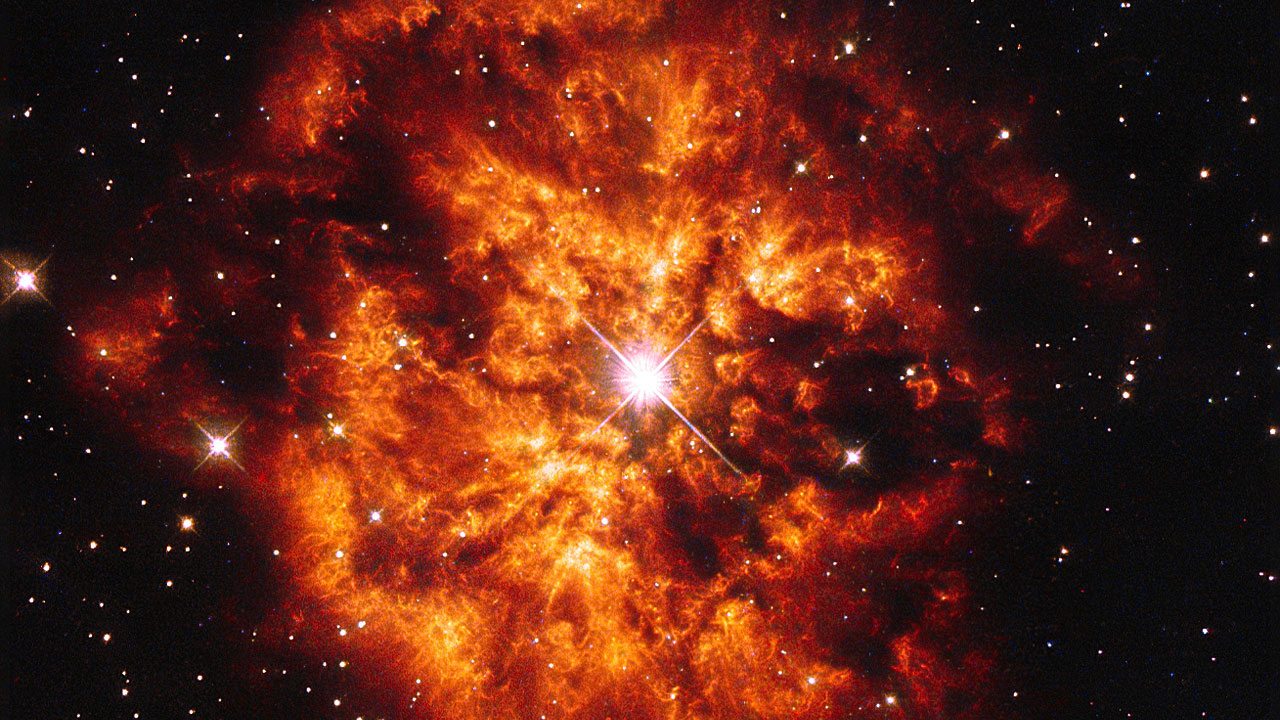
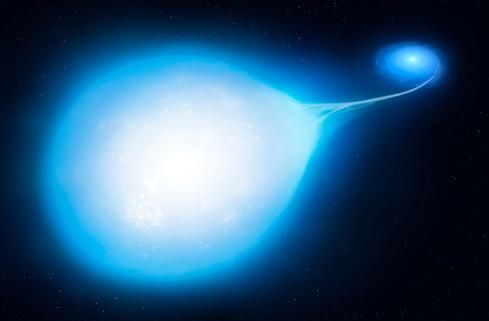
We often think of supernova explosions as inevitable for large stars. Big star runs out of fuel, gravity collapses its core and BOOM! But astronomers have long thought at least one type of large star didn’t end with a supernova. Known as Wolf-Rayet stars, they were thought to end with a quiet collapse of their core into a black hole. But a new discovery finds they might become supernovae after all.
Continue reading “A new Kind of Supernova has Been Discovered”Astronomers Watch a Star Die and Then Explode as a Supernova

It’s another first for astronomy.
