[/caption]
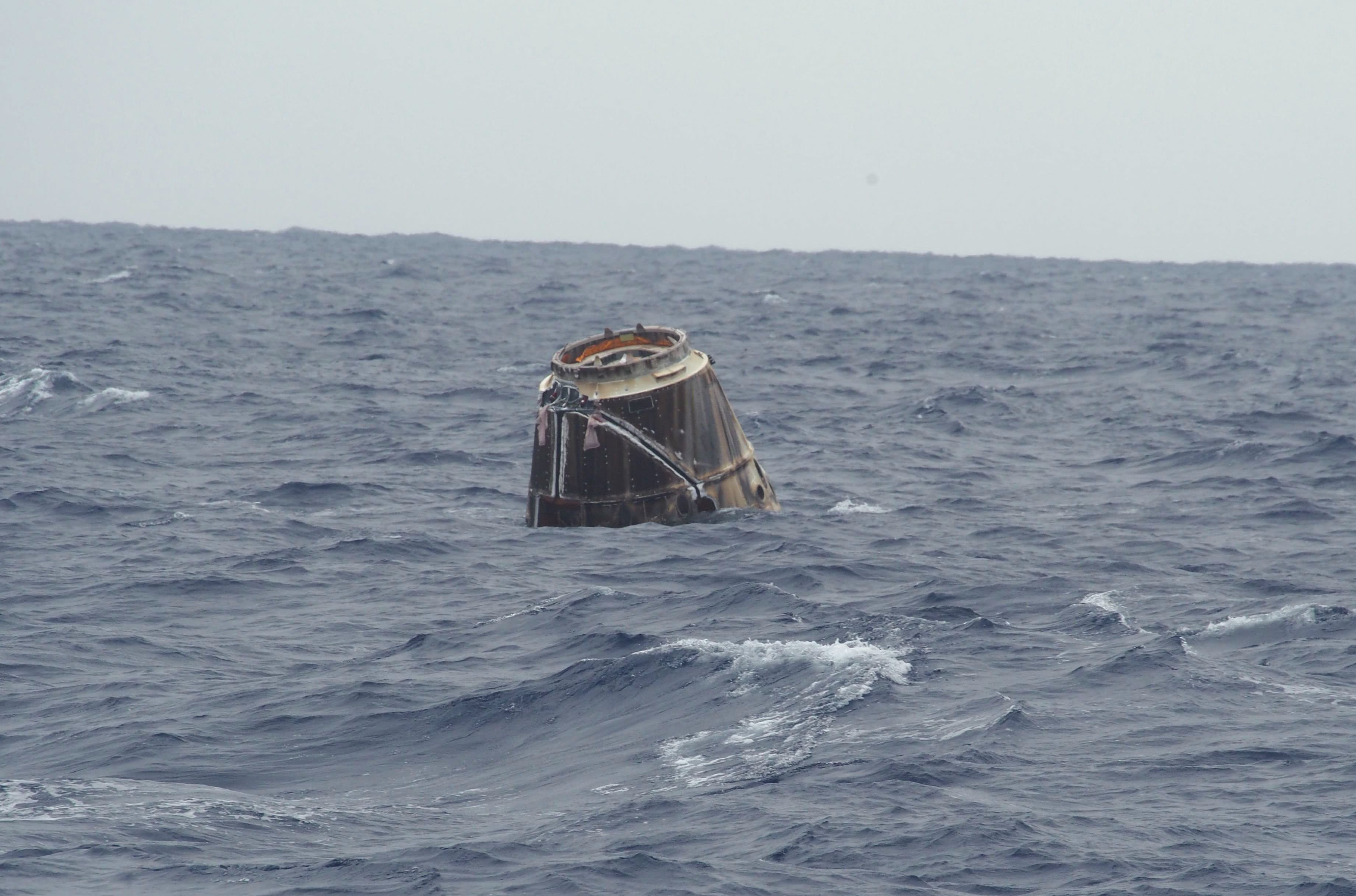
Concluding a perfectly executed and history making test flight, the first private spacecraft ever to visit and dock at the International Space Station (ISS) performed a picture perfect splashdown at 11:42 a.m. EDT (1542 GMT) today, May 31, in the Pacific Ocean, off the west coast of Baja, California, some 560 miles southwest of Los Angeles to cap the opening to a historic new Era in Space Exploration.
Dragon is the linchpin in NASA’s bold Commercial Crew and Cargo program aimed at significantly driving down the cost of transporting cargo and crews to low Earth orbit by using private commercial companies to foster competition and innovation in the free market setting of the new, post-shuttle Era of Commercial Space Transportation.
