Universe Today has explored the importance of studying impact craters and planetary surfaces and what these scientific disciplines can teach us about finding life beyond Earth. We learned that impact craters are caused by massive rocks that can either create or destroy life, and planetary surfaces can help us better understand the geologic processes on other worlds, including the conditions necessary for life. Here, we will venture far beyond the confines of our solar system to the many stars that populate our Milky Way Galaxy and the worlds they orbit them, also known as exoplanets. We will discuss why astronomers study exoplanets, challenges of studying exoplanets, what exoplanets can teach us about finding life beyond Earth, and how upcoming students can pursue studying exoplanets, as well. So, why is it so important to study exoplanets?
Continue reading “Exoplanets: Why study them? What are the challenges? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Exploring the Solar System with Swarms of Microprobes
It’s satisfying to sit back and take stock of all the places in the Solar System that we’ve explored. The Moon came first, then over the following decades, we’ve sent spacecraft to Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and even distant Pluto. We’ve also explored some of the asteroid belt’s inhabitants and even several comets.
That’s an impressive list, but it’s still dwarfed by the number of objects we haven’t visited. Could swarms of microprobes help us expand our reach? New research shows that tiny, solar sail microprobes could complete a round trip to asteroid Bennu faster than OSIRIS-REx did.
Continue reading “Exploring the Solar System with Swarms of Microprobes”Webb Sees Dozens Of Young Quasars in the First Billion Years of the Universe
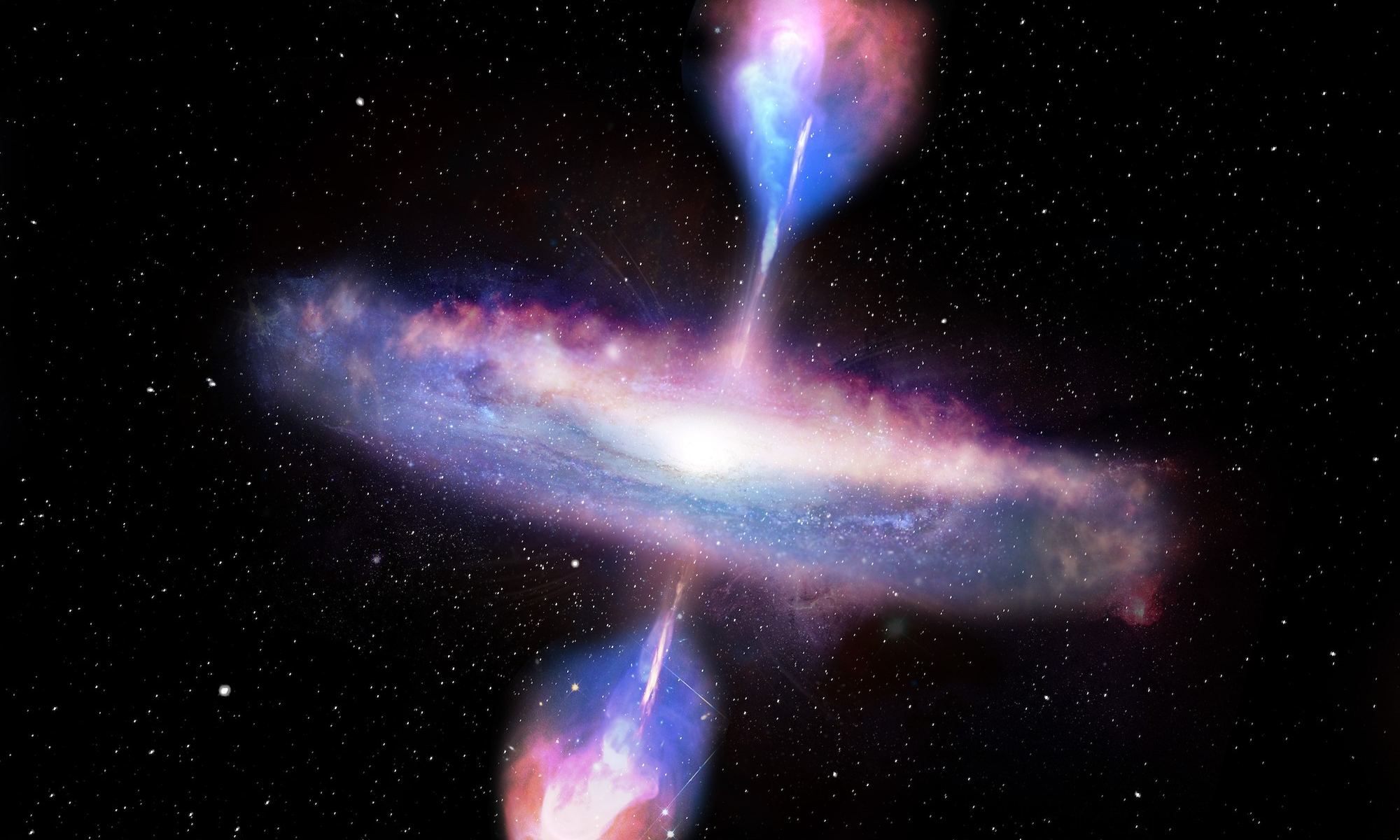
