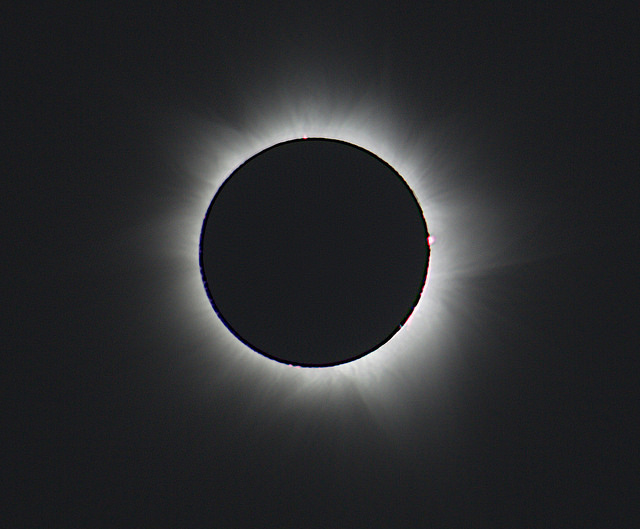
The chase is on. On Sunday, November 3rd, the shadow of the Moon will cross the Earth for one last time in 2013. We recently wrote about the prospects for viewing this “hybrid” annular-total solar eclipse as it crosses the Atlantic and central Africa. Viewers from northern South America across the U.S. Eastern Seaboard up into the Canadian Maritimes will also be treated to a brilliant rising partial eclipse over the Atlantic at sunrise. Tickets are already in hand for many, as umbraphiles wing their way (cue Indiana Jones music) to dusty and exotic far off locales to stand briefly in the shadow of our Moon…
But what if it’s cloudy?
Once the bane of eclipse-chasers, you can now thwart our sometimes murky atmosphere by catching the solar eclipse online.
I remember our first experience with eclipse-chasing on the internet, trying to catch an eclipse broadcast on ye ole dial up modem from an internet café (remember internet cafes?) way back in the late 90s. This was pre-You Tube, pre-UStream. Needless to say, the tenuous connection afforded nary a frozen glimpse of the partially eclipsed Sun, and crashed all together at the onset of totality.
Fast forward to 2013, when ginormous data packets routinely fly around the globe.
True, this eclipse presents a challenge, as it crosses some pretty wild and unconnected terrain. But one standby that we can expect is the good people at Slooh, who have dispatched a broadcast team to the African nations of Gabon and Kenya:
As of this writing, Slooh looks to be going live at around 11:45 UT on Sunday November 3rd. This is 6:45 AM EST, which takes into account our “falling back” one hour to UT -5 hours on Sunday morning. Astronomer Brian Cox will be broadcasting live from Kenya, and the broadcast starts just over two hours prior to the first landfall of totality at just before 14:00 UT. From Gabon, Maximum totality will be a brief 1 minute and 5 seconds, and will dwindle to an even briefer 14 seconds over Lake Turkana in Kenya before ending as a brilliant sunset eclipse over Somalia and Ethiopia. A backup broadcast of the partial phases of the eclipse is also planned from Slooh’s home base site in the Canary Islands.
Another fascinating potential broadcast may come our way from the BRCK organization basing their observations of the eclipse from the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. Billed as “Your Backup Generator for the Internet,” BRCK’s mission is to bring broadband access internet to people in remote regions of the world. This weekend’s eclipse certainly qualifies. As of writing this on Halloween, October 31st, the BRCK team had gone into the field to “stress test” their webcasting capability onsite; follow them on Twitter as @brcknet for the latest updates. As of yet, there’s no embed for the broadcast, though we’ll be sure to drop it in if it surfaces!
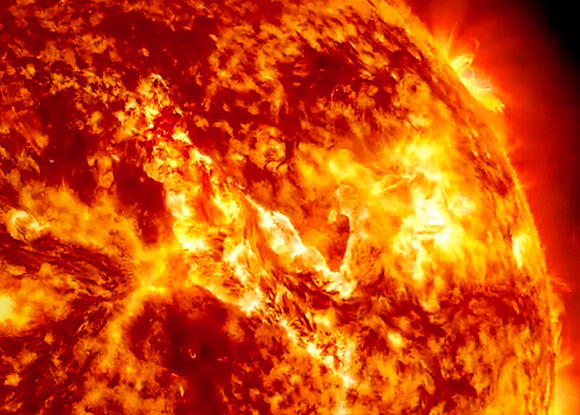
There’s also some interesting science afoot during this eclipse as well. A recent press release out from Williams College notes that Field Memorial Professor of Astronomy and chair of the International Astronomical Union’s Working Group on Eclipses Jay Pasachoff will observe the eclipse, along with a student and tourist expedition from Gabon. A veteran eclipse chaser, Pasachoff will be working in concert with Dr. Vojtech Rusin of the Astronomical Institute of Slovakia, solar researchers Aris Voulgaris and Robert Lucas and William College students to study the ethereal solar corona. Satellite-based coronagraphs, such as the one employed by SOHO, can create an “artificial eclipse” of the Sun to study the corona, but also face the challenge of scattered light via a phenomenon known as Fresnel-diffraction. Pasachoff and team hope to combine their observations with those being routinely carried out by NASA, the European Space Agency and the Royal Observatory in Belgium to characterize the solar corona and improve our understanding of the space weather environment. Pasachoff’s expedition is being assisted via support from the South African Astronomical Observatory, Nommo Astronomia, the Gabon Astronomy Society and the Gabon Space Agency. Veteran eclipse chaser and historian Michael Zeiler (@EclipseMaps) has also joined up with Pasachoff’s group in Gabon.
In space, the NASA/JAXA joint solar observing Hinode spacecraft and ESA’s Sun watching Proba-2 will also catch several partial eclipses from their respective perches in low Earth orbit. Expect to see these pics in the days following Sunday’s eclipse.
We’ll be dropping in more broadcasts as they come to our attention this weekend here at Universe Today. Planning an ad-hoc webcast of the eclipse? Let us know in the comments below! Even if it’s just a brief view of the rising partially eclipsed Sun from the beach, its worth the effort. Just remember that you’ll need a fairly long focal length (in the range of 200mm or longer) and a proper solar filter for the Sun to appear like anything more than a washed out dot in the broadcast. And always run a test of your rig beforehand!
Good luck, happy eclipse chasing, and don’t forget to send those eclipse pics to Universe Today!