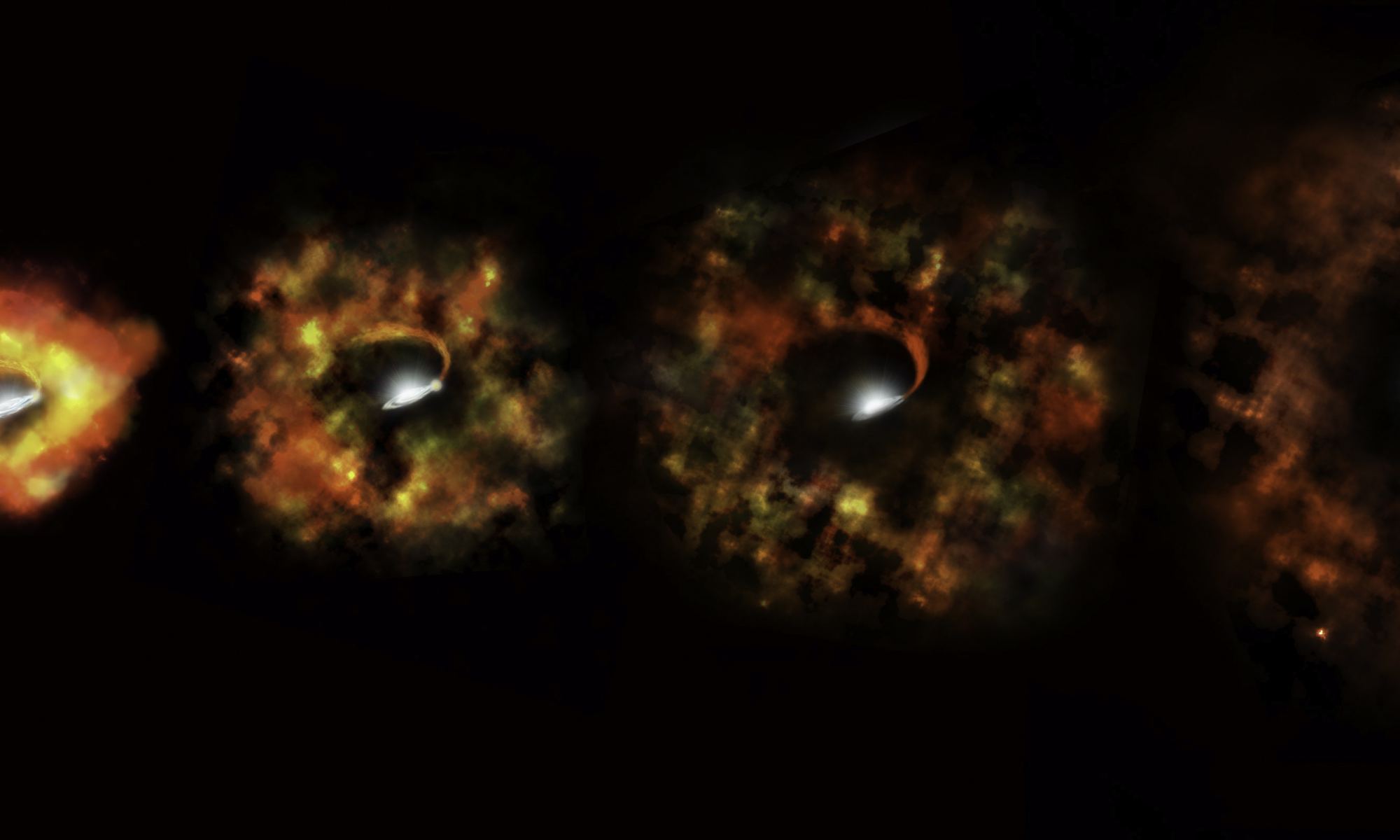
For the first time, a team of astronomers have imaged in real-time as a red supergiant star reached the end of its life. They watched as the star convulsed in its death throes before finally exploding as a supernova.
And their observations contradict previous thinking into how red supergiants behave before they blow up.
Continue reading “Astronomers Watch a Star Die and Then Explode as a Supernova”Nearby Supernovae Were Essential to Life on Earth
It’s almost impossible to comprehend a supernova explosion’s violent, destructive power. An exploding supernova can outshine its host galaxy for a few weeks or even months. That seems almost impossible when considering that a galaxy can contain hundreds of billions of stars. Any planet too close to a supernova would be completely sterilized by all the energy released, its atmosphere would be stripped away, and it may even be shredded into pieces.
