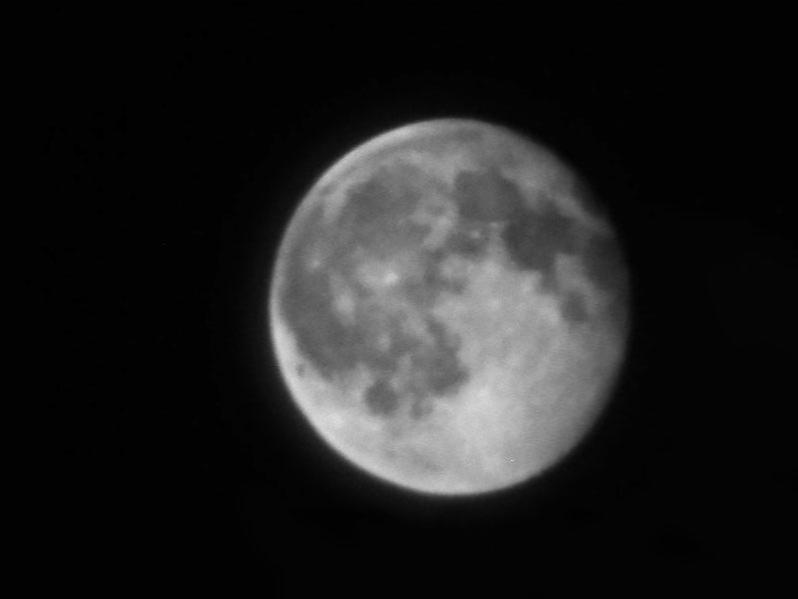
The picture of the Moon in the banner might not look all that spectacular, but it is absolutely astounding from a technical perspective. What makes it so unique is that it was taken via a telescope using a completely flat lens. This type of lens, called a metalens, has been around for a while, but a team of researchers from Pennsylvania State University (PSU) recently made the largest one ever. At eight cm in diameter, it was large enough to use in an actual telescope – and produce the above picture of the Moon, however, blurred it might be.
Continue reading “Researchers Build a Telescope with a Flat Lens”If an Earthlike Planet is Within 30 Light-Years, This Space Telescope Will Find it
There has long been a limiting factor in the development of space-based telescopes – launch fairings. These capsules essentially limit the overall size of the mirrors we are able to launch into space, thereby limiting the sensitivity of many of those instruments. Despite those limitations, some of the most successful telescopes ever have been space-based, but even with all the advantages of being in space, they have so far failed to find an exoplanet in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star. Enter a new project called the Diffractive Interfero Coronagraph Exoplanet Resolver (DICER), which recently received funding from NASA’s Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC).
Continue reading “If an Earthlike Planet is Within 30 Light-Years, This Space Telescope Will Find it”A Green Bank Telescope Prototype Radar System Can Image the Moon in High-Resolution and Detect Asteroids

Everyone loves taking pictures of the Moon. Whether it’s with their phones or through the wonders of astrophotography, photographing the Moon reminds us about the wonders and awesomeness of the universe. But while we can take awesome images of the whole Moon from the Earth, it’s extremely difficult to get close-up images of its surface given the enormous distance we are from our nearest celestial neighbor at 384,400 km (238,855 mi). This is because the closer we try to zoom in on its surface, the blurrier, or more pixelated, the images become. Essentially, the resolution of the images becomes worse and worse. But what if we could take high-resolution images of the Moon’s surface from Earth instead of relying on satellites presently in lunar orbit to take them for us?
