Explorers either have the benefit of having maps or the burden of creating them. Similarly, space explorers have been building maps as they go, using all available tools. Those tools might not always be up to the task, but at least something is better than nothing. Now, a new map of an exploration destination has emerged – a map of the river valleys of Titan.
Continue reading “A map of River Beds on Titan for Dragonfly to Explore”Accurately Forecasting the Weather on Mars and Titan
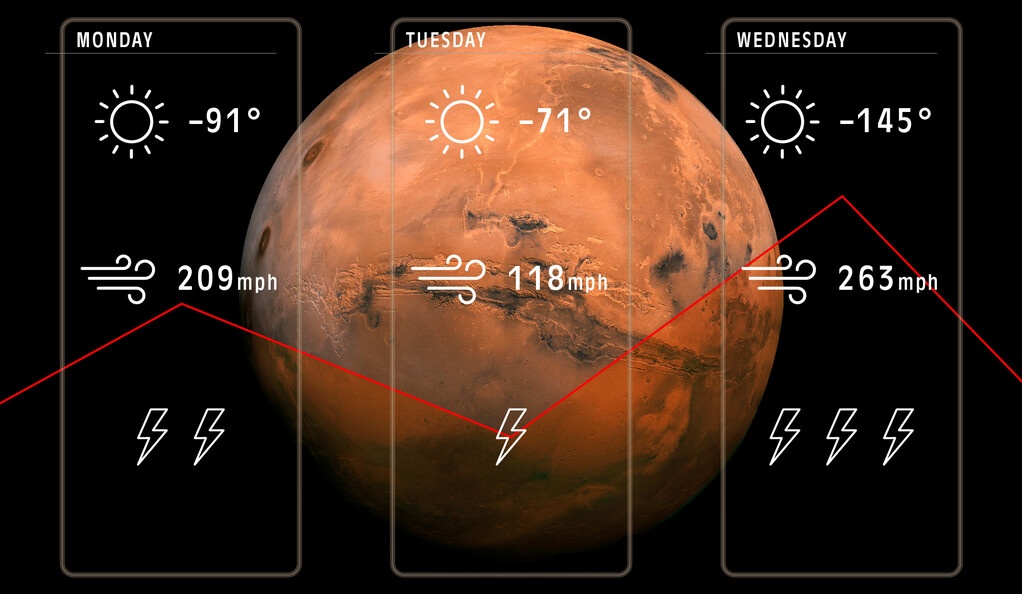
Even meteorologists who forecast the weather on Earth admit that they can’t always accurately predict the weather at a specific location on our planet any given time. And so, attempting to forecast the atmospheric conditions on another world can be downright impossible.
But a new study suggests that an oft-used forecasting technique on Earth can be applied to other worlds as well, such as on Mars or Titan, Saturn’s largest moon.
Continue reading “Accurately Forecasting the Weather on Mars and Titan”Dragonfly Mission has Some Ambitious Science Goals to Accomplish When it Arrives at Titan
As any good project manager will tell you, goals are necessary to complete any successful project. The more audacious the goal, the more potentially successful the project will be. But bigger goals are harder to hit, leading to an increased chance of failure. So when the team behind one of NASA’s most unique missions released a list of goals this week, the space exploration world took notice. One thing is clear – Dragonfly will not lack ambition.
Continue reading “Dragonfly Mission has Some Ambitious Science Goals to Accomplish When it Arrives at Titan”A Titan Mission Could Refuel on Site and Return a Sample to Earth