But like many things in nature, it all comes down to dose.
A certain amount of supernova activity might be necessary for life to exist.
Continue reading “Nearby Supernovae Were Essential to Life on Earth”Quick Action Let Hubble Watch the Earliest Stages of an Unfolding Supernova Detonation
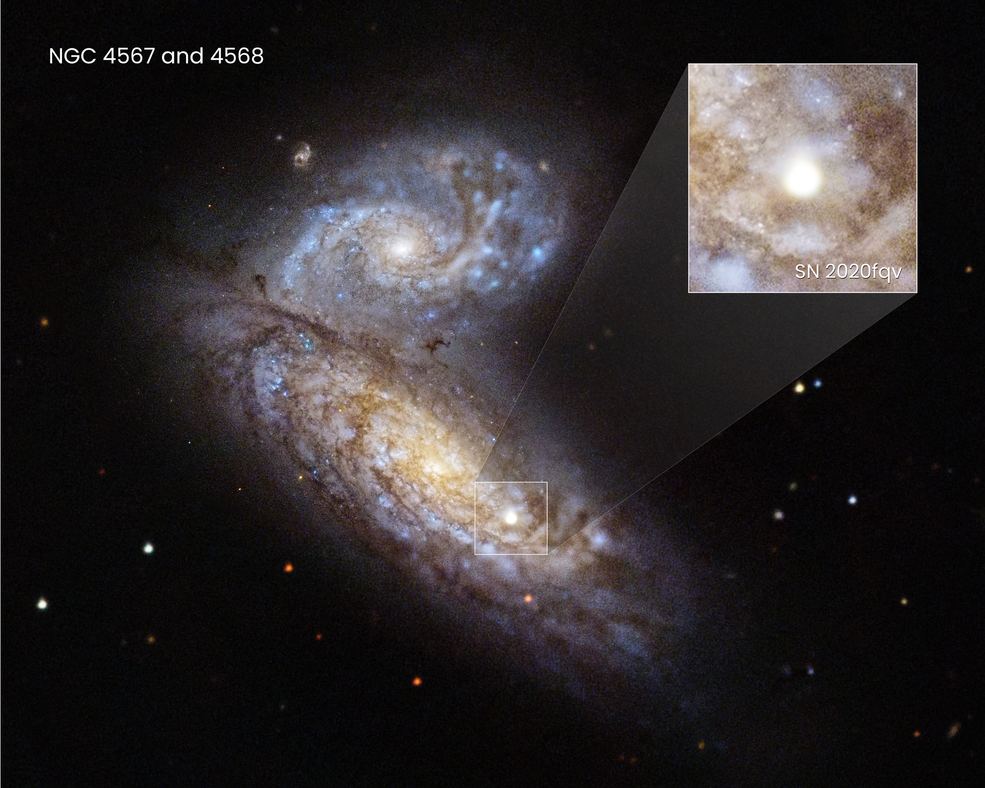

If it weren’t for supernova remnants we wouldn’t have much knowledge of supernovae themselves. If a supernova explosion is the end of a star’s life, then we can also thank forensic astrophysics for much of our knowledge. The massive exploding stars leave behind brilliant and mesmerizing evidence of their catastrophic ends, and much of what we know about supernovae comes from studying the remnants rather than the explosions themselves. Supernova remnants like the Crab Nebula and SN 1604 (Kepler’s Supernova) are some of our most-studied objects.
Observing an active supernova in the grip of its own destruction can be difficult. But it looks like the Hubble Space Telescope is up to the task.
