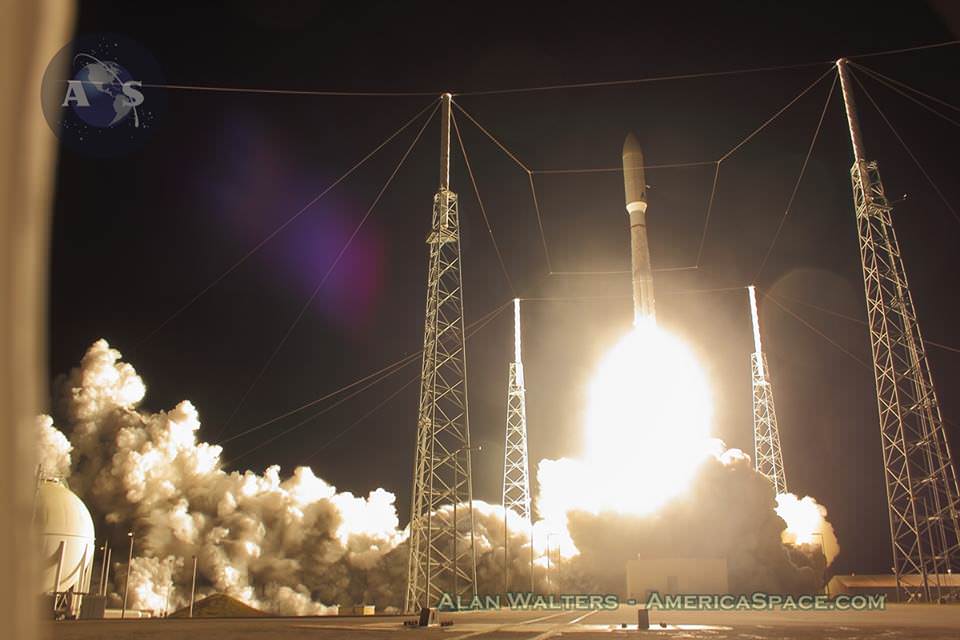
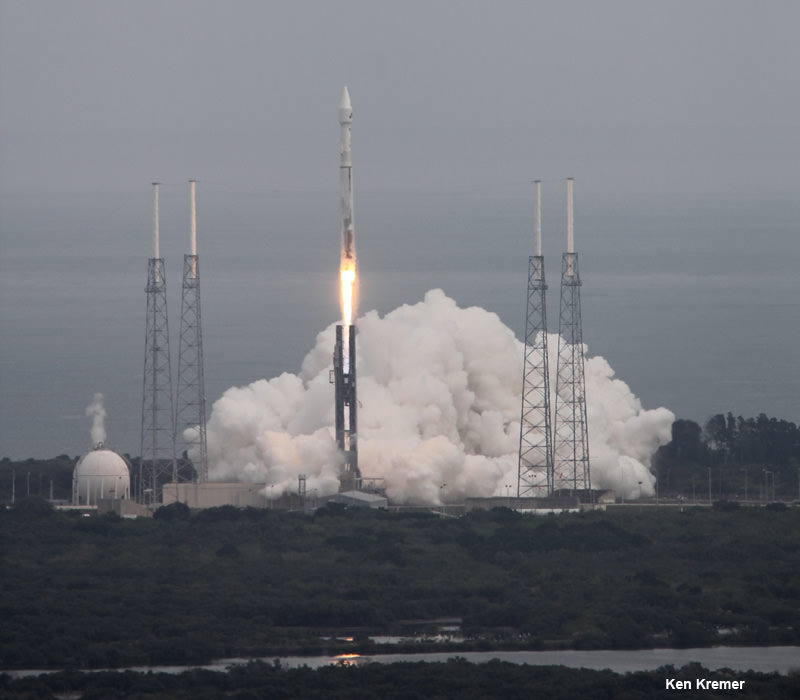
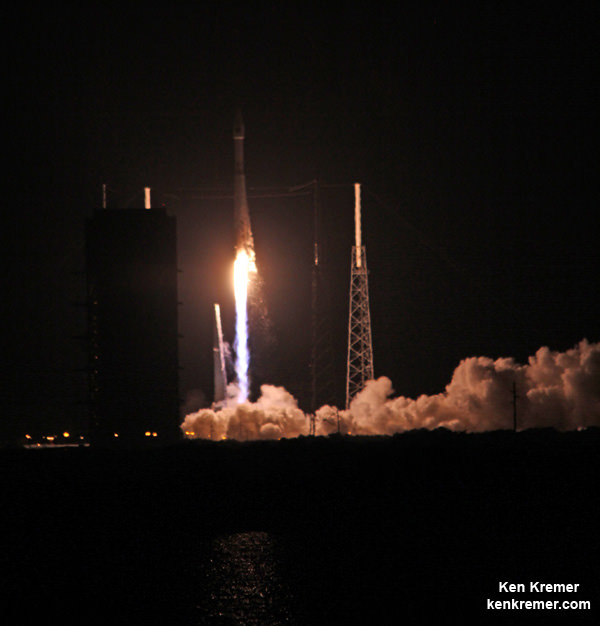
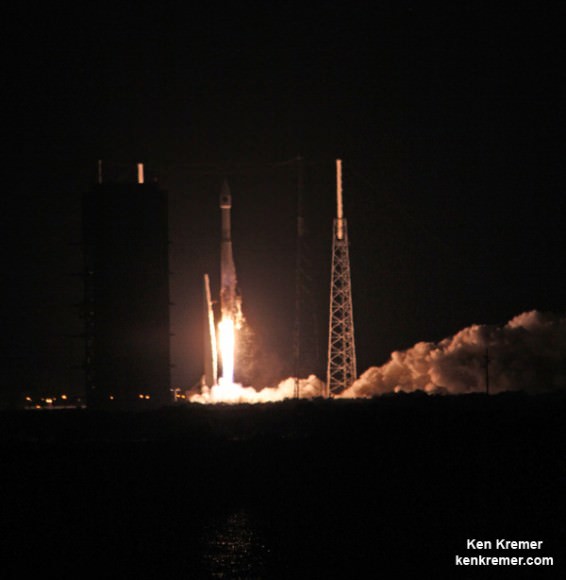
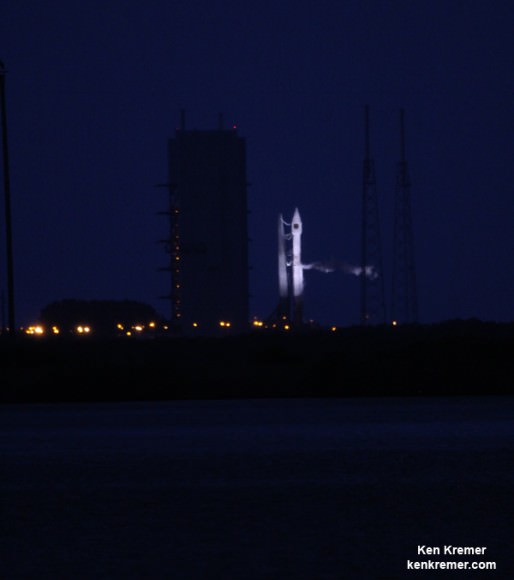
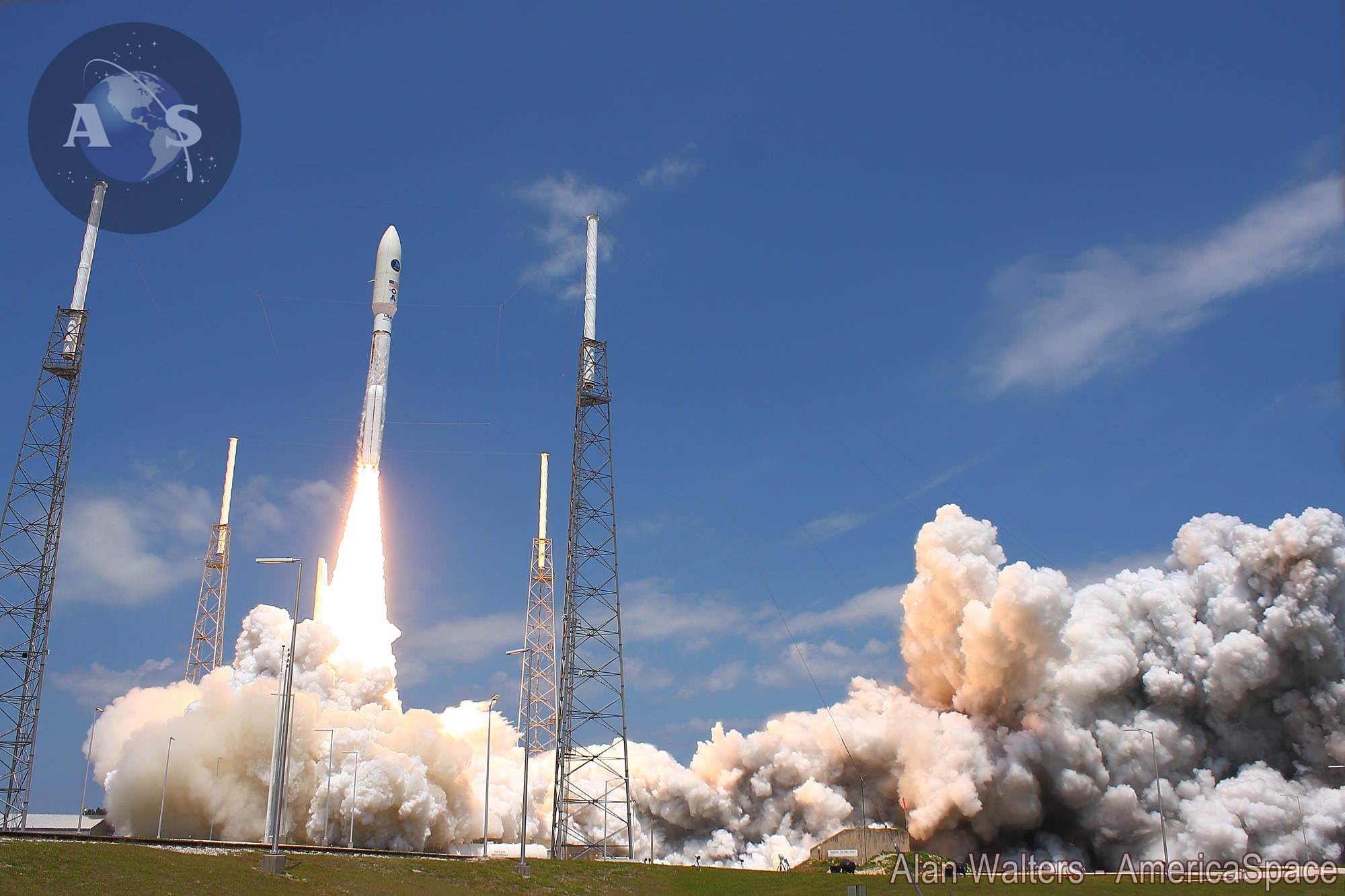
