Did the Moon appear a little on crimson side to you last night? It’s not your imagination, but it was a fine textbook example of a total lunar eclipse. This was the first total lunar eclipse visible from the Earth since late 2011, and the first of four visible from the Americas over the next 18 months.
And although much of the U.S. and Canadian eastern seaboard was under cloud cover, those west of the Mississippi River were treated to a fine show. We were the lucky exception here at Astroguyz HQ just north of Tampa Bay in Florida, as the storm front held off juuusst long enough to witness the eclipse in its entirety.
We will admit, though, that there were some tense moments. A wave of thick clouds threatened to end our session altogether just moments before the onset of totality before finally abating. We shot stills, streamed video, made observations, and heck, just stepped back once in a while to stare at the ruby-tinged beauty that was totality.
And judging from the flurry of web traffic, the odd late Monday night/ early Tuesday morning timing for this eclipse did little to stem folks interest. We noted to Virtual Star Party co-host that the excitement was reminiscent to the early morning landing of Curiosity on the Red Planet.
Anyhow, here’s just a sampling of some of the great pics currently pouring in to Universe Today:

Visually, we’d place this morning’s eclipse between a Danjon value of 3 and 4, with a bright yellowish rim contrasting with a dark, coppery core near the center of the umbra. One astute viewer noted during the webcast that the eclipsed Moon took on a decidedly 3-D appearance, versus its usual flat look when nearing Full.

And speaking of Mars, we fielded lots of “what are those bright stars nearby?” questions as well. The bright blue-white star Spica and the planet Mars “photobombed” many eclipse images. Spica just missed being occulted by the Moon during the eclipse by less than two degrees, And Mars just passed opposition this week and was at its closest approach to the Earth for 2014 on the night of the eclipse.
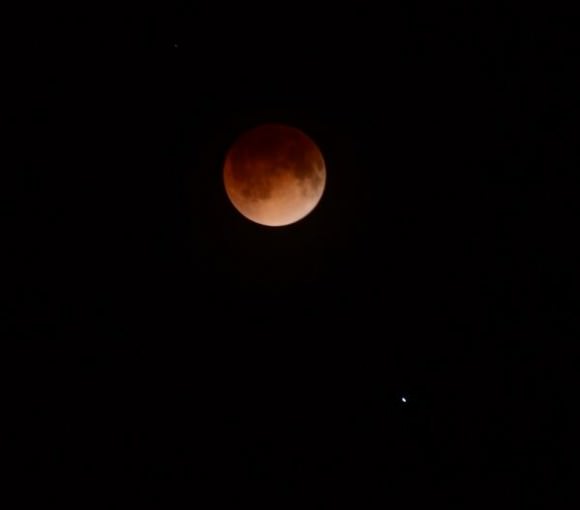

As totality approached, shutter-speeds became longer as the red edge of the Moon became apparent. It always amazes me to think that the Earth casts that long red shadow back into the void of space every night, but its only during a lunar eclipse that you actually get to see it. We’re always told that the Earth is round, but during a lunar eclipse is one of the only times that you can really witness this curve, up close and personal.

This eclipse was placed reasonably high in the sky for Northern hemisphere viewers, though that also meant a lack of pics with foreground, except of course for creative shots like the one above. And with the explosion of digital imaging technology, its amazing what folks are doing to image eclipses, even using mobile phones:
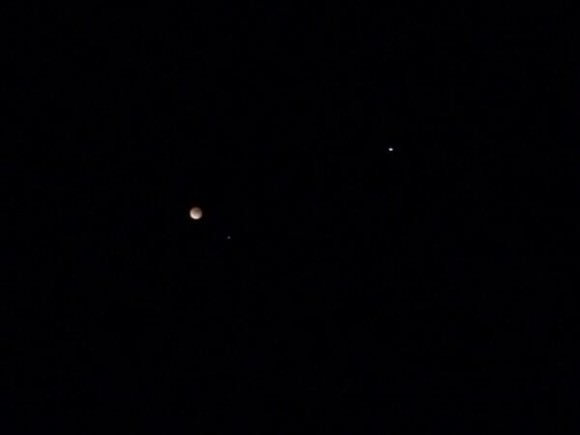

We’ve come a long way since the days of film and doing back of the envelope calculations for afocal SLR photography of the Moon, that’s for sure. Unlike solar totality, lunar eclipses are a long at stately affair. In fact, totality during this eclipse lasted for one hour and 18 minutes, about 29 minutes short of the theoretical maximum. This morning’s eclipse won’t be topped in length until 2018.

