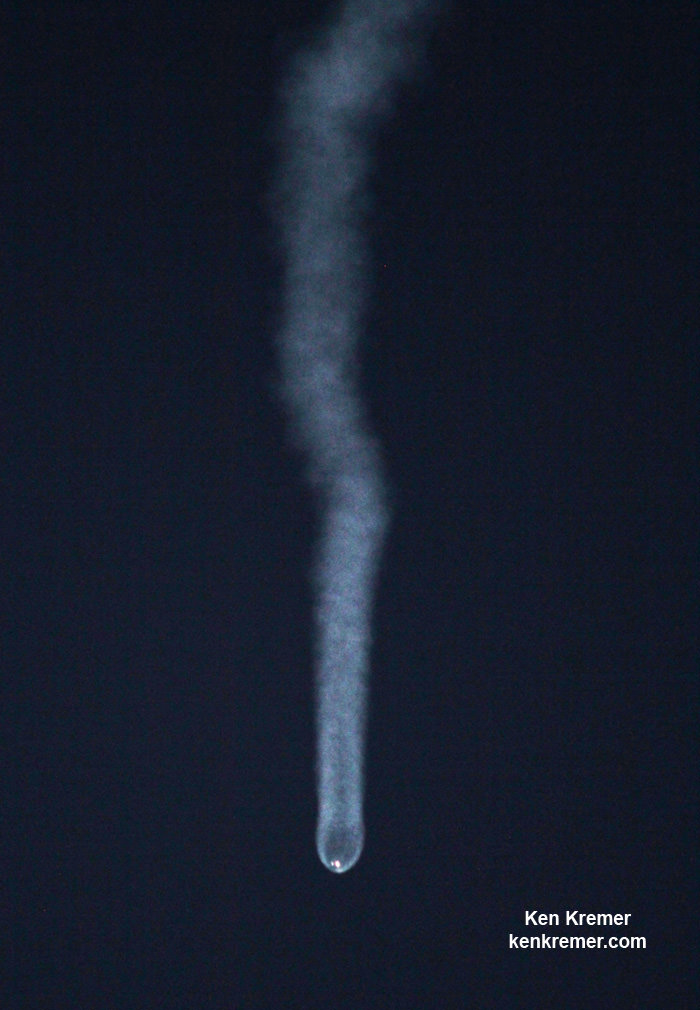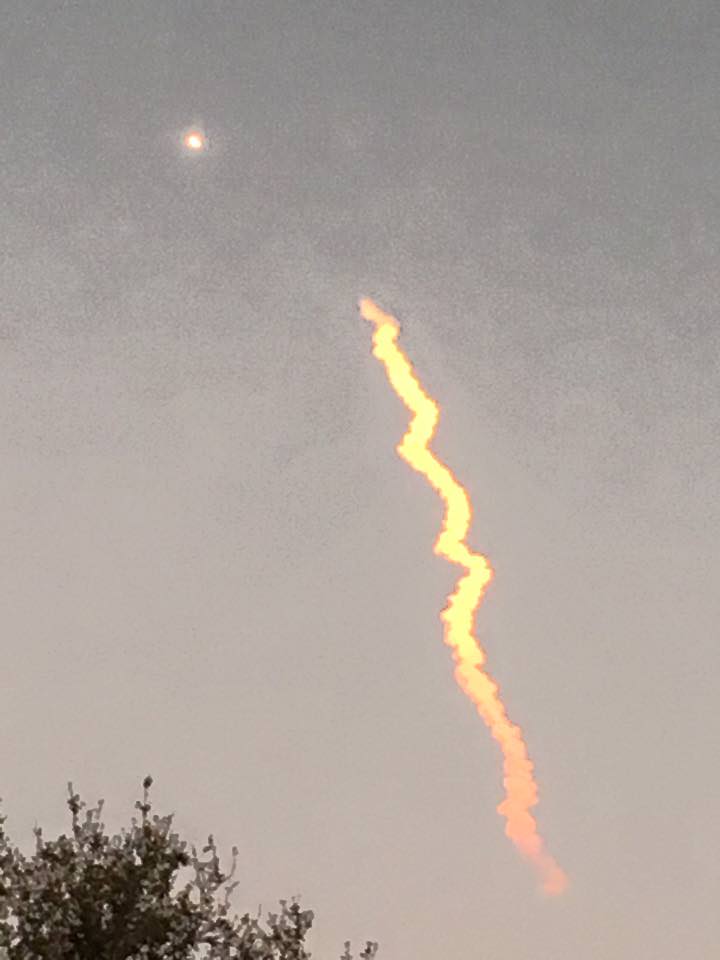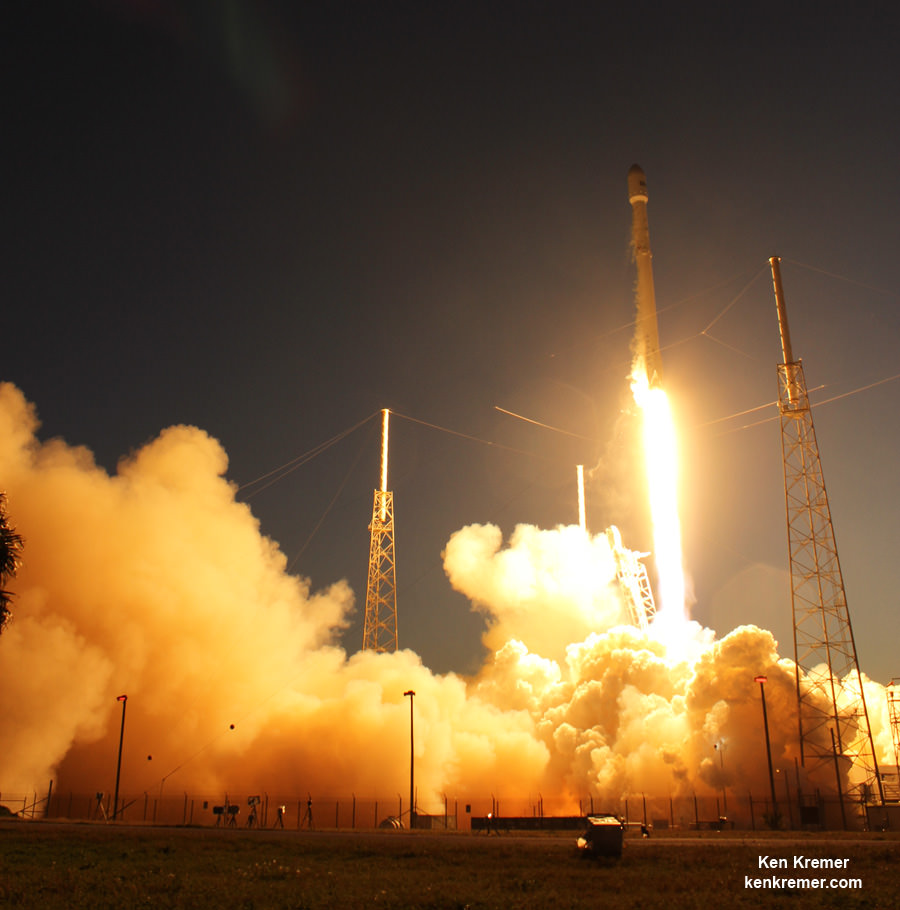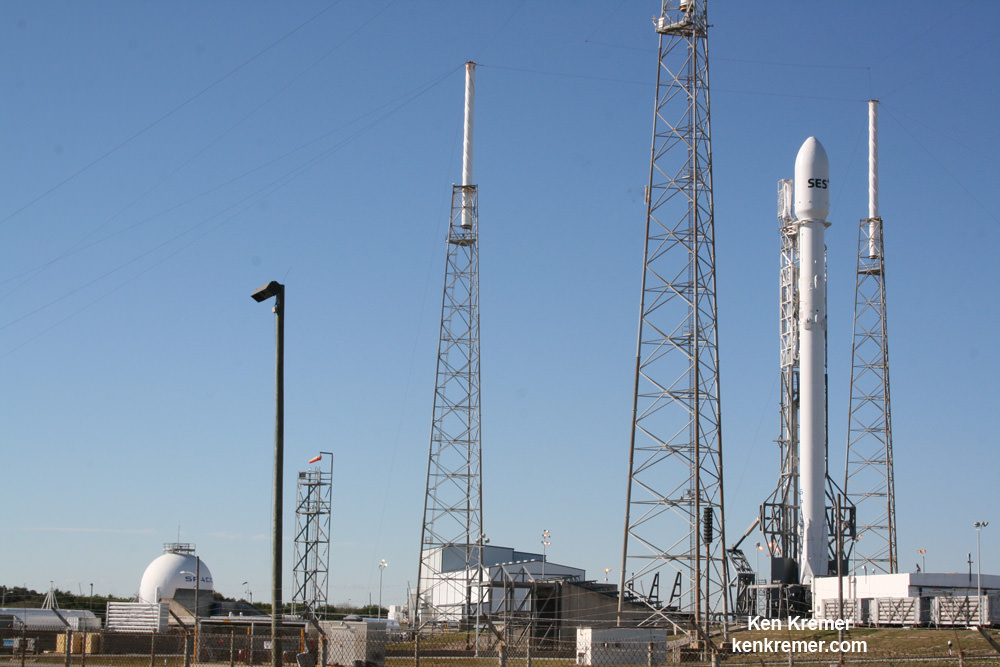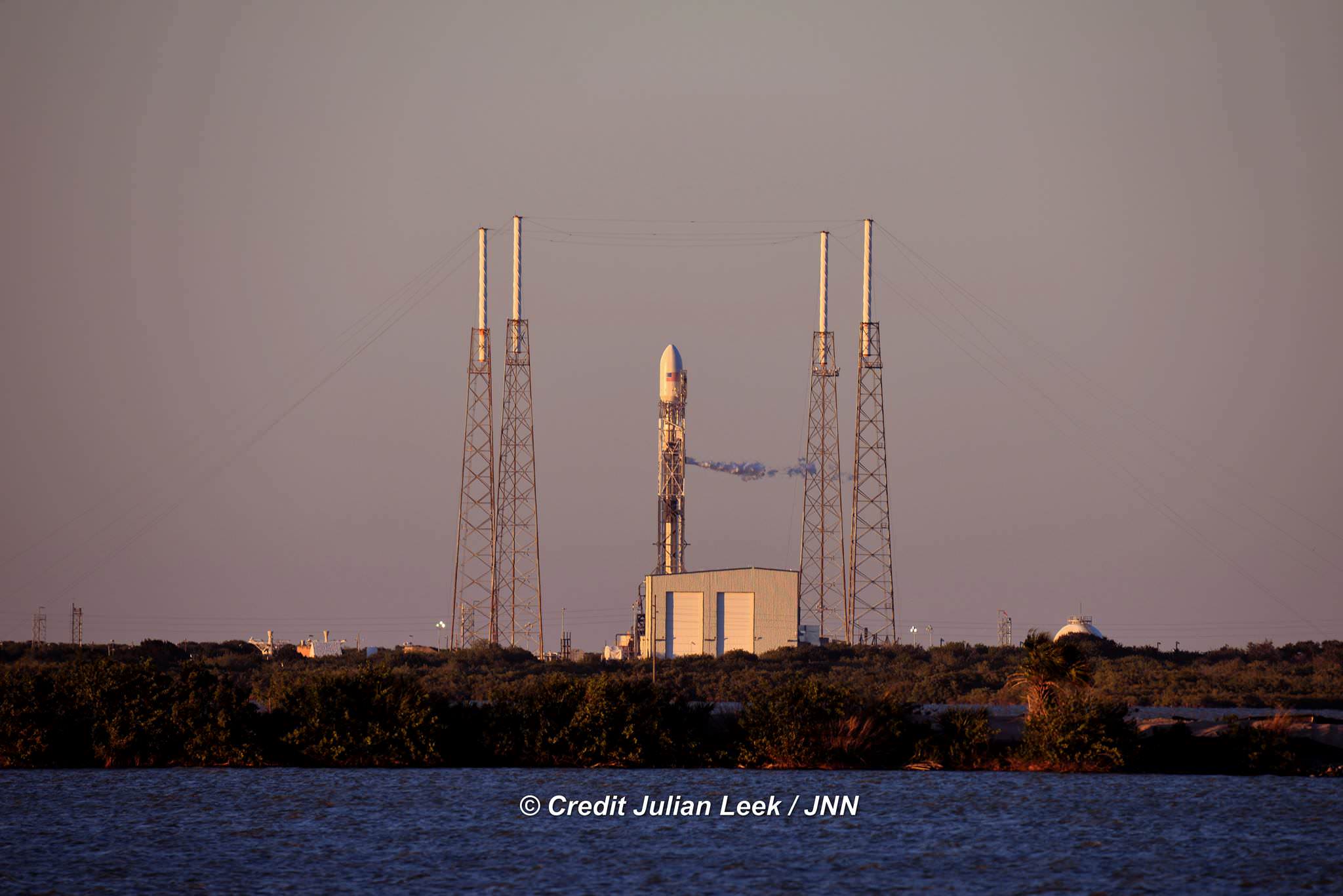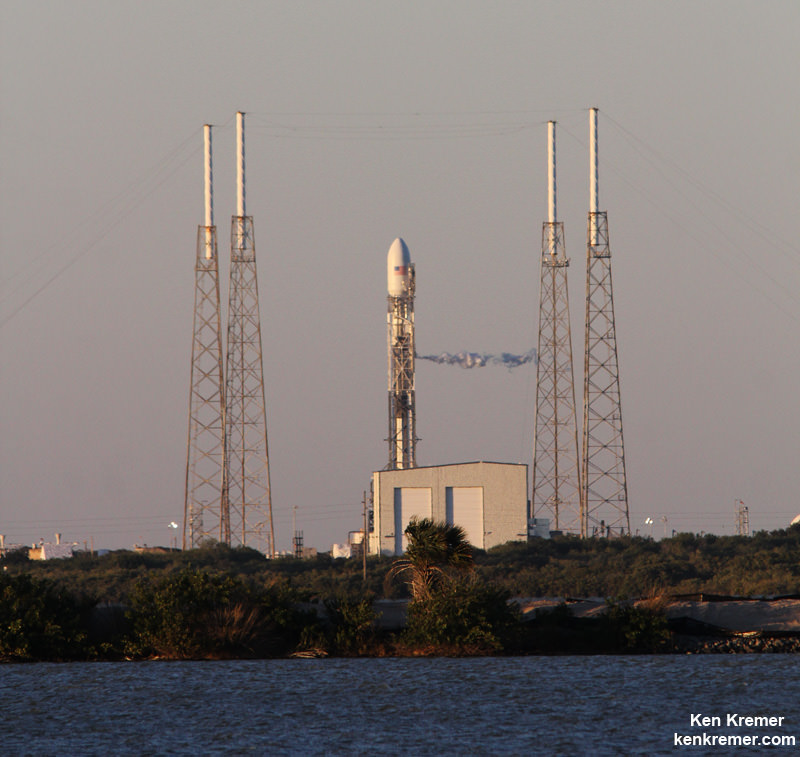