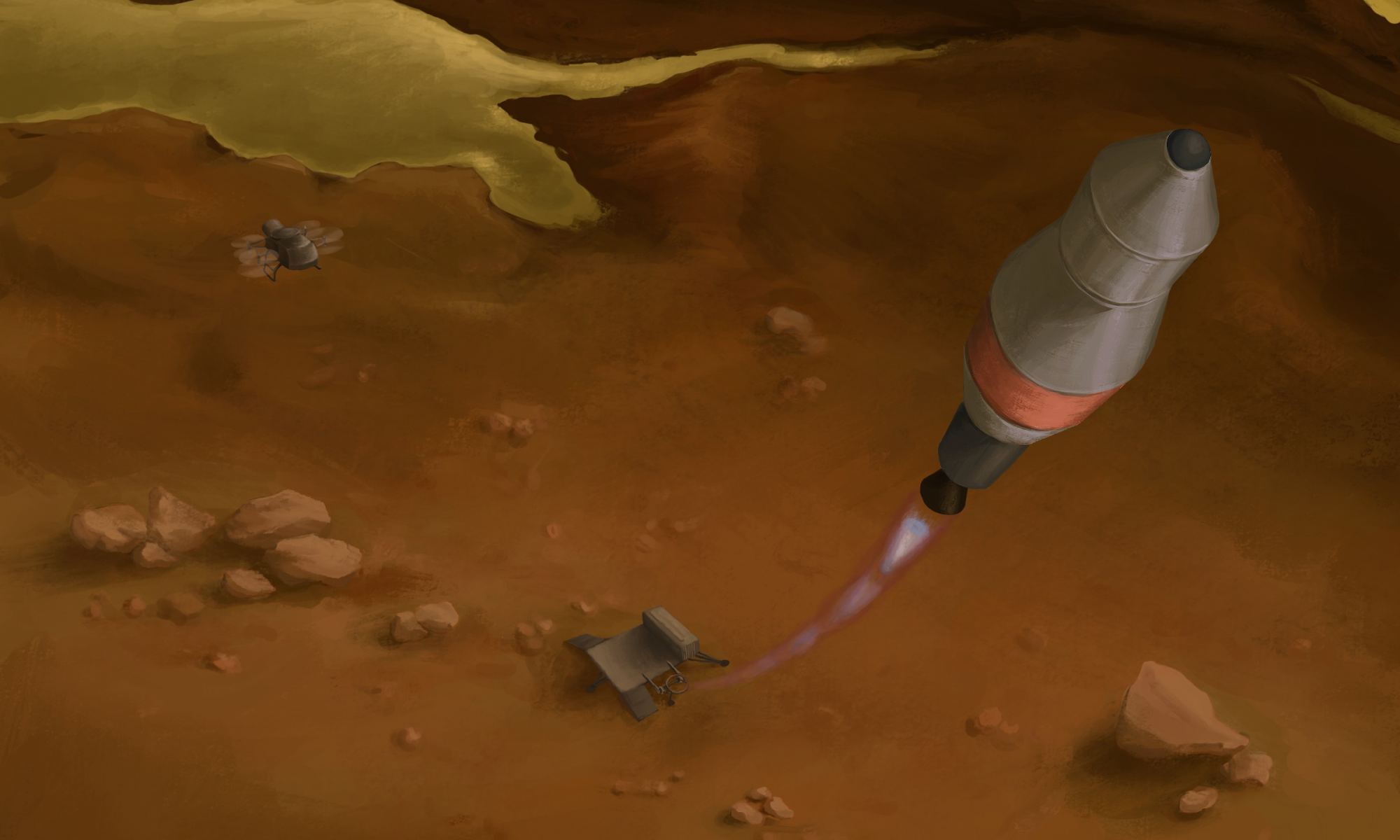
This decade promises to be an exciting time for space exploration! Already, the Perseverance rover landed on Mars and began conducting science operations. Later this year, the next-generation James Webb Space Telescope, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), and Lucy spacecraft (the first mission to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids) will launch. Before the decade is out, missions will also be sent to Europa and Titan to extend the search for signs of life in our Solar System.
Currently, NASA’s plan for exploring Titan (Saturn’s largest moon) is to send a nuclear-powered quadcopter to explore the atmosphere and surface (named Dragonfly). However, another possibility that was presented this year as part of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program is to send a sample-return vehicle with Dragonfly that could fuel up using liquid methane harvested from Titan’s surface.
Continue reading “A Titan Mission Could Refuel on Site and Return a Sample to Earth”Titan’s Atmosphere Recreated in an Earth Laboratory
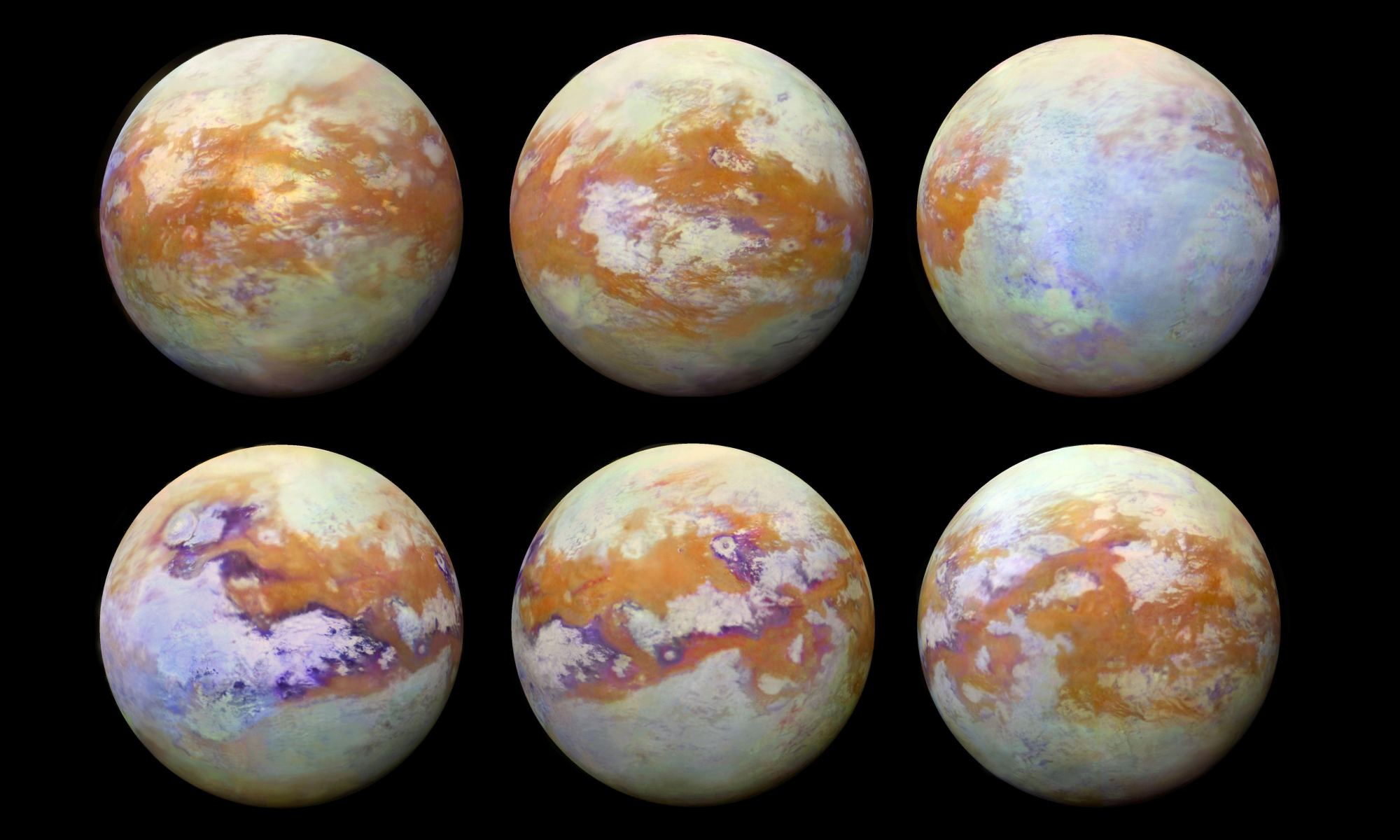
Beyond Earth, the general scientific consensus is that the best place to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life is Mars. However, it is by no means the only place. Aside from the many extrasolar planets that have been designated as “potentially-habitable,” there are plenty of other candidates right here in our Solar System. These include the many icy satellites that are thought to have interior oceans that could harbor life.
