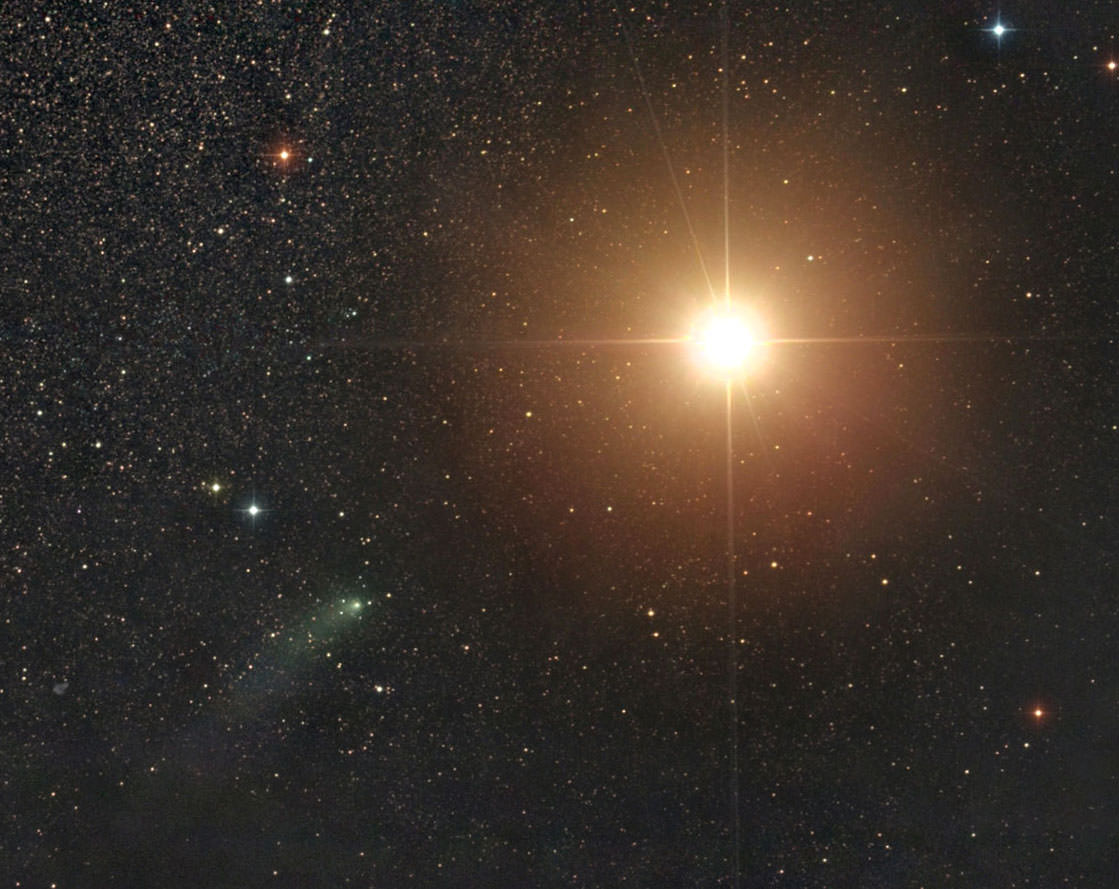
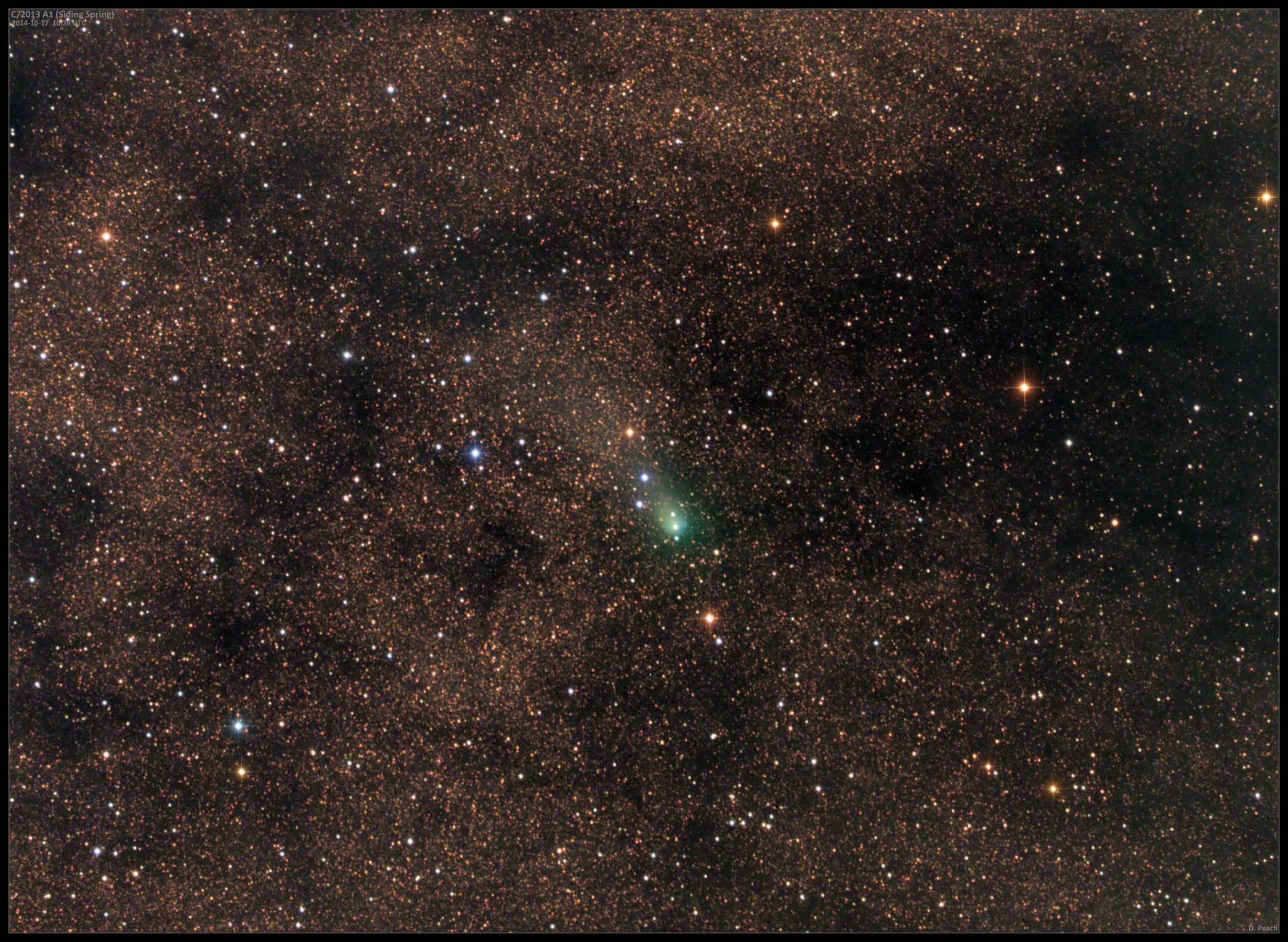
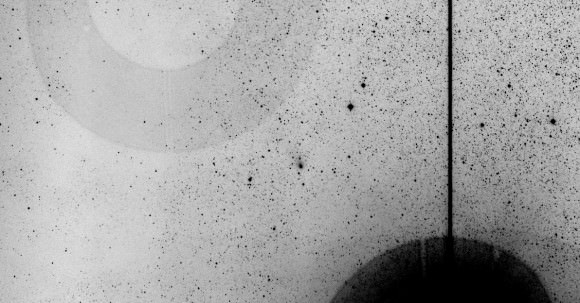
Astrophotographer Damian Peach shares this spectacular image of comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring approaching Mars taken just hours ago. The faint comet shows a small, condensed coma and bent tail against the glaring orange glow of the brilliant planet. Most photos of comets passing by a planet or deep sky object are lucky line-of-sight pairings with the comet in the foreground and object light years away in the background. Not this one. Both Siding Spring and Mars lie at nearly the identical distance from Earth of 151 million miles (243 million km).

When closest to Mars this afternoon, Siding Spring is expected to shine at around magnitude -5 or about twice as bright as Venus. Mind you, that estimate considers the entire comet crunched down into a dot. But for those who remember, Comet Hale-Bopp remained at zero magnitude, 100 times fainter than Siding Spring, and made for one of the most impressive naked eye sights on spring evenings in 1997.
More recently, Comet McNaught climaxed at magnitude -5 in the daytime sky near the Sun in January 2007. It was plainly visible in binoculars and telescopes in a blue sky if you knew exactly where to look and took care to avoid the Sun. Would-be Martians are far more fortunate, with Siding Spring appearing high overhead in a dark sky from some locations, including that of NASA’s Curiosity Rover.