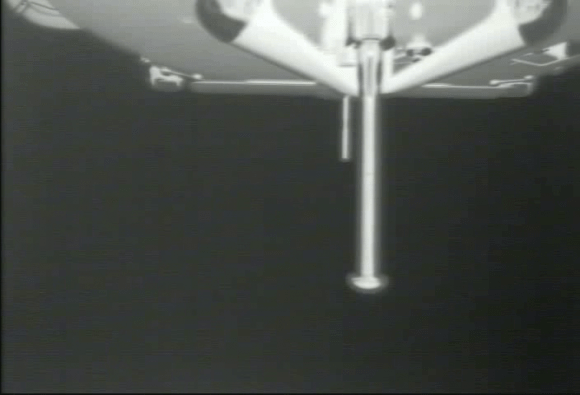
NASA aircraft were able to transmit live video of the last few minutes of the Dragon’s breathtaking descent, unfurling of the trio of parachutes and ocean splashdown – pretty much on target at 27 degrees latitude and 127 degrees west longitude.
The official mission elapsed time on landing was 9 days, 7 hours and 58 minutes.
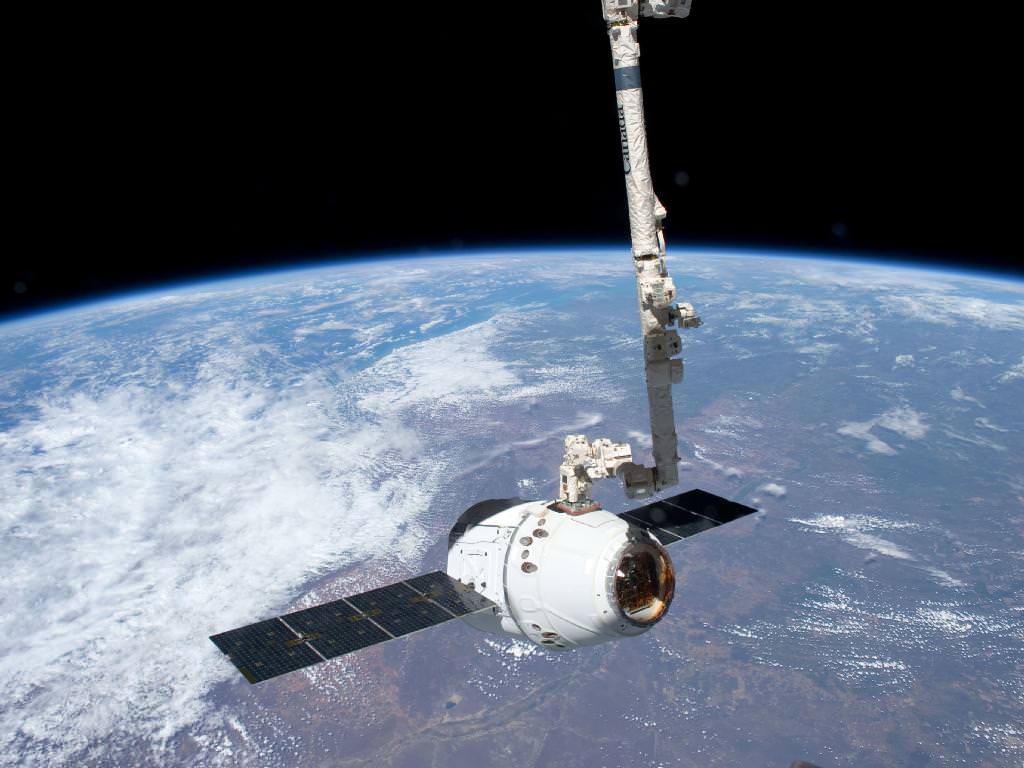
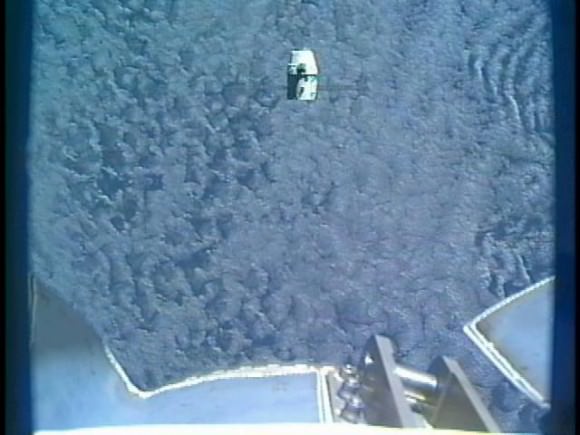
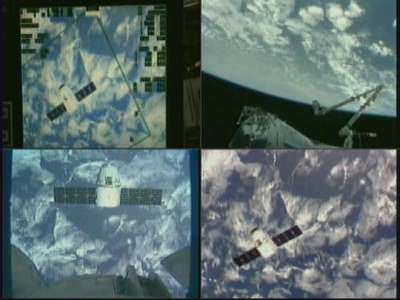
Splashdown of the Dragon cargo craft took place barely 6 hours after departing the orbiting lab complex following detachment from the station using the station robotic arm. The ISS astronauts released the craft from the grip of the station’s robot arm at 5:49 a.m. EST (949 GMT) this morning, May 31.
