[/caption]
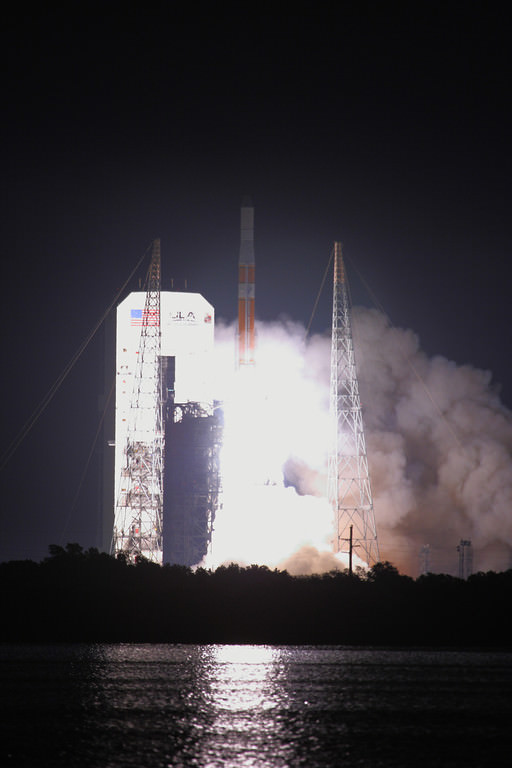
The potential to fly anywhere in the world in less than an hour took a nosedive today. The test flight of an unmanned, rocket-launched, Mach 20-capable, maneuverable aircraft called the Falcon Hypersonic Technology Vehicle 2 (HTV-2) ended when an anomaly caused loss of signal, and the plane crashed into the Pacific Ocean. Overseen by DARPA, the Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency, this second test flight of the HTV-2 seemingly started out well, as the Minotaur IV launch vehicle successfully inserted the aircraft into the correct trajectory, and the aircraft transitioned to Mach 20 aerodynamic flight. It flew for 9 minutes until it encountered problems and crashed.
Despite the crash, DARPA said the successful transition “represents a critical knowledge and control point in maneuvering atmospheric hypersonic flight.”
“Here’s what we know,” said Air Force Maj. Chris Schulz, DARPA HTV-2 program manager in a statement put out by DARPA. “We know how to boost the aircraft to near space. We know how to insert the aircraft into atmospheric hypersonic flight. We do not yet know how to achieve the desired control during the aerodynamic phase of flight. It’s vexing; I’m confident there is a solution. We have to find it.”
From launch until crash, the flight lasted for about a half an hour.
DARPA’s Falcon is designed to fly anywhere in the world in less than 60 minutes. This capability requires an aircraft that can fly at 13,000 mph, while experiencing temperatures in excess of 3500F.
During the first test flight of HTV-2 on April 23, 2010, telemetry was lost 9 minutes into the flight. A subsequent investigation found that the vehicle encountered unexpected yaw, followed by an uncontrollable roll. The onboard computer then set the vehicle to crash into the ocean.
“In the April 2010 test, we obtained four times the amount of data previously available at these speeds,” said DARPA Director Regina Dugan. “Today more than 20 air, land, sea and space data collection systems were operational. We’ll learn. We’ll try again. That’s what it takes. Filling the gaps in our understanding of hypersonic flight in this demanding regime requires that we be willing to fly.”
The military had hopes of using this type of super-fast plane to reach problem spots around the world quickly.
DARPA said that in the coming weeks, an independent Engineering Review Board will review and analyze the data collected. This data will inform policy, acquisition and operational decisions for future -hypersonic aircraft of this kind. It’s not clear yet whether any development of Falcon HTV-2 will continue.
This is the second major hypersonic setback of 2011. In June, the Boeing X-51 waverider failed when its scramjet encountered a problem on engine startup.
Source: DARPA