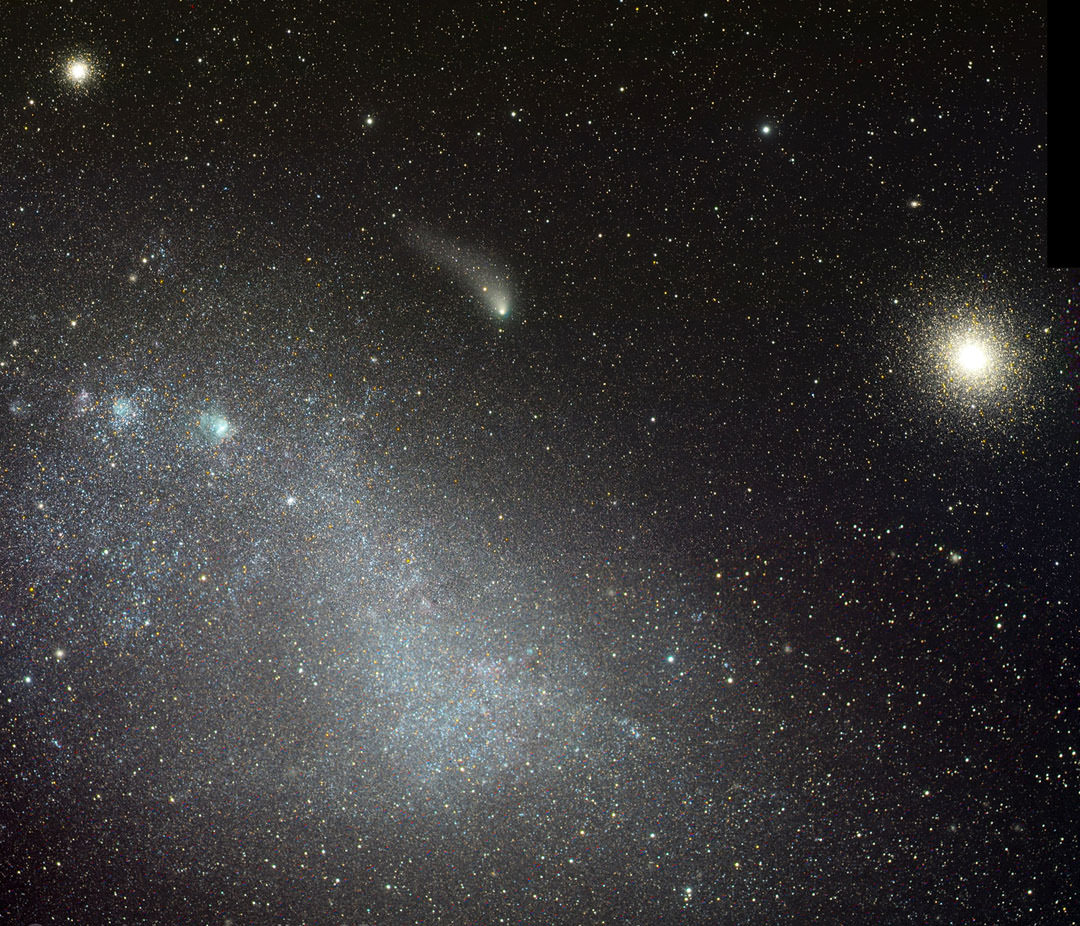
Comet C/2013 Siding Spring as it rises and sets over the Curiosity Rover this weekend October 18-19. Credit: Solarsystemscope.com
Right on time for today’s encounter, the folks at Solarsystemscope.com have rolled out an interactive simulation of Comet Siding Spring’s appearance in the sky above Curiosity. Just click the play button on the control panel above to run it live. Seen from Mars, the comet bobs along Eridanus the River southwest of Orion, passing high in the southern sky overnight. What a sight!
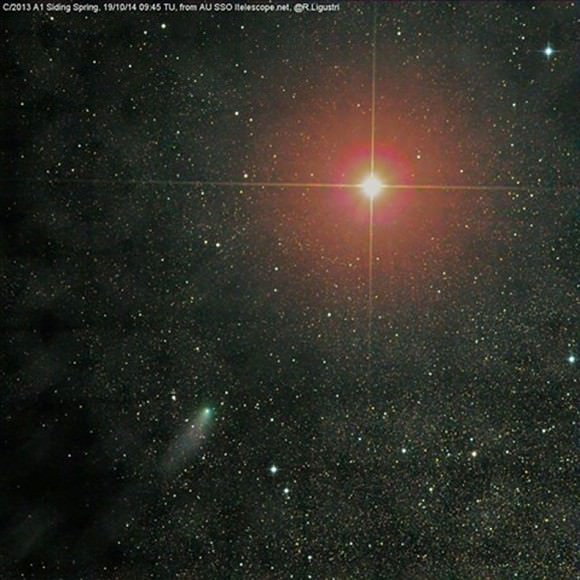

The comet nucleus is only about 0.4 miles (700 meters) across, but the coma or atmosphere fluffs out to around 12,000 miles (19,300 km). Seen from the ground, Siding Spring would span about 8°of sky or 16 full Moons from head to tail. Moving at 1.5° per minute, we could watch crawl across the heavens in real time with the naked eye. Wish I zoom to Mars for a look, but the rovers and orbiters will be our eyes as they study and photograph the comet during its brief flyby. As soon as those pictures become available, we’ll publish them here. Can’t wait!
Come Siding Spring comes out the other side!
While we’re waiting, amateur astronomers have been busy shooting additional photos and creating videos from their images. Fritz Helmut Hemmerich made this video from 1200-meters at Tenerife in the Canary Islands showing Comet Siding Spring immediately after its Mars encounter. One thing we know for certain is that the comet is intact after its close brush.
And find our more amazing photos and information at Sen TV, and you can follow them on Twitter at @sen.