Space exploration is a tricky and at times, dangerous business. The safety of the crews is of paramount importance and escape technology is always factored into spacecraft design. Whilst Artemis I did not require such provisions when it launched Artemis II with astronauts on board is being prepared with a ski-lift style escape system to take them far away from the launch pad.
Continue reading “This is How Astronauts Would Escape from the Artemis II Launch Pad”Did We Find Exomoons or Not? The Question Lingers.
Do exoplanets have exomoons? It would be extraordinary if they didn’t, but as with all things, we don’t know until we know. Astronomers thought they may have found exomoons several years ago around two exoplanets: Kepler-1625b and Kepler-1708b. Did they?
Continue reading “Did We Find Exomoons or Not? The Question Lingers.”Atmosphere Pressure Changes Could Explain Mars Methane

One ongoing mystery on Mars is the sporadic detection of atmospheric methane. Since 1999 detections have been made by Earth-based observatories, orbital missions, and on the surface by the Curiosity Rover. However, other missions and observatories have not detected methane at all, and even when detected, the abundances appear to fluctuate seasonally or even daily.
So, where does this intermittent methane come from? A group of scientists have proposed an interesting theory: the methane is being sucked out of the ground by changes in pressure in the Martian atmosphere. The researchers simulated how methane moves underground on Mars through networks of underground fractures and found that seasonal changes can force the methane onto the surface for a short time.
