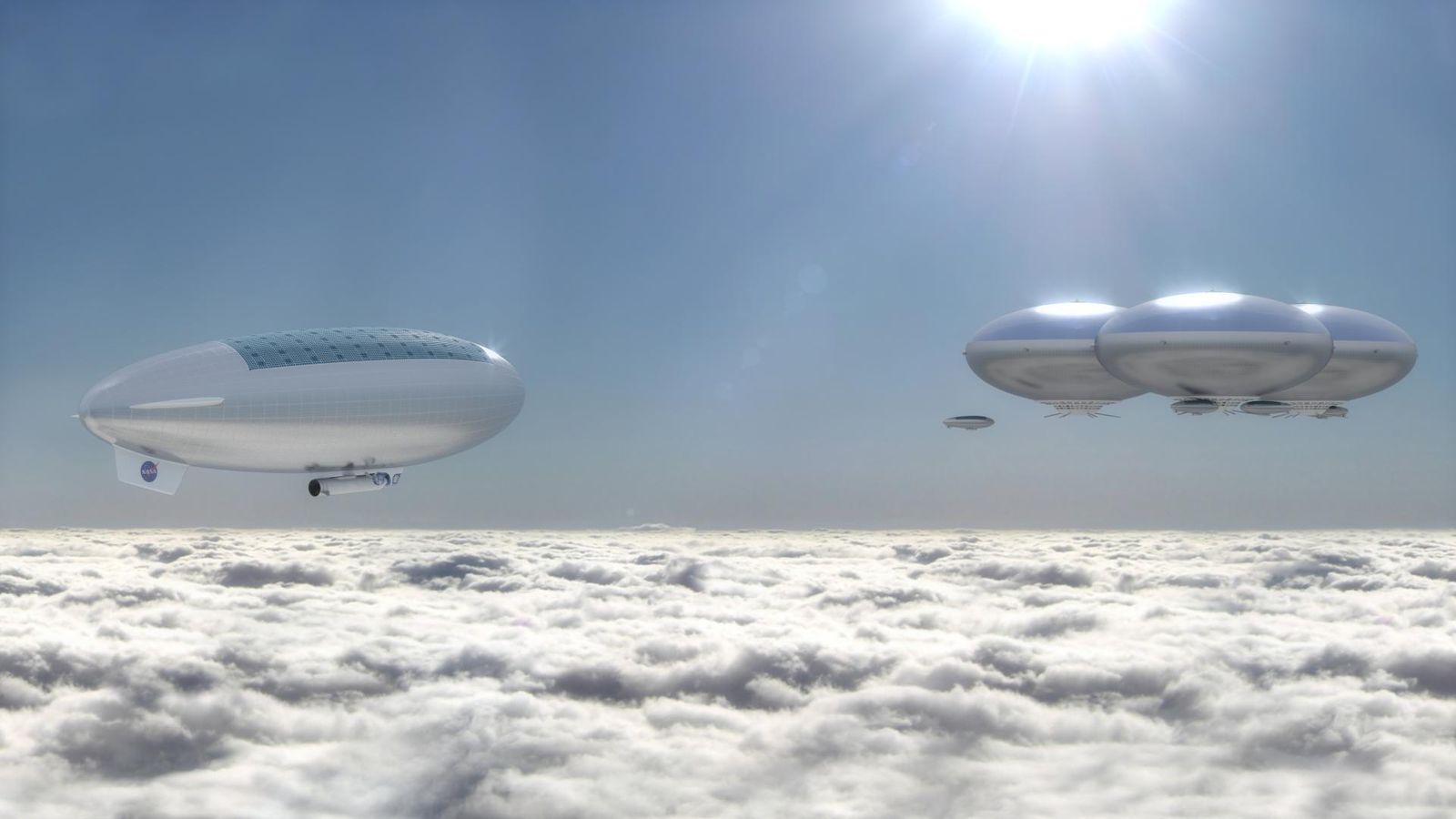
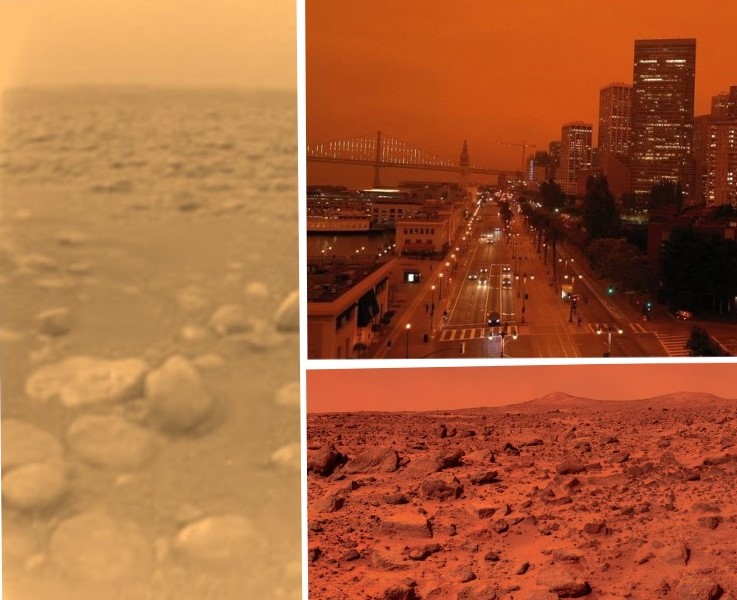
So, Venus might have life! But how do we find out for sure?! We need to GO there.
