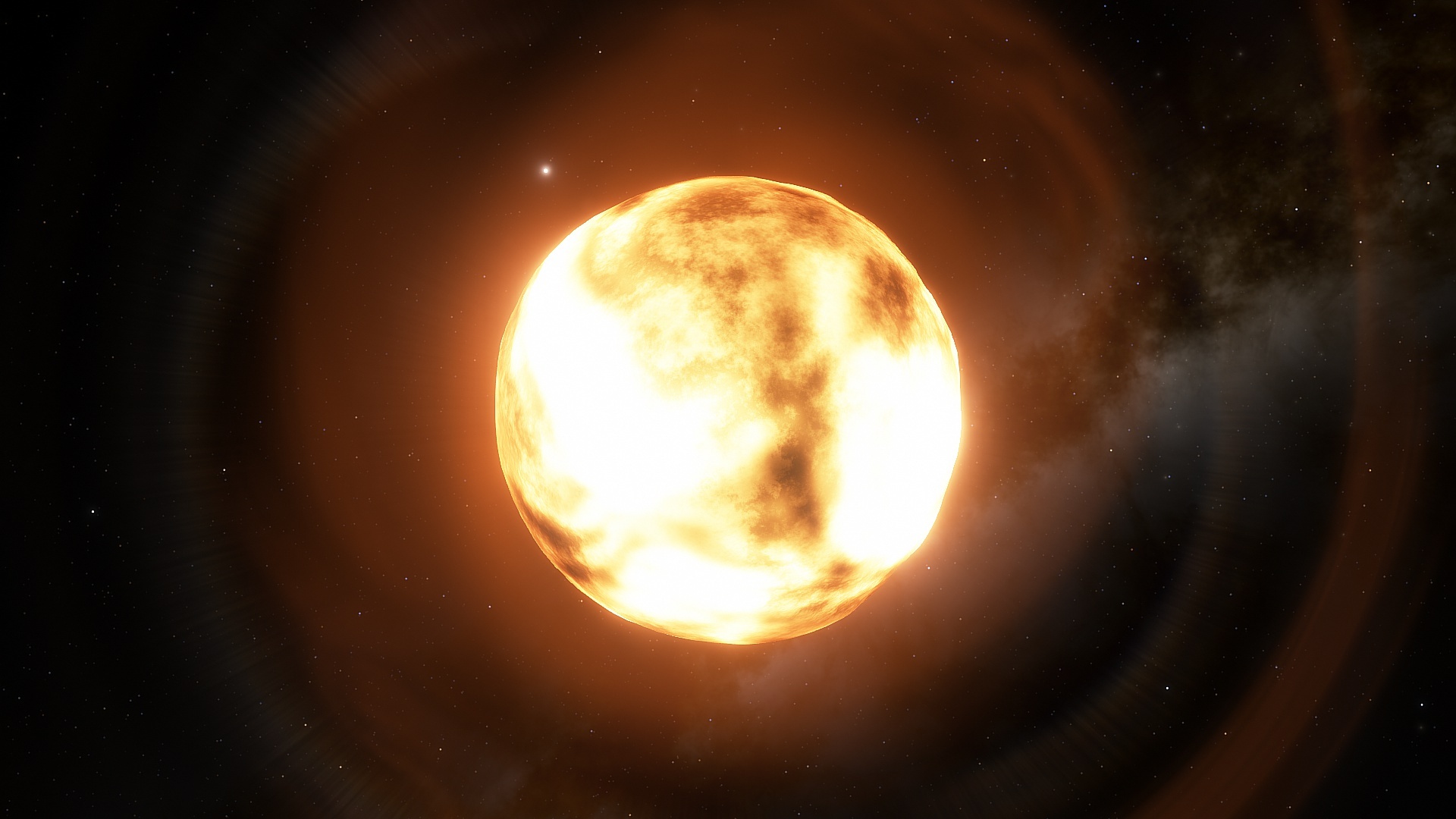
The disappearance of a star can take many forms. It could go supernova. It could turn into a black hole. Or it could just fade away quietly. Sometimes, the last of these is actually the most interesting to observe. That is the case for one of the largest stars ever found – VY Canis Majoris, a red supergiant approximately 3840 light years away in the Canis Major constellation.