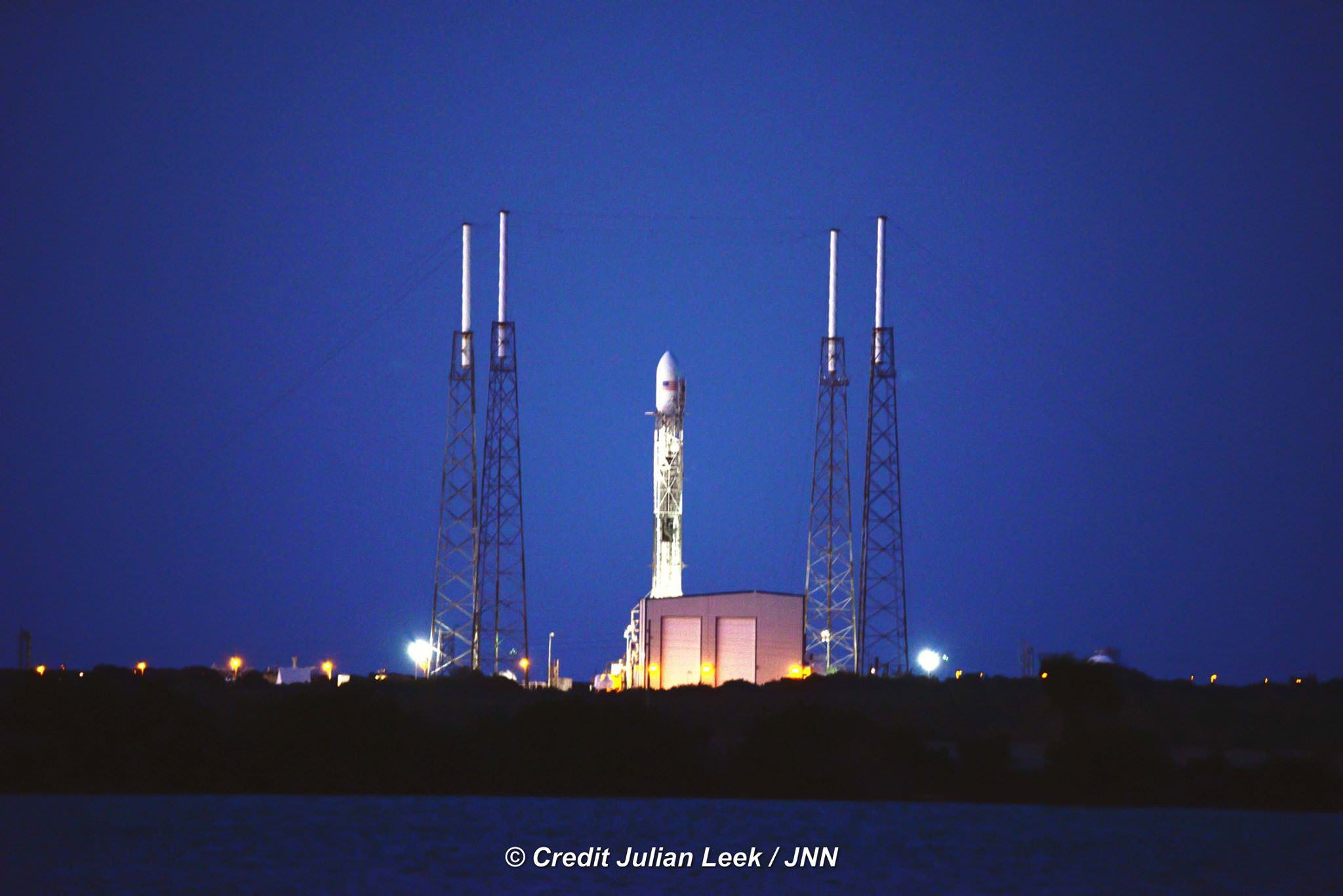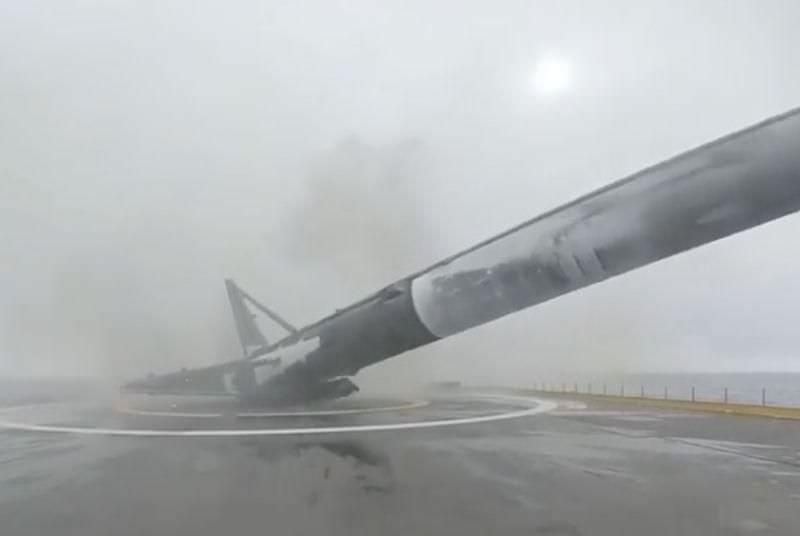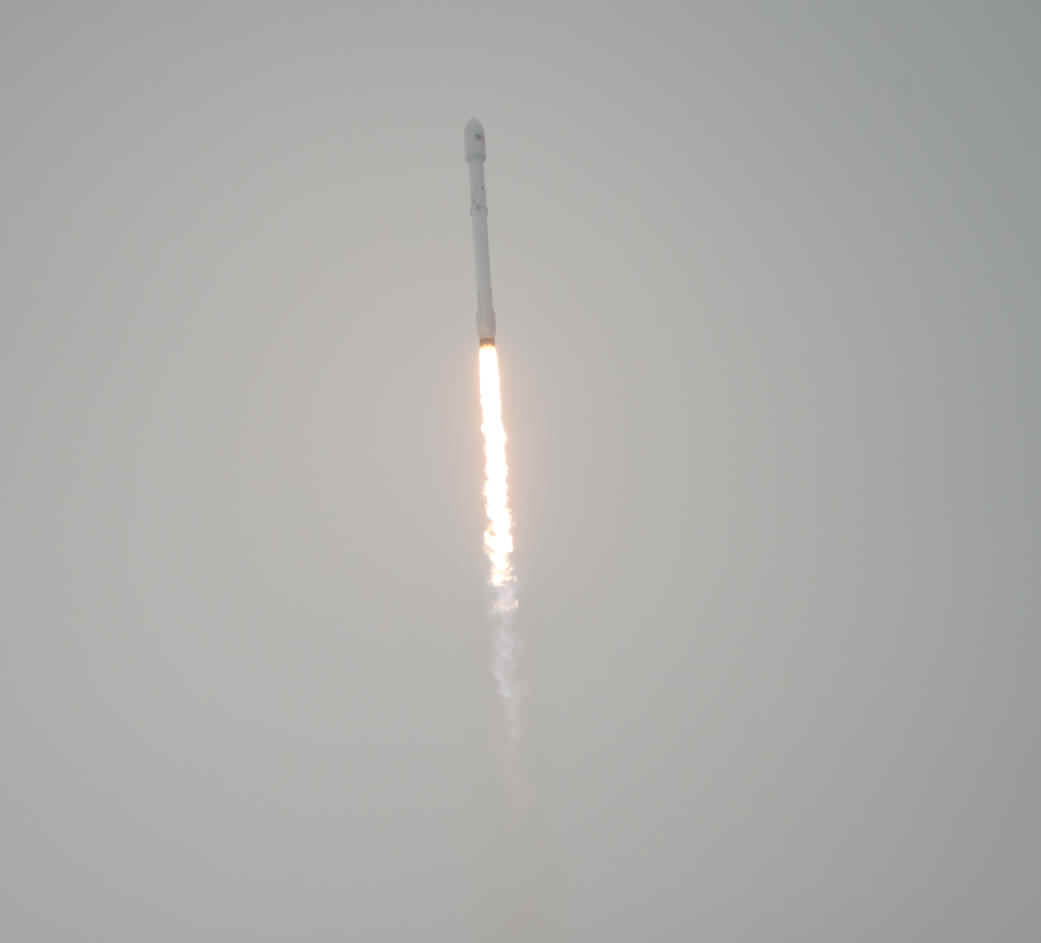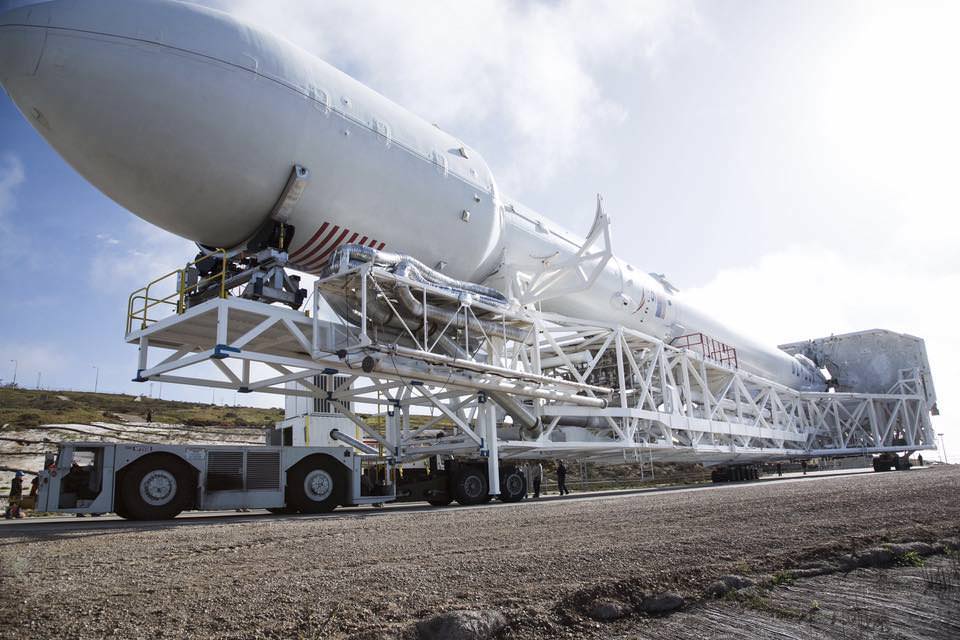
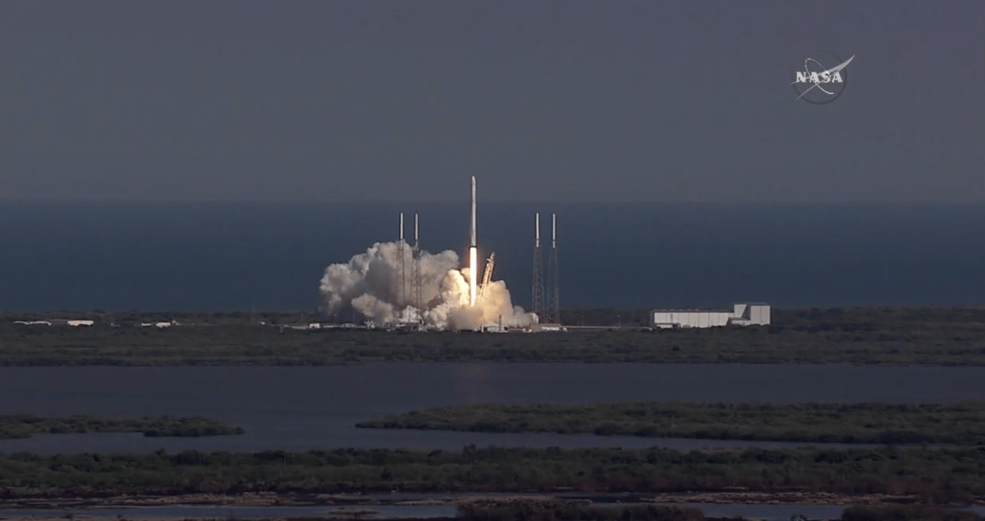
All around, today, April 8, was a great day for the future of space exploration. SpaceX successfully restarted their critical cargo flights for NASA to stock the International Space Station (ISS) with essential supplies and groundbreaking science experiments, while the innovative firm also successfully landed the first stage of their Falcon 9 rocket on a barge at sea.
The triumphant ‘Return to Flight’ launch of the upgraded SpaceX Falcon 9 with the Dragon CRS-8 cargo freighter was the primary goal of Friday’s launch and validated the hardware fixes put in place following the catastrophic failure of the previous Dragon CRS-7 cargo ship two minutes after liftoff on June 28, 2015 due to a faulty strut in the boosters second stage.