Within almost every galaxy is a supermassive black hole. Millions, sometimes billions of solar masses locked within an event horizon of space and time. They can power luminous quasars, drive star formation, and change the evolution of a galaxy. Because of their size and abundance, supermassive black holes must have formed early in cosmic history. But how early is still an unanswered question. It’s a focus of a recent study on the arXiv.
Continue reading “Webb Sees Dozens Of Young Quasars in the First Billion Years of the Universe”Chinese Firm Successfully Tests a New Reusable Booster
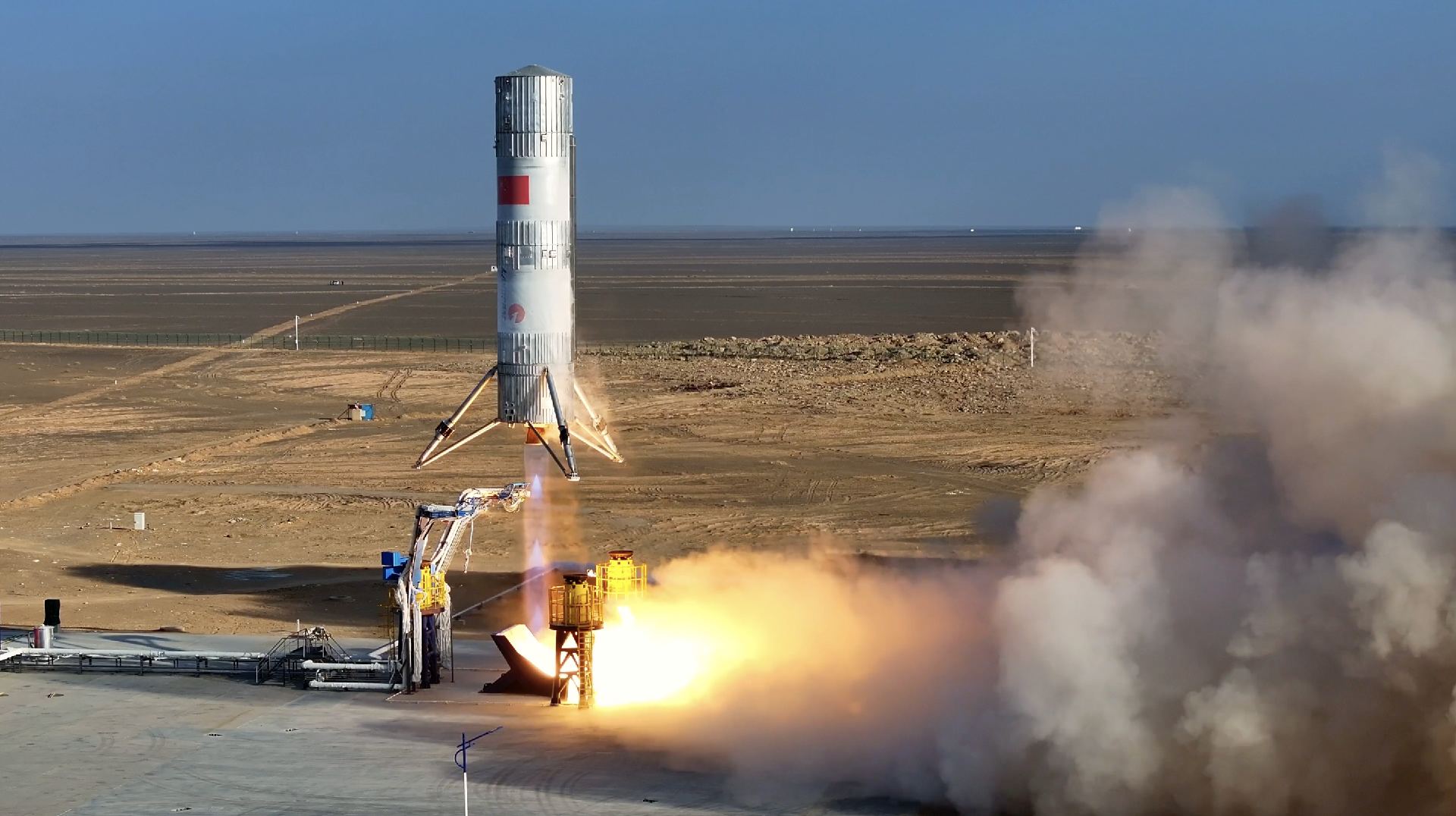
The sight of a Falcon-9 rocket landing in an upright orientation is not an unusual sight. It seems that the Chinese aerospace firm LandSpace is getting in on the act with their new Zhuque-3 (I don’t even know how to pronounce that) reusable methane rocket. The prototype booster took off, reached a height of 350 metres and landed 60 seconds later about 100 metres away on a landing pad. LandSpace have revealed this test showcases key technologies that will be used for their upcoming reusable rocket.