This also marked our first attempts at adventures in live-streaming an eclipse both on UStream and G+, which was a blast. Thanks to co-hosts and saros chasers Scott Lewis, Fraser Cain, Thad Szabo and Katie Mack (@AstroKatie) for making the broadcast a success!
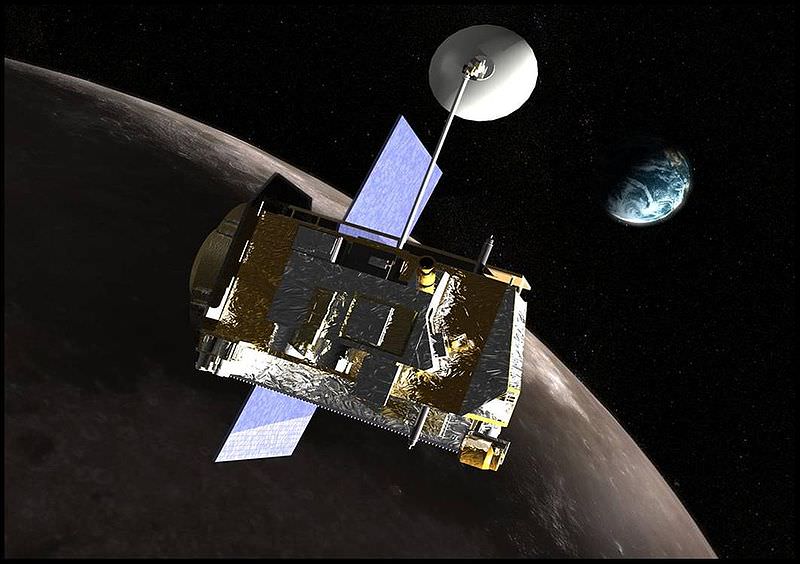
As of yet, there’s no images of the eclipse from space-based assets, though some may surface. Universe Today’s Elizabeth Howell noted that NASA engineers took precautions to protect the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter during the event: an extended lack of sunlight is a bad thing for solar-powered spacecraft. As of yet, there’s no word as to how the LADEE spacecraft also in orbit around the Moon fared, though its due to complete its mission and crash into the Moon this month.

And like the “Blue,” “Super” and “Mini” Moon, the Blood Moon meme is now — for better or worse — here to stay. We’ve already fielded multiple queries for media sources asking if the current tetrad of eclipses has any special significance, and the answer is no; I would still file your taxes on this April the 15th. Eclipses happen, as do wars, earthquakes and lost car keys… each and every year.

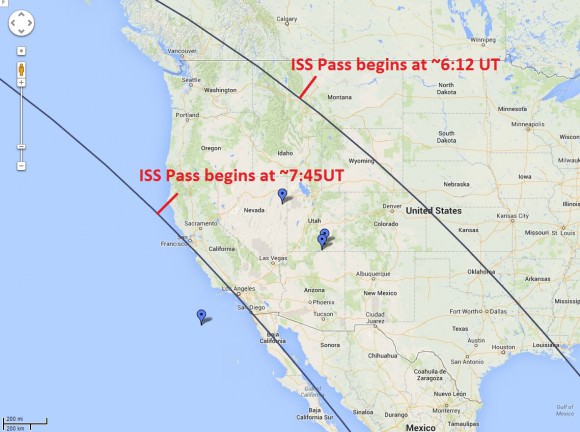
Want more? There’s no word yet as to if anyone caught any of the more bizarre challenges during this eclipse, such as completing a triple saros exeligmos, catching an ISS transit, spotting a selenelion or catching a stellar occultation during the eclipse. If you did any of the above, let us know!
And finally, the biggest post-eclipse question on everyone’s mind is always: when’s the next one? Well, Australians only have to wait two weeks until a partial solar eclipse graces their continent on April 29th… and the next total lunar eclipse once again favors North America and the Pacific region on October 8th, 2014.
T’was a great kickoff this morning of eclipse season 1 of 2 for 2014!