Since the dawn of the Space Age in 1957, thousands of artifacts and memorabilia have been flown into space. Some have been hoisted on brief suborbital flights, while others have been flung out of the solar system, never to return. And of course, it’s become a fashionable — and highly commercialized — trend as of late to briefly loft products, stuffed animals, etc via balloon towards the tenuous boundary of space. Fly a souvenir or artifact into orbit, and it goes from mundane to priceless. But a few may also serve as a final testament to the our ephemeral existence as a species long after our passing.
Here’s a look at some of the most memorable objects sent into space:
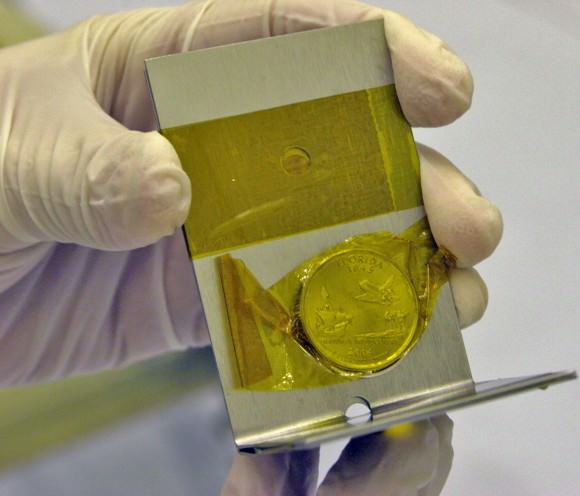

New Horizons Memorabilia
Launched on January 19th, 2006, New Horizons is headed towards a historic encounter with Pluto and its moons next year. From there, New Horizons will survey any Kuiper Belt objects of opportunity along its path and then head out of the solar system, becoming the fifth spacecraft to do so. In addition to a suite of scientific instruments, New Horizons also carries the ashes of Pluto discoverer Clyde Tombaugh, a Florida & Maryland state quarter, a piece of Scaled Composites SpaceShipOne, and an American flag. These will doubtless confuse any extraterrestrial salvagers!
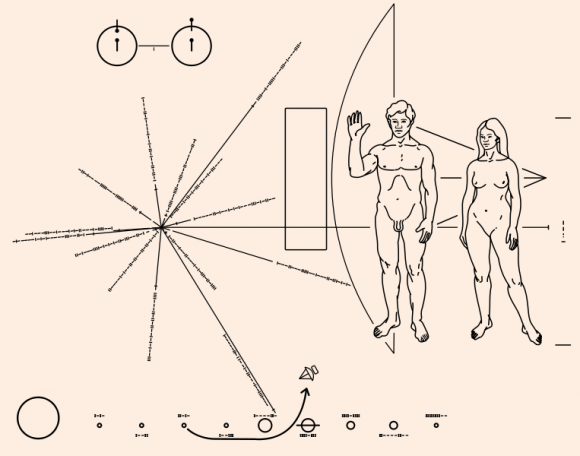
The Pioneer Plaques
The first spacecraft sent on escape trajectories out of our solar system, the Pioneer 10 and 11 spacecraft each carry a plaque which serves as a sort of postcard “greeting” to any future interceptors. The plaque depicts a diagram of the solar system, a map of our location in the galaxy using the positions of known pulsars, and a nude man & woman, which actually generated lots of controversy. Scientist James Van Allen tells of deliberately placing a fingerprint on the Pioneer 10 plaque in his biography The First Eight Billion Miles.