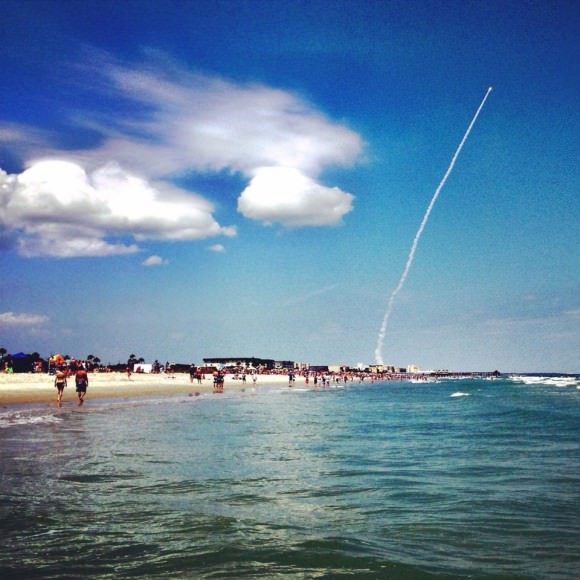
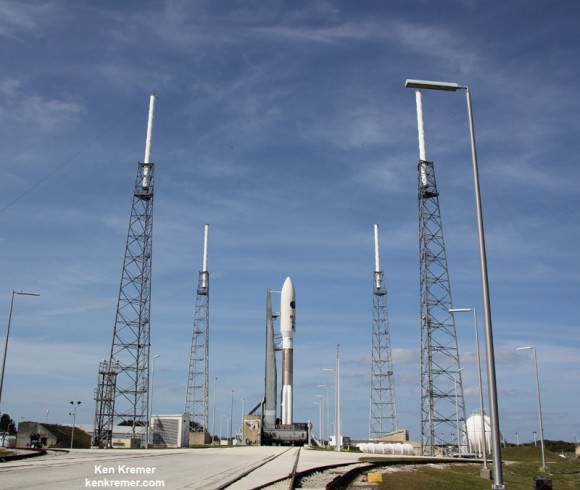
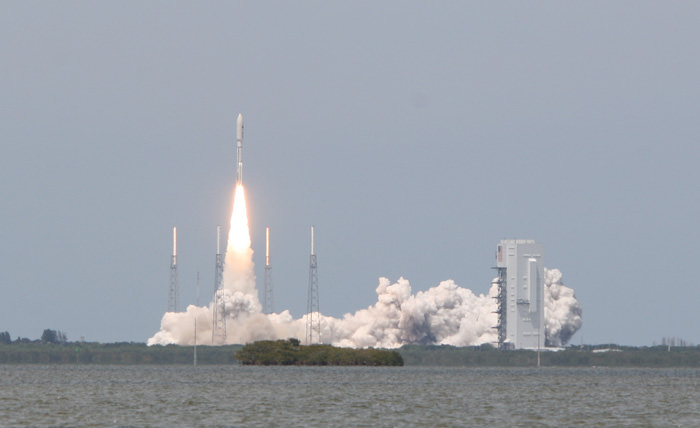
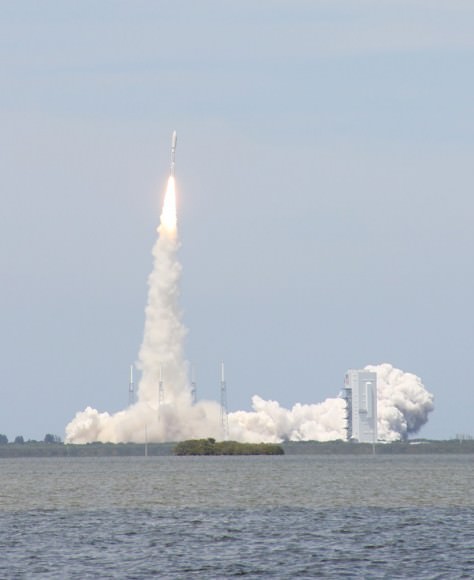
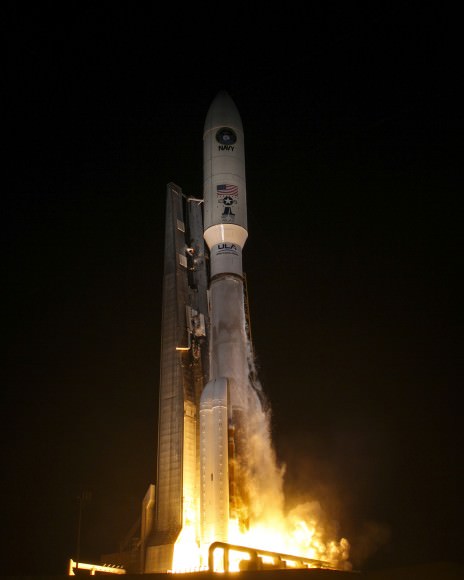
Blastoff of ULA Atlas V rocket lofting MUOS-3 to orbit for the US Navy from Space Launch Complex-41 at 8:04 p.m. EST on Jan. 20, 2015. Credit: Alan Walters/AmericaSpace
See launch gallery below![/caption]
Launching on its milestone 200th mission, the most powerful version of the venerable Atlas-Centaur rocket put on a most spectacular nighttime sky show on Tuesday evening, (Jan. 20) that mesmerized spectators along the Florida Space Coast on a mission to deliver a powerful new next-generation communications satellite to orbit for the US Navy.
