By now, you may have already heard the latest tale of gloom and doom surrounding the upcoming series of lunar eclipses.
This latest “End of the World of the Week” comes to us in what’s being termed as a “Blood Moon,” and it’s an internet meme that’s elicited enough questions from friends, family and random people on Twitter that it merits addressing from an astronomical perspective.
Like the hysteria surrounding the supposed Mayan prophecy back in 2012 and Comet ISON last year, the purveyors of Blood Moon lunacy offer a pretty mixed and often contradictory bag when it comes down to actually what will occur.
But just like during the Mayan apocalypse nonsense, you didn’t have to tally up just how many Piktuns are in a Baktun to smell a rat. December 21st 2012 came and went, the galactic core roughly aligned with the solstice — just like it does every year — and the end of the world types slithered back into their holes to look for something else produce more dubious YouTube videos about.
Here’s the gist of what’s got some folks wound up about the upcoming cycle of eclipses. The April 15th total lunar eclipse is the first in series of four total eclipses spanning back-to-back years, known as a tetrad. There are eight tetrads in the 21st century: if you observed the set total lunar eclipses back in 2003 and 2004, you saw the first tetrad of the 21st century.
The eclipses in this particular tetrad, however, coincide with the Full Moon marking Passover on April 15th and April 4th and the Jewish observance of Sukkot on October 8th and September 28th. Many then go on to cite the cryptic biblical verse from Revelation 6:12, which states;
“I watched as he opened the sixth seal. There was a great earthquake. The Sun turned black like sackcloth made of goat hair. The whole Moon turned blood red.”
Whoa, some scary allegory, indeed… but does this mean the end of the world is nigh?
I wouldn’t charge that credit card through the roof just yet.
First off, looking at the eclipse tetrads for the 21st century, we see that they’re not really all that rare:
21st century eclipse tetrads:
| Eclipse #1 | Eclipse #2 | Eclipse #3 | Eclipse #4 |
| May 16th, 2003 | November 9th, 2003 | May 4th , 2004 | October 28th, 2004 |
| April 15th, 2014*+ | October 8th, 2014 | April 4th, 2015*+ | September 28th, 2015 |
| April 25th, 2032 | October 18th, 2032 | April 14th, 2033*+ | October 8th, 2033 |
| March 25th, 2043* | September 19th, 2043 | March 13th, 2044 | September 7th, 2044 |
| May 6th, 2050 | October 30th, 2050 | April 26th, 2051 | October 19th, 2051 |
| April 4th, 2061*+ | September 29th, 2061 | March 25th, 2062* | September 18th, 2062 |
| March 4th, 2072 | August 28th, 2072 | February 22nd, 2073 | August 17th, 2073 |
| March 15th, 2090 | September 8th, 2090 | March 5th, 2091 | August 29th, 2091 |
| *Paschal Full Moon | |||
| +Eclipse coincides with Passover | |||
Furthermore, Passover is always marked by a Full Moon, and a lunar eclipse always coincides with a Full Moon by definition, meaning it cannot occur at any other phase. The Jewish calendar is a luni-solar based calendar that attempts to mark the passage of astronomical time via the apparent course that the Sun and the Moon tracks through the sky. The Muslim calendar is an example of a strictly lunar calendar, and our western Gregorian calendar is an example of a straight up solar one. The Full Moon marking Passover often, though not always, coincides with the Paschal Moon heralding Easter. And for that matter, Passover actually starts at sunset the evening prior in 2014 on April 14th. Easter is reckoned as the Sunday after the Full Moon falling after March 21st which is the date the Catholic Church fixes as the vernal equinox, though in this current decade, it falls on March 20th. Easter can therefore fall anywhere from March 22nd to April 25th, and in 2014 falls on the late-ish side, on April 20th.