Continue reading “Quick Action Let Hubble Watch the Earliest Stages of an Unfolding Supernova Detonation”A Black Hole or Neutron Star Fell Into Another Star and Triggered a Supernova
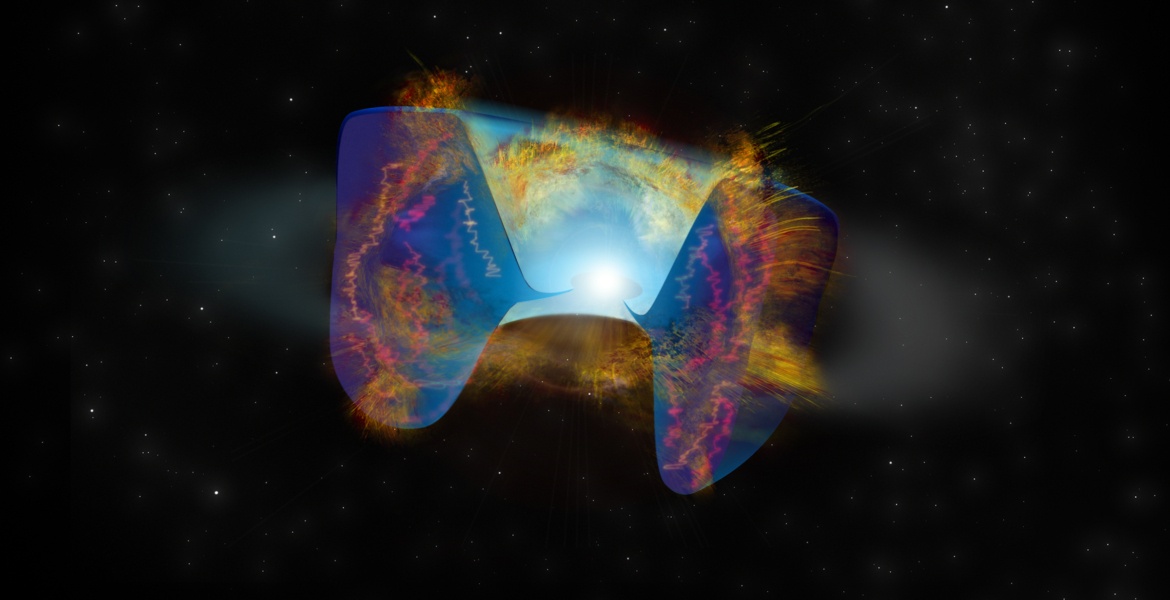
What happens when you slam a neutron star (or black hole, take your pick) into a companion star? A supernova, that’s what. And for the first time ever, astronomers think they’ve spotted one.
Continue reading “A Black Hole or Neutron Star Fell Into Another Star and Triggered a Supernova”Heavier Stars Might not Explode as Supernovae, Just Quietly Implode Into Black Holes
A supernova is a brilliant end to a giant star. For a brief moment of cosmic time, a star makes one last effort to keep shining, only to fade and collapse on itself. The end result is either a neutron star or a stellar-mass black hole. We’ve generally thought that all stars above about ten solar masses will end as a supernova, but a new study suggests that isn’t the case.
Continue reading “Heavier Stars Might not Explode as Supernovae, Just Quietly Implode Into Black Holes”Astronomers Locate the Source of High-Energy Cosmic Rays

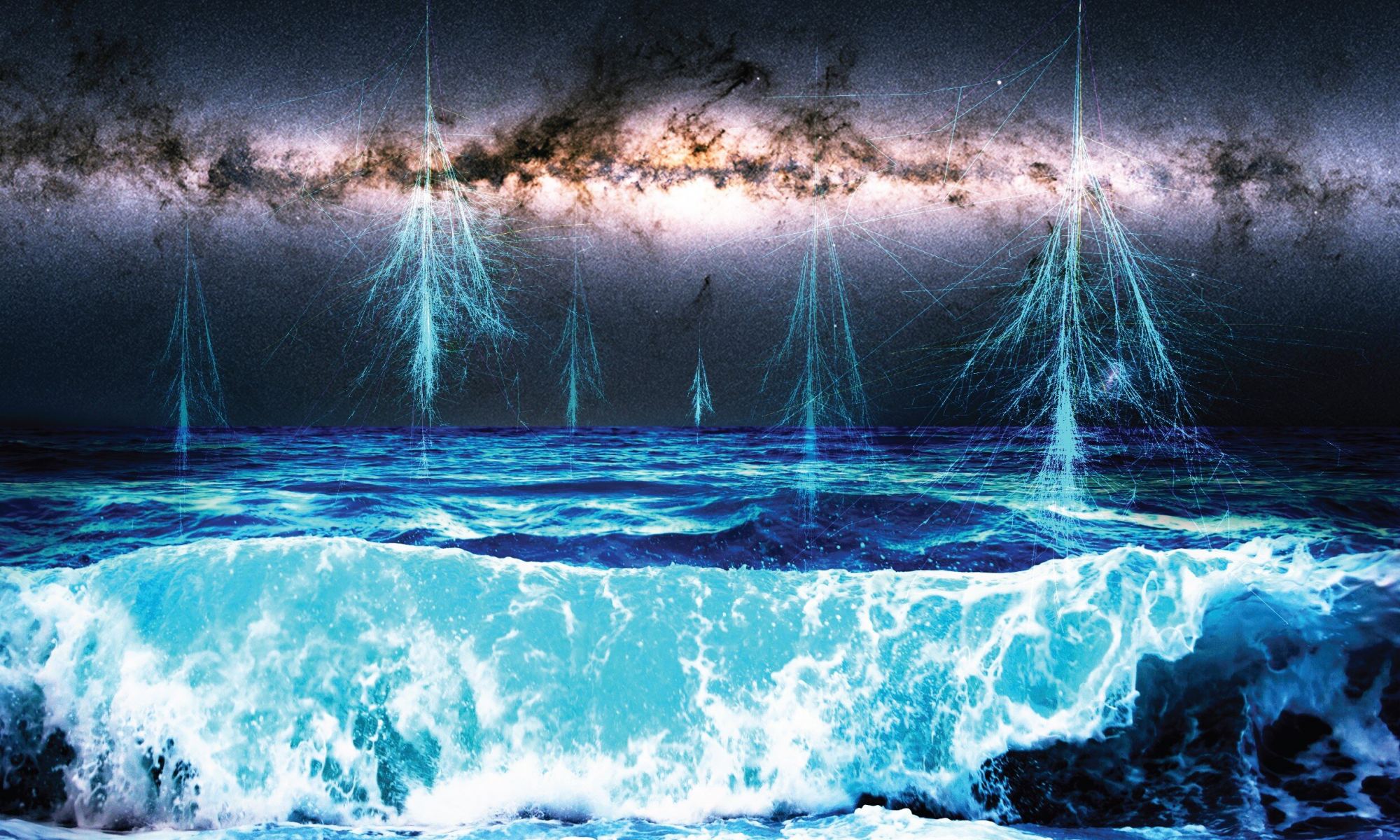
Roughly a century ago, scientists began to realize that some of the radiation we detect in Earth’s atmosphere is not local in origin. This eventually gave rise to the discovery of cosmic rays, high-energy protons and atomic nuclei that have been stripped of their electrons and accelerated to relativistic speeds (close to the speed of light). However, there are still several mysteries surrounding this strange (and potentially lethal) phenomenon.
This includes questions about their origins and how the main component of cosmic rays (protons) are accelerated to such high velocity. Thanks to new research led by the University of Nagoya, scientists have quantified the amount of cosmic rays produced in a supernova remnant for the first time. This research has helped resolve a 100-year mystery and is a major step towards determining precisely where cosmic rays come from.
Continue reading “Astronomers Locate the Source of High-Energy Cosmic Rays”It Turns out There Were Supernovae Exploding all Over, we Just Couldn’t see Them
When the poet Horace said “We are but dust and shadow”, he probably didn’t think that dust itself could create a shadow. But it can, and that shadow can obscure even some of the most powerful explosions in the universe. At least that’s the finding from new research from an international team using data from the recently retired Spitzer telescope. It turns out dust in far away galaxies can obscure supernovas.
Continue reading “It Turns out There Were Supernovae Exploding all Over, we Just Couldn’t see Them”From the way These Stars Look, a Supernova is Inevitable
Sometimes loud explosions are easier to deal with when you know they’re coming. They are also easier to watch out for. So when astronomers from the University of Warwick found a rare tear-drop shaped star, known as HD265435, they knew they were looking at a potential new supernova waiting to happen. The only caveat – it might not actually happen until 70 million years from now.
