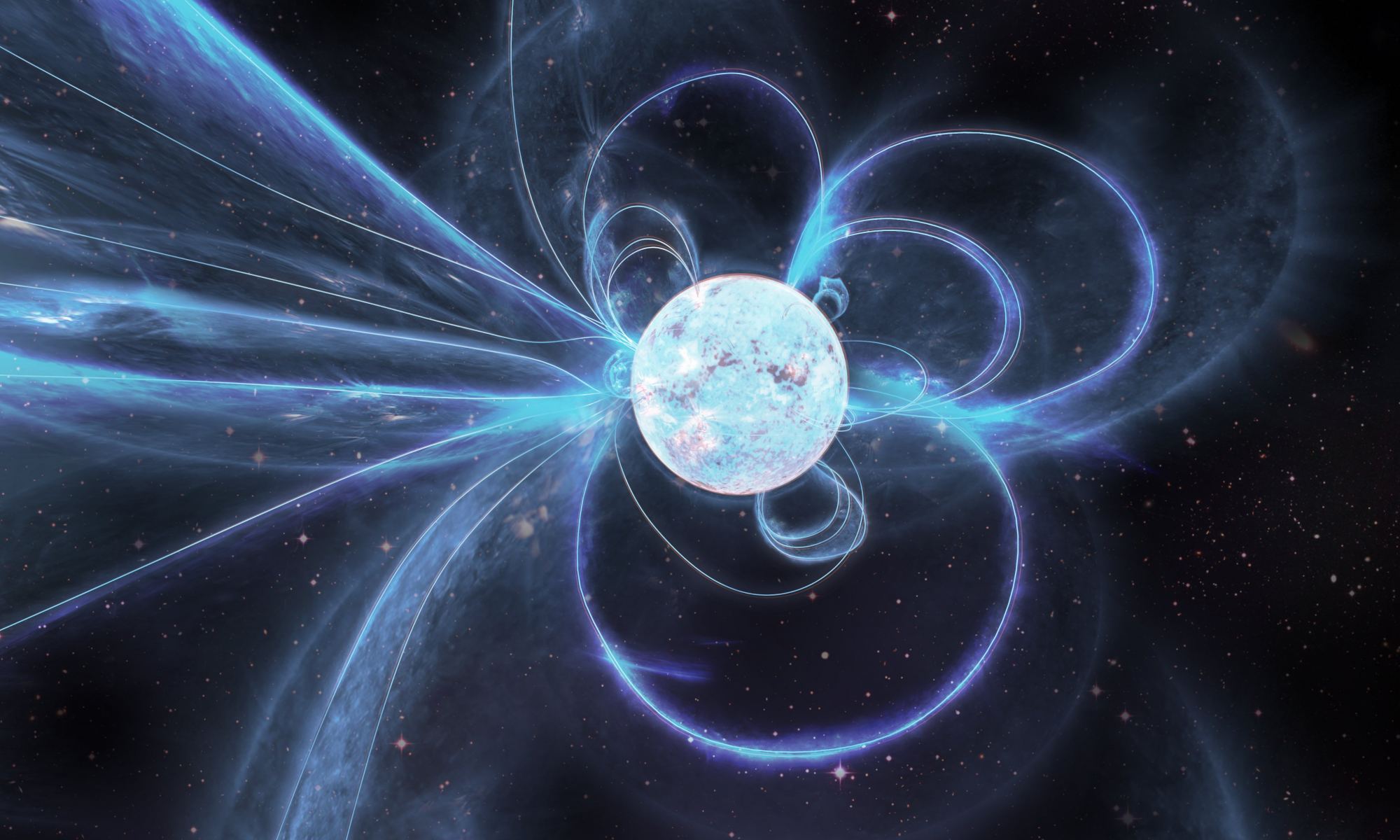
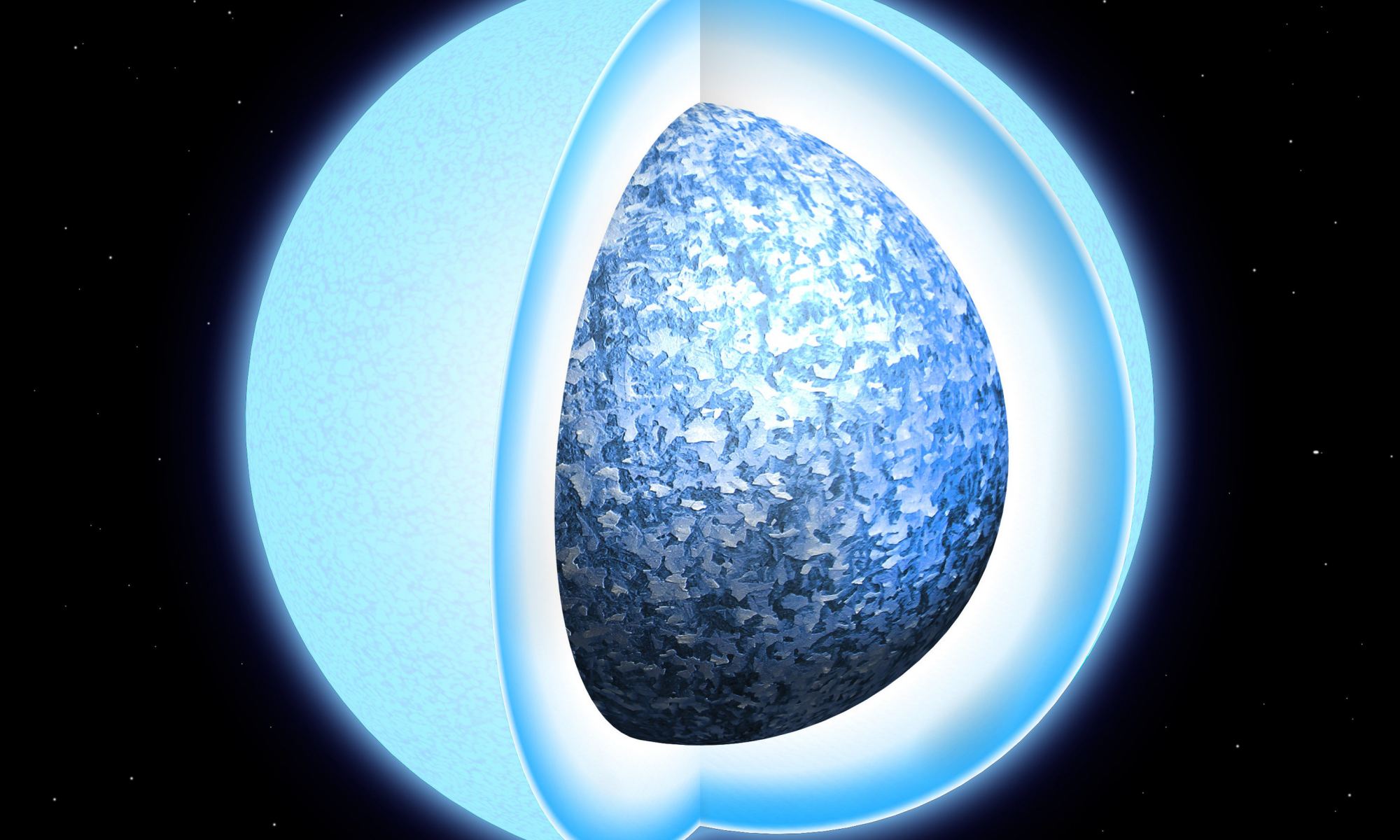
About 97% of all stars in our Universe are destined to end their lives as white dwarf stars, which represents the final stage in their evolution. Like neutron stars, white dwarfs form after stars have exhausted their nuclear fuel and undergo gravitational collapse, shedding their outer layers to become super-compact stellar remnants. This will be the fate of our Sun billions of years from now, which will swell up to become a red giant before losing its outer layers.
Unlike neutron stars, which result from more massive stars, white dwarfs were once about eight times the mass of our Sun or lighter. For scientists, the density and gravitational force of these objects is an opportunity to study the laws of physics under some of the most extreme conditions imaginable. According to new research led by researchers from Caltech, one such object has been found that is both the smallest and most massive white dwarf ever seen.
Continue reading “A Nearby White Dwarf Might be About to Collapse Into a Neutron Star”