Continue reading “Chinese Firm Successfully Tests a New Reusable Booster”Why Mars Died
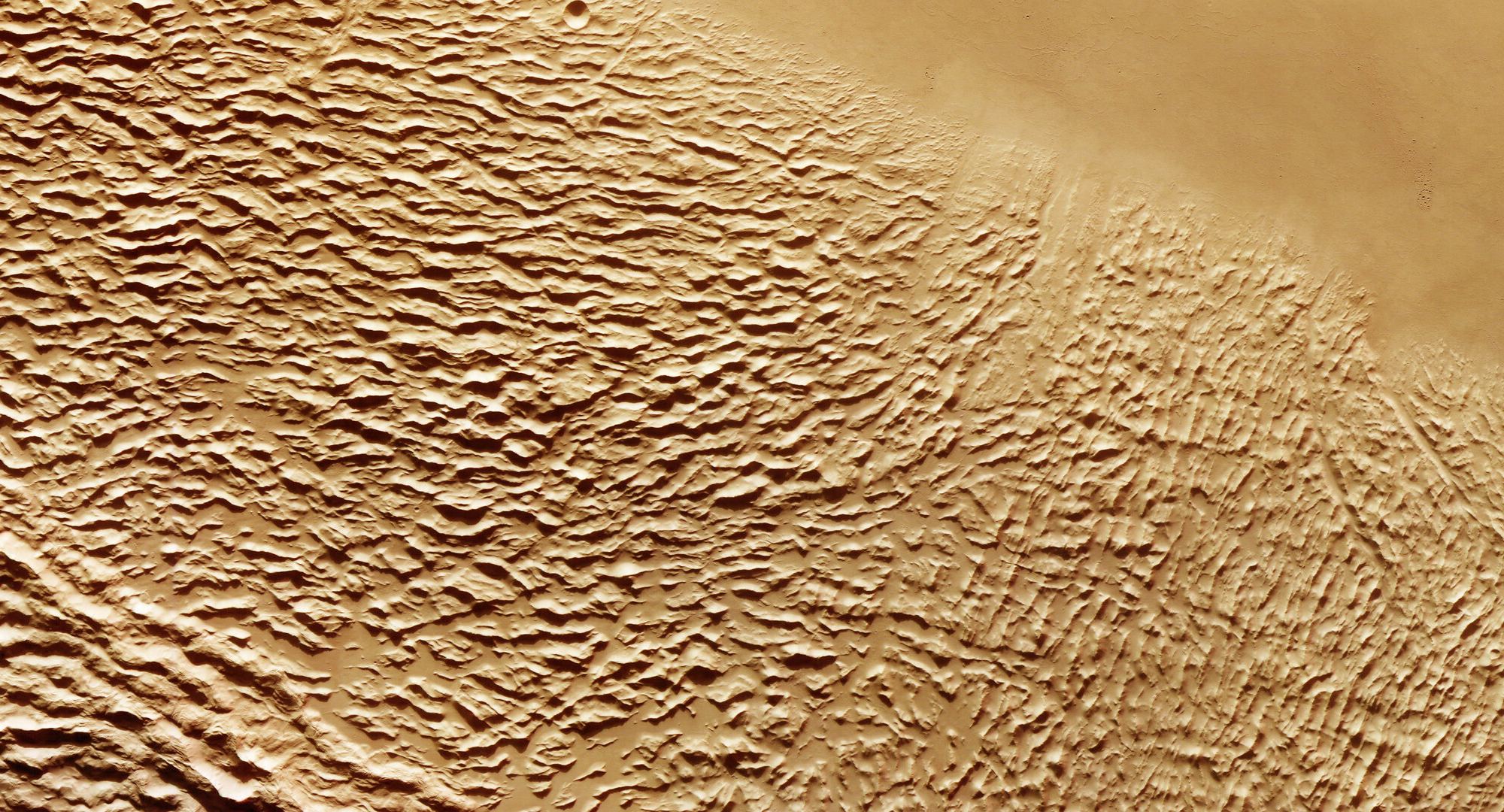

We know of Mars as the Red Planet, for its surface and atmosphere is caked in endless swirling dust of rusted iron, the rusting action provided by the always-eager oxygen. But this was not always so.
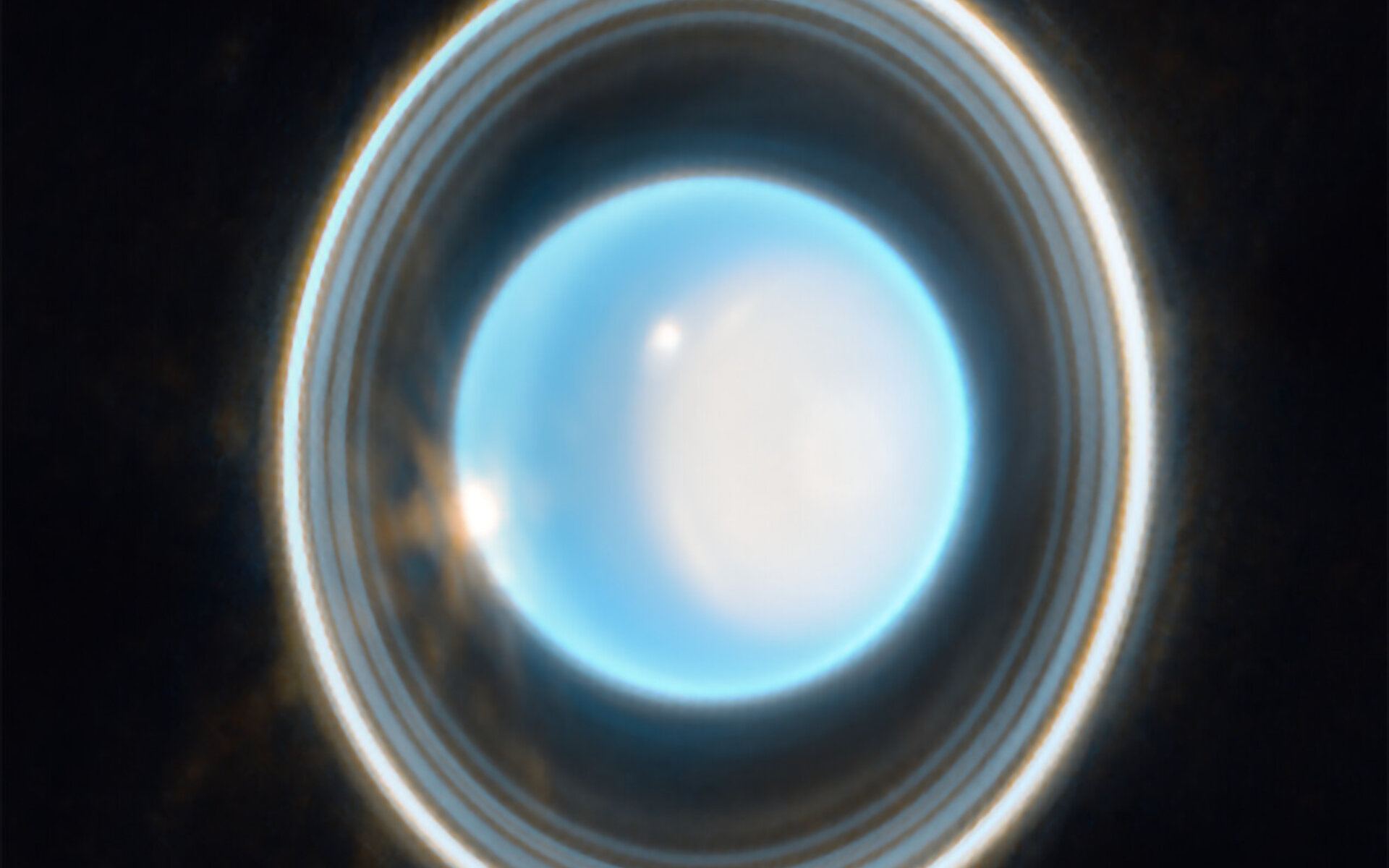
Continue reading “Why Mars Died”It’s Time to Go Back to Uranus. What Questions do Scientists Have About the Ice Giants?
It seems crazy that Uranus was discovered in 1781 yet here we are, in 2024 and we have only sent one spacecraft to explore Uranus. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have given us close-up images of Uranus (and Neptune) but since their visit in 1986, we have not returned. There have of course been great images from the Hubble Space Telescope and from the James Webb Space Telescope but we still have lots to learn about them.