The two spacecraft were soaring some 250 miles (400 km) high above the Indian Ocean east of Africa at the moment of release and departure. Altogether, Dragon spent 5 days, 16 hours and 5 minutes mated to the station.
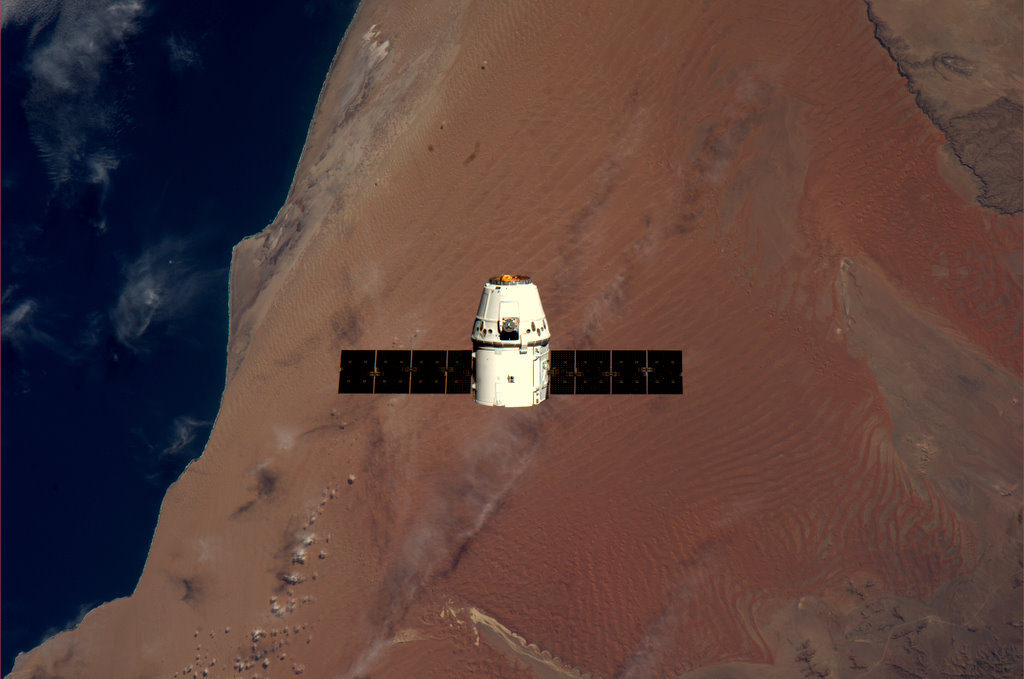
The gumdrop shaped Dragon capsule is 4.4 meters (14.4 ft) tall, and 3.66 m (12 ft) in diameter and has an internal pressurized volume of about 350 cubic feet .
The Dragon cargo resupply capsule was built by SpaceX and is being retrieved from the ocean by a flotilla of three recovery ships. The ships reached Dragon, detached the chutes and are in the process of recovery. It will take about two days to deliver the craft to the port of Los Angeles where the most critical cargo items will be removed for quick shipment to NASA. The capsule will then be shipped to SpaceX’s McGregor,Texas facility for post-flight evaluation.
Dragon is the world’s first commercial spacecraft whose purpose is to carry supplies to and from the ISS and partially replace the cargo capabilities previously performed by NASA’s now retired fleet of space shuttle orbiters. Dragon was designed, developed and built by Hawthorne, Calif., based SpaceX Corporation, founded in 2002 by CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk.
“This has been a fantastic day,” said Musk at a post splashdown briefing for reporters. “I want to thank NASA and the whole SpaceX team for an amazing job.”
“I’m really proud of everyone. This really couldn’t have gone better. We’re looking forward to doing lots more missions in the future and continuing to upgrade the technology and push the frontier of space transportation.”
“In baseball terminology this would be a grand slam. I am overwhelmed with joy.”
The de-orbit burn to drop Dragon out of orbit took place precisely on time at 10:51 a.m. EDT for a change in velocity of 100 m/sec about 246 miles above the Indian Ocean directly to the south of India as the craft was some 200 miles in front of the ISS.