Continue reading “VY Canis Majoris is “Like Betelgeuse on Steroids””A New Study Says That Betelgeuse Won’t Be Exploding Any Time Soon
I have stood under Orion The Hunter on clear evenings willing its star Betelgeuse to explode. “C’mon, blow up!” In late 2019, Betelgeuse experienced an unprecedented dimming event dropping 1.6 magnitude to 1/3 its max brightness. Astronomers wondered – was this dimming precursor to supernova? How cosmically wonderful it would be to witness the moment Betelgeuse explodes. The star ripping apart in a blaze of light scattering the seeds of planets, moons, and possibly life throughout the Universe. Creative cataclysm.
Only about ten supernova have been seen with the naked eye in all recorded history. Now we can revisit ancient astronomical records with telescopes to discover supernova remnants like the brilliant SN 1006 (witnessed in 1006AD) whose explosion created one of the brightest objects ever seen in the sky. Unfortunately, latest research suggests we all might be waiting another 100,000 years for Betelgeuse to pop. However, studying this recent dimming event gleaned new information about Betelgeuse which may help us better understand stars in a pre-supernova state.
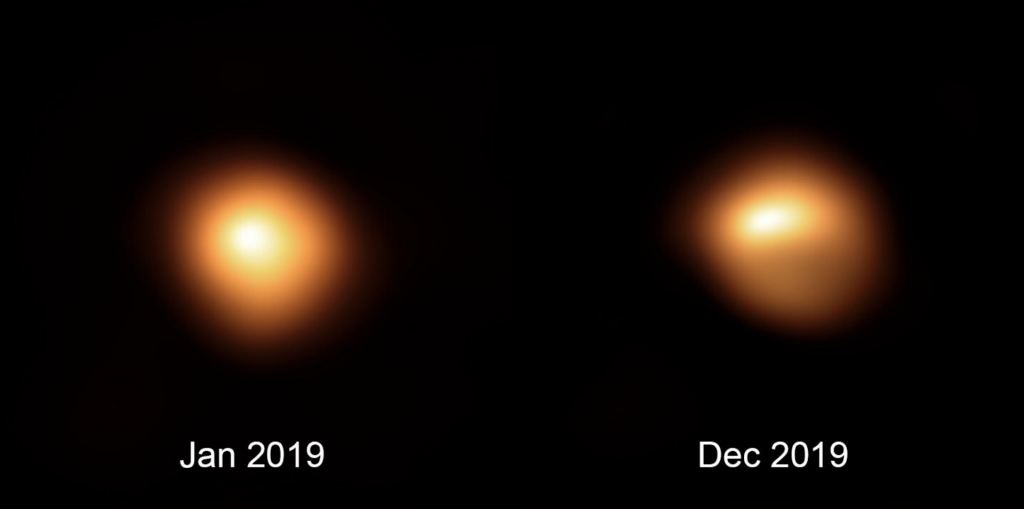

ESO / M. Montargès et al.
