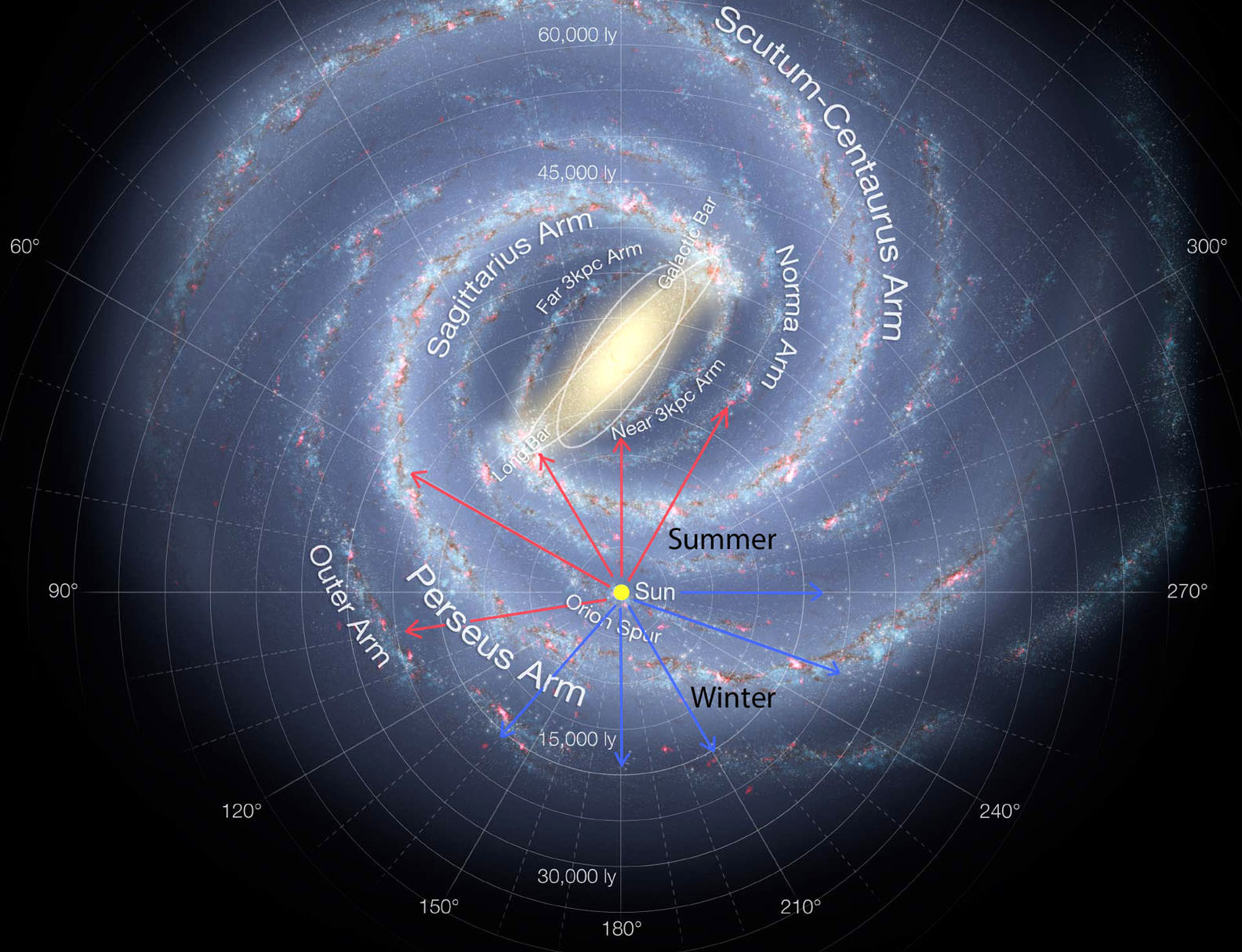
The Milky Way Galaxy is an immense and very interesting place. Not only does it measure some 120,000–180,000 light-years in diameter, it is home to planet Earth, the birthplace of humanity. Our Solar System resides roughly 27,000 light-years away from the Galactic Center, on the inner edge of one of the spiral-shaped concentrations of gas and dust particles called the Orion Arm.
But within these facts about the Milky Way lie some additional tidbits of information, all of which are sure to impress and inspire. Here are ten such facts, listed in no particular order:
1. It’s Warped:
For starters, the Milky Way is a disk about 120,000 light years across with a central bulge that has a diameter of 12,000 light years (see the Guide to Space article for more information). The disk is far from perfectly flat though, as can be seen in the picture below. In fact, it is warped in shape, a fact which astronomers attribute to the our galaxy’s two neighbors -the Large and Small Magellanic clouds.
These two dwarf galaxies — which are part of our “Local Group” of galaxies and may be orbiting the Milky Way — are believed to have been pulling on the dark matter in our galaxy like in a game of galactic tug-of-war. The tugging creates a sort of oscillating frequency that pulls on the galaxy’s hydrogen gas, of which the Milky Way has lots of (for more information, check out How the Milky Way got its Warp).

