Sometimes, it seems to be a cosmic misfortune that we only get to view the universe from a singular vantage point.
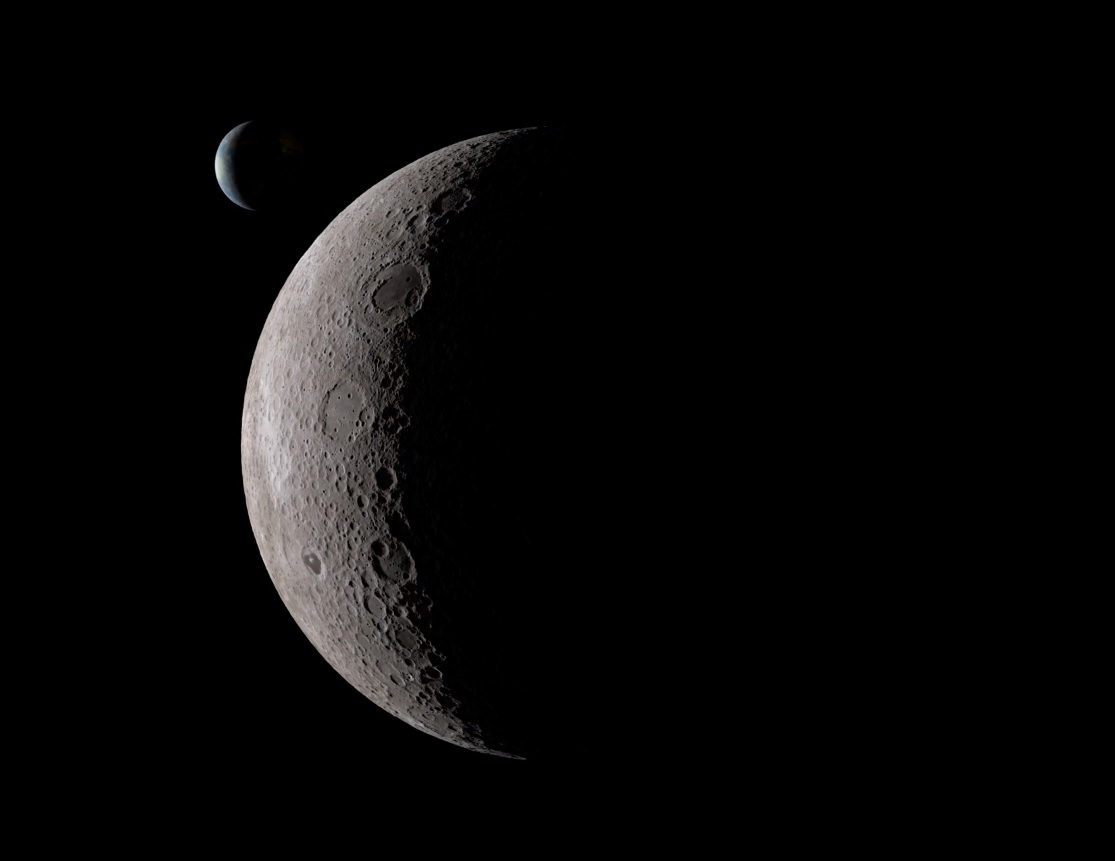
Take the example of our single natural satellite. As the Moon waxes and wanes through its cycle of phases, we see the familiar face of the lunar nearside. This holds true from the day we’re born until the day we die. The Romans and Paleolithic man saw that same face, and until less than a century ago, it was anyone’s guess as to just what was on the other side.
Enter the Space Age and the possibility to finally get a peek at the universe from different perspective via our robotic ambassadors. This week, the folks over at NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio released a unique video simulation that utilized data from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter to give us a view unseen from Earth. This perspective shows just what the phases of the Moon would look like from the vantage point of the lunar farside:
You can see the Moon going through the synodic 29.5 day period a familiar phases, albeit with an unfamiliar face. Note that the Sun zips by, as the lunar farside wanes towards New. And in the background, the Earth can be seen, presenting an identical phase and tracing out a lazy figure eight as it appears and disappears behind the lunar limb.
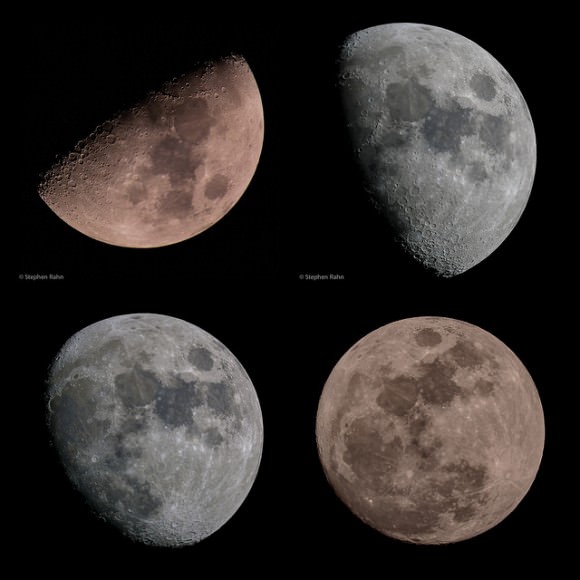