This is a Simulation of the Interstellar Medium Flowing Like Smoke Throughout the Milky Way
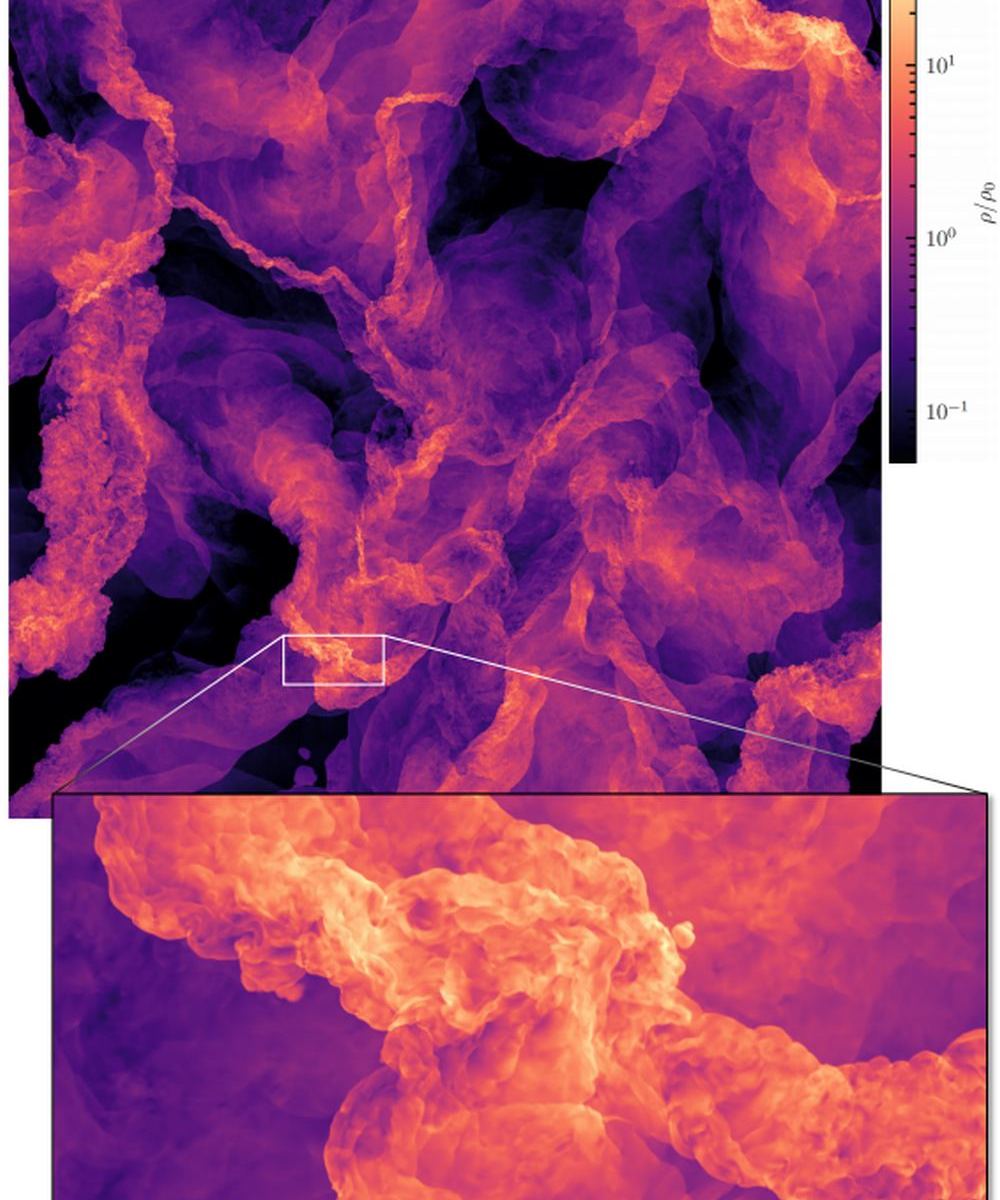
How do stars form?
We know they form from massive structures called molecular clouds, which themselves form from the Interstellar Medium (ISM). But how and why do certain types of stars form? Why, in some situations, does a star like our Sun form, versus a red dwarf or a blue giant?
That’s one of the central questions in astronomy. It’s also a very complex one.
