NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN) has been responsible for maintaining contact with missions venturing beyond Low Earth Orbit (LEO) since 1963. In addition to relaying communications and instructions, the DSN has sent breathtaking images and invaluable science data back to Earth. As missions become more sophisticated, the amount of data they can gather and transmit is rapidly rising. To meet these growing needs, NASA has transitioned to higher-bandwidth radio spectrum transmissions. However, there is no way to increase data rates without scaling the size of its antennas or the power of its radio transmitters.
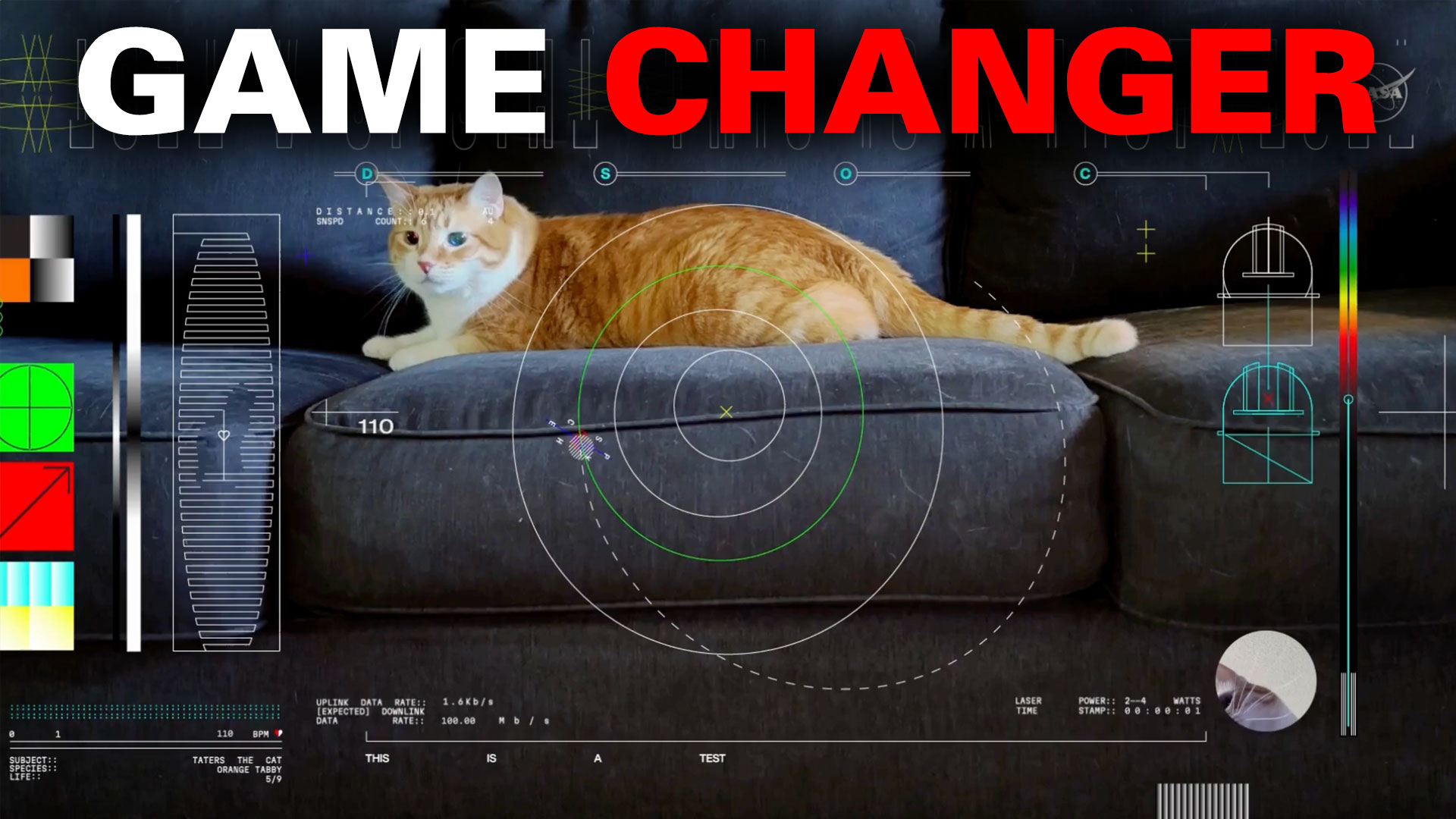
To meet these needs, NASA has created the Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC), which relies on focused light (lasers) to stream very high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space. Compared to conventional radio, optical arrays are typically faster, more secure, lighter, and more flexible. In a recent test, NASA used this technology demonstrator to beam a video to Earth from a record-setting distance of 31 million km (19 million mi) – about 80 times the distance between the Earth and the Moon. The video, featuring a cat named Taters, marks a historic milestone and demonstrates the effectiveness of optical communications.
Continue reading “NASA Tightbeams a Cat Video From 31 Million Kilometers Away”