Continue reading “A Balloon Mission that Could Try to Confirm Life On Venus”Maybe Volcanoes Could Explain the Phosphine in Venus’ Atmosphere

The detection of phosphine in Venus’ atmosphere was one of those quintessential moments in space science. It was an unexpected discovery, and when combined with our incomplete understanding of planetary science, and our wistful hopefulness around the discovery of life, the result was a potent mix that lit up internet headlines.
As always, some of the headlines were a bit of an over-reach. But that’s the way it goes.
At the heart of it all, there is compelling science. And the same, overarching question that keeps popping up: Are we alone?
Continue reading “Maybe Volcanoes Could Explain the Phosphine in Venus’ Atmosphere”Ancient Terrain on Venus Looks Like it Was Formed Through Volcanism
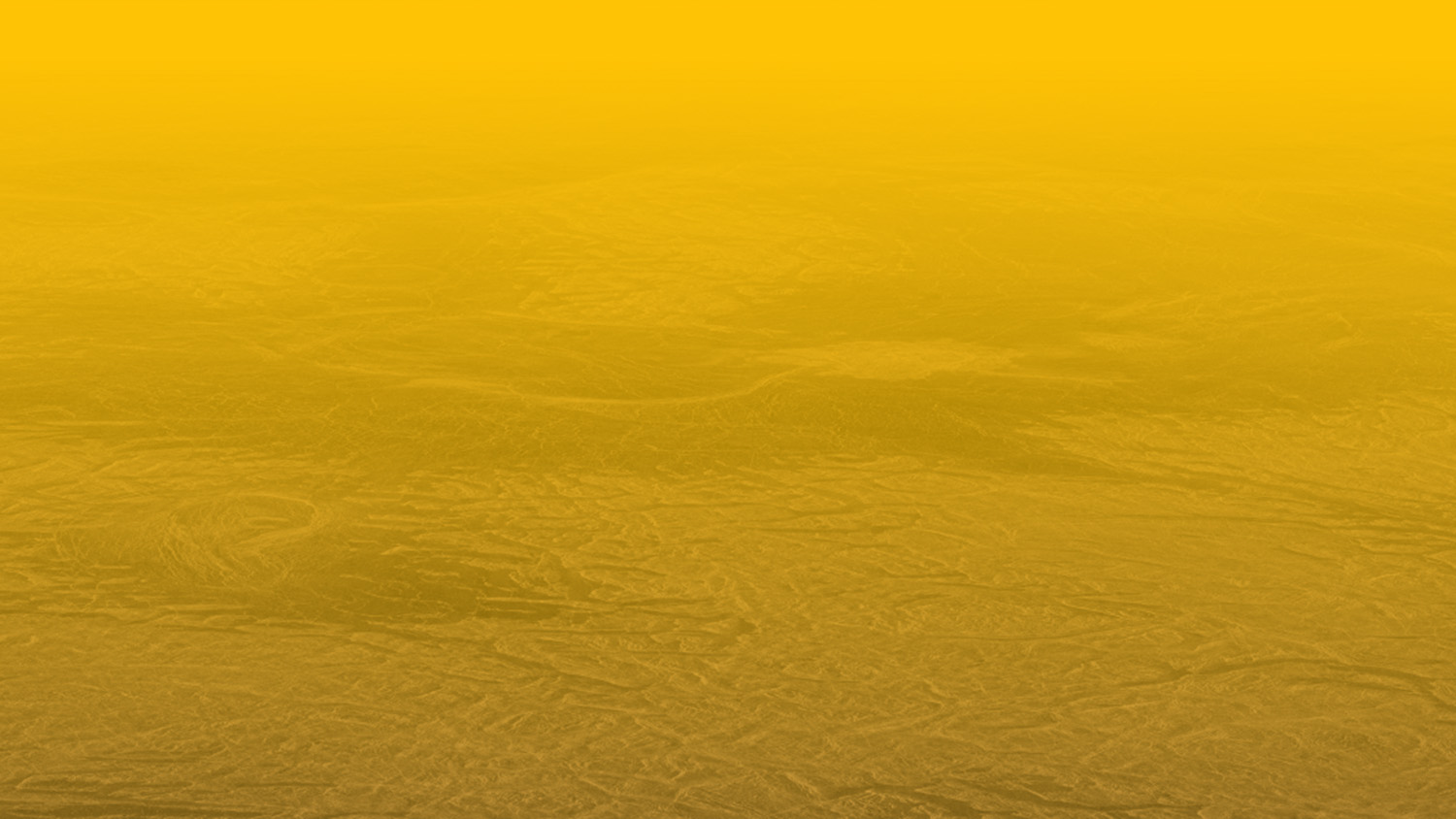

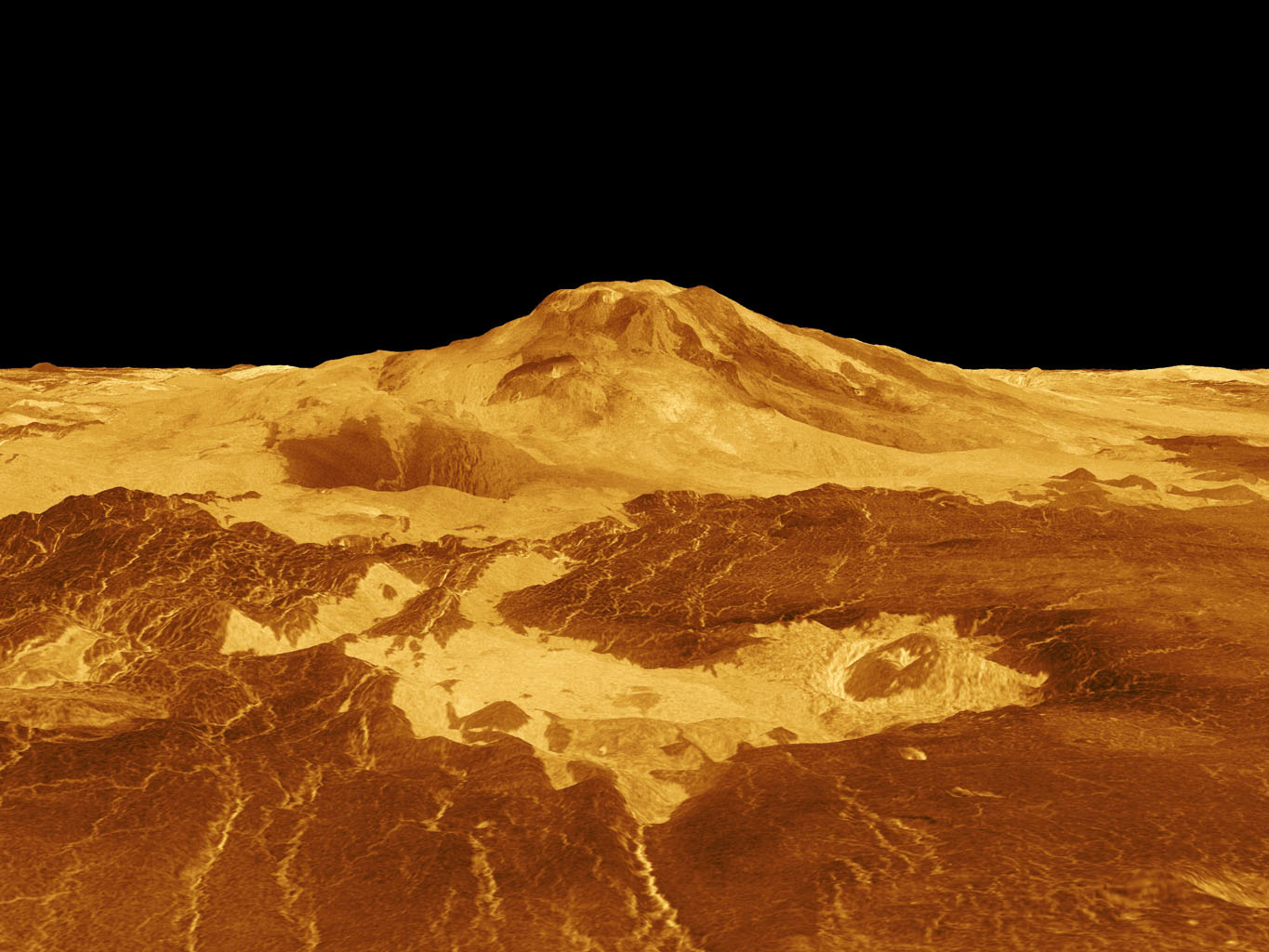
Ever since NASA’s Magellan orbiter was able to peak beneath Venus’ dense cloud layer and map out the surface, scientists have puzzled over the planet’s geological history. One of the greatest mysteries is the role volcanic activity has played in shaping Venus’ surface. In particular, there are what is known as “tesserae,” tectonically deformed regions on the surface that often stand above the surrounding landscape.