Continue reading “This is a Simulation of the Interstellar Medium Flowing Like Smoke Throughout the Milky Way”Astronomers Discover Hundreds of High-Velocity Stars, Many on Their Way Out of the Milky Way
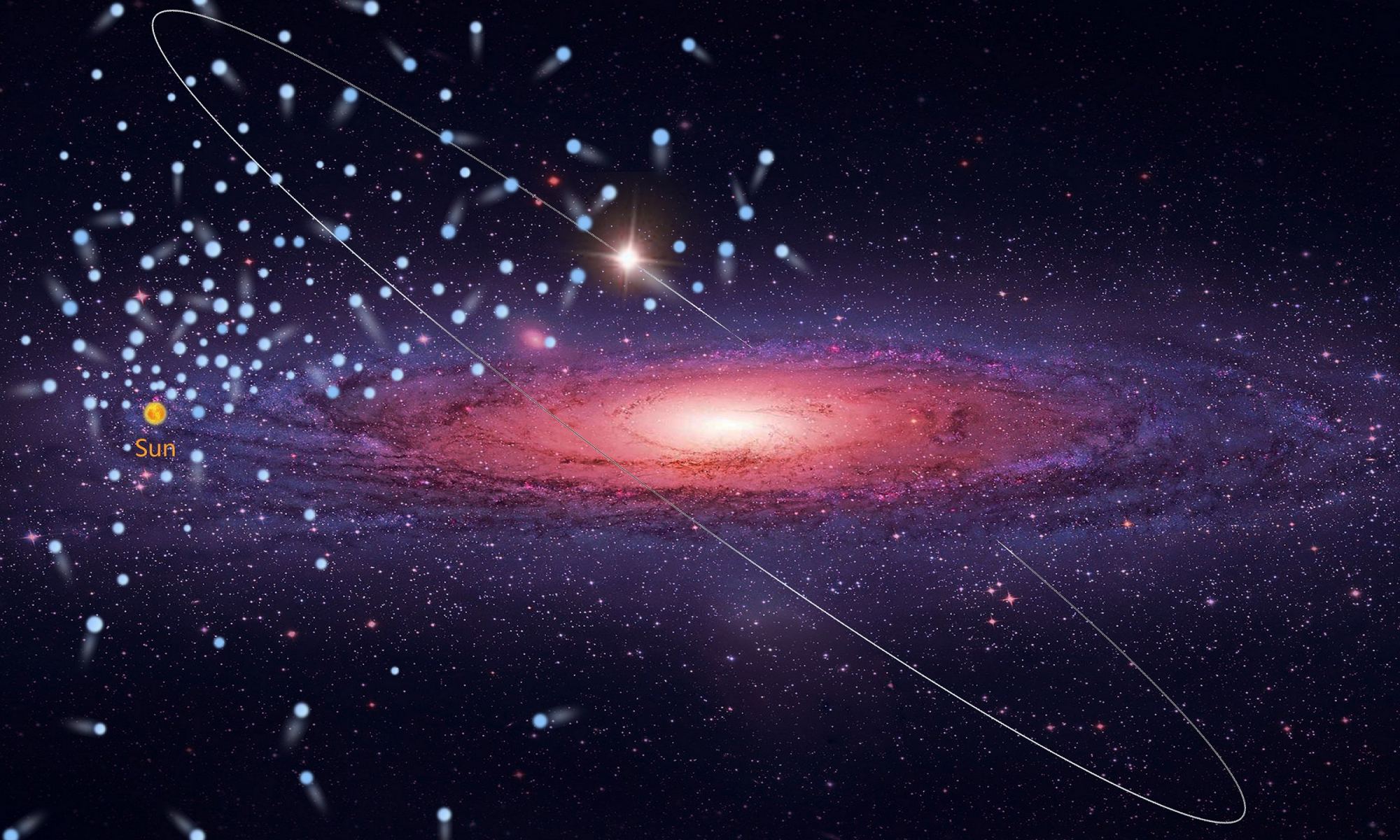

Within our galaxy, there are thousands of stars that orbit the center of the Milky Way at high velocities. On occasion, some of them pick up so much speed that they break free of our galaxy and become intergalactic objects. Because of the extreme dynamical and astrophysical processes involved, astronomers are most interested in studying these stars – especially those that are able to achieve escape velocity and leave our galaxy.
However, an international team of astronomers led from the National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) recently announced the discovery of 591 high-velocity stars. Based on data provided by the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) and the ESA’s Gaia Observatory, they indicated that 43 of these stars are fast enough to escape the Milky Way someday.
