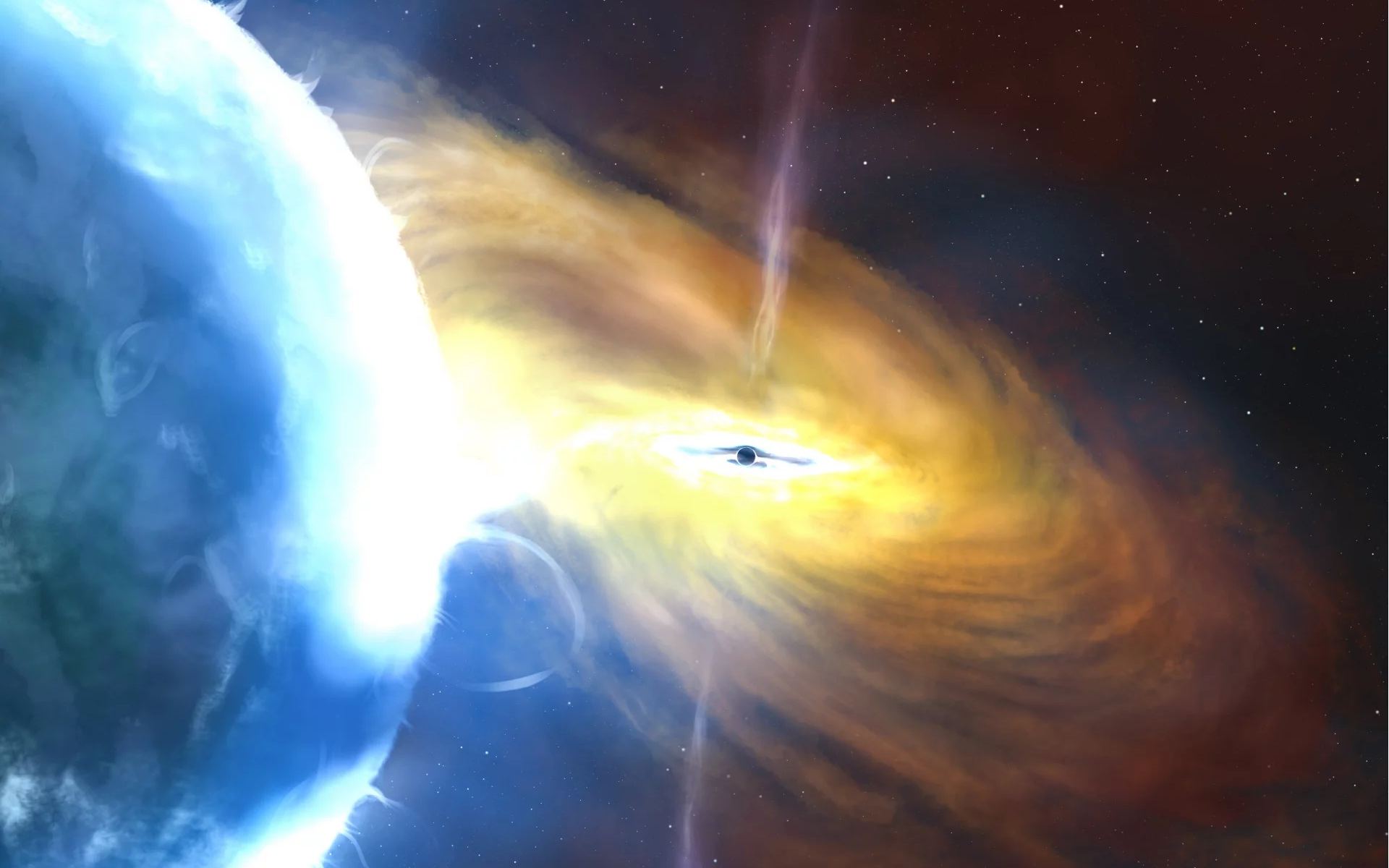
Throughout recorded history, humans have looked up at the night sky and witnessed the major astronomical events known as a “supernova.” The name, still used by astronomers, referred to the belief that these bursts of light in the “firmament” signaled the birth of a “new star.” With the birth of telescopes and modern astronomy, we have since learned that supernovae are what occur at the end of a star’s lifecycle. At this point, when a star has exhausted its hydrogen and helium fuel, it experiences gravitational collapse at its center.
This leads to a tremendous explosion that can be seen billions of light-years distant, releasing tremendous amounts of energy and blowing the star’s outer layers off. Thanks to an international team of astronomers led by the University of Southhampton, the most powerful cosmic explosion has been confirmed! The stellar explosion, AT2021lwx, took place about 8 billion light-years away in the constellation Vulpecula and was over ten times brighter than any supernova ever observed and 100 times brighter than all the stars in the Milky Way combined!
Continue reading “The Largest Explosion Ever Seen in the Universe”