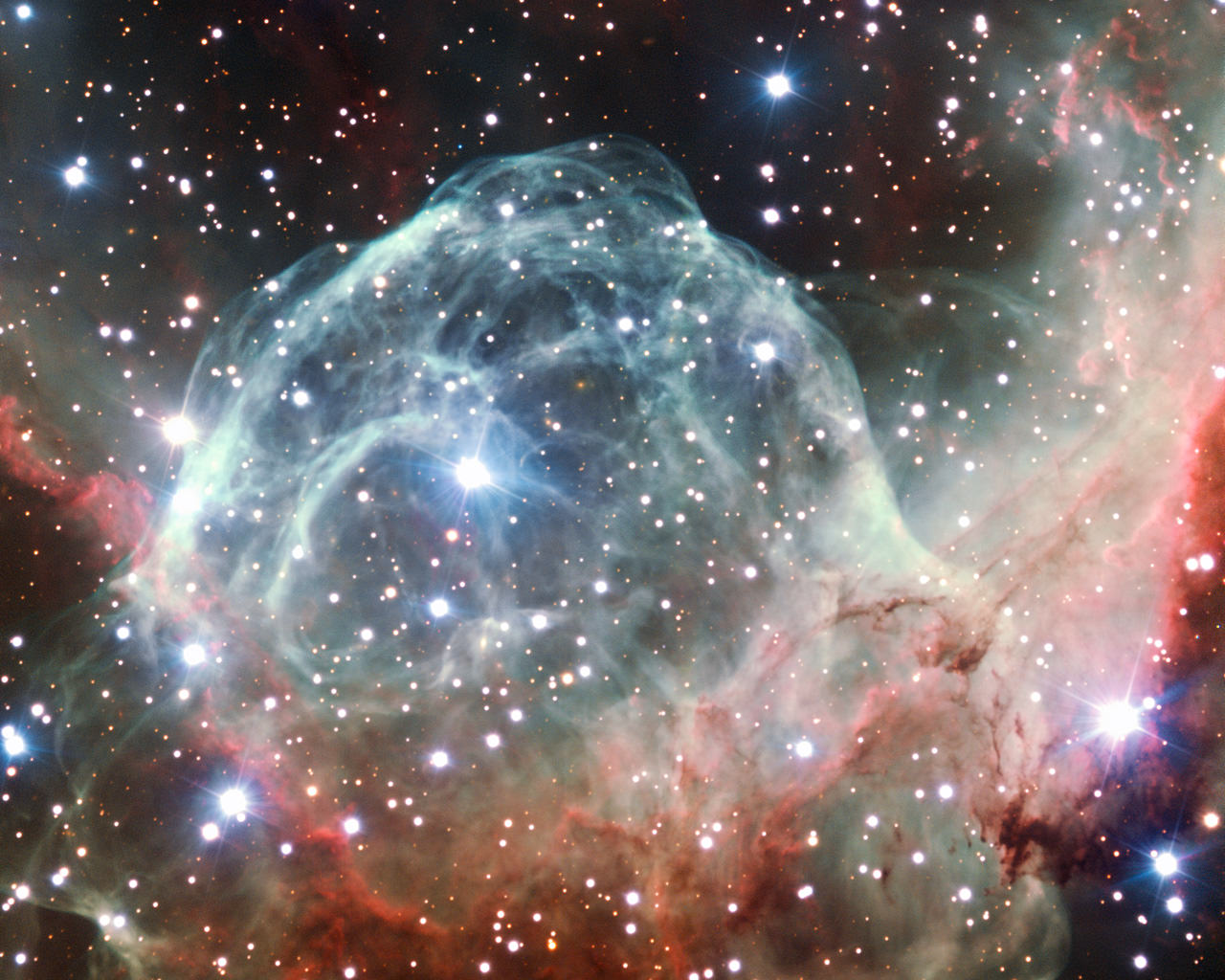
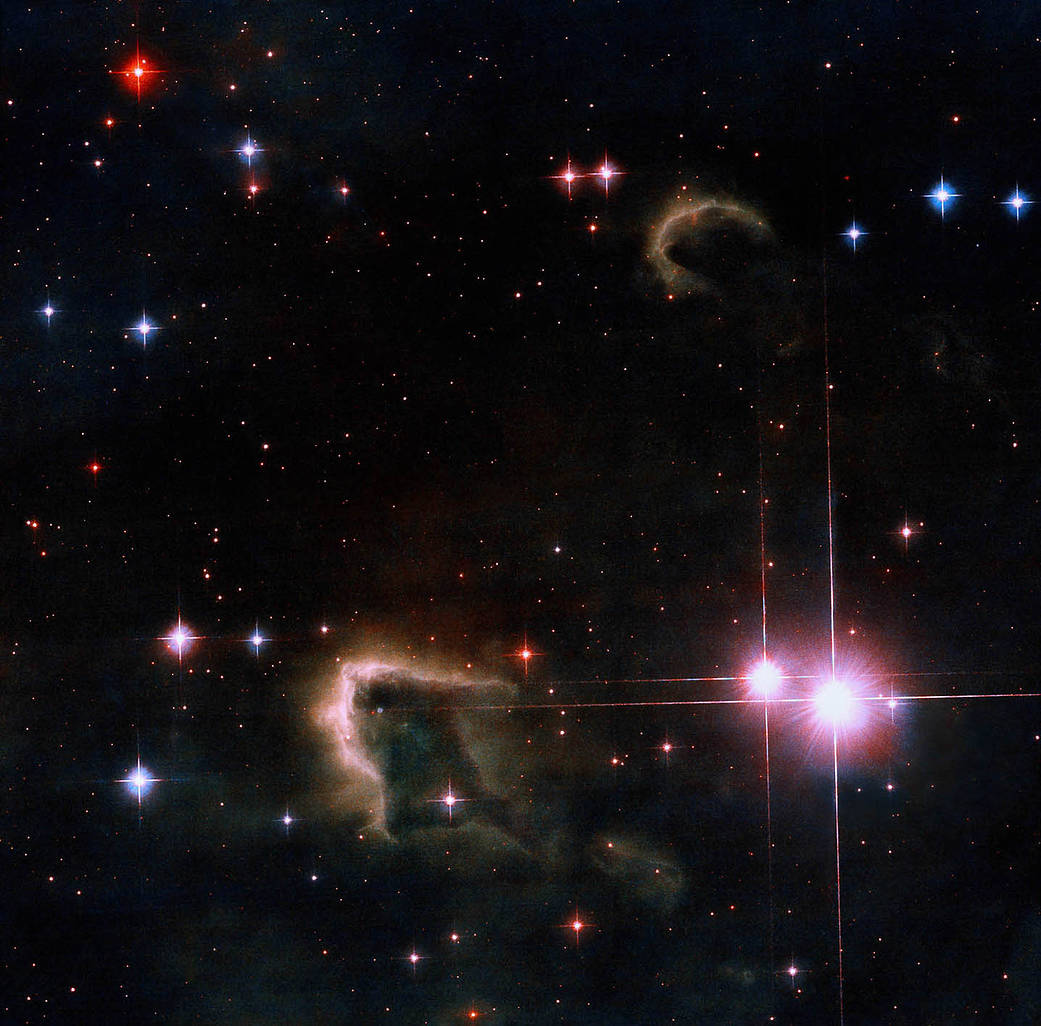
Star formation is a complex process. But in simple terms, a star forms due to clumps and instabilities in a cloud of molecular hydrogen called a Giant Molecular Cloud (GMC). As more and more gas accumulates and collapses inward, the pressure becomes immense, the gas eventually heats up to millions of degrees, and fusion begins.
But what happens to the gas that remains as the young star forms? Some of it can form a type of dark halo called a frEGG—a free-floating Evaporating Gaseous Globule. And, proving that the Universe is indeed strange, the frEGG itself can contain another stellar embryo. The frEGG can be quite opaque, making it difficult to observe the star’s formation process in all its complexity.
Continue reading “New Hubble Image Shows Dark Cocoons Where New Stars are Forming”