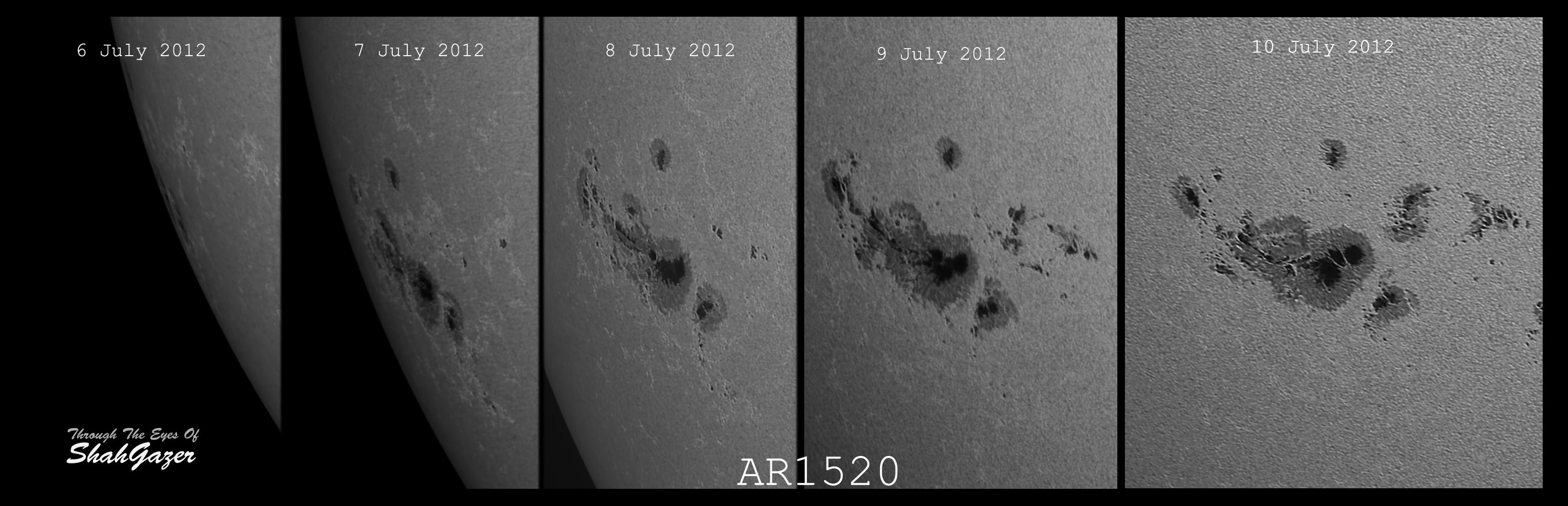
Caption: A 5-day sequence of sunspot group AR1520. Credit: Shahrin Ahmad, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Click to see a larger version.
There’s a monster sunspot making its way across the face of the Sun, and it’s captured the attention of several astrophotographers. This first image is from Shahrin Ahmad, who created a sequence of images as the sunspot moved to face towards Earth from the southeastern limb. He used a Skywatcher 120ED at F/15 (2X barlow) with a Baader Solar Filter and a IMG132E camera for his images.
AR1520 stretches more than 127,000 km (10 Earth diameters) from end to end, and the magnetic field of this enormous sunspot harbors energy for strong solar flares. NOAA forecasters estimate an 80% chance of M-flares and a 25% chance of X-flares during the next 24 hours, according to Spaceweather.com.
Here are some more looks at AR1520:
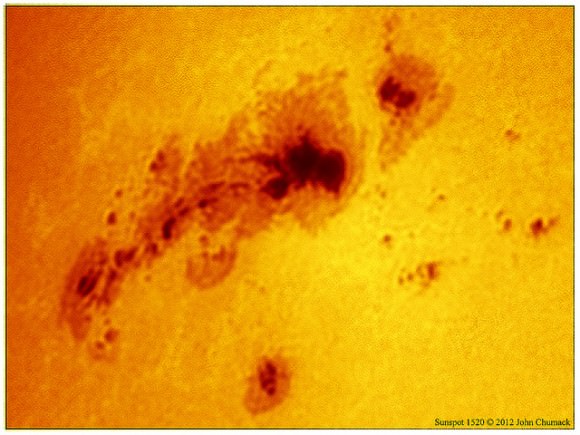
Caption: Closeup of monster sunspot AR1520. Credit: John Chumack.
