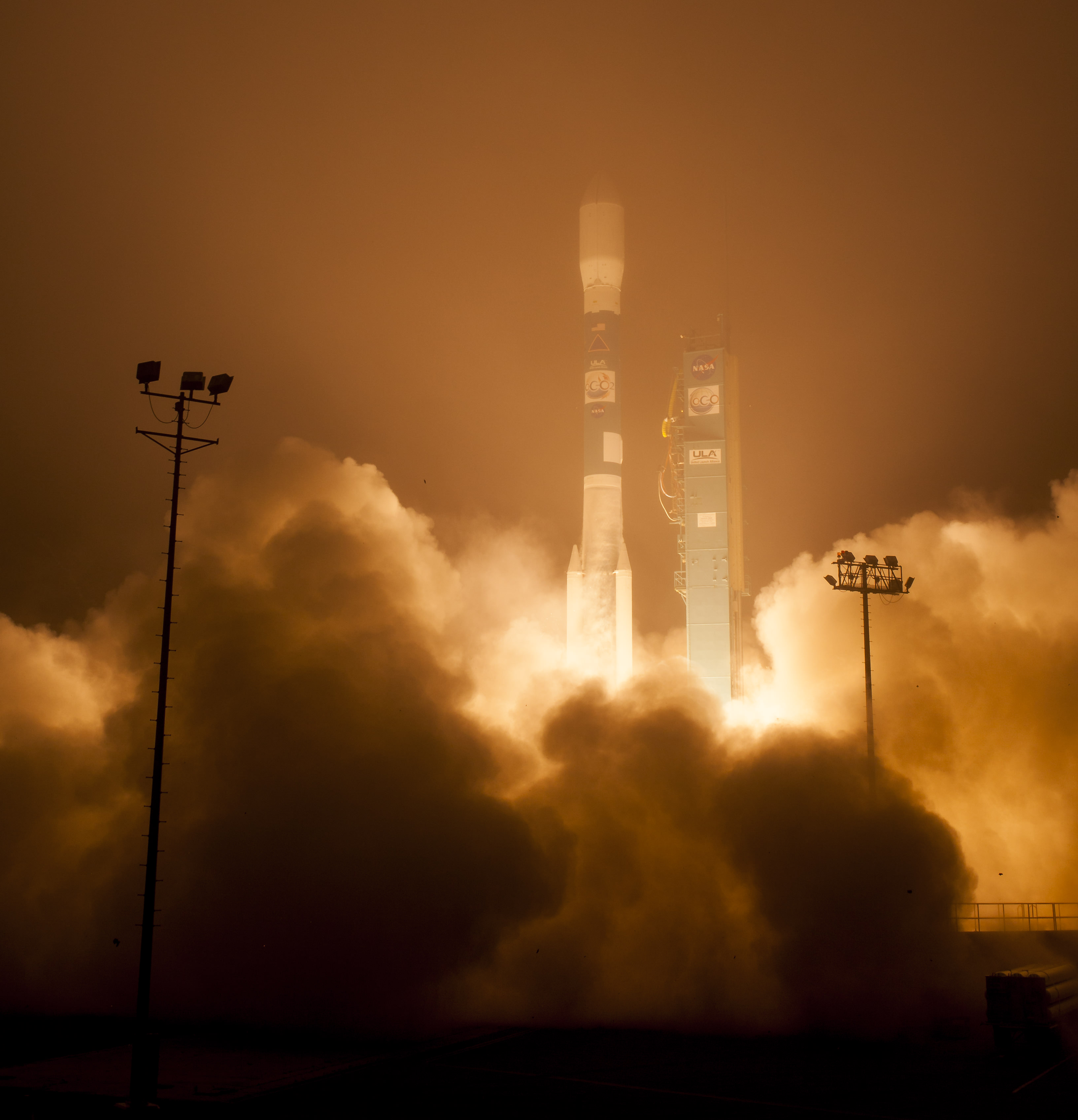
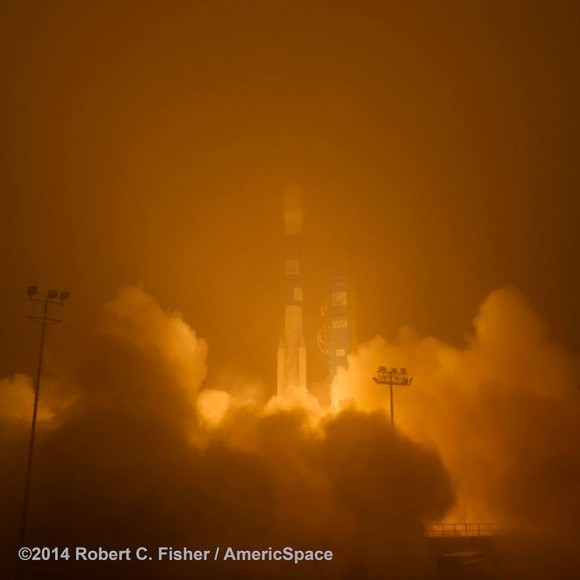
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere, lifts off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, at 2:56 a.m. Pacific Time, July 2, 2014 on a Delta II rocket. The two-year mission will help scientists unravel key mysteries about carbon dioxide. Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Story updated[/caption]
Following a nearly three-year long hiatus, the workhorse Delta II rocket successfully launched NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to watching Earth breathe by studying Earth’s atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) – the leading human-produced greenhouse gas and the principal human-produced driver of climate change.
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) raced to orbit earlier this morning, during a spectacular nighttime blastoff at 2:56 a.m. PDT (5:56 a.m. EDT), Tuesday, July 2, 2014, from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket.
The flawless launch marked the ‘return to flight’ of the venerable Delta II and was broadcast live on NASA TV.

