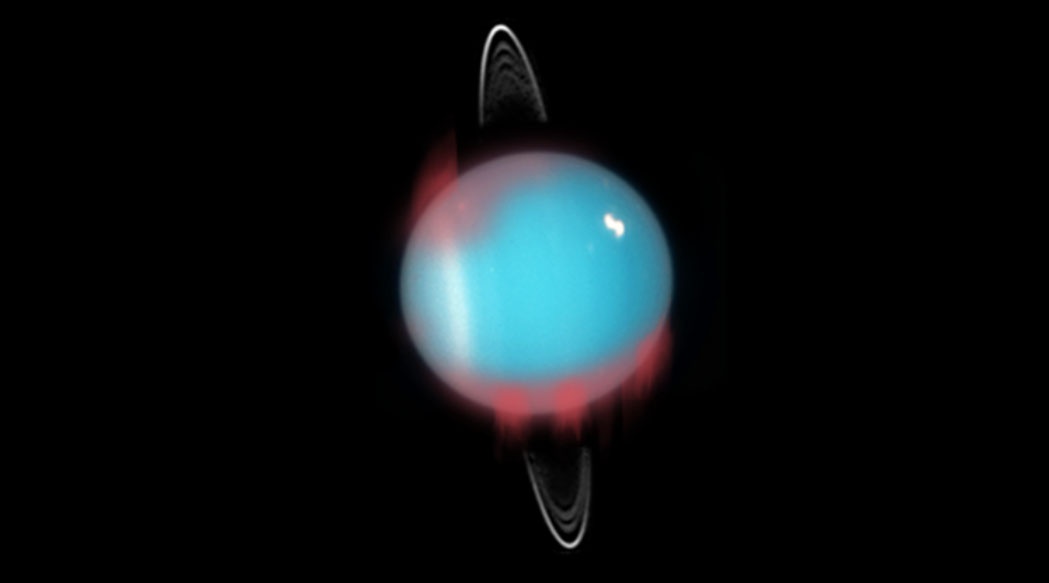
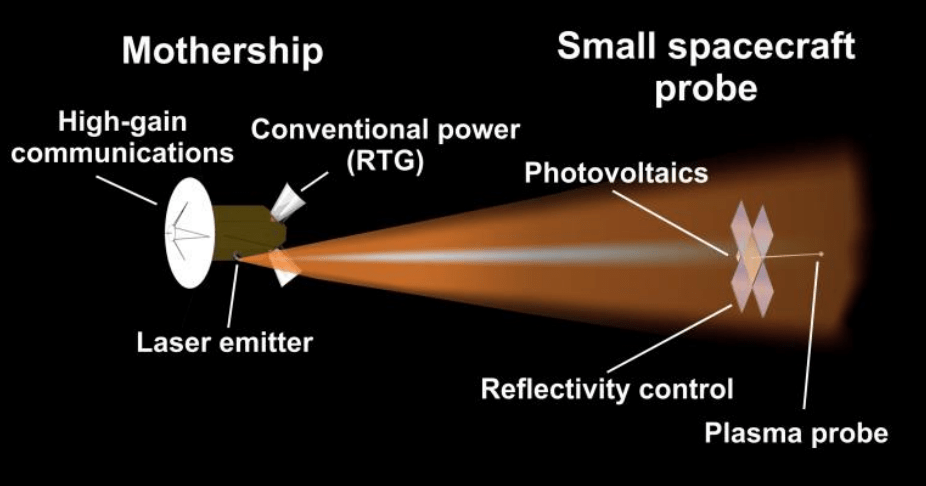
Exploration missions to the outer solar system are still sorely lacking, even though they were highly prioritized in the Planetary Science Decadal Survey from 2013-2022. In fact, many planets in the outer solar system have never even been orbited by a probe. For one in particular – Uranus – we must rely on data from Voyager 2, with instruments designed over 50 years ago, or Earth-based observations. Neither solution can genuinely understand the weird physics going on with this planet that is essentially lying on its side. And while there have been plenty of proposed mission architectures to go and look at it, it’s always fun to take a look at a new one when it pops up. A team from Stanford came up with a new concept called the Sustained CubeSat Activity Through Transmitter Electromagnetic Radiation (SCATTER). It was given a NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts grant to develop the idea further. They released a paper a little while ago, and it’s worth digging into here.
Continue reading “We Could SCATTER CubeSats Around Uranus To Track How It Changes”