Continue reading “Astronomers Discover Hundreds of High-Velocity Stars, Many on Their Way Out of the Milky Way”Massive stars get kicked out of clusters
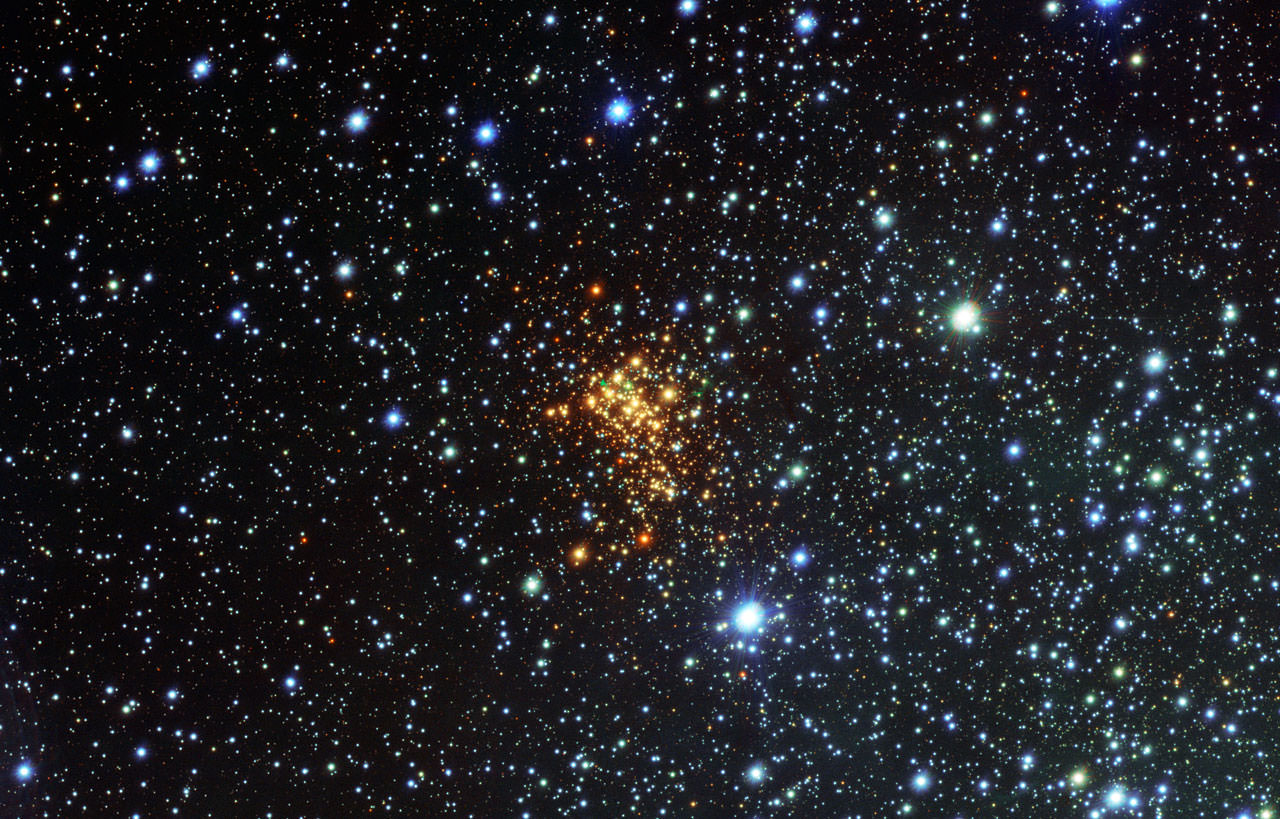

The largest stars in the universe tend to be loners, and new research points to the reason why. Although massive stars are born in clusters of many smaller brethren, they quickly get kicked out, forced to spend their lives alone.
Continue reading “Massive stars get kicked out of clusters”We’re Made of Starstuff. Especially From Extremely Massive Stars

A new study shows how massive young stars create the kind of organic molecules that are necessary for life.
A team of researchers used an airborne observatory to examine the inner regions around two massive young stars. Along with water, they found things like ammonia and methane. These molecules are swirling around in a disk of material that surrounds the young stars.
That material is the same stuff that planets form from, and the study presents some new insights into how the stuff of life becomes incorporated into planets.