A camera mounted on the Delta II’s second stage captured a breathtaking live view of the OCO-2 spacecraft during separation from the upper stage, which propelled it into an initial 429-mile (690-kilometer) orbit.
The life giving solar arrays were unfurled soon thereafter and NASA reports that the observatory is in excellent health.
“Climate change is the challenge of our generation,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden in a statement.
“With OCO-2 and our existing fleet of satellites, NASA is uniquely qualified to take on the challenge of documenting and understanding these changes, predicting the ramifications, and sharing information about these changes for the benefit of society.”

Over the next three weeks the OCO-2 probe will undergo a thorough checkout and calibration process. It will also be maneuvered into a 438-mile (705-kilometer) altitude, near-polar orbit where it will become the lead science probe at the head of the international Afternoon Constellation, or “A-Train,” of Earth-observing satellites.
“The A-Train, the first multi-satellite, formation flying “super observatory” to record the health of Earth’s atmosphere and surface environment, collects an unprecedented quantity of nearly simultaneous climate and weather measurements,” says NASA.
Science operations begin in about 45 days.
The 999 pound (454 kilogram) observatory is the size of a phone booth.
OCO-2 is equipped with a single science instrument consisting of three high-resolution, near-infrared spec¬trometers fed by a common telescope. It will collect global measurements of atmospheric CO2 to provide scientists with a better idea of how CO2 impacts climate change and is responsible for Earth’s warming.

During a minimum two-year mission the $467.7 million OCO-2 will take near global measurements to locate the sources and storage places, or ‘sinks’, for atmospheric carbon dioxide, which is a critical component of the planet’s carbon cycle.
OCO-2 was built by Orbital Sciences as a replacement for the original OCO which was destroyed during the failed launch of a Taurus XL rocket from Vandenberg back in February 2009 when the payload fairing failed to open properly and the spacecraft plunged into the ocean.
The OCO-2 mission will provide a global picture of the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide, as well as their “sinks,” the natural ocean and land processes by which carbon dioxide is pulled out of Earth’s atmosphere and stored, according to NASA.
“This challenging mission is both timely and important,” said Michael Freilich, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
“OCO-2 will produce exquisitely precise measurements of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations near Earth’s surface, laying the foundation for informed policy decisions on how to adapt to and reduce future climate change.”
It will record around 100,000 precise individual CO2 measurements around the worlds entire sunlit hemisphere every day and help determine its source and fate in an effort to understand how human activities impact climate change and how we can mitigate its effects.
At the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, there were about 280 parts per million (ppm) of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere. As of today the CO2 level has risen to about 400 parts per million.
“Scientists currently don’t know exactly where and how Earth’s oceans and plants have absorbed more than half the carbon dioxide that human activities have emitted into our atmosphere since the beginning of the industrial era,” said David Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, in a statement.
“Because of this, we cannot predict precisely how these processes will operate in the future as climate changes. For society to better manage carbon dioxide levels in our atmosphere, we need to be able to measure the natural source and sink processes.”
OCO-2 is the second of NASA’s five new Earth science missions planned to launch in 2014 and is designed to operate for at least two years during its primary mission. It follows the successful blastoff of the joint NASA/JAXA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory satellite on Feb 27.
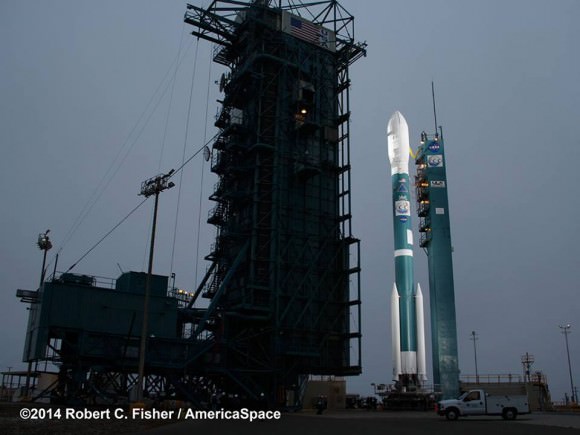

The two stage Delta II 7320-10 launch vehicle is 8 ft in diameter and approximately 128 ft tall and was equipped with a trio of first stage strap on solid rocket motors. This marked the 152nd Delta II launch overall and the 51st for NASA since 1989.
The last time a Delta II rocket flew was nearly three years ago in October 2011 from Vandenberg for the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) weather satellite.
The final Delta II launch from Cape Canaveral on Sept. 10, 2011 boosted NASA’s twin GRAIL gravity mapping probes to the Moon.
The next Delta II launch later this year from Vandenberg involves NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission and counts as another of NASA’s five Earth science missions launching in 2014.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing OCO-2, GPM, Curiosity, Opportunity, Orion, SpaceX, Boeing, Orbital Sciences, MAVEN, MOM, Mars and more Earth & Planetary science and human spaceflight news.