The venerable Hubble Space Telescope has given us so much during the history of its service (32 years, 7 months, 6 days, and counting!) Even after all these years, the versatile and sophisticated observatory is still pulling its weight alongside more recent addition, like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and other members of NASA’s Great Observatories family. In addition to how it is still conducting observation campaigns, astronomers and astrophysicists are combing through the volumes of data Hubble accumulated over the years to find even more hidden gems.
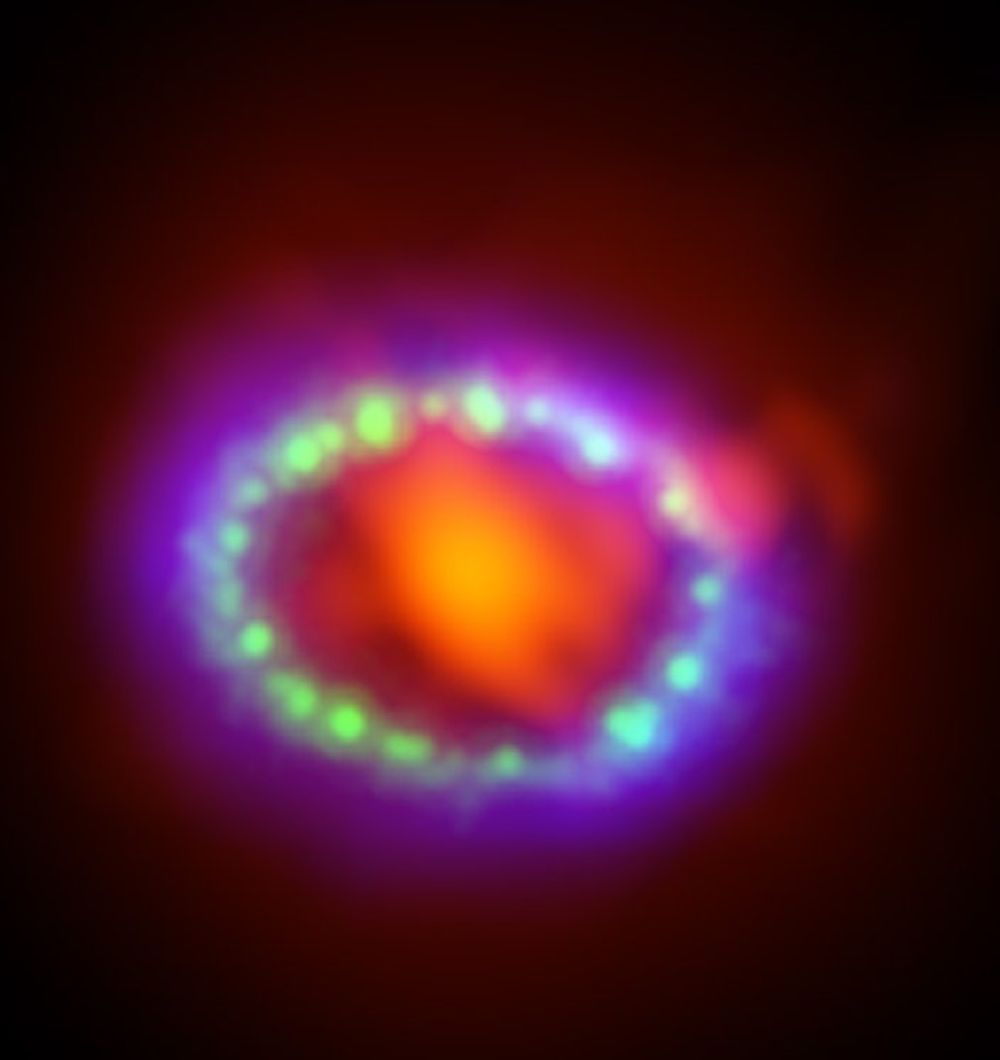
A team led by Caltech’s recently made some very interesting finds in the Hubble archives, where they observed the sites of six supernovae to learn more about their progenitor stars. Their observations were part of the Hubble Space Telescope Snapshot program, where astronomers use HST images to chart the life cycle and evolution of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. From this, they were able to place constraints on the size, mass, and other key characteristics of the progenitor stars and what they experienced before experiencing core collapse.
Continue reading “By Looking Back Through Hubble Data, Astronomers Have Identified six Massive Stars Before They Exploded as Core-Collapse Supernovae”