In their paper, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, the scientists say their simulations predict short-lived methane pulses prior to sunrise for Mars’ upcoming northern summer period, which is a candidate time frame for Curiosity’s next atmospheric sampling campaign.
Continue reading “Atmosphere Pressure Changes Could Explain Mars Methane”Another Explanation for K2-18b? A Gas-Rich Mini-Neptune with No Habitable Surface
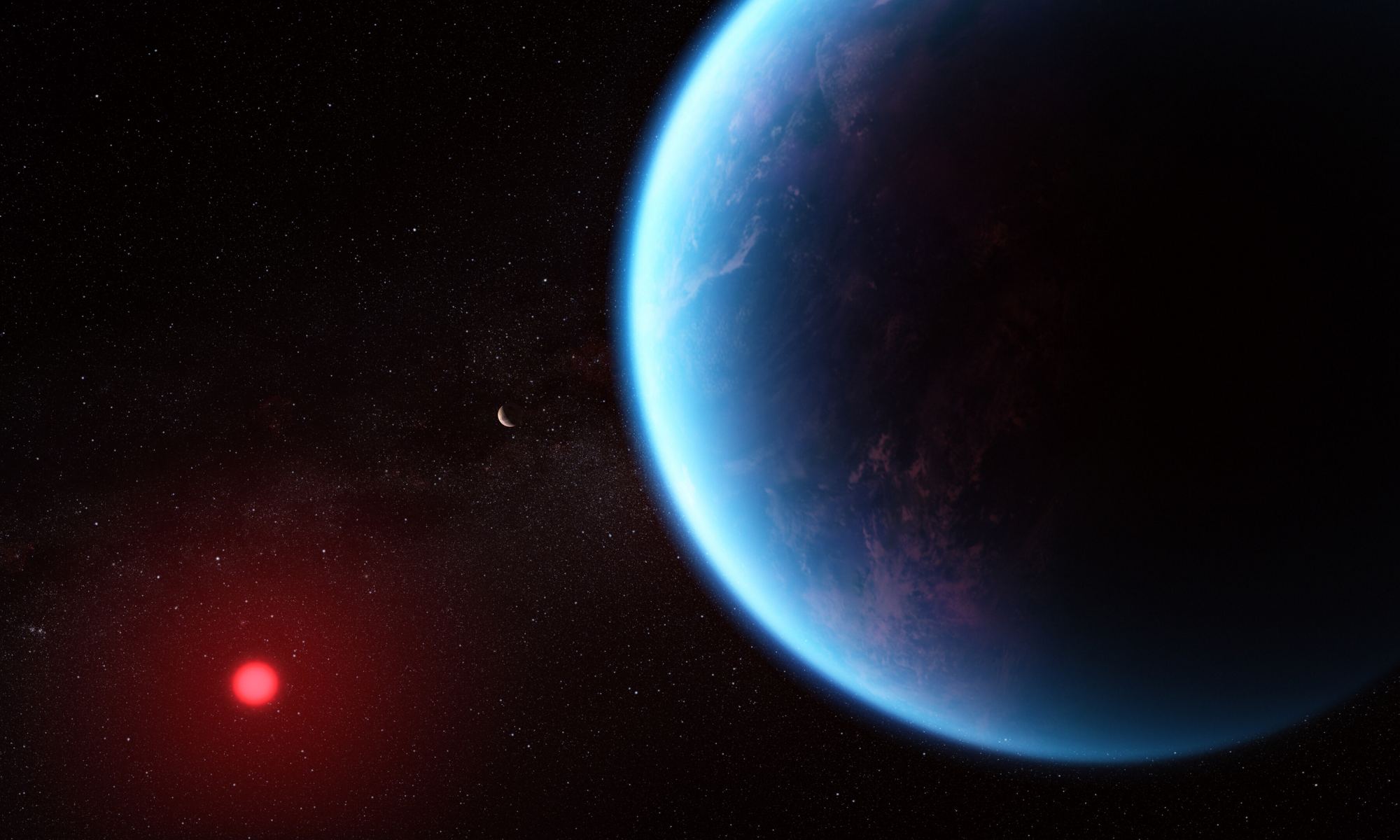

Exoplanet K2-18b is garnering a lot of attention. James Webb Space Telescope spectroscopy shows it has carbon and methane in its atmosphere. Those results, along with other observations, suggest the planet could be a long-hypothesized ‘Hycean World.’ But new research counters that.
Instead, the planet could be a gaseous mini-Neptune.
Continue reading “Another Explanation for K2-18b? A Gas-Rich Mini-Neptune with No Habitable Surface”It's a Fine Line Between a Black Hole Energy Factory and a Black Hole Bomb
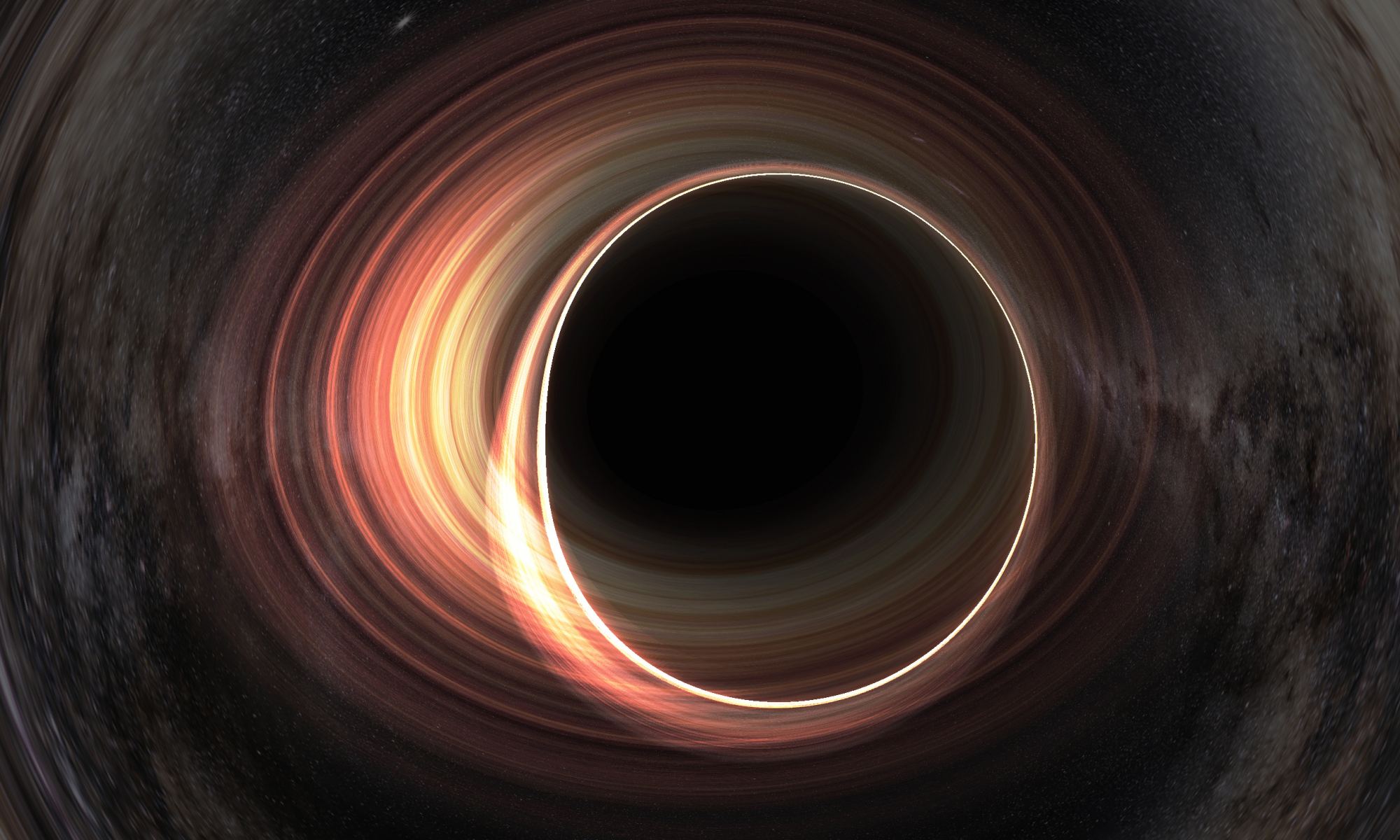
Black holes are powerful gravitational engines. So you might imagine that there must be a way to extract energy from them given the chance, and you’d be right. Certainly, we could tap into all the heat and kinetic energy of a black hole’s accretion disk and jets, but even if all you had was a black hole in empty space, you could still extract energy from a trick known as the Penrose process.
