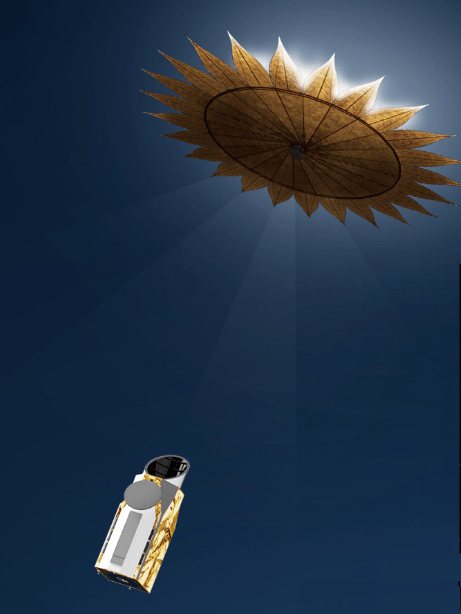
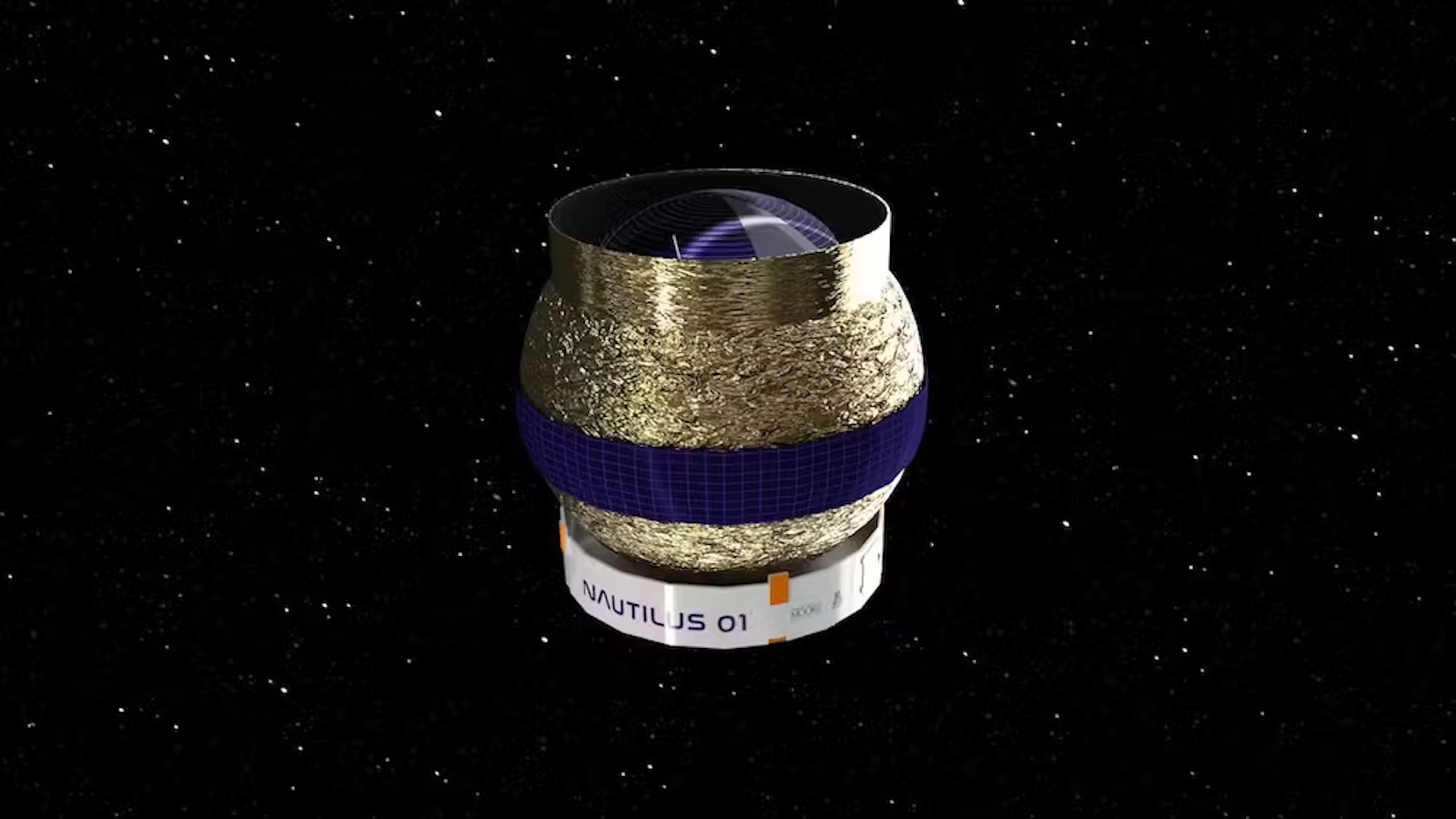
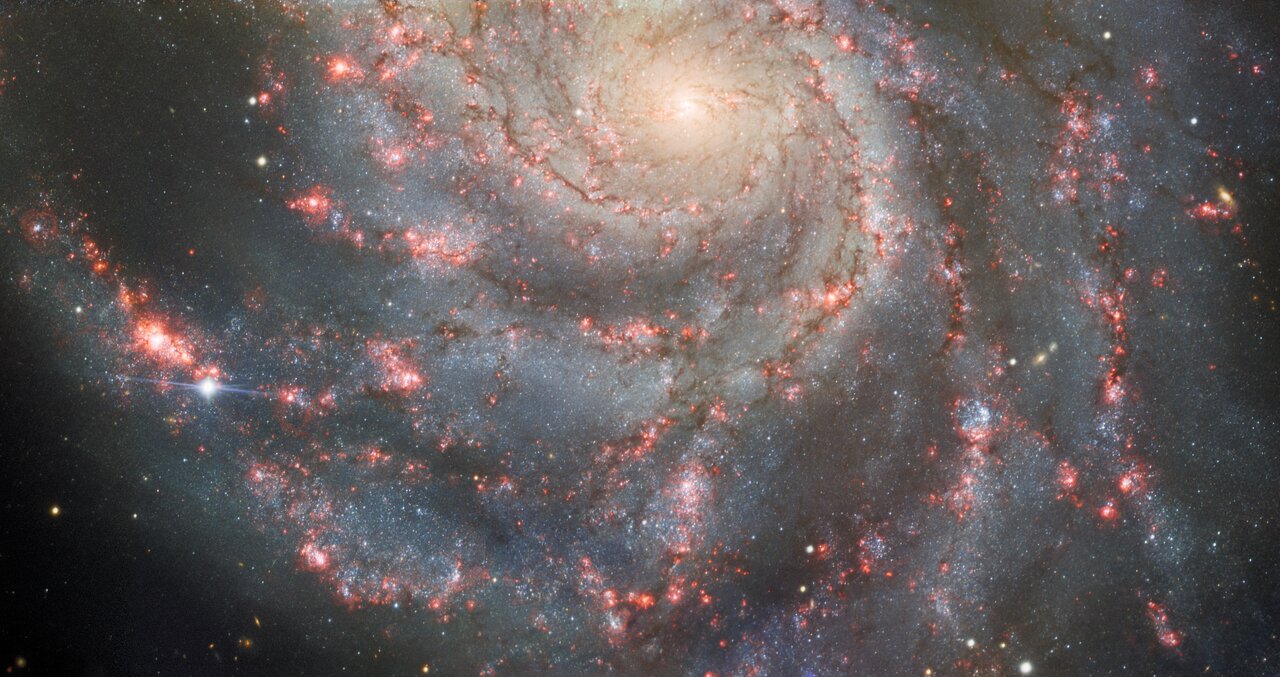
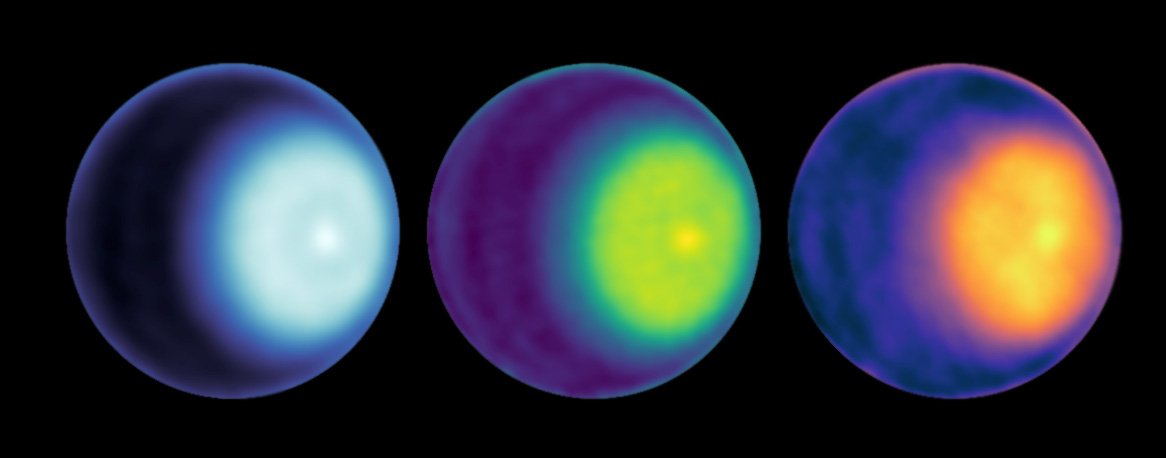
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has only been operational for just over a year, but this isn’t stopping the world’s biggest space agency from discussing the next big space telescope that could serve as JWST’s successor sometime in the future. Enter the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO), which was first proposed as NASA’s next flagship Astrophysics mission during the National Academy of Sciences’ Decadal Survey on Astronomy and Astrophysics 2020 (Astro2020). While its potential technological capabilities include studying exoplanets, stars, galaxies, and a myriad of other celestial objects for life beyond Earth, there’s a long way to go before HWO will be wowing both scientists and the public with breathtaking images and new datasets.
Continue reading “Planning is Underway for NASA’s Next Big Flagship Space Telescope”Planning is Underway for NASA’s Next Big Flagship Space Telescope