Continue reading “We’re Made of Starstuff. Especially From Extremely Massive Stars”Just How Bad are Superflares to a Planet’s Habitability?
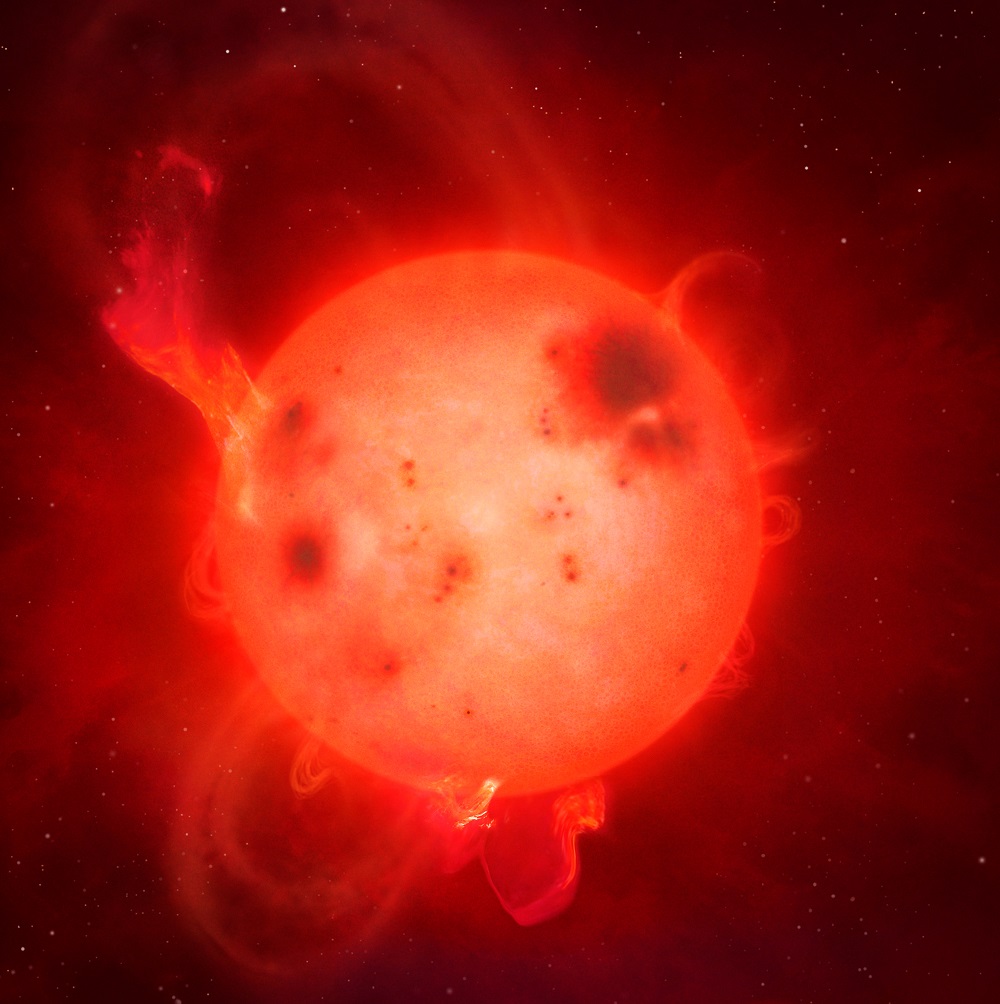

Star’s can be full of surprises; some of them nasty. While our own Sun appears pretty placid, science has shown us that’s not the case. Coronal mass ejections and solar flares are the Sun’s angry side.
And the Sun has only a mild case of the flares, compared to some other stars.