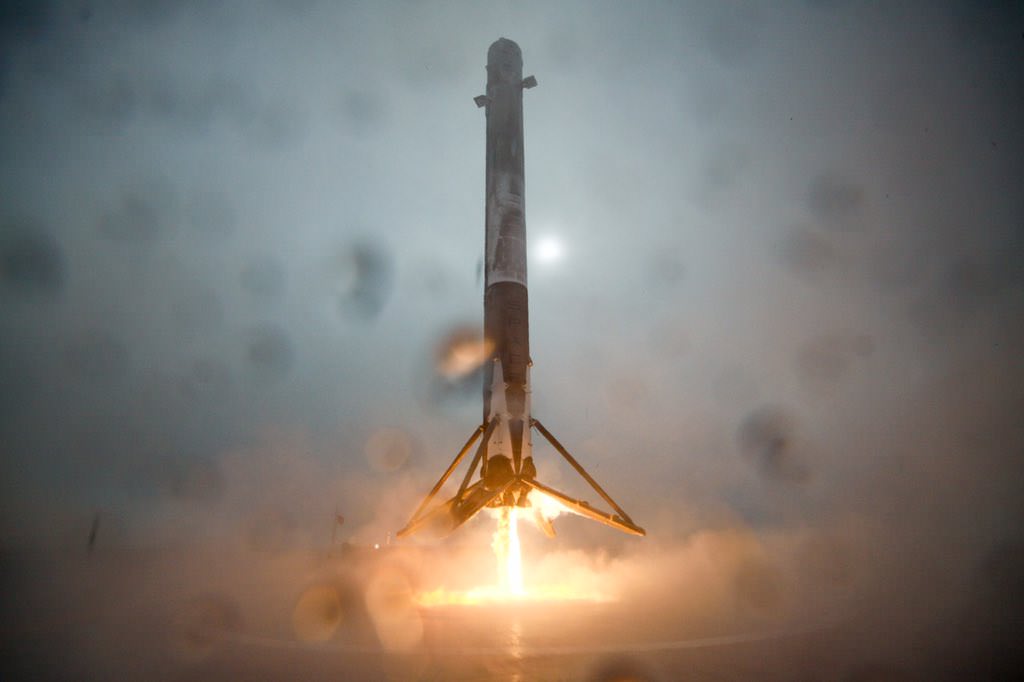
Landing the booster safely on a drone ship at sea was the secondary goal of the flight but is critical towards achieving the vision of rocket recovery and reusability at the heart of SpaceX Founder Elon Musk’s dream of slashing the cost of access to space and one day establishing a ‘City on Mars.”
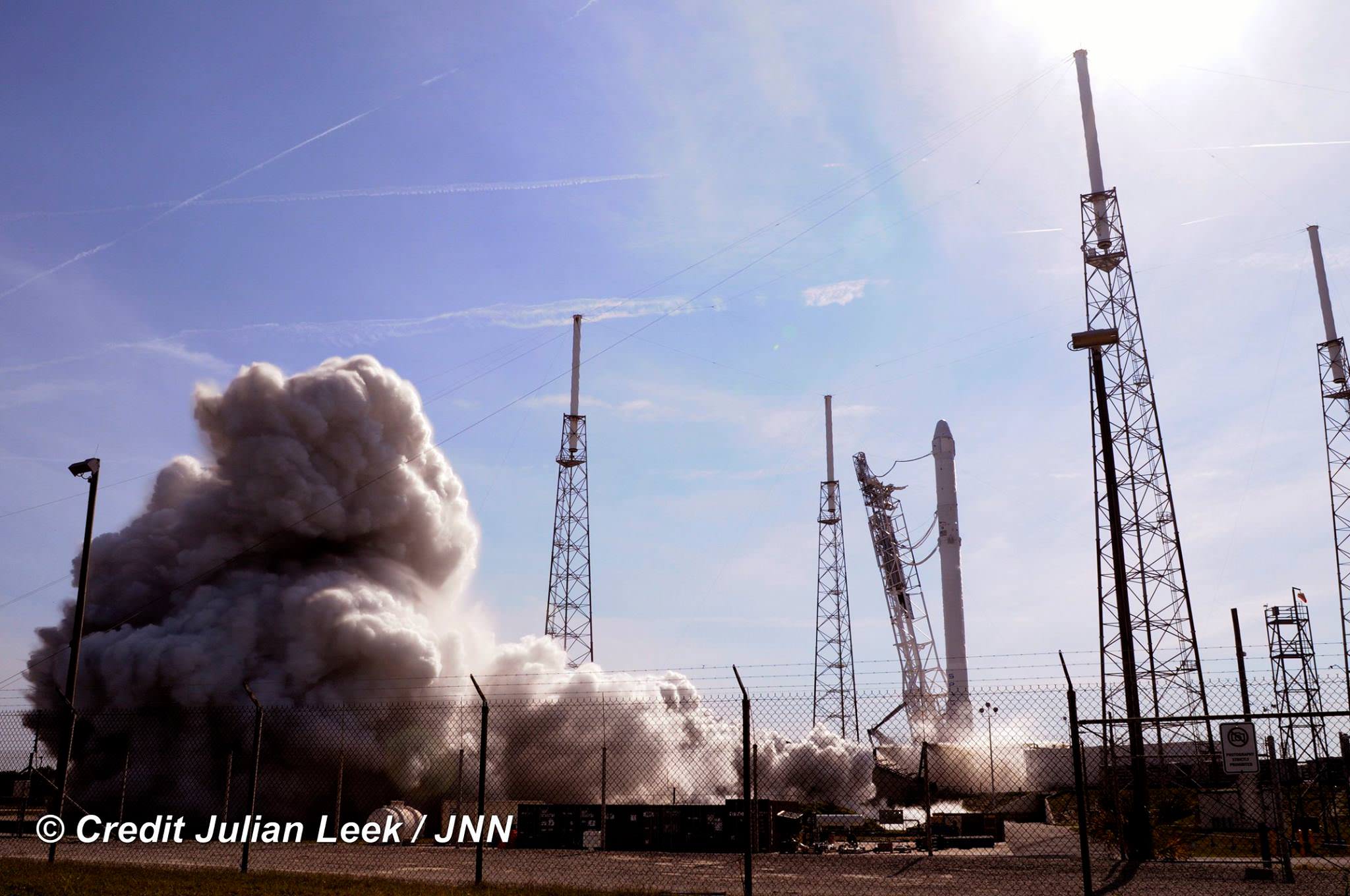
The weather was fantastic in the sunshine state as the two stage SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket boasting over 1.3 million pounds of thrust launched on time Friday at 4:43 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The Dragon spacecraft is delivering almost 7,000 pounds of cargo, including the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), to the orbital laboratory.
