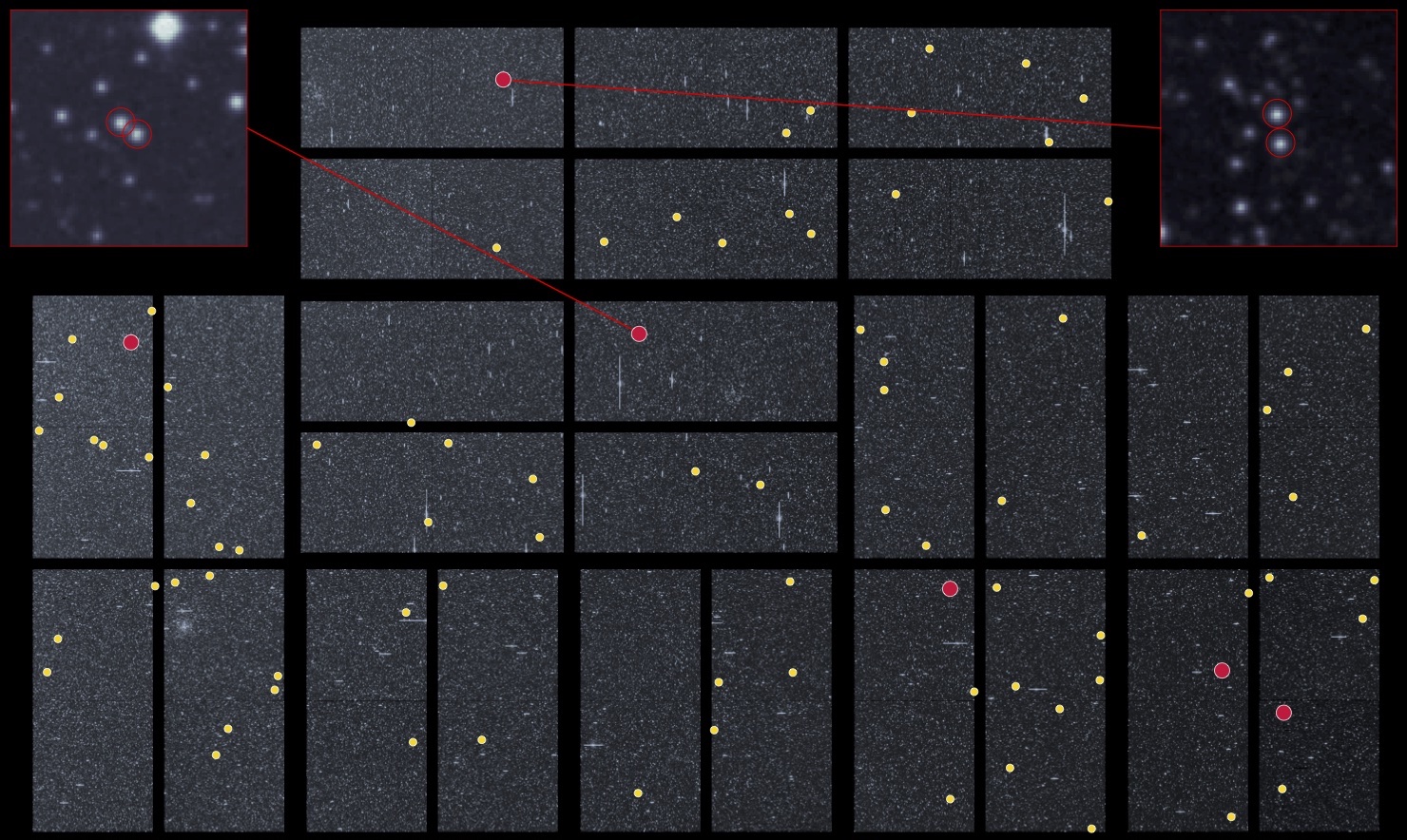
Twinkle, twinkle little star, I wonder just how old you are.
It isn’t an easy question to answer. Stars are notoriously difficult to age. We know the age of the Sun because we happen to live on one of its orbiting rocks, and we know very well how old the rock is. Without that information, things become a bit more fuzzy. But that could change thanks to a new study.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have a New Trick to Work out the Age of Stars”