The Draco thruster firing lasted 9 minutes and 50 seconds and sent Dragon plummeting through the Earth’s atmosphere where it had to survive extreme temperatures exceeding 3000 degrees F (1600 degrees C) before landing.
The Dragon capsule is the first US vehicle of any kind to arrive at the ISS since the July 2011 forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle Program resulted in the total loss of all US capability to send cargo and humans crews to the massive orbiting outpost.
SpaceX signed a contract with NASA in 2006 to conduct twelve Falcon 9/Dragon resupply missions to carry about 44,000 pounds of cargo to the ISS at a cost of some $1.6 Billion over the next few years.
This was the third test flight of the Falcon 9 rocket and the first test flight of the Dragon in this vastly upgraded configuration with solar panels. A future variant of Dragon will eventually blast US astronauts to space and restore US crew capability – perhaps by 2017 thanks to repeated cuts to NASA’s budget.
Only four entities have ever sent a spacecraft to dock at the ISS – the United States, Russia, Japan and the European Union. SpaceX is the first commercial entity to accomplish the same feat.
The precedent setting Dragon mission has opened a new era in spaceflight by giving birth to the first fully commercial mission to the orbiting space station complex and unlocking vast new possibilities for its utilization in science and exploration.
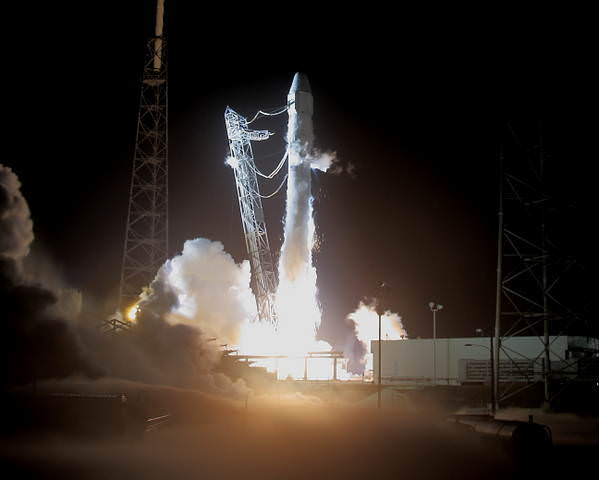
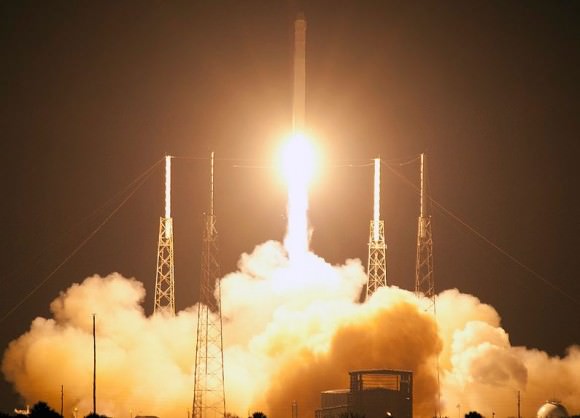
On May 22, Dragon thundered to orbit atop a SpaceX built Falcon 9 rocket during a pre-dawn liftoff at 3:44 a.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
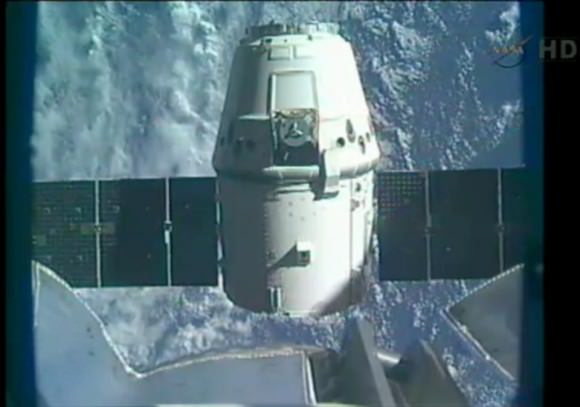
After a three day chase, Dragon arrived at the ISS on May 25 and was deftly berthed at an open Earth-facing port on the Harmony Node 2 module after being dramatically captured by the astronaut crew using the station’s robotic arm in a landmark event in space history as the Dragon and the ISS were passing about 251 miles above Earth. Capture was confirmed at a mission elapsed time of 3 days, 6 hours and 11 minutes and 23 seconds.