Friday’s launch marks the first for a Dragon since the catastrophic failure of the SpaceX Falcon 9 last June.
CRS-8 counts as the company’s eighth flight to deliver supplies, science experiments and technology demonstrations to the ISS for the crews of Expeditions 47 and 48 to support dozens of the approximately 250 science and research investigations in progress.
Packed aboard the Dragon’s unpressurized trunk section is the experimental Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) – an experimental expandable capsule that the crew will attach to the space station. The 3115 pound (1413 kg) BEAM will test the use of an expandable space habitat in microgravity. BEAM will expand to roughly 13-feet-long and 10.5 feet in diameter after it is installed.
Among the new experiments arriving to the station will be Veggie-3 to grow Chinese lettuce in microgravity as a followup to Zinnias recently grown, an investigation to study muscle atrophy and bone loss in space, using microgravity to seek insight into the interactions of particle flows at the nanoscale level and use protein crystal growth in microgravity to help in the design of new drugs to fight disease, as well as reflight of 25 student experiments from Student Spaceflight Experiments Program (SSEP) Odyssey II payload that were lost during the CRS-7 launch failure.
“The cargo will allow investigators to use microgravity conditions to test the viability of expandable space habitats, assess the impact of antibodies on muscle wasting, use protein crystal growth to aid the design of new disease-fighting drugs and investigate how microbes could affect the health of the crew and their equipment over a long duration mission,” said NASA Deputy Administrator Dava Newman.
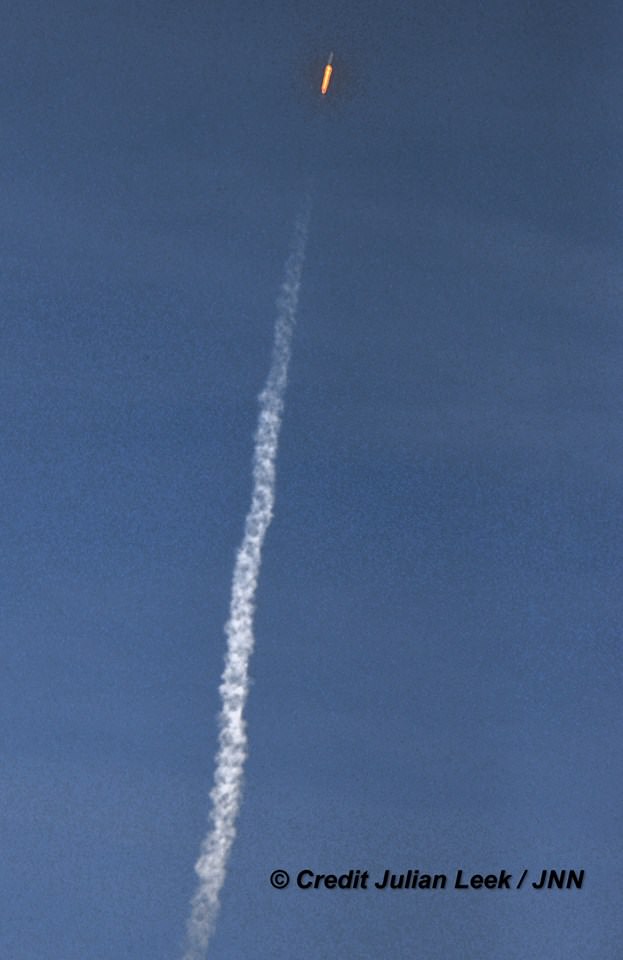

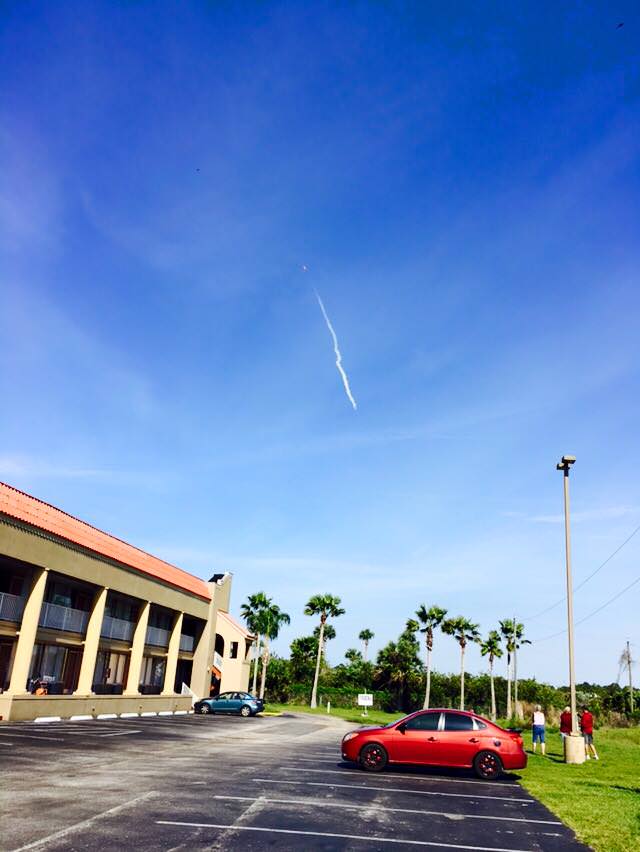
Dragon reached its preliminary orbit about 10 minutes after launch and deployed its solar arrays as targeted and as seen on the live webcast. It now begins a carefully choreographed series of thruster firings to reach the space station.