Continue reading “Just How Bad are Superflares to a Planet’s Habitability?”Planets Don’t Wait for Their Star to Form First
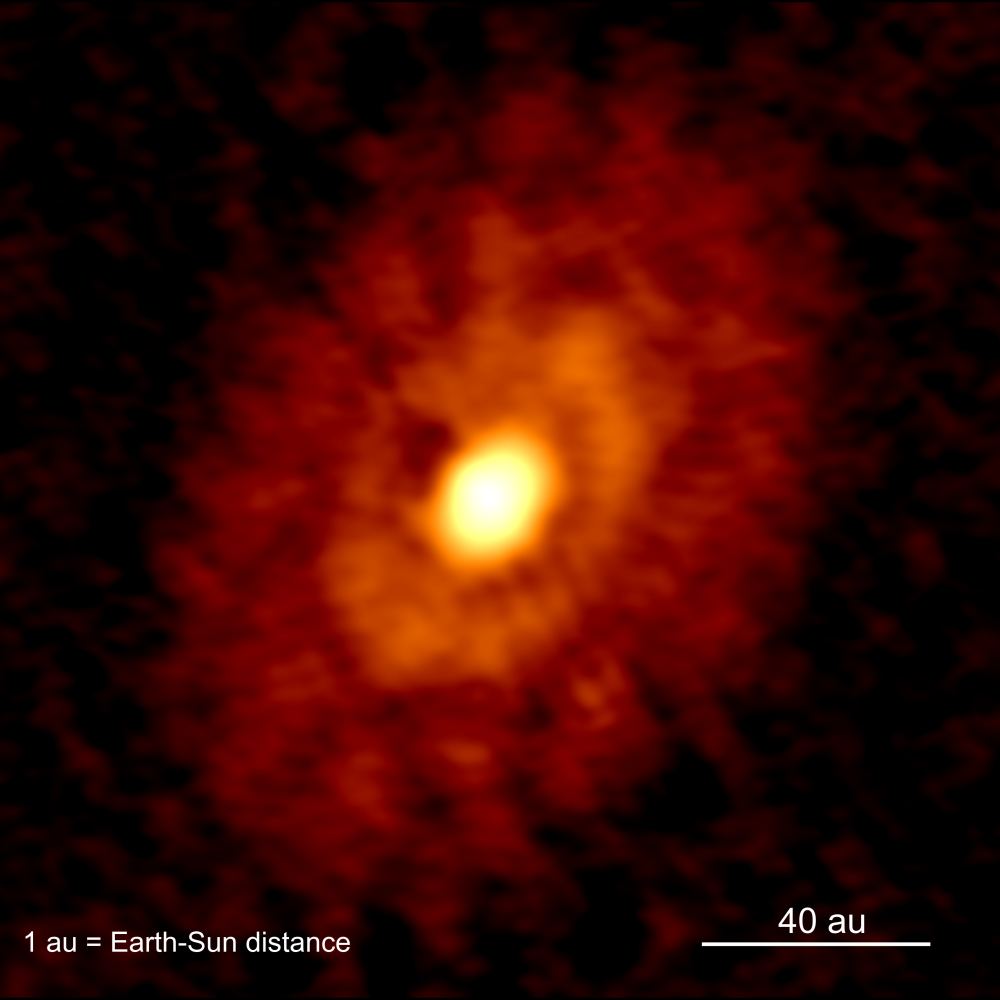

It looks like we may have to update our theories on how stars and planets form in new solar systems. A team of astronomers has discovered young planets forming in a solar system that’s only about 500,000 years old. Prior to this discovery, astronomers thought that stars are well into their adult life of fusion before planets formed from left over material in the circumstellar disk.
Now, according to a new study, it looks like planets and stars can form and grow up together.
