Water. It’s always about the water when it comes to sizing up a planet’s potential to support life. Mars may possess some liquid water in the form of occasional salty flows down crater walls, but most appears to be locked up in polar ice or hidden deep underground. Set a cup of the stuff out on a sunny Martian day today and depending on conditions, it could quickly freeze or simply bubble away to vapor in the planet’s ultra-thin atmosphere.

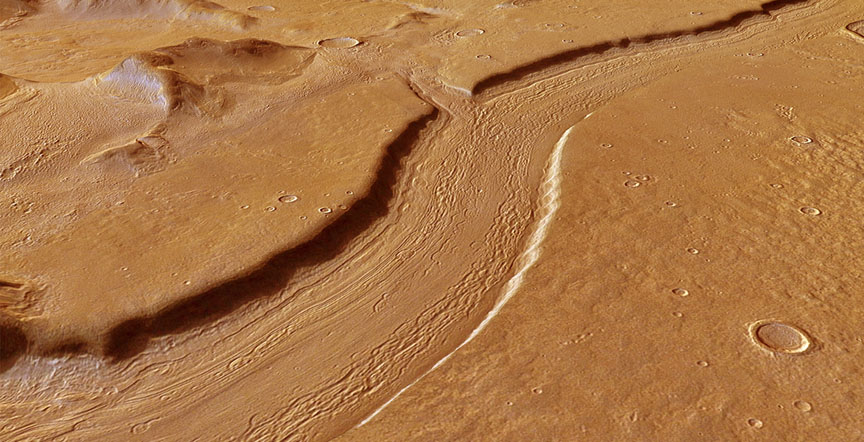
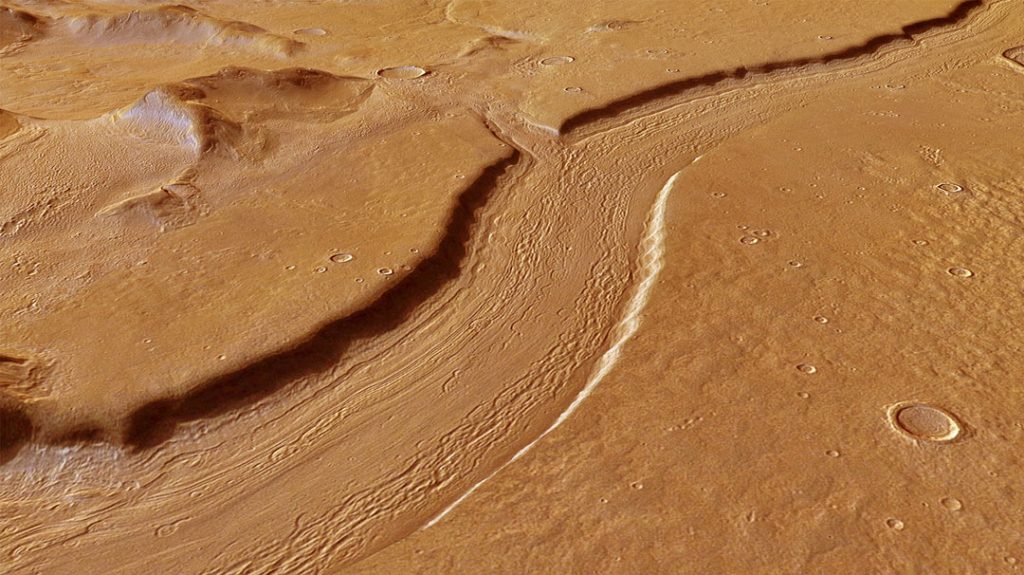
Evidence of abundant liquid water in former flooded plains and sinuous river beds can be found nearly everywhere on Mars. NASA’s Curiosity rover has found mineral deposits that only form in liquid water and pebbles rounded by an ancient stream that once burbled across the floor of Gale Crater. And therein lies the paradox. Water appears to have gushed willy-nilly across the Red Planet 3 to 4 billion years ago, so what’s up today?