2. It Has a Halo, but You Can’t Directly See It:
Scientists believe that 90% of our galaxy’s mass consists of dark matter, which gives it a mysterious halo. That means that all of the “luminous matter” – i.e. that which we can see with the naked eye or a telescopes – makes up less than 10% of the mass of the Milky Way. Its halo is not the conventional glowing sort we tend to think of when picturing angels or observing comets.
In this case, the halo is actually invisible, but its existence has been demonstrated by running simulations of how the Milky Way would appear without this invisible mass, and how fast the stars inside our galaxy’s disk orbit the center.
The heavier the galaxy, the faster they should be orbiting. If one were to assume that the galaxy is made up only of matter that we can see, then the rotation rate would be significantly less than what we observe. Hence, the rest of that mass must be made up of an elusive, invisible mass – aka. “dark matter” – or matter that only interacts gravitationally with “normal matter”.
To see some images of the probable distribution and density of dark matter in our galaxy, check out The Via Lactea Project.
3. It has Over 200 Billion Stars:
As galaxies go, the Milky Way is a middleweight. The largest galaxy we know of, which is designated IC 1101, has over 100 trillion stars, and other large galaxies can have as many as a trillion. Dwarf galaxies such as the aforementioned Large Magellanic Cloud have about 10 billion stars. The Milky Way has between 100-400 billion stars; but when you look up into the night sky, the most you can see from any one point on the globe is about 2,500. This number is not fixed, however, because the Milky Way is constantly losing stars through supernovae, and producing new ones all the time (about seven per year).
4. It’s Really Dusty and Gassy:
Though it may not look like it to the casual observer, the Milky Way is full of dust and gas. This matter makes up a whopping 10-15% of the luminous/visible matter in our galaxy, with the remainder being the stars. Our galaxy is roughly 100,000 light years across, and we can only see about 6,000 light years into the disk in the visible spectrum. Still, when light pollution is not significant, the dusty ring of the Milky Way can be discerned in the night sky.
The thickness of the dust deflects visible light (as is explained here) but infrared light can pass through the dust, which makes infrared telescopes like the Spitzer Space Telescope extremely valuable tools in mapping and studying the galaxy. Spitzer can peer through the dust to give us extraordinarily clear views of what is going on at the heart of the galaxy and in star-forming regions.
5. It was Made From Other Galaxies:
The Milky Way wasn’t always as it is today – a beautiful, warped spiral. It became its current size and shape by eating up other galaxies, and is still doing so today. In fact, the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy is the closest galaxy to the Milky Way because its stars are currently being added to the Milky Way’s disk. And our galaxy has consumed others in its long history, such as the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy.
6. Every Picture You’ve Seen of the Milky Way Isn’t It:
Currently, we can’t take a picture of the Milky Way from above. This is due to the fact that we are inside the galactic disk, about 26,000 light years from the galactic center. It would be like trying to take a picture of your own house from the inside. This means that any of the beautiful pictures you’ve ever seen of a spiral galaxy that is supposedly the Milky Way is either a picture of another spiral galaxy, or the rendering of a talented artist.

Imaging the Milky Way from above is a long, long way off. However, this doesn’t mean that we can’t take breathtaking images of the Milky Way from our vantage point!
7. There is a Black Hole at the Center:
Most larger galaxies have a supermassive black hole (SMBH) at the center, and the Milky Way is no exception. The center of our galaxy is called Sagittarius A*, a massive source of radio waves that is believed to be a black hole that measures 22,5 million kilometers (14 million miles) across – about the size of Mercury’s orbit. But this is just the black hole itself.
All of the mass trying to get into the black hole – called the accretion disk – forms a disk that has 4.6 million times the mass of our Sun and would fit inside the orbit of the Earth. Though like other black holes, Sgr A* tries to consume anything that happens to be nearby, star formation has been detected near this behemoth astronomical phenomenon.
8. It’s Almost as Old as the Universe Itself:
The most recent estimates place the age of the Universe at about 13.7 billion years. Our Milky Way has been around for about 13.6 billion of those years, give or take another 800 million. The oldest stars in our the Milky Way are found in globular clusters, and the age of our galaxy is determined by measuring the age of these stars, and then extrapolating the age of what preceded them.
Though some of the constituents of the Milky Way have been around for a long time, the disk and bulge themselves didn’t form until about 10-12 billion years ago. And that bulge may have formed earlier than the rest of the galaxy.
9. It’s Part of the Virgo Supercluster:
As big as it is, the Milky Way is part of an even larger galactic structures. Our closest neighbors include the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, and the Andromeda Galaxy – the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way. Along with some 50 other galaxies, the Milky Way and its immediate surroundings make up a cluster known as the Local Group.

And yet, this is still just a small fraction of our stellar neighborhood. Farther out, we find that the Milky Way is part of an even larger grouping of galaxies known as the Virgo Supercluster. Superclusters are groupings of galaxies on very large scales that measure in the hundreds of millions of light years in diameter. In between these superclusters are large stretches of open space where intrepid explorers or space probes would encounter very little in the way of galaxies or matter.
In the case of the Virgo Supercluster, at least 100 galaxy groups and clusters are located within it massive 33 megaparsec (110 million light-year) diameter. And a 2014 study indicates that the Virgo Supercluster is only a lobe of a greater supercluster, Laniakea, which is centered on the Great Attractor.
10. It’s on the move:
The Milky Way, along with everything else in the Universe, is moving through space. The Earth moves around the Sun, the Sun around the Milky Way, and the Milky Way as part of the Local Group, which is moving relative to the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation – the radiation left over from the Big Bang.
The CMB is a convenient reference point to use when determining the velocity of things in the universe. Relative to the CMB, the Local Group is calculated to be moving at a speed of about 600 km/s, which works out to about 2.2 million km/h. Such speeds stagger the mind and squash any notions of moving fast within our humble, terrestrial frame of reference!
We have written many interesting articles about the Milky Way for Universe Today. Here’s 10 Interesting Facts about the Milky Way, How Big is the Milky Way?, What is the Closest Galaxy to the Milky Way?, and How Many Stars Are There in the Milky Way?
For many more facts about the Milky Way, visit the Guide to Space, listen to the Astronomy Cast episode on the Milky Way, or visit the Students for the Exploration and Development of Space at seds.org.