Continue reading “It's a Fine Line Between a Black Hole Energy Factory and a Black Hole Bomb”NASA Gives us an Update on its Long-term Plans for the Moon and Mars

Going to Mars is a major step in space exploration. It’s not a quick jaunt nor will it be easy to accomplish. The trip is already in the planning stages, and there’s a good chance it’ll happen in the next decade or so. That’s why NASA and other agencies have detailed mission scenarios in place, starting with trips to the Moon. Recently, NASA updated its “Moon to Mars Architecture” documents, including a closer look at some key decisions about Mars exploration.
Continue reading “NASA Gives us an Update on its Long-term Plans for the Moon and Mars”There’s Less Dark Matter at the Core of the Milky Way
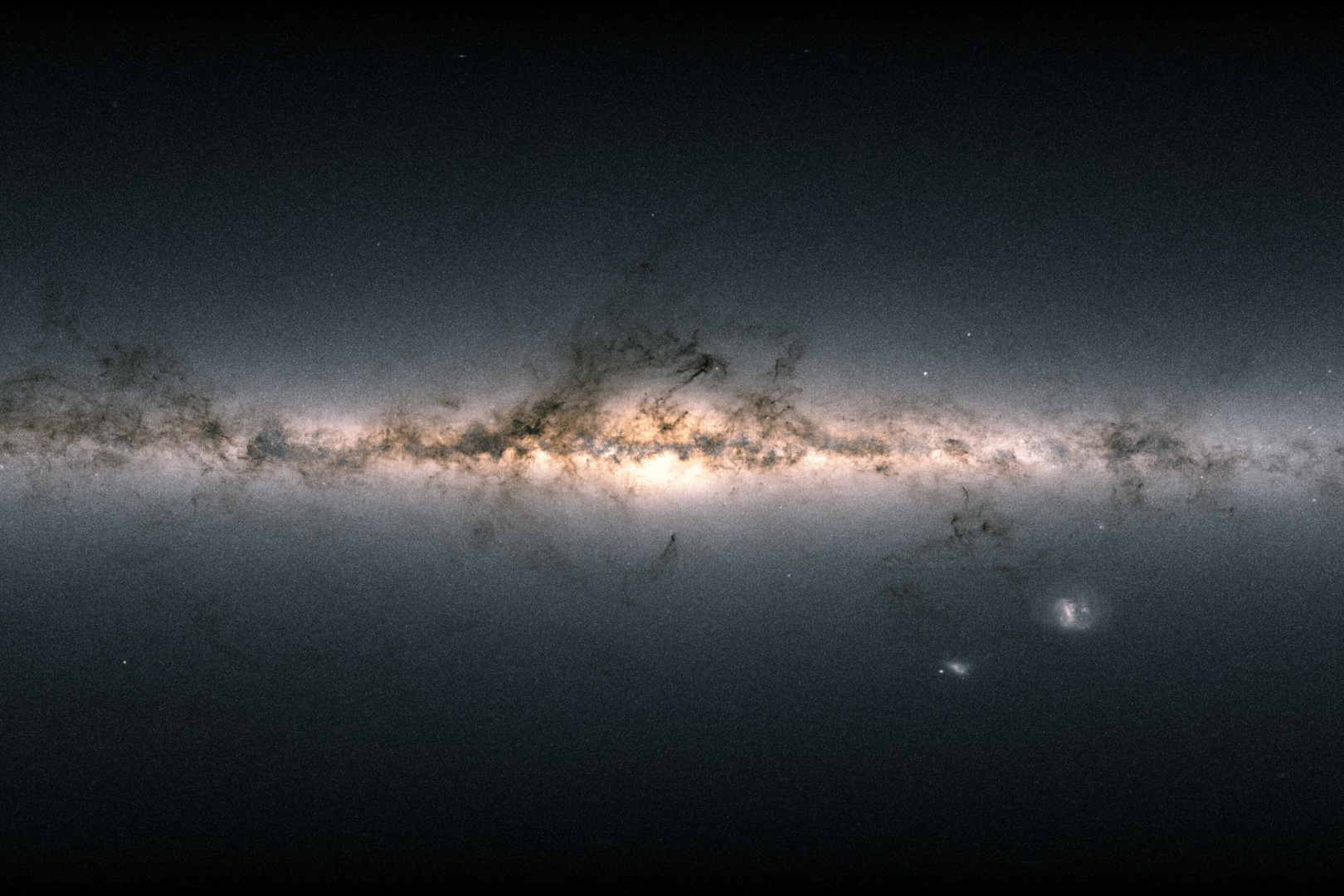

Science really does keep you on your toes. First there was matter and then there were galaxies. Then those galaxies had more stuff in the middle so stars further out were expected to move slowly, then there was dark matter as they actually seemed to move faster but now they seem to be moving slower in our Galaxy so perhaps there is less dark matter than we thought after all!