Blame Mars’ wimpy atmosphere. Thicker, juicier air and the increase in atmospheric pressure that comes with it would keep the water in that cup stable. A thicker atmosphere would also seal in the heat, helping to keep the planet warm enough for liquid water to pool and flow.
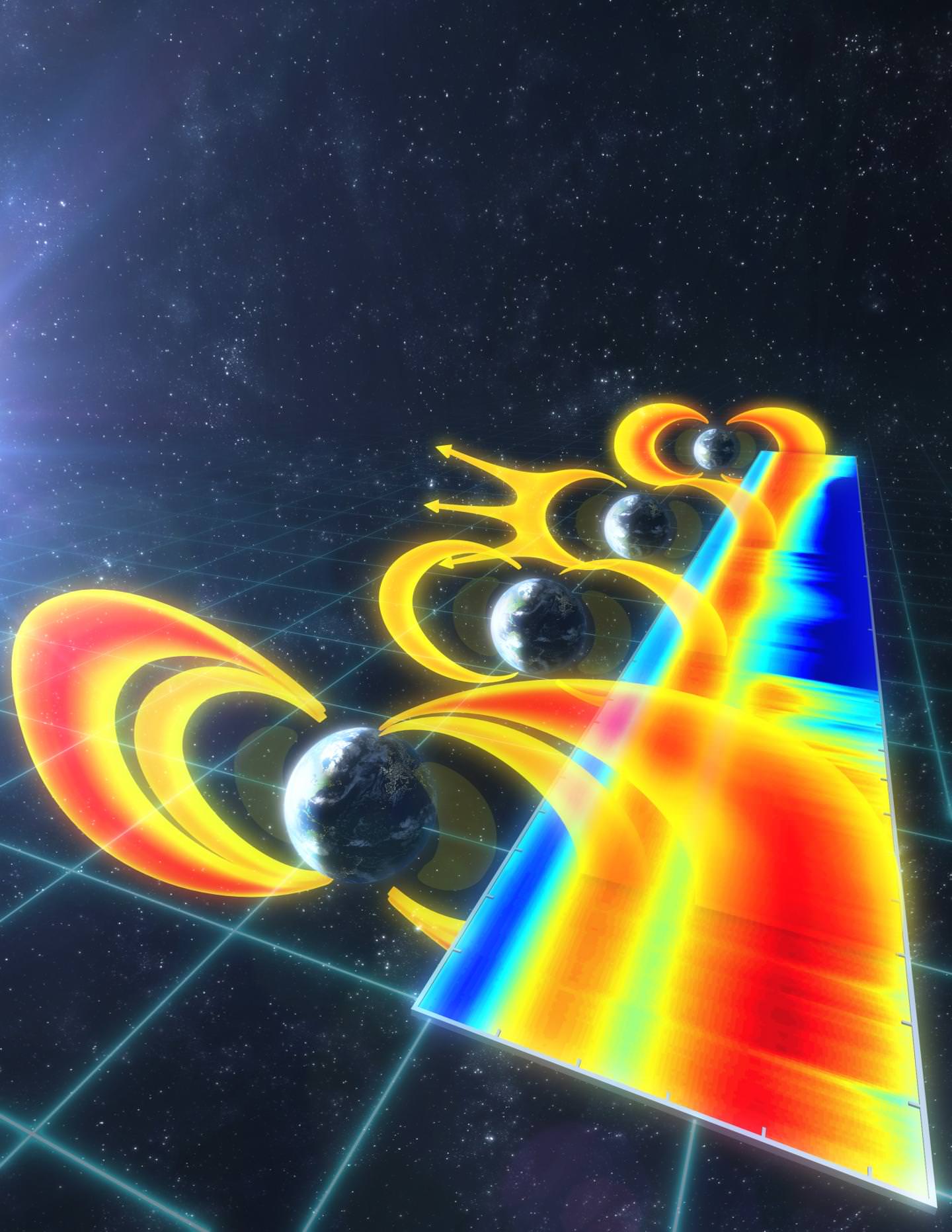
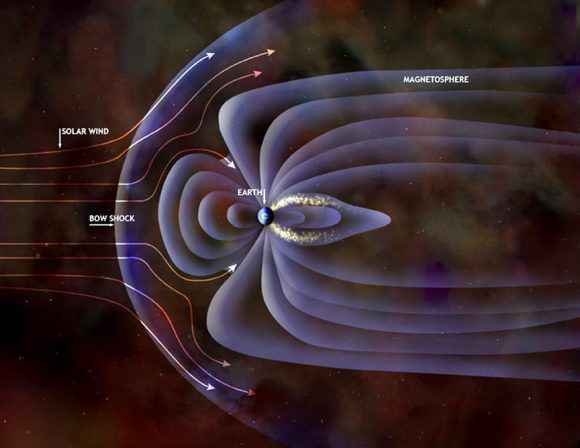
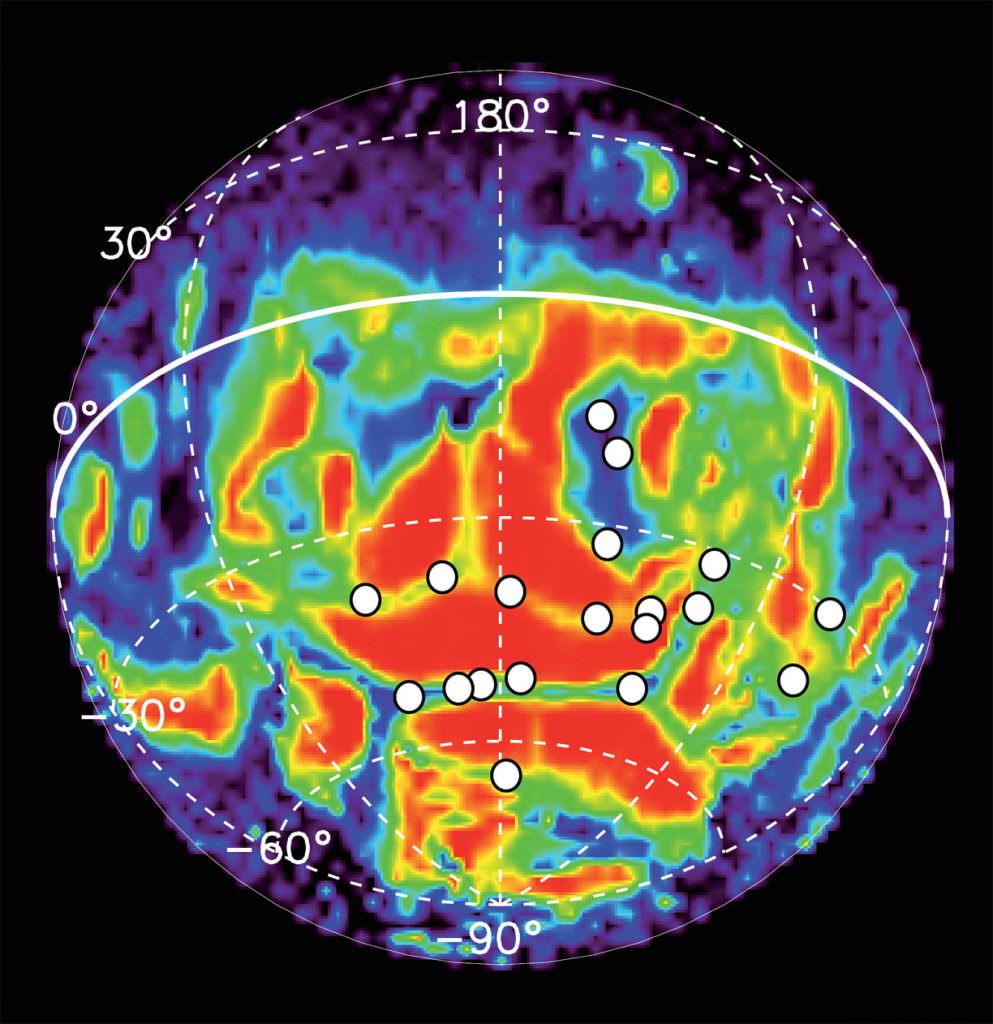
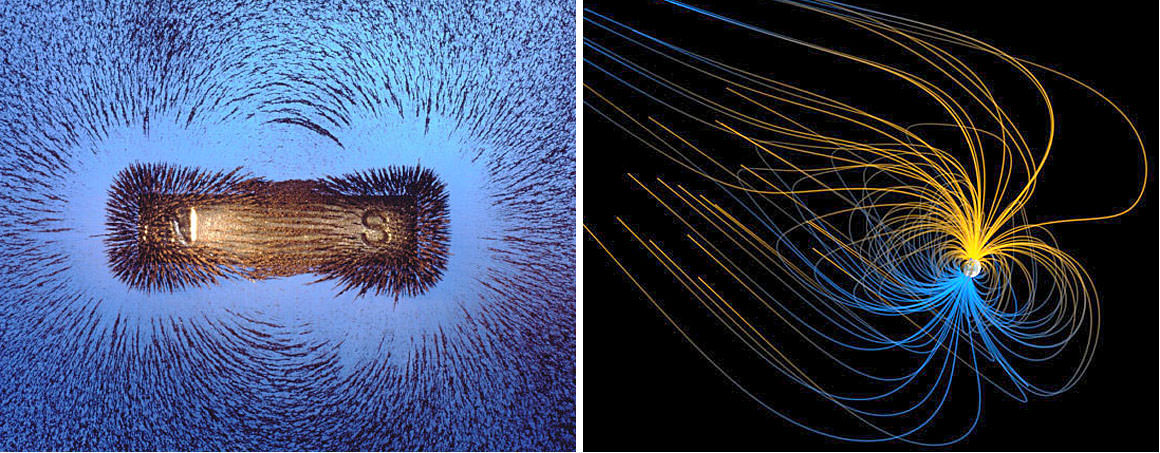
Different ideas have been proposed to explain the putative thinning of the air including the loss of the planet’s magnetic field, which serves as a defense against the solar wind.

Convection currents within its molten nickel-iron core likely generated Mars’ original magnetic defenses. But sometime early in the planet’s history the currents stopped either because the core cooled or was disrupted by asteroid impacts. Without a churning core, the magnetic field withered, allowing the solar wind to strip away the atmosphere, molecule by molecule.
Solar wind eats away the Martian atmosphere
Measurements from NASA’s current MAVEN mission indicate that the solar wind strips away gas at a rate of about 100 grams (equivalent to roughly 1/4 pound) every second. “Like the theft of a few coins from a cash register every day, the loss becomes significant over time,” said Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator.
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) suggest a different, less cut-and-dried scenario. Based on their studies, early Mars may have been warmed now and again by a powerful greenhouse effect. In a paper published in Geophysical Research Letters, researchers found that interactions between methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen in the early Martian atmosphere may have created warm periods when the planet could support liquid water on its surface.