Continue reading “A Green Bank Telescope Prototype Radar System Can Image the Moon in High-Resolution and Detect Asteroids”Future Space Telescopes Could be 100 Meters Across, Constructed in Space, and Then Bent Into a Precise Shape
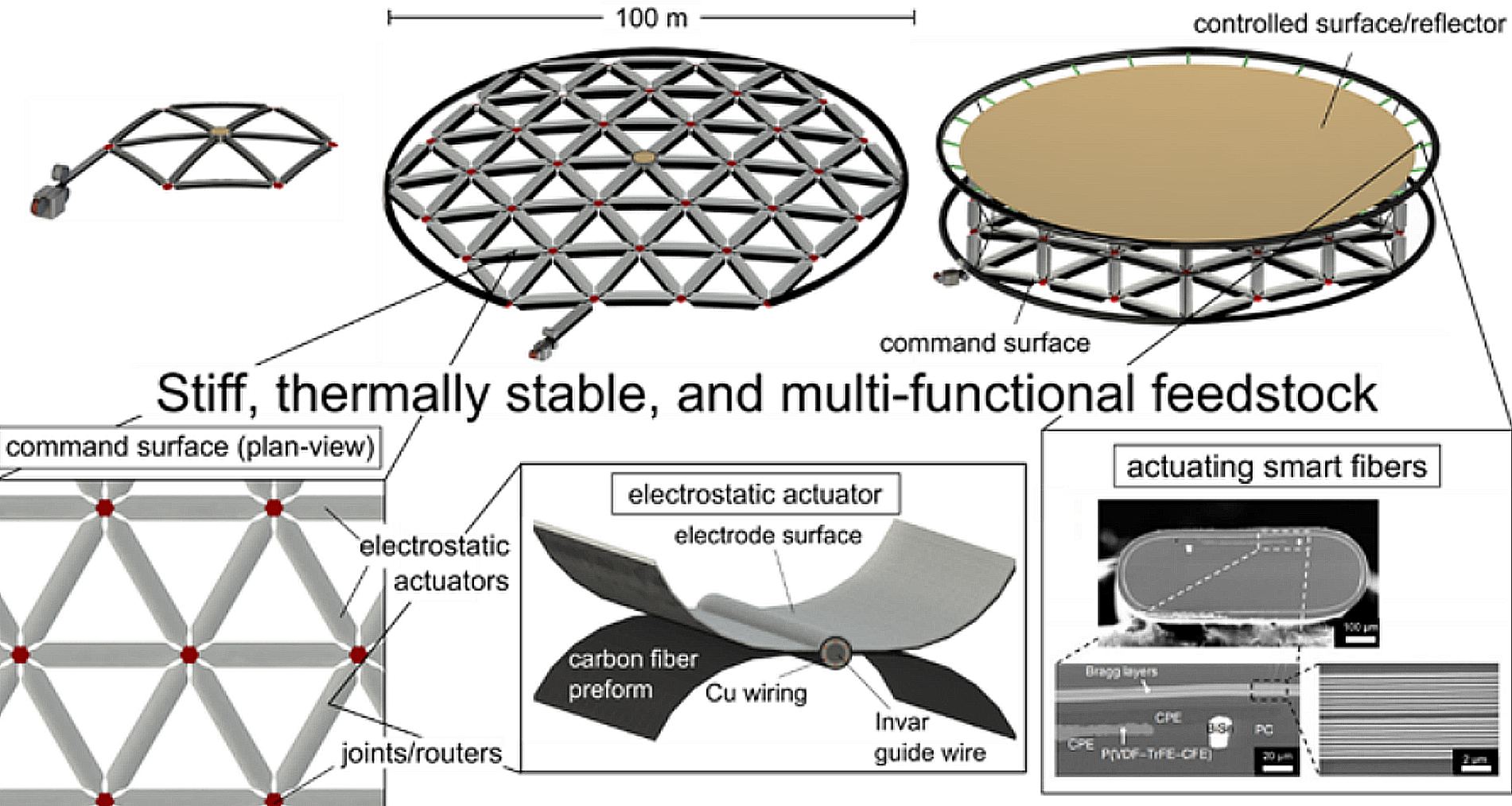
It is an exciting time for astronomers and cosmologists. Since the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have been treated to the most vivid and detailed images of the Universe ever taken. Webb‘s powerful infrared imagers, spectrometers, and coronographs will allow for even more in the near future, including everything from surveys of the early Universe to direct imaging studies of exoplanets. Moreover, several next-generation telescopes will become operational in the coming years with 30-meter (~98.5 feet) primary mirrors, adaptive optics, spectrometers, and coronographs.
Even with these impressive instruments, astronomers and cosmologists look forward to an era when even more sophisticated and powerful telescopes are available. For example, Zachary Cordero
of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently proposed a telescope with a 100-meter (328-foot) primary mirror that would be autonomously constructed in space and bent into shape by electrostatic actuators. His proposal was one of several concepts selected this year by the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program for Phase I development.
It’s Already Hard Enough to Block a Single Star’s Light to See its Planets. But Binary Stars? Yikes

Detecting exoplanets was frontier science not long ago. But now we’ve found over 5,000 of them, and we expect to find them around almost every star. The next step is to characterize these planets more fully in hopes of finding ones that might support life. Directly imaging them will be part of that effort.
But to do that, astronomers need to block out the light from the planets’ stars. That’s challenging in binary star systems.
Continue reading “It’s Already Hard Enough to Block a Single Star’s Light to See its Planets. But Binary Stars? Yikes”Subaru Telescope can now Analyze 2,400 Galaxies Simultaneously
First light is an exciting time for astronomers and engineers who help bring new telescopes up to speed. One of the most recent and significant first light milestones recently occurred at the Subaru Telescope in Hawai’i. Though it has been in operation since 2005, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan’s (NAOJ) main telescope recently received an upgrade that will allow it to simultaneously observe 2400 astronomical objects at once over a patch of sky the size of several moons.