Continue reading “Planets Don’t Wait for Their Star to Form First”What Decides the Shape of Planetary Nebulae? Whatever’s Orbiting a Star When it Dies
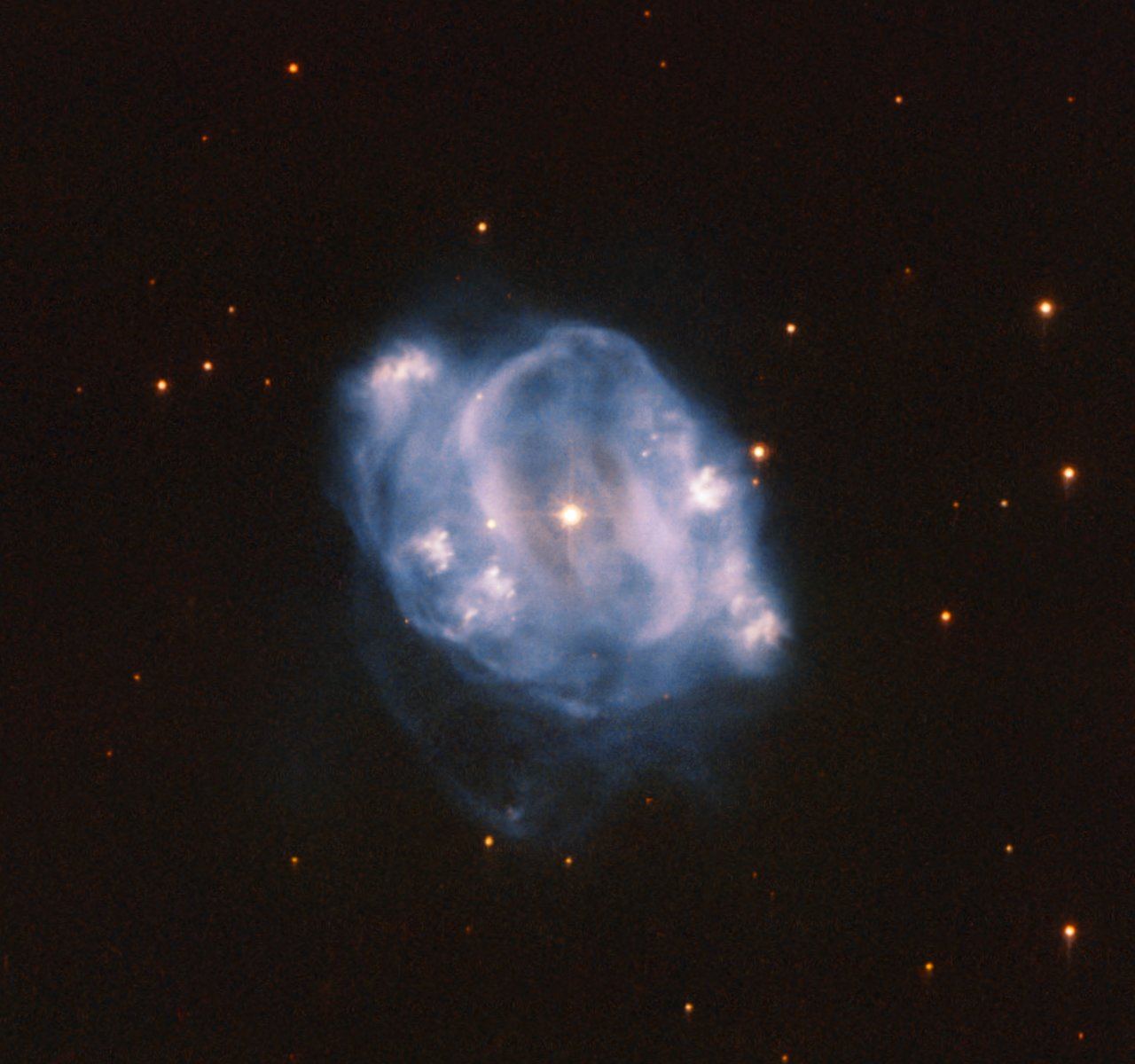
Planetary nebulae are some of the most beautiful objects in the galaxy, spanning a variety of shapes and sizes. They’re created in the death throes of stars like the sun, and new research sheds light into how they get their distinctive and unique shapes. The answer: anything unlucky enough to orbit that dying star.
Continue reading “What Decides the Shape of Planetary Nebulae? Whatever’s Orbiting a Star When it Dies”If dark matter is a particle, it should get inside red giant stars and change the way they behave

Dark matter makes up the vast majority of matter in the universe, but we can’t see it. At least, not directly. Whatever the dark matter is, it must interact with everything else in the universe through gravity, and astronomers have found that if too much dark matter collects inside of red giant stars, it can potentially cut their lifetimes in half.
Continue reading “If dark matter is a particle, it should get inside red giant stars and change the way they behave”

