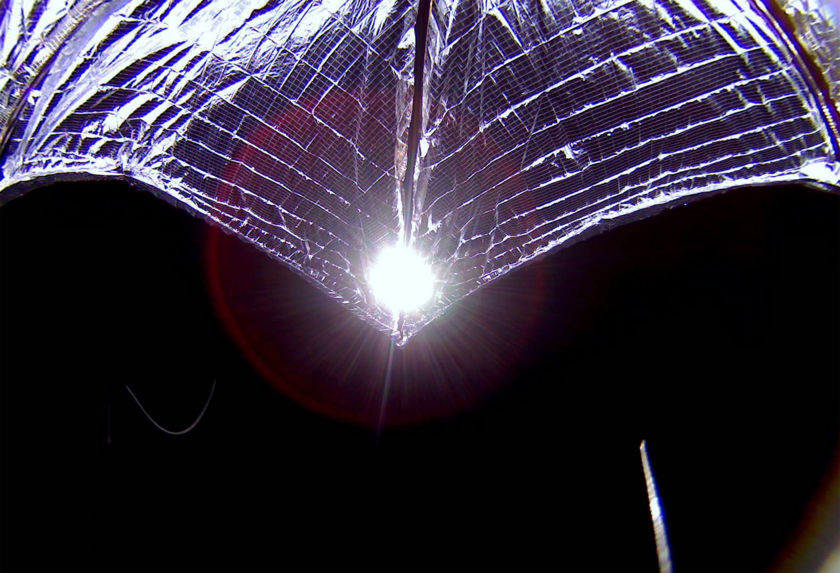
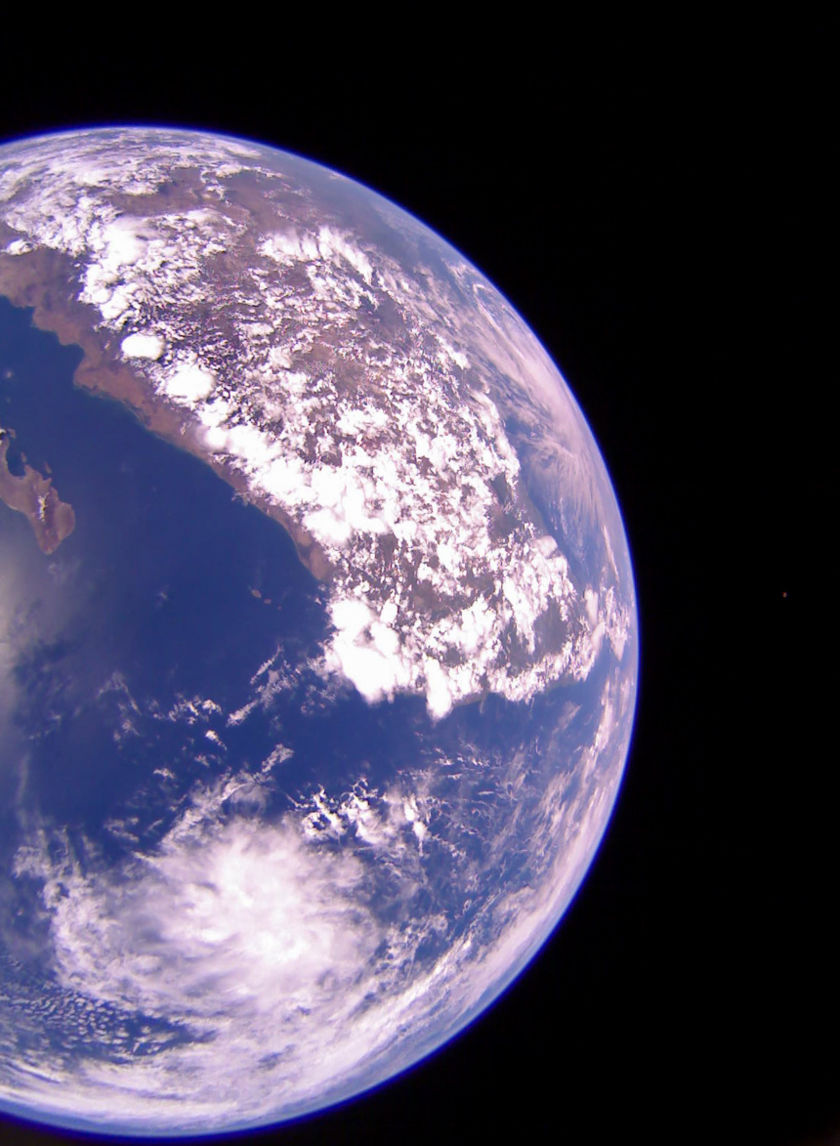
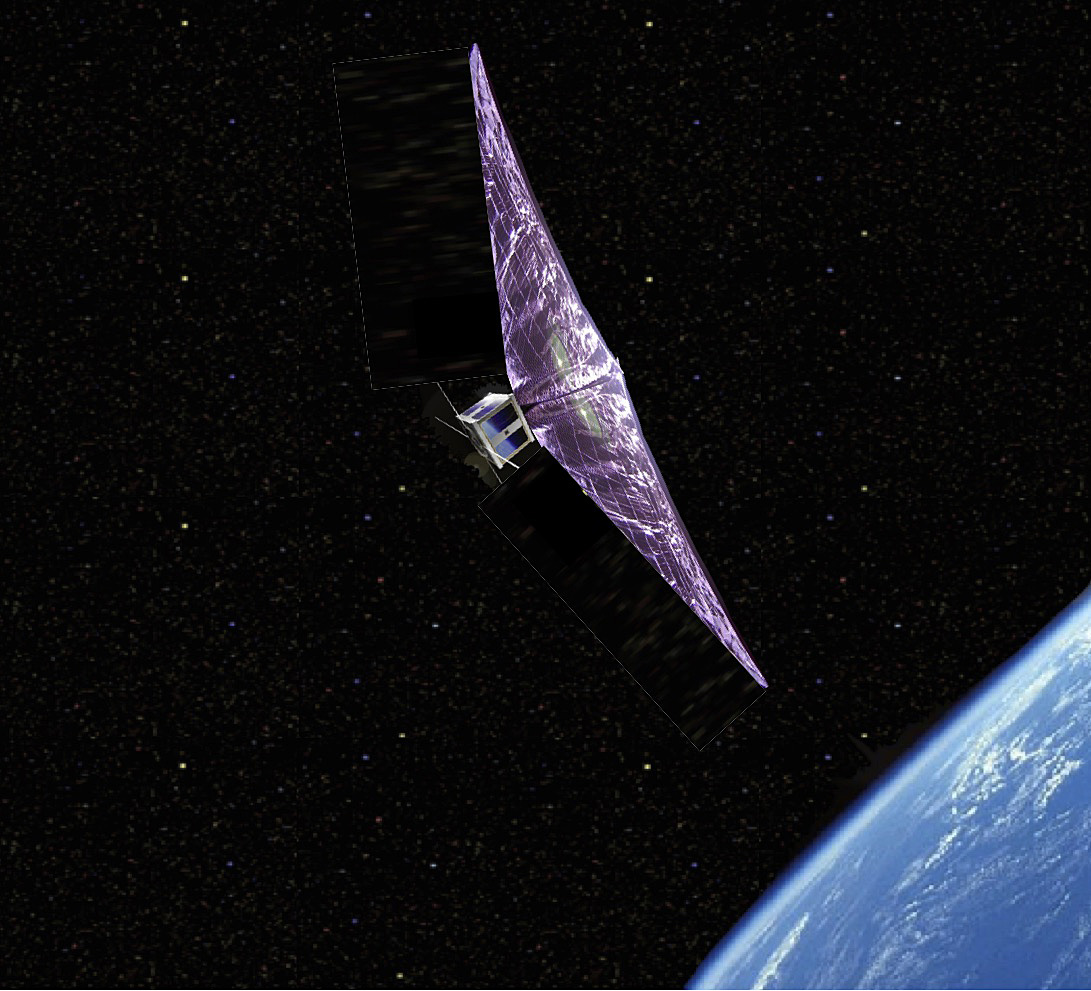
Good news from The Planetary Society: LightSail 2’s solar sail is functioning as intended. After launching on June 25th, then deploying its solar sail system on July 23rd, mission managers have been working with the solar sail to optimize they way LightSail 2 orients itself towards the Sun. Now The Planetary Society reports that the spacecraft has used its solar sail to raise its orbit.
Continue reading “The Light Sail is Working… It’s Working!”The Light Sail is Working… It’s Working!