Continue reading “Subaru Telescope can now Analyze 2,400 Galaxies Simultaneously”A New Instrument Gives the Very Large Telescope an Even Sharper View of the Cosmos
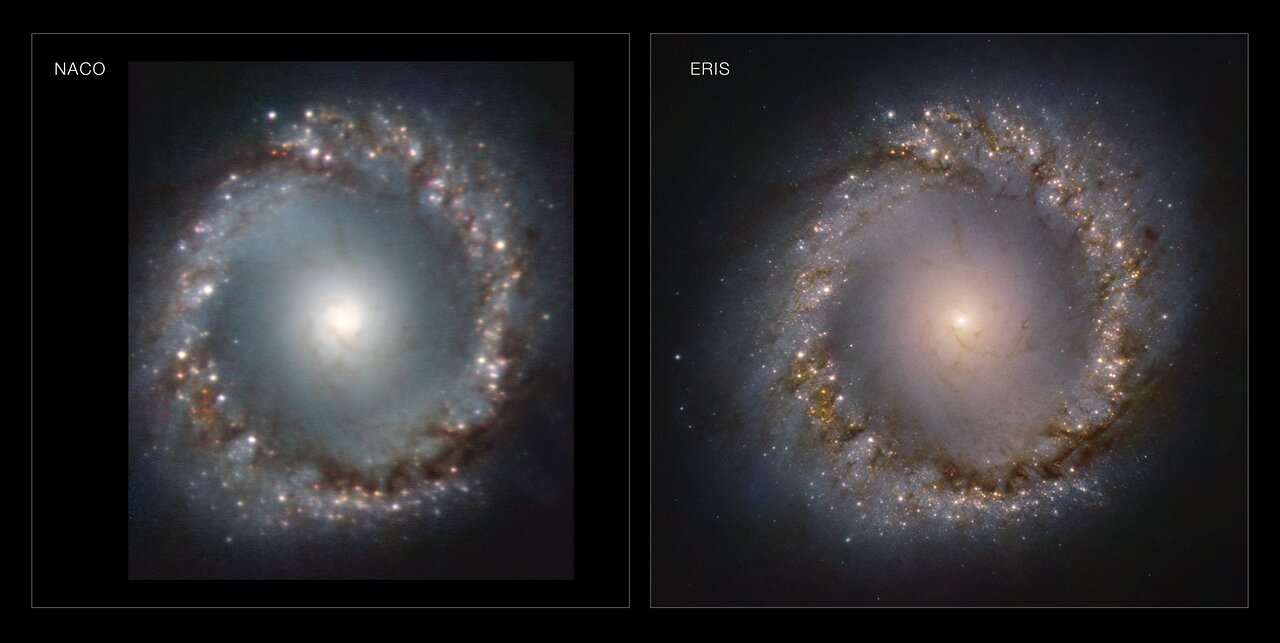

The Very Large Telescope (VLT) at Cerro Paranal in northern Chile, is undoubtedly one of the premier ground-based observatories. But a new infrared instrument recently installed on the telescope has made the VLT even better.
The Enhanced Resolution Imager and Spectrograph (ERIS) was delivered to Chile in December, 2021 and the first test observations were carried out beginning in February of this year. ESO, the European Organization for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, an international organization which coordinates the use of VLT and several other observatories, says this infrared instrument “will be able to see further and in finer detail, leading the way in Solar System, exoplanet and galaxy observations.”
Continue reading “A New Instrument Gives the Very Large Telescope an Even Sharper View of the Cosmos”Three New Potentially Hazardous Asteroids Discovered, Including a big one That Measures 1.5 km Across

An asteroid 1.5 km across is no joke. Even a much smaller one, about the size of a house, can explode with more power than the first nuclear weapons. When an asteroid is greater than 1 km in diameter, astronomers call them “planet-killers.” The impact energy released from a planet-killer striking Earth would be devastating, so knowing where these asteroids are and where they’re headed is critically important.
Our defensive capability against asteroid strikes is in its infancy, so advance notice of asteroids that could cross Earth’s orbit is critical. We’ll need time to prepare.