Continue reading “There’s Less Dark Matter at the Core of the Milky Way”Plants Growing in Space are at Risk from Bacterial Infections
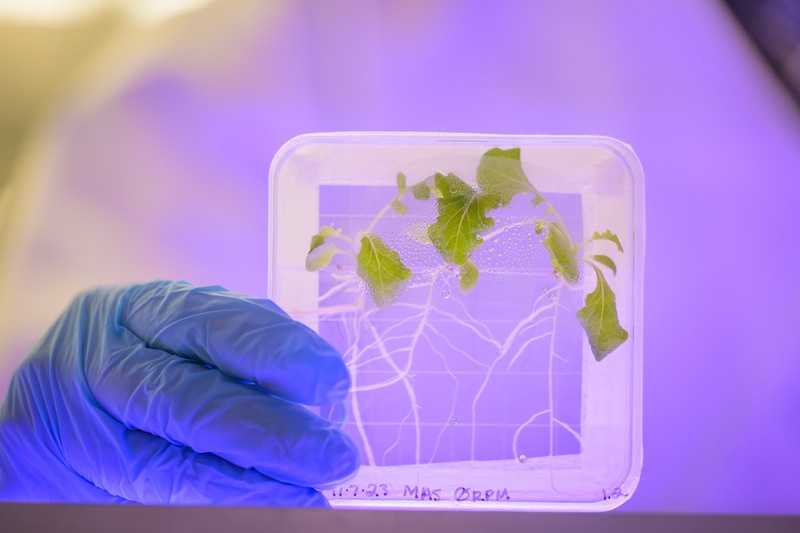

I have spent the last few years thinking, perhaps assuming that astronauts live off dried food, prepackaged and sent from Earth. There certainly is an element of that but travellers to the International Space Station have over recent years been able to feast on fresh salad grown in special units on board. Unfortunately, recent research suggests that pathogenic bacteria and fungi can contaminate the ‘greens’ even in space.
Continue reading “Plants Growing in Space are at Risk from Bacterial Infections”Is the Habitable Zone Really Habitable?

The water that life knows and needs, the water that makes a world habitable, the water that acts as the universal solvent for all the myriad and fantastically complicated chemical reactions that make us different than the dirt and rocks, can only come in one form: liquid.