To achieve synchrony, the Jewish calendar must add what’s known as embolismic or intercalculary months (a second month of Adar) every few years, which in fact it did just last month. Eclipses happen, and sometimes they occur on Passover. It’s rare that they pop up on tetrad cycles, yes, but it’s at best a mathematical curiosity that is a result of our attempt to keep our various calendrical systems in sync with the heavens. It’s interesting to check out the tally of total eclipses versus tetrads over a two millennium span:
| Century | Number of Total Lunar Eclipses | Number of Tetrads | Century | Number of Total Lunar Eclipses | Number of Tetrads |
| 11th |
62 |
0 |
21st |
85 |
8 |
| 12th |
59 |
0 |
22nd |
69 |
4 |
| 13th |
60 |
0 |
23rd |
61 |
0 |
| 14th |
77 |
6 |
24th |
60 |
0 |
| 15th |
83 |
4 |
25th |
69 |
4 |
| 16th |
77 |
6 |
26th |
87 |
8 |
| 17th |
61 |
0 |
27th |
79 |
7 |
| 18th |
60 |
0 |
28th |
64 |
0 |
| 19th |
62 |
0 |
29th |
57 |
0 |
| 20th |
81 |
5 |
30th |
63 |
1 |
Note that over a five millennium span from 1999 BC to 3000 AD, the max number of eclipse tetrads that any century can have is 8, which occurs this century and last happened in the 9th century AD.
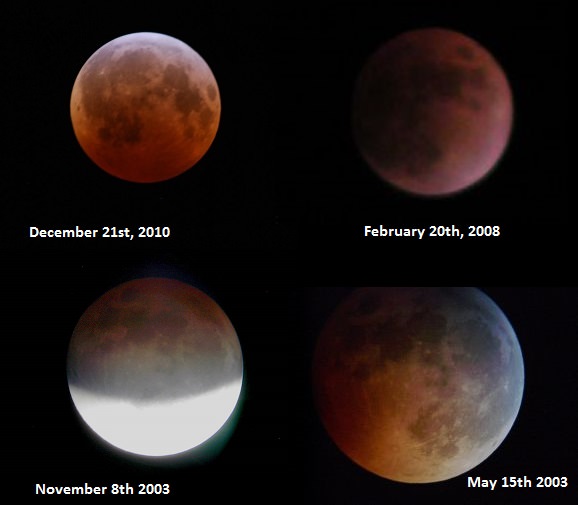
Of course, the visual appearance of a “Blood of the Moon” that’s possibly alluded to in Revelation is a real phenomena that you can see next week from North and South America as the Moon enters into the dark umbra or core of the shadow of the Earth. But this occurs during every total lunar eclipse, and the redness of the Moon is simply due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere. Incidentally, this redness can vary considerably due to the amount of dust, ash, and particulate aerosols aloft in the Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in anything from a bright cherry red eclipse during totality to an eclipsed Moon almost disappearing from view altogether… but it’s well understood by science and not at all supernatural.

Curiously, the Revelation passage could be read to mean a total solar eclipse as well, though both can never happen on the same day. Lunar and solar eclipses occur in pairs two weeks apart at Full and New Moon phases when the nodes of the Moon’s ecliptic crossing comes into alignment with the Sun — known as a syzygy, an ultimate triple word score in Scrabble, by the way — and this eclipse season sees a non-central annular eclipse following the April 15th eclipse on April 29th.
And yes, earthquakes, wars, disease, relationship breakups and lost car keys are on tap to occur in 2014 and 2015… just like during any other year. Lunar eclipses marked the fall of Constantinople in 1453 and the World Series victory of the Red Sox in 2004, but they’re far from rare. We humans love to see patterns, and sometimes this habit works against us, making us see them where none exists. This is simply a case of the gambler’s fallacy, counting the hits at the cost of the misses. We could just as easily make a case that the upcoming eclipse tetrad of April 15th, October 8th, April 4th and September 28th marks US Tax Day, Croatian Independence Day, The Feast of Benedict of the Moor & — Michael Scott take note — International World Rabies Day… perhaps the final 2015 eclipse should be known as a “Rabies Moon?”
So, what’s the harm in believing in a little gloom and doom? The harm in believing the world ends tomorrow comes when we fail to plan for still being here the day after. The harm comes when something like the Heavens Gate mass suicide goes down. We are indeed linked to the universe, but not in the mundane and trivial way that astrologers and doomsdayers would have you believe. Science shows us where we came from and where we might be headed. We’ve already fielded queries from folks asking if it’s safe (!) to stare at the Blood Moon during the eclipse, and the answer is yes… don’t give in to superstition and miss out on this spectacular show of nature because of some internet nonsense.
The upcoming lunar eclipse next week won’t mean the end of the world for anyone, except, perhaps, NASA’s LADEE spacecraft… be sure not to miss it!