Working in tandem, NASA astronaut Don Pettit and ESA astronaut Andre Kuipers snared the Dragon craft as it was drifting in free space about 10 m (32 ft) away with the 18 m (58 ft) long Canadian robot arm at 9:56 a.m. EDT and parked the first privately built capsule to an open port at 12:02 p.m. EDT on May 25.
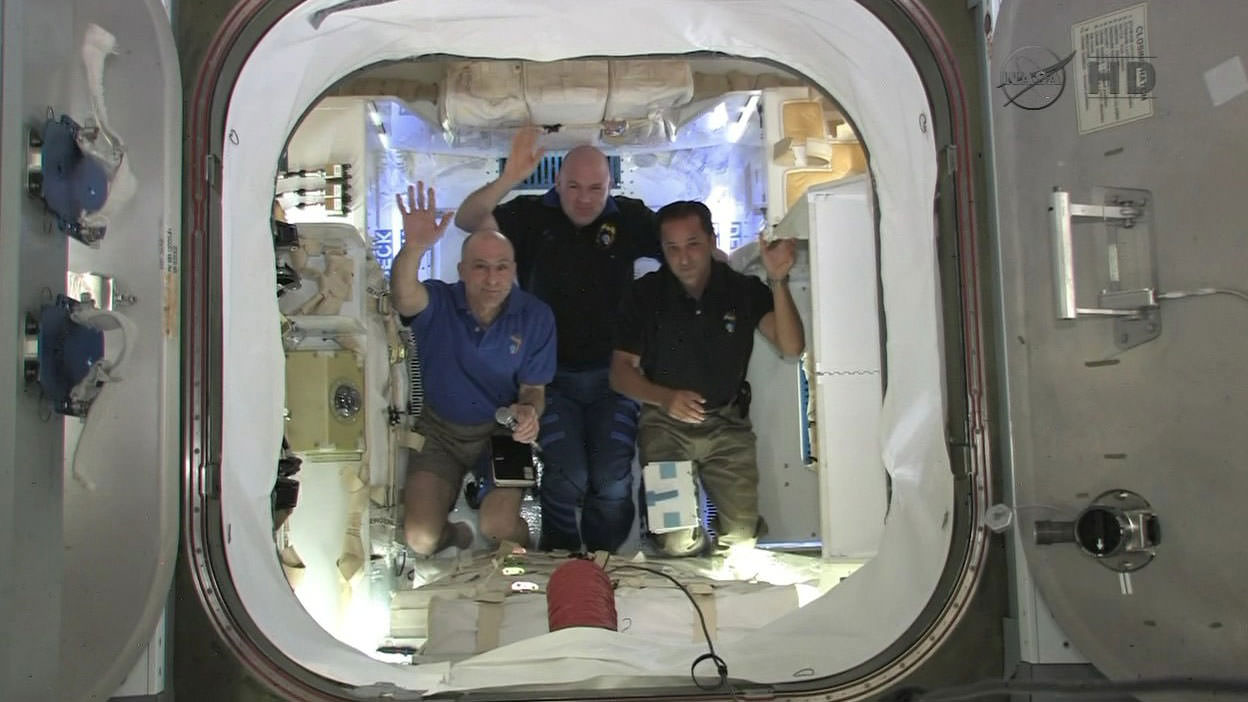
The astronauts opened the hatch and ‘Entered the Dragon’ for the first time a day later on May 26 and then proceeded to unload the stowed cargo and refill it for the return trip to Earth.
On this first NASA sponsored Dragon test flight to rendezvous and dock at the ISS, the cargo craft was packed with 460 kilograms (1014 lbs) of non-critical cargo including 306 kg (674 lbs) of food and crew provisions; 21 kg (46 lbs) of science experiment; 123 kg (271 lbs) prepositioned cargo bags to be used for future flights; and 10 kg (22 lbs) of assorted computer supplies and a laptop.

Unlike the other Russian, European and Japanese cargo freighters that service the ISS and then disintegrate on reentry, the SpaceX Dragon is uniquely equipped with a state of the art PICA-X heat shield that allows it to plunge safely through the Earth’s atmosphere and survive the fiery temperatures exceeding more than 3000 degrees F (1600 degrees C).

The down mass capability restores another critical capability lost with the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle orbiters in July 2011. The astronauts filled Dragon with about 620 kilograms (1367 pounds) of science experiments, trash and non-critical items on this historic test flight.
The first operational Dragon resupply mission to the ISS could blast off as early as September, said Alan Lindenmoyer, manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Program.
“We’ll await the final post flight report to make the determination that this was an extremely successful mission. But they should be well on their way to starting [delivery] services,” said Lindenmoyer at the briefing. “Of course, officially we will look at the post flight data and make an official determination. But I would say at this point it looks like 100 percent success.”