These features comprise about 7% of the planet’s surface and are consistently the oldest features in their immediate surroundings (dating to about 750 million years ago). In a new study, an international team of geologists and Earth scientists showed how a significant portion of these tesserae appear to be made up of layered rock, which is similar to features on Earth that are the result of volcanic activity.
Continue reading “Ancient Terrain on Venus Looks Like it Was Formed Through Volcanism”How Much Life Would Be Required to Create the Phosphine Signal on Venus?

A Biosignature
Last week, an incredible announcement was made about the search for extraterrestrial life: Phosphine gas detected in the clouds of Venus – a potential indicator of life or “biosignature.” Now some gases might be a false positive for biosignatures because they can be created by other chemical processes on a planet like photochemical processes in the atmosphere or geological processes beneath the surface that create a given gas. For example, methane can also be a biosignature, and we’ve been hunting it down on Mars, but we know that methane can also be created geologically. Finding phosphine in Venusian clouds is truly remarkable because we don’t presently know of any way to create phosphine abiotically or without life being a part of the equation. Question is – how much life??

Missions Are Already Being Planned to Figure Out What’s Creating the Biosignature on Venus
The discovery of phosphine in the upper clouds in Venus’ atmosphere has generated a lot of excitement. On Earth, phosphine is produced biologically, so it’s a sign of life. If it’s not produced by life, it takes an enormous amount of energy to be created abiologically.
On other planets like Jupiter, there’s enough energy to produce phosphine, so finding it there isn’t surprising. But on a small rocky world like Venus, where there’s no powerful source of energy, its existence is surprising.
This discovery clearly needs some more investigating.
Continue reading “Missions Are Already Being Planned to Figure Out What’s Creating the Biosignature on Venus”Astronomers Have Discovered a 2-km Asteroid Orbiting Closer to the Sun than Venus
Astronomers have painstakingly built models of the asteroid population, and those models predict that there will be ~1 km sized asteroids that orbit closer to the Sun than Venus does. The problem is, nobody’s been able to find one. Until now.
Astronomers working with the Zwicky Transient Facility say they’ve finally found one. But this one’s bigger, at about 2 km. If its existence can be confirmed, then asteroid population models may have to be updated.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have Discovered a 2-km Asteroid Orbiting Closer to the Sun than Venus”Did Scientists Just Find Signs of Life on Venus?

A team of scientists has just published a paper announcing their discovery of a peculiar chemical in the cloudtops of Venus. As far as scientists can tell, this chemical, called phosphine, could only be produced by living processes on a planet like Venus. So the whole internet is jumping on this story.
But did they find signs of life? Or is there another explanation?
Continue reading “Did Scientists Just Find Signs of Life on Venus?”Can you tell the difference between California, Venus, Titan and Mars? Hint: California is the one with buildings.
Californians woke up to an alien-looking sky this morning, Wednesday, September 9, 2020.
Continue reading “Can you tell the difference between California, Venus, Titan and Mars? Hint: California is the one with buildings.”Could There Be Life in the Cloudtops of Venus?

When it comes to places with the potential for habitability, Venus isn’t usually considered on that list. The hot, greenhouse-effect-gone-mad neighboring planet with a crushing surface pressure and sulfuric acid clouds certainly isn’t friendly to life as we know it, and the few spacecraft humanity has sent to Venus’ surface have only endured a few minutes.
But up about 40 to 60 km (25 to 37 miles) above the surface, the atmosphere of Venus is the most Earth-like of any other place in the Solar System. There, Venus has air pressure of approximately 1 bar and temperatures in the 0°C to 50°C range. It’s not quite a shirtsleeves environment, as humans would need air to breathe and protection from the sulfuric acid in the atmosphere. Plus, also consider that Venus is considered to be in the habitable zone of our star.
Continue reading “Could There Be Life in the Cloudtops of Venus?”It Looks Like There are Still Active Volcanoes on Venus
Venus’ surface is no stranger to volcanoes. Radar images show more than 1,000 volcanic structures on the planet. But for the most part, they appear to be ancient and inactive.
Now a new study says that Venus is still volcanically active, and has identified 37 volcanic structures that were recently active. If true, there’s more going on inside Venus than thought.
Continue reading “It Looks Like There are Still Active Volcanoes on Venus”