What’s with the lunar-planetary game of peek-a-boo? Well, the point of view for the video assumes that your looking at down at the lunar farside from a stationary point above the Moon. Note that the disk of the Moon stays fixed in place. The Moon actually ‘rocks’ or nods back and forth and side-to-side in motions referred to as libration and nutation, and you’re seeing these expressed via the motion of the Earth in the video. This assures that we actually get a peek over the lunar limb and see a foreshadowed extra bit of the lunar farside, with grand 59% of the lunar surface visible from the Earth. Such is the wacky motion of our Moon, which gave early astronomers an excellent crash course in celestial mechanics 101.
Now, to dispel some commonly overheard lunar myths:
Myth #1: The moon doesn’t rotate. Yes, it’s tidally locked from our perspective, meaning that it keeps one face turned Earthward. But it does turn on its axis in lockstep as it does so once every 27.3 days, known as a sidereal month.
Myth #2: The Farside vs. the Darkside. (Cue Pink Floyd) We do in fact see the dark or nighttime side of the Moon just as much as the daytime side. Despite popular culture, the farside is only synonymous with the darkside of the Moon during Full phase.
Humanity got its first glimpse of the lunar farside in 1959, when the Soviet Union’s Luna 3 spacecraft looked back as it flew past the Moon and beamed us the first blurry image. The Russians got there first, which is why the lunar farside now possesses names for features such as the “Mare Moscoviense”.

Think we’ve explored the Moon? Thus far, no mission – crewed or otherwise – has landed on the lunar farside. The Apollo missions were restricted to nearside landing sites at low latitudes with direct line of sight communication with the Earth. The same goes for the lunar poles: the Moon is still a place begging for further exploration.

Why go to the lunar farside? Well, it would be a great place to do some radio astronomy, as you have the bulk of the Moon behind you to shield your sensitive searches from the now radio noisy Earth. Sure, the dilemmas of living on the lunar farside might forever outweigh the benefits, and abrasive lunar dust will definitely be a challenge to lunar living… perhaps an orbiting radio astronomy observatory in a Lissajous orbit at the L2 point would be a better bet?
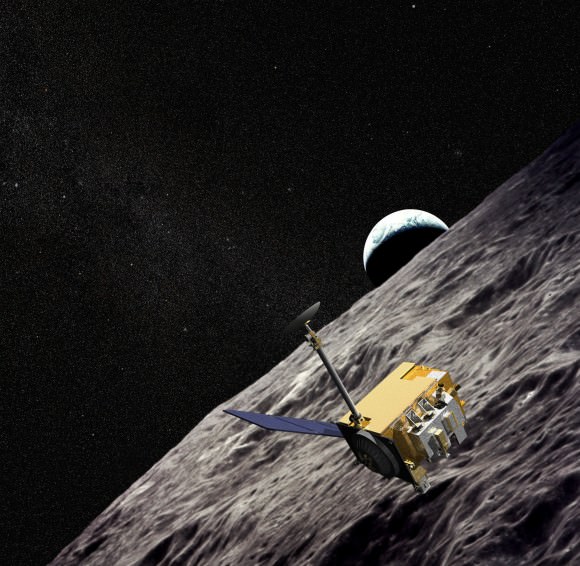

And exploration of the Moon continues. Earlier this week, the LRO team released a finding suggesting that surface hydrogen may be more abundant on the poleward facing slopes of craters that litter the lunar south pole region. Locating caches of lunar ice in permanently shadowed craters will be key to a ‘living off of the land’ approach for future lunar colonists… and then there’s the idea to harvest helium-3 for nuclear fusion (remember the movie Moon?) that’s still science fiction… for now.
Perhaps the Moonbase Alpha of Space: 1999 never came to pass… but there’s always 2029!