Continue reading “Is the Habitable Zone Really Habitable?”NASA Wants to Put a Massive Telescope on the Moon
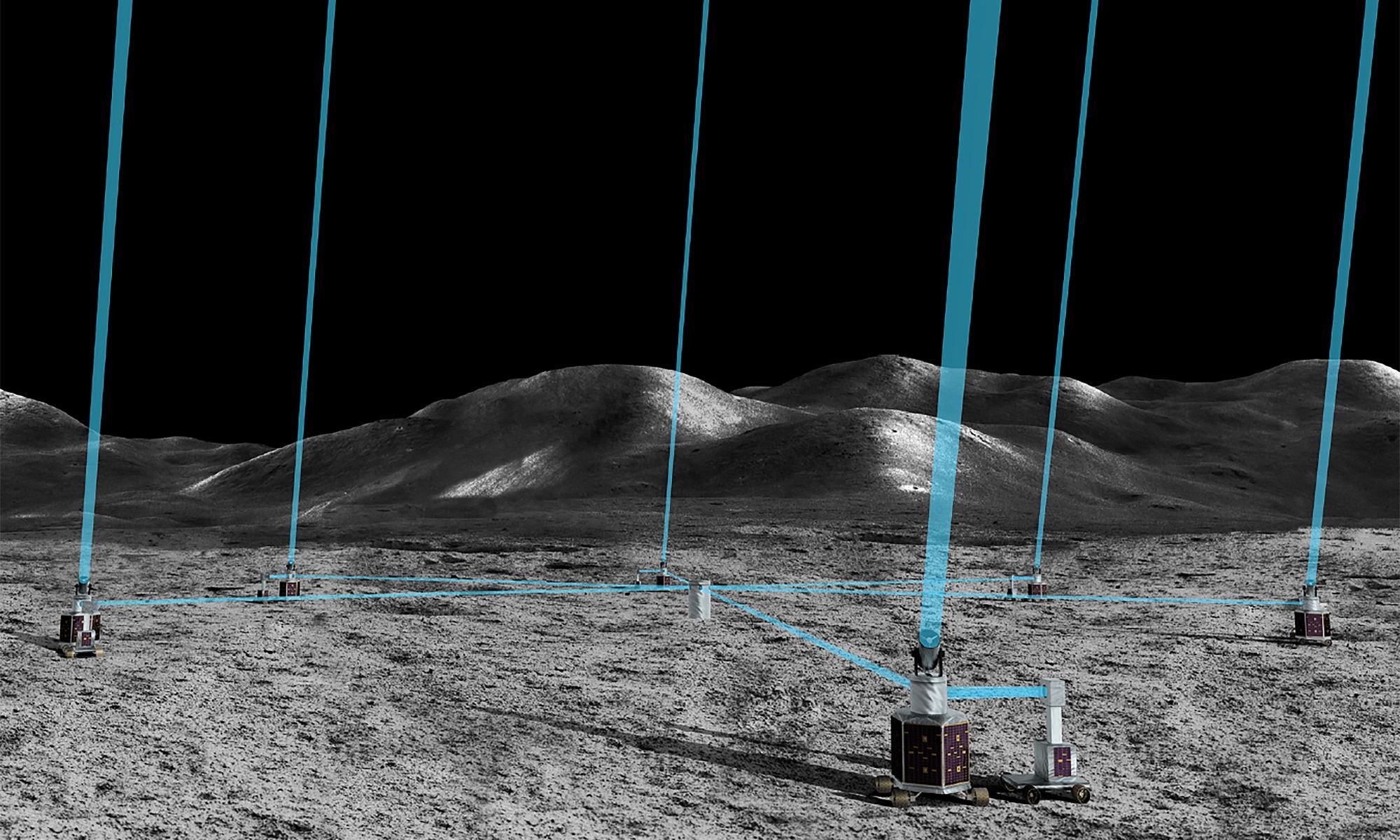
As part of the Artemis Program, NASA intends to establish all the necessary infrastructure to create a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development.” This includes the Lunar Gateway, an orbiting habitat that will enable regular trips to and from the surface, and the Artemis Base Camp, which will permit astronauts to remain there for up to two months. Multiple space agencies are also planning on creating facilities that will take advantage of the “quiet nature” of the lunar environment, which includes high-resolution telescopes.
As part of this year’s NASA Innovative Advance Concepts (NIAC) Program, a team from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center has proposed a design for a lunar Long-Baseline Optical Imaging Interferometer (LBI) for imaging at visible and ultraviolet wavelengths. Known as the Artemis-enabled Stellar Imager (AeSI), this proposed array of multiple telescopes was selected for Phase I development. With a little luck, the AeSI array could be operating on the far side of the Moon, taking detailed images of stellar surfaces and their environments.
Continue reading “NASA Wants to Put a Massive Telescope on the Moon”