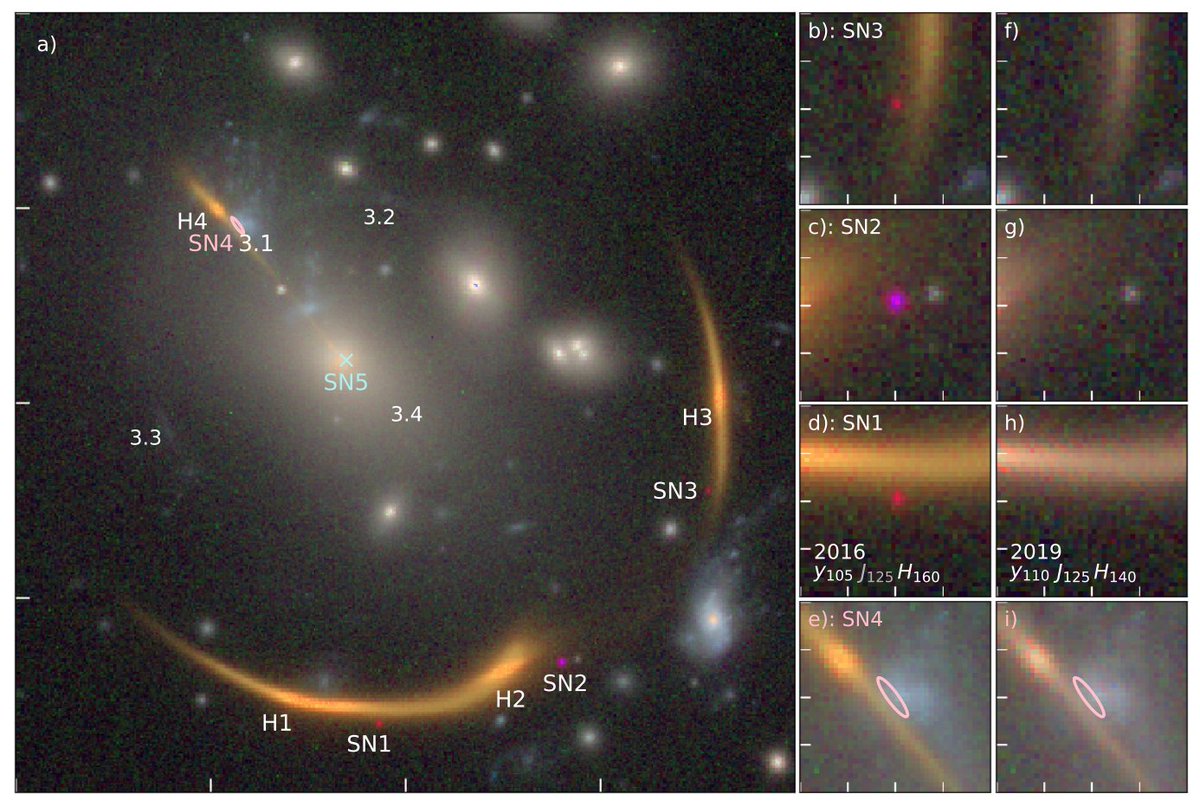
Continue reading “From the way These Stars Look, a Supernova is Inevitable”Astronomers saw the Same Supernova Three Times Thanks to Gravitational Lensing. And in Twenty Years They Think They’ll see it one More Time
It is hard for humans to wrap their heads around the fact that there are galaxies so far away that the light coming from them can be warped in a way that they actually experience a type of time delay. But that is exactly what is happening with extreme forms of gravitational lensing, such as those that give us the beautiful images of Einstein rings. In fact, the time dilation around some of these galaxies can be so extreme that the light from a single event, such as a supernova, can actually show up on Earth at dramatically different times. That is exactly what a team led by Dr. Steven Rodney at the University of South Carolina and Dr. Gabriel Brammer of the University of Copenhagen has found. Except three copies of this supernova have already appeared – and the team thinks it will show up again one more time, 20 years from now.
Continue reading “Astronomers saw the Same Supernova Three Times Thanks to Gravitational Lensing. And in Twenty Years They Think They’ll see it one More Time”