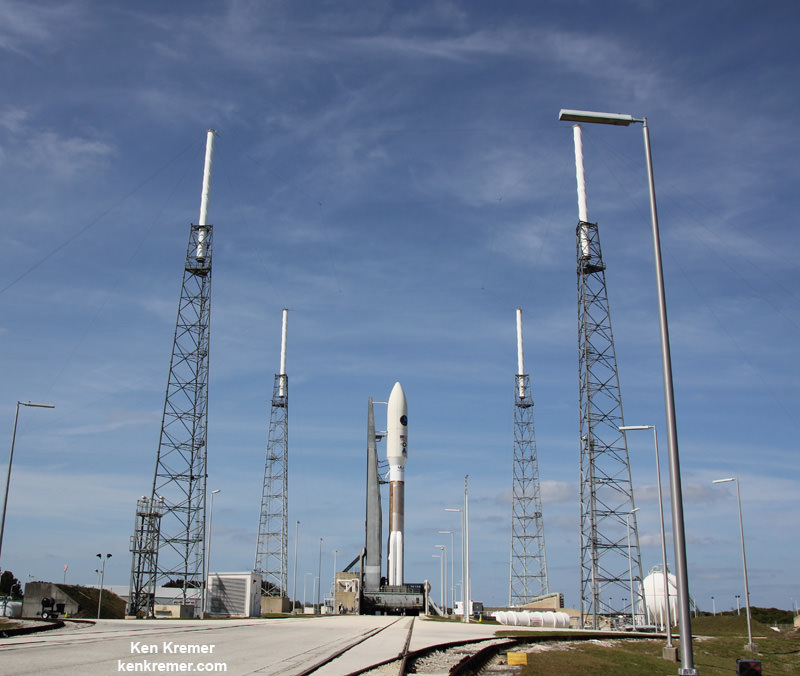
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket carrying the third Mobile User Objective System satellite (MUOS-3) for the United States Navy successfully launched to geostationary orbit from Space Launch Complex-41 at 8:04 p.m. EST from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida on Jan. 20, 2015.
The MUOS-3 launch opened ULA’s planned 13 mission manifest for 2015 with a boisterous bang as the Atlas V booster thundered off the seaside space coast pad.

The MUOS constellation is a next-generation narrowband US Navy tactical satellite communications system designed to significantly improve ground communications to US forces on the move and around the globe.
“The ULA team is honored to deliver this critical mission into orbit for the U.S. Navy and U.S. Air Force with the support of our many mission partners,” said Jim Sponnick, ULA vice president, Atlas and Delta Programs.
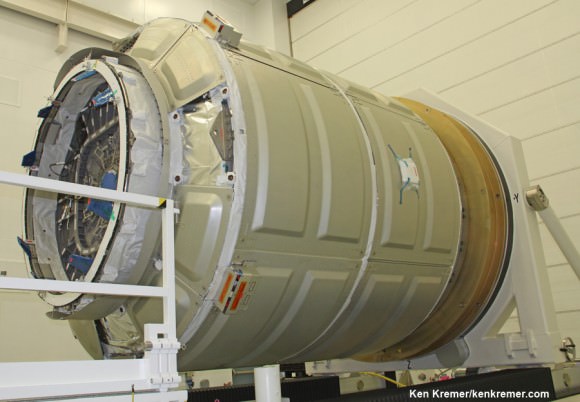
This is the third satellite in the MUOS series and will provide military users 10 times more communications capability over existing systems, including simultaneous voice, video and data, leveraging 3G mobile communications technology. It was built by Lockheed Martin.