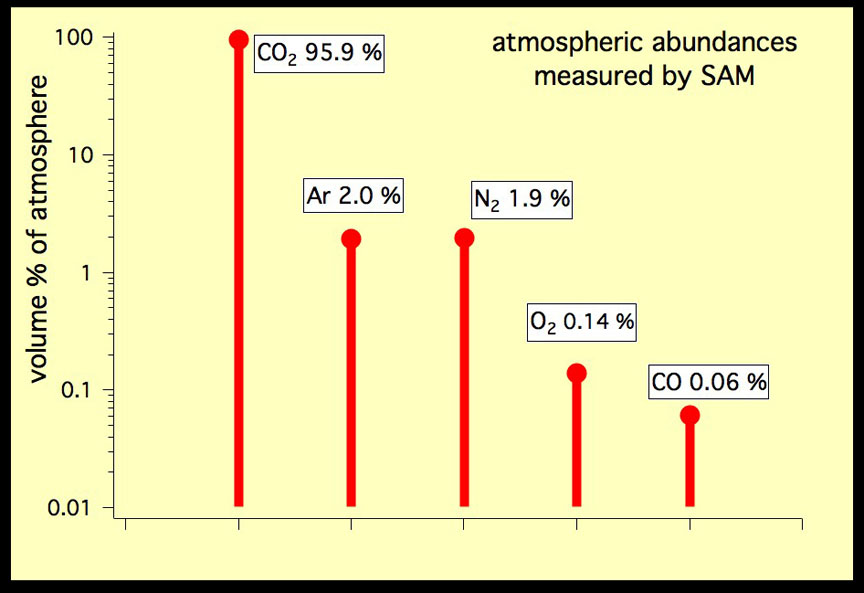
The team first considered the effects of CO2, an obvious choice since it comprises 95% of Mars’ present day atmosphere and famously traps heat. But when you take into account that the Sun shone 30% fainter 4 billion years ago compared to today, CO2 alone couldn’t cut it.
“You can do climate calculations where you add CO2 and build up to hundreds of times the present day atmospheric pressure on Mars, and you still never get to temperatures that are even close to the melting point,” said Robin Wordsworth, assistant professor of environmental science and engineering at SEAS, and first author of the paper.

Carbon dioxide isn’t the only gas capable of preventing heat from escaping into space. Methane or CH4 will do the job, too. Billions of years ago, when the planet was more geologically active, volcanoes could have tapped into deep sources of methane and released bursts of the gas into the Martian atmosphere. Similar to what happens on Saturn’s moon Titan, solar ultraviolet light would snap the molecule in two, liberating hydrogen gas in the process.
When Wordsworth and his team looked at what happens when methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide collide and then interact with sunlight, they discovered that the combination strongly absorbed heat.
Carl Sagan, American astronomer and astronomy popularizer, first speculated that hydrogen warming could have been important on early Mars back in 1977, but this is the first time scientists have been able to calculate its greenhouse effect accurately. It is also the first time that methane has been shown to be an effective greenhouse gas on early Mars.

When you take methane into consideration, Mars may have had episodes of warmth based on geological activity associated with earthquakes and volcanoes. There have been at least three volcanic epochs during the planet’s history — 3.5 billion years ago (evidenced by lunar mare-like plains), 3 billion years ago (smaller shield volcanoes) and 1 to 2 billion years ago, when giant shield volcanoes such as Olympus Mons were active. So we have three potential methane bursts that could rejigger the atmosphere to allow for a mellower Mars.
The sheer size of Olympus Mons practically shouts massive eruptions over a long period of time. During the in-between times, hydrogen, a lightweight gas, would have continued to escape into space until replenished by the next geological upheaval.
“This research shows that the warming effects of both methane and hydrogen have been underestimated by a significant amount,” said Wordsworth. “We discovered that methane and hydrogen, and their interaction with carbon dioxide, were much better at warming early Mars than had previously been believed.”
 I’m tickled that Carl Sagan walked this road 40 years ago. He always held out hope for life on Mars. Several months before he died in 1996, he recorded this:
I’m tickled that Carl Sagan walked this road 40 years ago. He always held out hope for life on Mars. Several months before he died in 1996, he recorded this:
” … maybe we’re on Mars because of the magnificent science that can be done there — the gates of the wonder world are opening in our time. Maybe we’re on Mars because we have to be, because there’s a deep nomadic impulse built into us by the evolutionary process, we come after all, from hunter gatherers, and for 99.9% of our tenure on Earth we’ve been wanderers. And, the next place to wander to, is Mars. But whatever the reason you’re on Mars is, I’m glad you’re there. And I wish I was with you.”