Among them is Titan, Saturn’s largest moon that has all kinds of organic chemistry taking place between its atmosphere and surface. For some time, scientists have suspected that the study of Titan’s atmosphere could yield vital clues to the early stages of the evolution of life on Earth. Thanks to new research led by tech-giant IBM, a team of researchers has managed to recreate atmospheric conditions on Titan in a laboratory.
Continue reading “Titan’s Atmosphere Recreated in an Earth Laboratory”The Largest Sea On Titan Could Be Over 300 Meters Deep
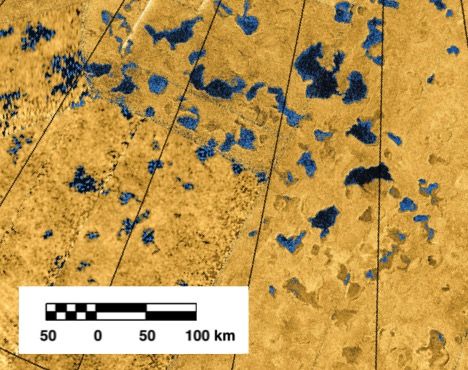
The Earth’s oceans are notoriously unexplored, and stand as a monument to the difficult of exploring underwater. But they aren’t the only unexplored seas in the solar system. Titan’s vast collection of liquid methane lakes are another challenge facing future solar system explorers.
A submarine mission to Saturn’s largest moon has long been under discussion. More recently, scientists have discovered that if such a mission was ever launched, it would have plenty of room to operate, because Titan’s largest sea is likely more than 300 m (1000 ft) deep.
Continue reading “The Largest Sea On Titan Could Be Over 300 Meters Deep”Titan’s Atmosphere Has All the Ingredients For Life. But Not Life as We Know It

Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a team of scientists has identified a mysterious molecule in Titan’s atmosphere. It’s called cyclopropenylidene (C3H2), a simple carbon-based compound that has never been seen in an atmosphere before. According to the team’s study published in The Astronomical Journal, this molecule could be a precursor to more complex compounds that could indicate possible life on Titan.