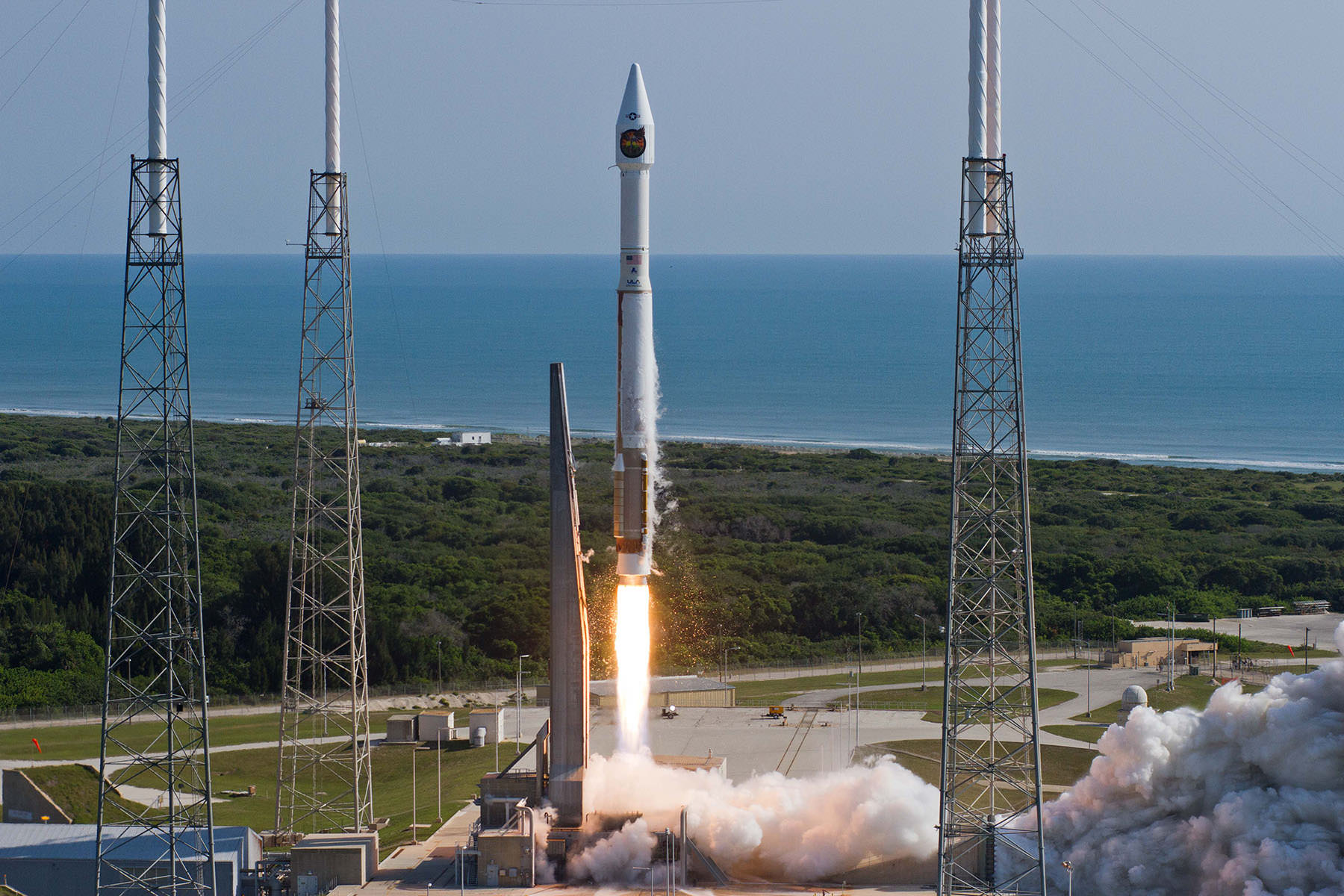
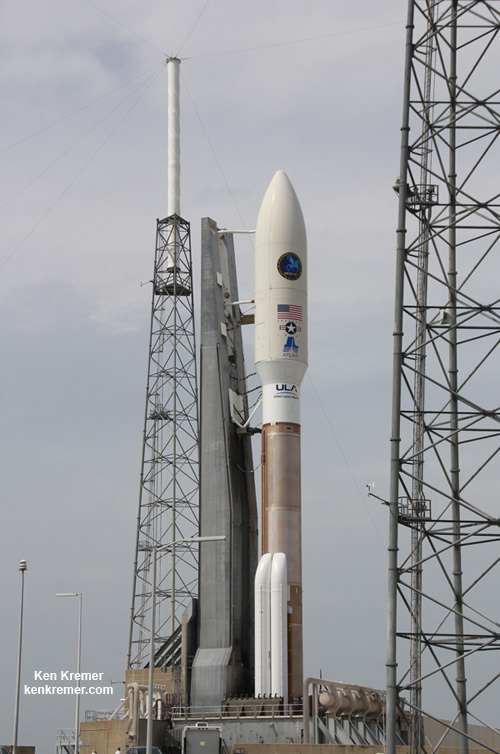
The unmanned Atlas V expendable rocket launched in its mightiest configuration known as the Atlas V 551.
