I live in the frozen north by choice, but occasionally I yearn for warmer places like Tucson and Key West. These feelings usually start in late February, when after nearly four months of winter, the season feels endless. Today I wish I could head down south for another reason – to see a very bright supernova in a galaxy in Lupus.

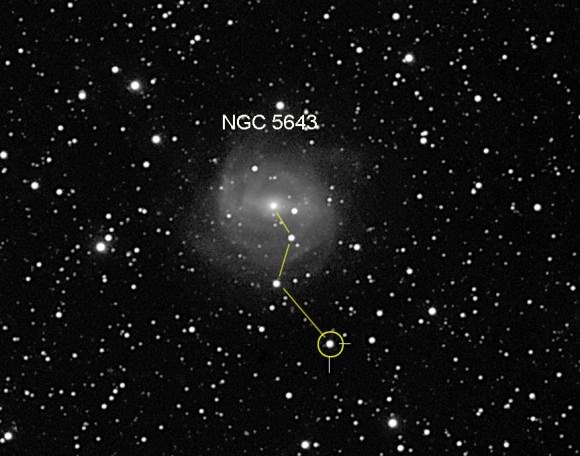
SN 2013aa popped off in the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5643 in the constellation Lupus the Wolf 34 million years ago, but no one knew its light was wiggling its way across the cosmos to Earth until New Zealand amateur astronomer Stu Parker nailed it during one of his regular supernovae hunts. Parker recorded it on Feb. 13, 2013. Since it was so far from the galaxy, he thought at first it was a hot pixel (electronic artifact) or an asteroid. Another look at the galaxy 5 minutes later confirmed it was really there.
Good thing. It turned out upon confirmation to be the brightest supernova he and his band of supernova hunters had ever discovered.
Stu is a member of a 6-man amateur supernova search team from Australia and New Zealand called BOSS (Backyard Observatory Supernova Search). They’ve been working together since 2008 with the goal of searching for and reporting supernovae in the southern sky. When a member finds a candidate, they contact profession astronomers who follow up using large telescopes. To date the group has found 56 supernovae with Stu discovering or co-discovering 45 of them!
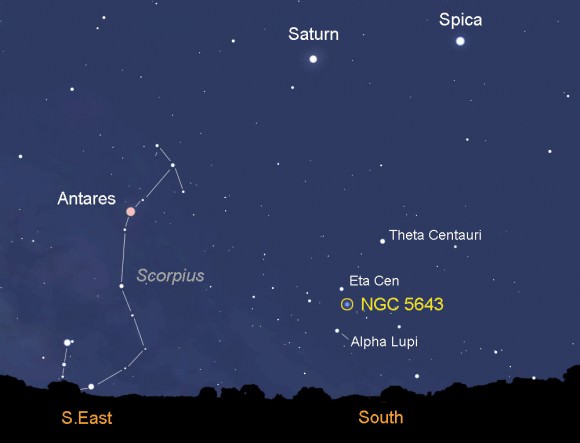
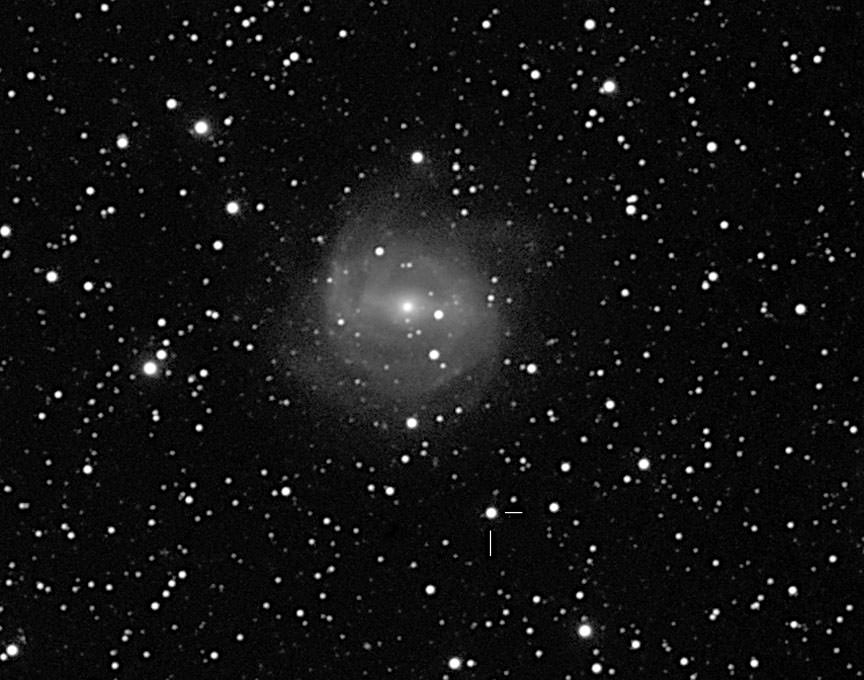
From the northern U.S., much of Lupus and especially the supernova never make it above the horizon, but from about 35 degrees north and points south, SN 2013aa is fair game. The “new star” lies southwest of the core of galaxy NGC 5643, which shines at magnitude 10, bright enough to see in a 6-inch telescope from a dark sky. The supernovae is still climbing in brightness and today gleams at about 11.6 magnitude – no problem in that 6-inch if you’re equipped with a good map or photo to help get you there.

Based on the study of 2013aa’s light, astronomers have classified it as Type Ia. Before the explosion, the star was a white dwarf, a superdense, planet-sized object with the mass of the sun. Tiny but mighty, the white dwarf’s powerful gravity pulled material from a nearby companion star down to its surface. When a dwarf puts on enough pounds to exceed 1.4 times the sun’s mass, the extra material increases the pressure and temperature of the core and the star burns explosively.

The energy released increases the star’s brightness to 5 billion times that of the sun. Matter from the blast streaks into space at speeds of 3,000-12,000 miles per second. Yes, this is a BIG deal and one of the most energetic events the universe has to offer. No wonder amateurs like myself can’t get enough of them.
NGC 5643 is best placed in the southern sky around 5 a.m. local time. From Lexington, KY. (latitude 38 degrees N.) it’s only 8 degrees high or slightly less than one fist held at arm’s length. Tuscon’s better at 14 degrees and Key West (latitude 25 N) best at 21. Farther south, your views will continue to improve. And the pleasant temperatures can’t hurt either.
You can start with the bright pair of Saturn and Spica midway up in the southern sky. Look about two outstretched fists below them to find Theta Centauri and from there “three fingers” to the lower left (southeast) to Eta Centauri. The galaxy is about 1 1/2 degrees southwest of Eta. The supernova will look like an 11 1/2 magnitude star 74″ west and 180″ south of the galaxy’s bright core. Use the annotated photo to help guide you straight to it.
To keep track of the 2013aa’s progress as well as view many more photos, I highly recommend David Bishop’s Latest Supernovae site.