Continue reading “It’s Time to Go Back to Uranus. What Questions do Scientists Have About the Ice Giants?”NASA Invests in New Nuclear Rocket Concept for the Future of Space Exploration and Astrophysics
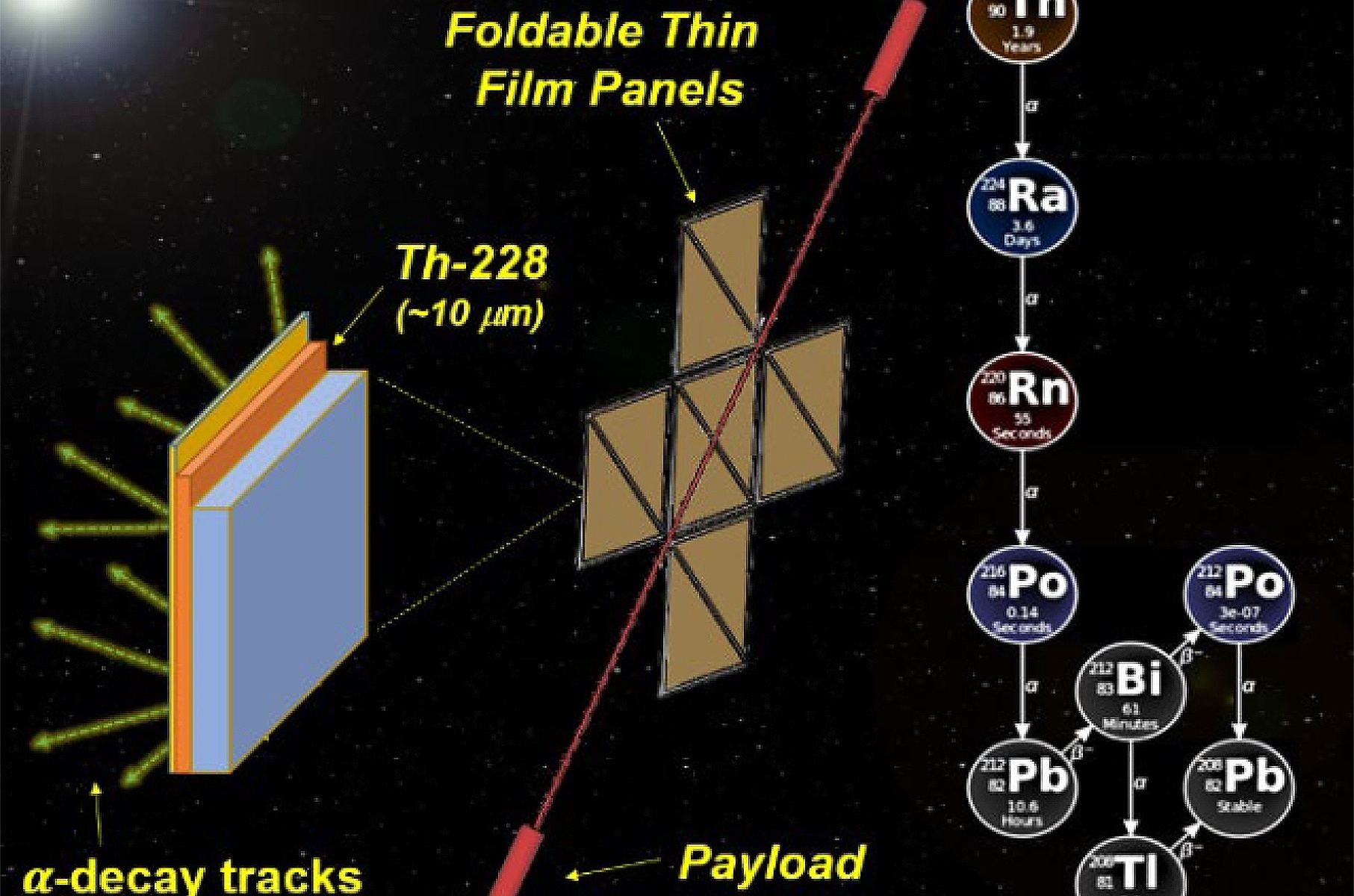
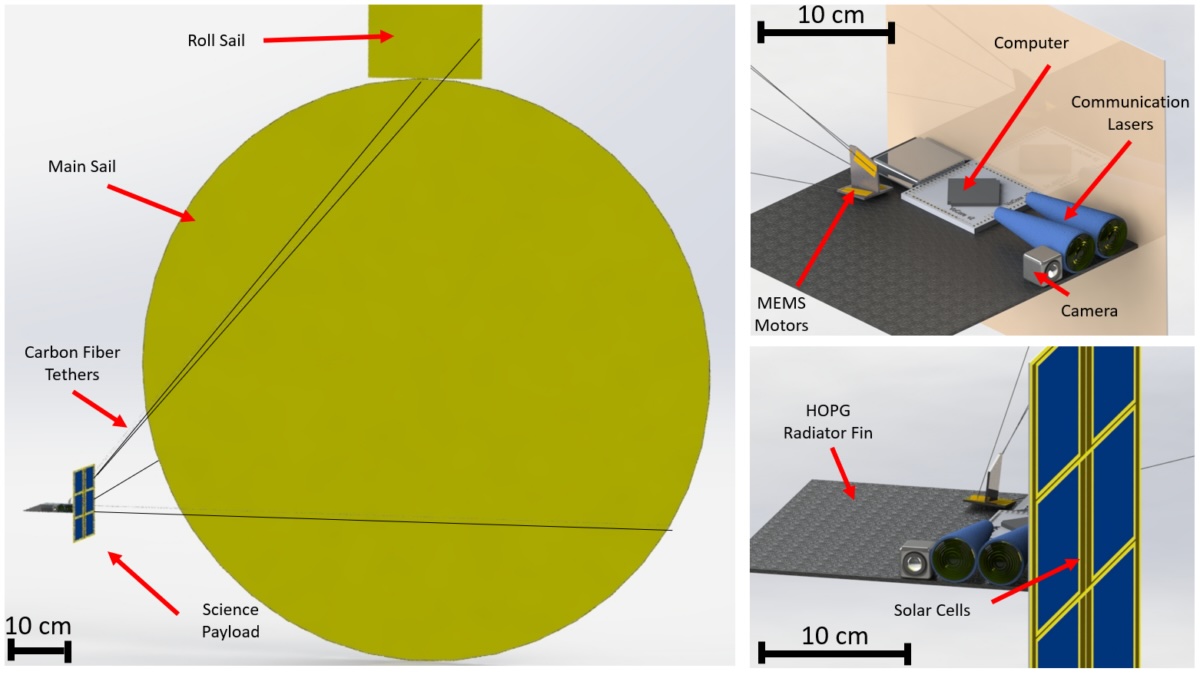
In the coming years, NASA plans to send several astrobiology missions to Venus and Mars to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life. These will occur alongside crewed missions to the Moon (for the first time since the Apollo Era) and the first crewed missions to Mars. Beyond the inner Solar System, there are ambitious plans to send robotic missions to Europa, Titan, and other “Ocean Worlds” that could host exotic life. To accomplish these objectives, NASA is investing in some interesting new technologies through the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program.