The 206 foot-tall rocket features a 5-meter diameter payload fairing, five Aerojet Rocketdyne first stage strap on solid rocket motors and a single engine Centaur upper stage powered by the Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10C-1 engine.
The first stage is powered by the Russian-built dual nozzle RD AMROSS RD-180 engine. Combined with the five solid rocket motors, the Atlas V first stage generates over 2.5 million pounds of liftoff thrust.
The RD-180 burns RP-1 (Rocket Propellant-1 or highly purified kerosene) and liquid oxygen and delivers 860,200 lb of thrust at sea level.
And the rocket needed all that thrust because the huge MUOS-3 was the heftiest payload lofted by an Atlas V booster, weighing in at some 15,000 pounds.
“The MUOS-3 spacecraft is the heaviest payload to launch atop an Atlas V launch vehicle. The Atlas V generated more than two and half million pounds of thrust at liftoff to meet the demands of lifting this nearly 7.5-ton satellite,” noted Sponnick.
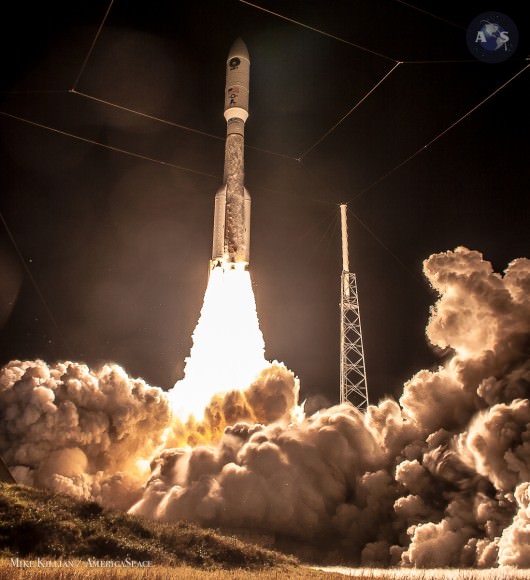

The first Atlas rocket was first launched some 52 years ago.
“Today’s launch was the 200th Atlas-Centaur launch – a very sincere congratulations to the many women and men responsible for the incredible success of the Centaur upper stage over the last 5 decades!”
Overall this was the 52nd Atlas V mission and the fifth in the Atlas V 551 configuration.
The Atlas V 551 version has previously launched two prominent NASA planetary science missions including the New Horizons mission in 2006 that is about to reach Pluto and the Juno orbiter in 2011 that will arrive at Jupiter in July 2016. It was also used to launch MUOS-1 and MUOS-2.

ULA’s second launch in 2015 thunders aloft from the US West Coast with NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive mission (SMAP) next week.
SMAP is the first US Earth-observing satellite designed to collect global observations of surface soil moisture.
SMAP will blastoff from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg AFB at 9:20 a.m. EST (6:20 a.m. PST) on ULA’s Delta II rocket.

In another major milestone coming soon, the Atlas V is right now being man rated since it was chosen to launch the Boeing CST-100 space taxi, which NASA selected as one of two new commercial crew vehicles to launch US astronauts to the ISS as soon as 2017.

The next Atlas launch involves NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission (MMS) to study Earth’s magnetic reconnection. It is scheduled for launch on an Atlas V 421 booster on March 12 from Cape Canaveral. See my up close visit with MMS and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center detailed in my story – here.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.