Similarly, Dr. Catherine Neish of the University of Western Ontario’s Institute for Earth and Space Exploration (Western Space) and her colleagues in the European Space Agency (ESA) found that Titan has other chemicals that could be the ingredients for exotic life forms. In their study, which appeared in Astronomy & Astrophysics, they present Cassini mission data that revealed the composition of impact craters on Titan’s surface.
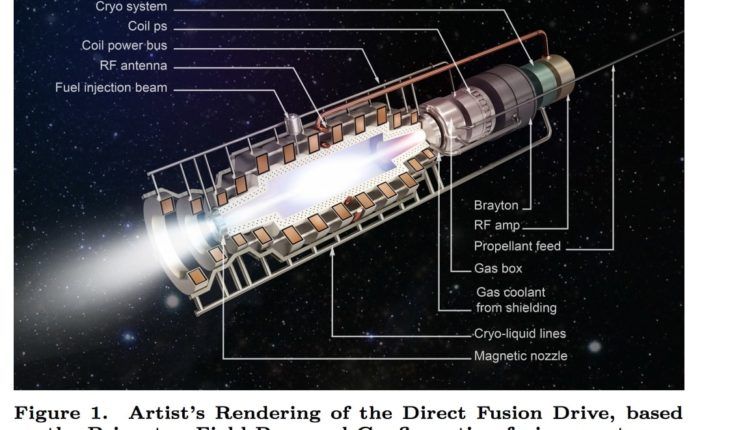
Continue reading “Titan’s Atmosphere Has All the Ingredients For Life. But Not Life as We Know It”Impatient? A Spacecraft Could Get to Titan in Only 2 Years Using a Direct Fusion Drive
Fusion power is the technology that is thirty years away, and always will be – according to skeptics at least. Despite its difficult transition into a reliable power source, the nuclear reactions that power the sun have a wide variety of uses in other fields. The most obvious is in weapons, where hydrogen bombs are to this day the most powerful weapons we have ever produced. But there’s another use case that is much less destructive and could prove much more interesting – space drives.
Continue reading “Impatient? A Spacecraft Could Get to Titan in Only 2 Years Using a Direct Fusion Drive”Lakes On Titan Will Have Layers, Like Lakes On Earth, But for a Completely Different Reason
Lakes on Earth are a common sight in many locales. They’re central to the recreation and livelihood of millions of people. Few of those people think of the hydrodynamics that happen in a lake system. It is common for lakes to stratify into different layers. On Earth that stratification is the result of the sun heating the upper layer of water, which then becomes less dense and floats on top of the colder, more dense layer beneath it. Now, scientists from the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) have found similar dynamic cycles in a different kind of lake – the ethane and methane lakes on Titan.
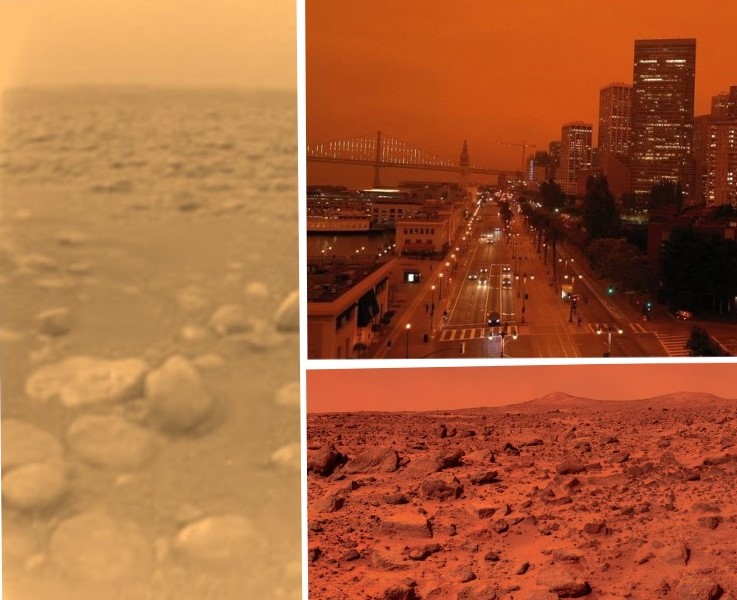
Continue reading “Lakes On Titan Will Have Layers, Like Lakes On Earth, But for a Completely Different Reason”Can you tell the difference between California, Venus, Titan and Mars? Hint: California is the one with buildings.
Californians woke up to an alien-looking sky this morning, Wednesday, September 9, 2020.
Continue reading “Can you tell the difference between California, Venus, Titan and Mars? Hint: California is the one with buildings.”