Continue reading “Three New Potentially Hazardous Asteroids Discovered, Including a big one That Measures 1.5 km Across”A Planet has Been Found That Shifts In and Out of the Habitable Zone
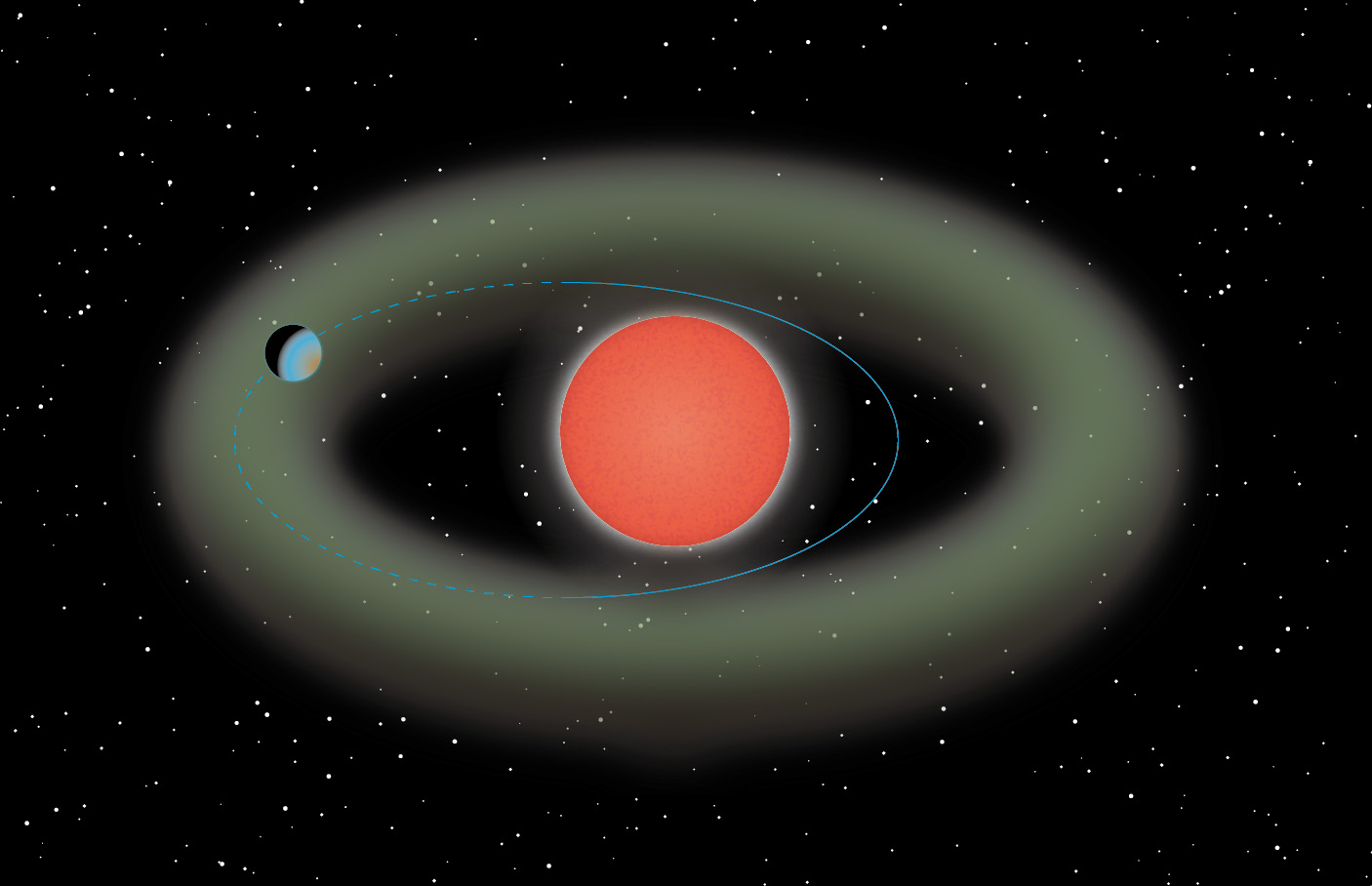
A super-Earth planet has been found orbiting a red dwarf star, only 37 light-years from the Earth. Named Ross 508 b, the newly found world has an unusual elliptical orbit that causes it to shift in and out of the habitable zone. Therefore, part of the time conditions would be conducive for liquid water to exist on the planet’s surface, but other times it wouldn’t.
Continue reading “A Planet has Been Found That Shifts In and Out of the Habitable Zone”The World's Largest Liquid-Mirror Telescope Comes Online
Ask any astronomer, astrophysicist, or cosmologist, and they’ll probably tell you that a new age of astronomy is upon us! Between breakthroughs in gravitational-wave astronomy, the explosion in exoplanet studies, and the next-generation ground-based and space-based telescopes coming online, it’s pretty evident that we are on the verge of an era of near-continuous discovery! As always, major discoveries, innovations, and the things they enable inspire scientists and researchers to look ahead and take the next big step.
Take, for example, the research into liquid mirrors and advanced interferometers, which would rely on entirely new types of telescopes and light-gathering to advance the science of astronomy. A pioneering example is the newly-commissioned International Liquid Mirror Telescope (ILMT) telescope that just came online at Devasthal Peak, a 2,450 m (8,040 ft) tall mountain located in the central Himalayan range. Unlike conventional telescopes, the ILMT relies on a rapidly-rotating 4-meter (13 ft) mirror coated with a layer of mercury to capture cosmic light.
Continue reading “The World's Largest Liquid-Mirror Telescope Comes Online”



