A new study paints a dire picture about Earth's orbital debris environment and highlights the need for mitigation strategies
Continue reading

A NASA-funded study by a team from the University of Arizona has identified possible tools for identifying life on other planets.
Continue reading

In preparation for missions to Mars, NASA and HeroX have launched their third challenge for dealing with space waste: The Trash-to-Gas Challenge!
Continue reading

Earth Observatory System Data Analytics is urging fellow satellite companies and space agencies to share their data to assist the people of Ukraine
Continue reading
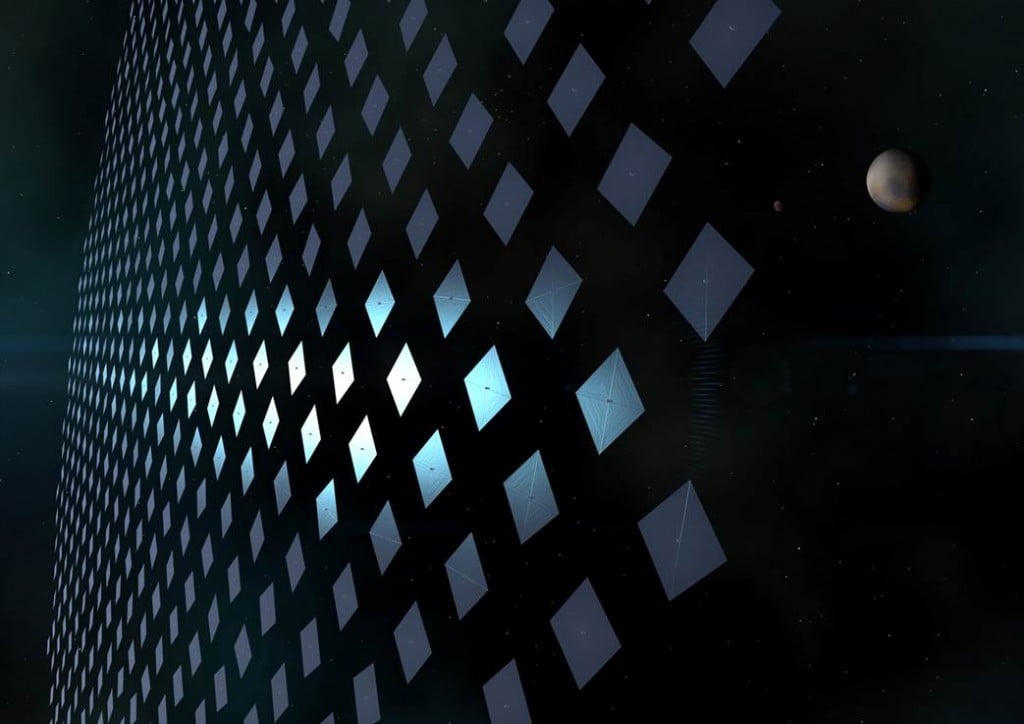
A new study from UCLA shows how laser-driven light sails could be a cost-effective method for exploring the Solar System as well.
Continue reading

An international team of astronomers has detected the closest repeating Fast Radio Burst to date, which is providing new insights into this mysterious phenomenon
Continue reading

An international team of astrophysicists has created the most accurate simulation of cosmic evolution to date, which reproduced many of the familiar structures we see today
Continue reading