This year’s selection includes solar-powered aircraft, bioreactors, lightsails, hibernation technology, astrobiology experiments, and nuclear propulsion technology. This includes a concept for a Thin Film Isotope Nuclear Engine Rocket (TFINER), a proposal by senior technical staff member James Bickford and his colleagues at the Charles Stark Draper Laboratory – a Massachusetts-based independent technology developer. This proposal relies on the decay of radioactive isotopes to generate propulsion and was recently selected by the NIAC for Phase I development.
Continue reading “NASA Invests in New Nuclear Rocket Concept for the Future of Space Exploration and Astrophysics”This Galaxy Hosted One of the Most Powerful Supernovae Ever Seen

In 2010, an exceptionally luminous supernova exploded in a small galaxy about 150 million light-years away called UGC 5189A. The Hubble Space Telescope has kept its eye on this galaxy because of the extraordinary supernova, which for three years released more than 2.5 billion times the energy of our Sun in visible light alone.
Though the supernova, named SN 2010jl, died down years ago, astronomers are still watching its aftermath.
Continue reading “This Galaxy Hosted One of the Most Powerful Supernovae Ever Seen”NASA Lost Contact With its Ingenuity Helicopter Briefly, but it's Back

Imagine remotely flying a drone or small aircraft from a great distance and loosing contact with it during flight. You’d likely assume the worst, that your aircraft was probably laying in a crashed heap in some remote location.
That’s what engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory went through with the beloved Ingenuity helicopter on Mars, millions of miles away. During a recent quick pop-up flight that was supposed to last just 32 seconds, Ingenuity lost communications before it touched back down. The engineers back on Earth had no idea if the little helicopter landed safely or not.
Continue reading “NASA Lost Contact With its Ingenuity Helicopter Briefly, but it's Back”What Could the Extremely Large Telescope See at Proxima Centauri's Planet?