After a 2 day orbital chase Dragon is set to arrive at the orbiting outpost on Sunday, April 10.
NASA astronaut Jeff Williams and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Tim Peake will then reach out with the station’s Canadian-built robotic arm to grapple and capture the Dragon spacecraft.
Ground commands will be sent from Houston to the station’s arm to install Dragon on the Earth-facing bottom side of the Harmony module for its stay at the space station. Live coverage of the rendezvous and capture will begin at 5:30 a.m. on NASA TV, with installation set to begin at 9:30 a.m.
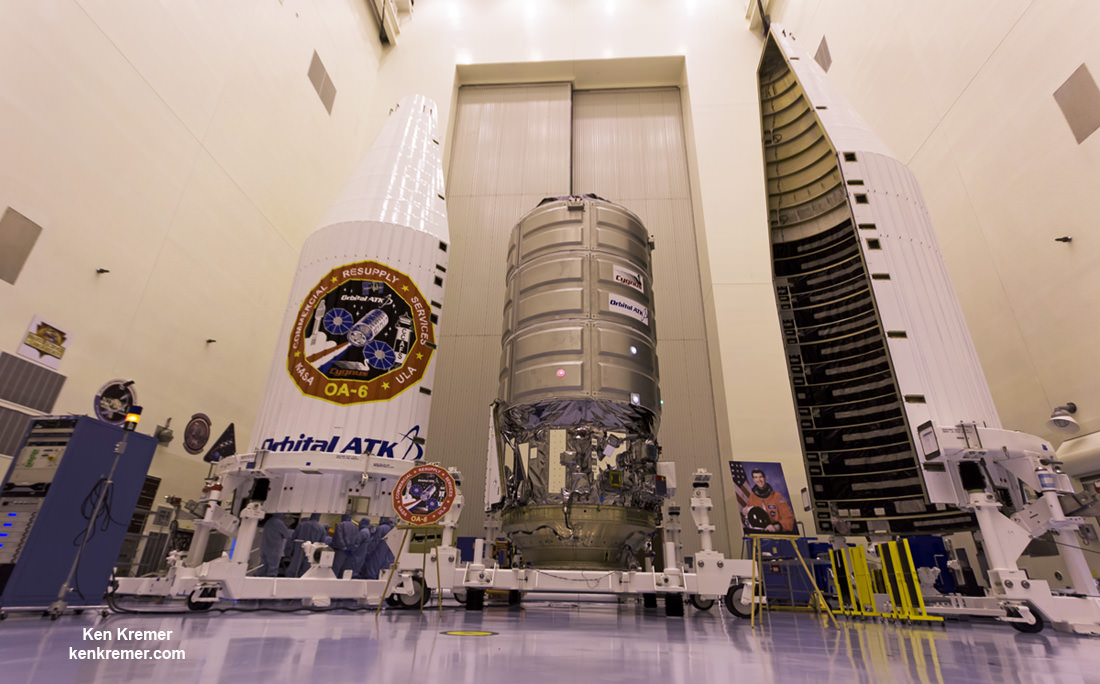
In a historic first, the launch of a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft sets the stage for the first time that two American cargo ships will be simultaneously attached to the ISS. The Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo freighter launched just launched on March 22 and arrived on March 26 at a neighboring docking port on the Unity module.
Dragon will remain at the station until it returns for Earth on May 11 for a parachute assisted splash down in the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Baja California. It will be packed with almost 3,500 pounds off cargo and numerous science samples, including those biological samples collected by 1 year ISS crew member Scott Kelly, for return to investigators, hardware and spacewalking tools, some additional broken hardware for repair and some items of trash for disposal.

SpaceX CRS-8 is the eighth of up to 20 missions to the ISS that SpaceX will fly for NASA under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, NASA Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, ISS, Orbital ATK, ULA, Boeing, Space Taxis, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 9/10: “NASA and the Road to Mars Human Spaceflight programs” and “Curiosity explores Mars” at NEAF (NorthEast Astronomy and Space Forum), 9 AM to 5 PM, Suffern, NY, Rockland Community College and Rockland Astronomy Club – http://rocklandastronomy.com/neaf.html
Apr 12: Hosting Dr. Jim Green, NASA, Director Planetary Science, for a Planetary sciences talk about “Ceres, Pluto and Planet X” at Princeton University; 7:30 PM, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton, Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ – http://www.princetonastronomy.org/
Apr 17: “NASA and the Road to Mars Human Spaceflight programs”- 1:30 PM at Washington Crossing State Park, Nature Center, Titusville, NJ – http://www.state.nj.us/dep/parksandforests/parks/washcros.html