One of our favorite astrophotographer, John Chumack, took this image of AR1520 in white light on July 8, 2012 using a Lunt Solar Herschel Solar Wedge filter, DMK 21AF04 Fire-wire Camera, 2x barlow, with 1/1000 second exposure. See more at his Flickr page, or his website, Galactic Images.

Caption: Sun and sunspots: Credit: Mike Black
Mike Black took this one on July 9, 2012
Gear: Canon 1D Mark IV + Canon 400mm f/2.8 + 2x Extender III. Baader solar film in front of lens. See more on Mike’s Flickr page.
Want to see a size comparison of AR1520? The mascot of the Solar Dynamics Observatory, Camilla the Rubber Chicken posted this comparison to Jupiter, the biggest planet in the solar system:
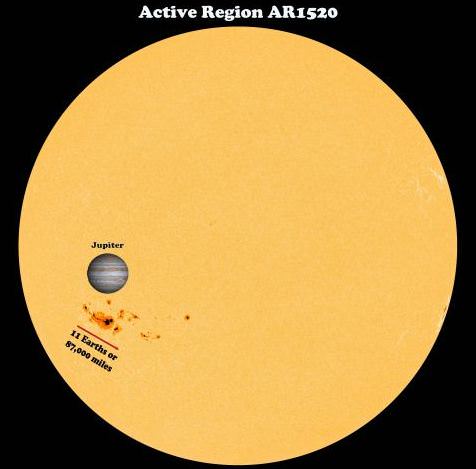

Caption: Size comparison of AR1520 to Jupiter. Credit: Camilla_SDO on Twitter.
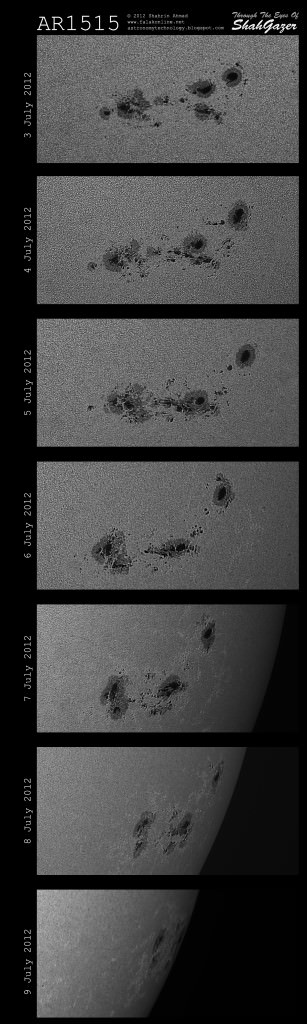
Here’s a look at the previously active region on the Sun, which last week blasted out numerous M-class flares and at least one X.1-class flares, again a sequence of images from Shahrin Ahmad:
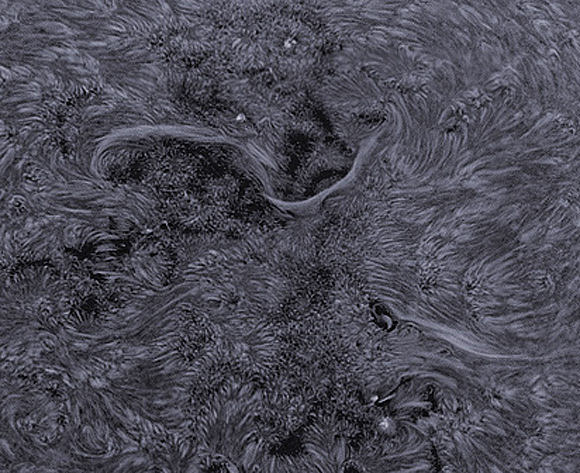
Caption: A 7-day sequence of sunspot AR1515. Credit: Shahrin Ahmad, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Thanks to everyone for sharing their images!
Want to get your astrophoto featured on Universe Today? Join our Flickr group or send us your images by email (this means you’re giving us permission to post them). Please explain what’s in the picture, when you took it, the equipment you used, etc.