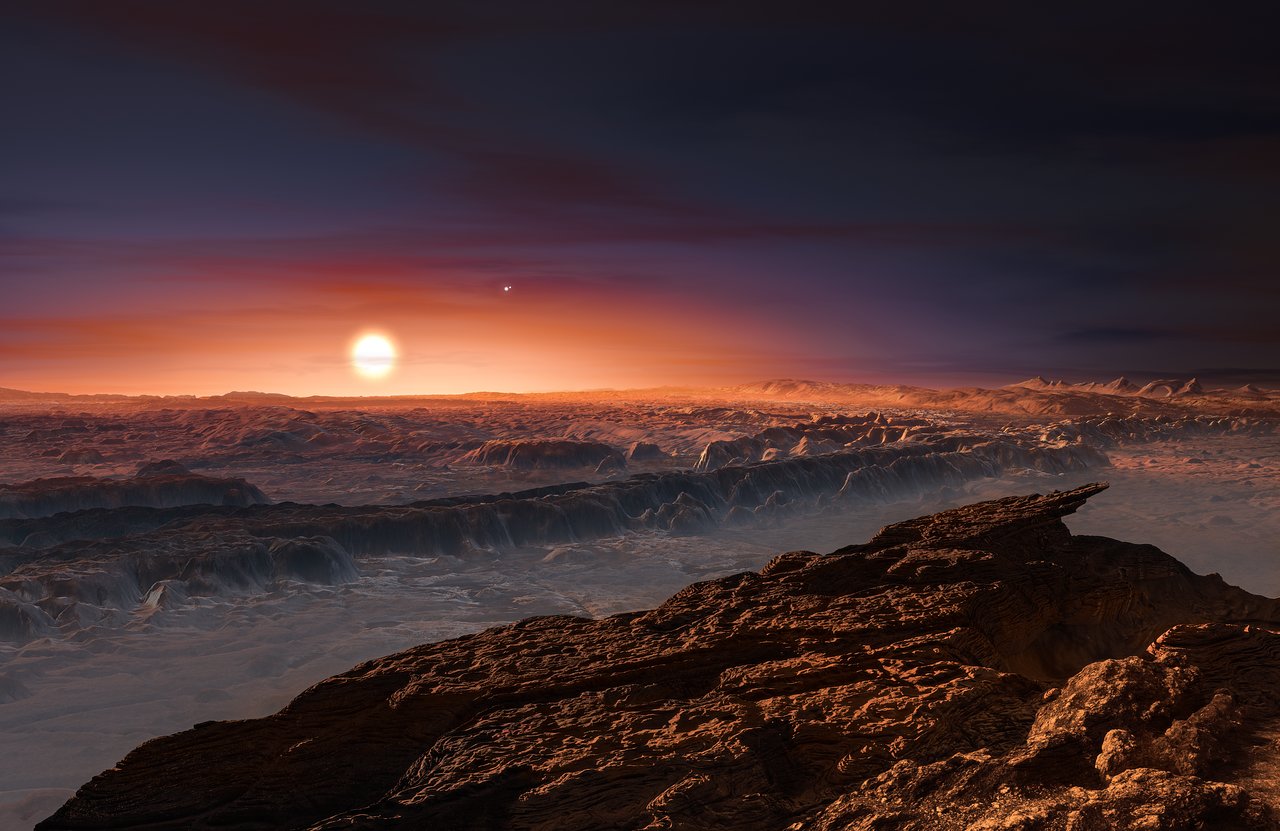

Proxima Centauri B is the closest exoplanet to Earth. It is an Earth-mass world right in the habitable zone of a red dwarf star just 4 light-years from Earth. It receives about 65% of the energy Earth gets from the Sun, and depending on its evolutionary history could have oceans of water and an atmosphere rich with oxygen. Our closest neighbor could harbor life, or it could be a dry rock, but is an excellent target in the search for alien life. There’s just one catch. Our usual methods for detecting biosignatures won’t work with Proxima Centauri B.
Continue reading “What Could the Extremely Large Telescope See at Proxima Centauri's Planet?”