The Voyager 1 and 2 Golden Records
Conceived and designed in part by Carl Sagan, these records contain images and sounds of the Earth that’ll most likely outlive humanity. The records carry greetings in 55 languages, music ranging from Mozart to Chuck Berry, 116 images and more, along with instructions and a stylus for playback. The record is also enclosed in an aluminum cover electroplated with Uranium-238, which an alien civilization could use to date its manufacture via half-life decay.
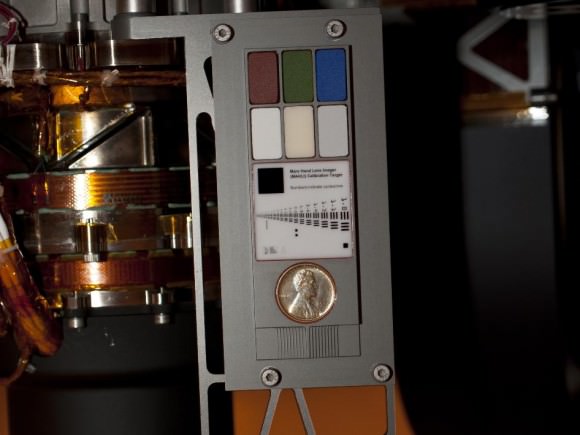
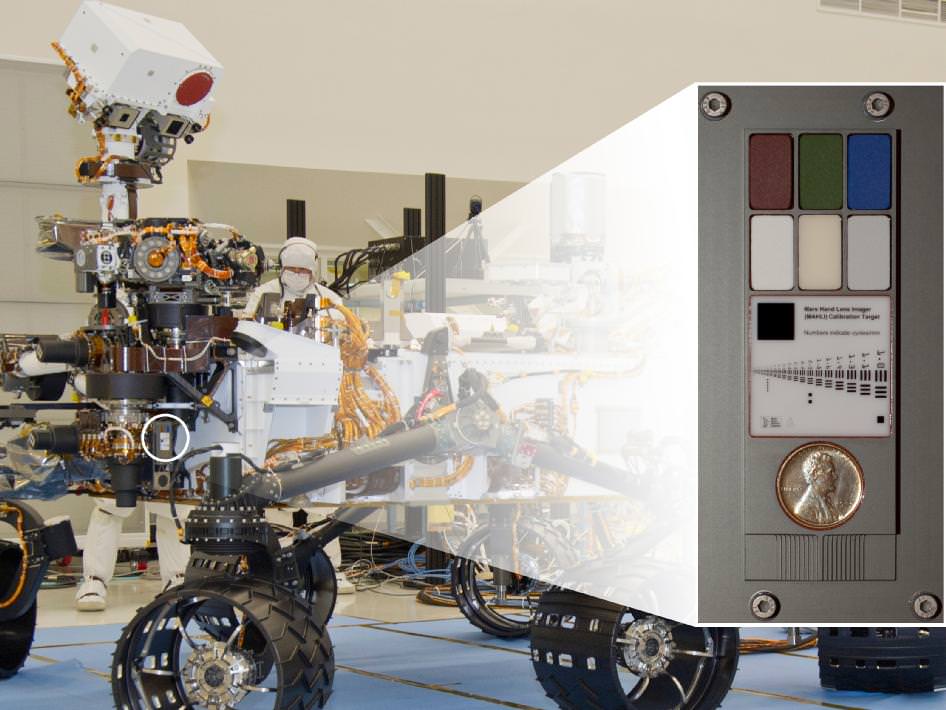
The Mars Curiosity Penny
Strange but true: The Mars rover Curiosity carries a 1909 U.S. Penny for a backup camera calibration target. The penny itself is embedded just below the primary color calibration targets used by Curiosity’s MArs Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI). Rare enough on Earth, the 1909 Lincoln “Mars penny” will be priceless to future collectors!
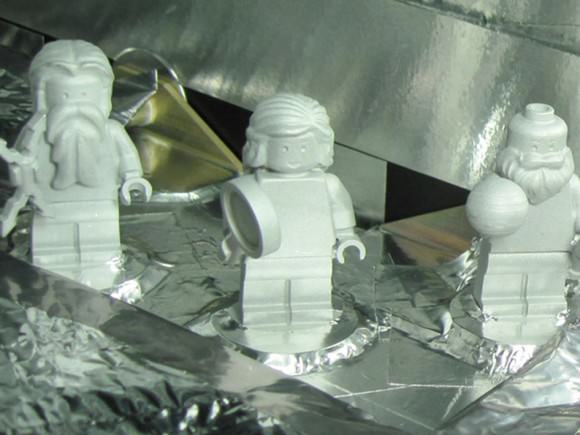

Juno’s LEGO Figurines
Mini-figurines of Galileo and the Roman deities Jupiter and Juno were launched in 2011 aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft en route to Jupiter . LEGO has flown products aboard the U.S. Space Shuttles and to the International Space Station previously, but Juno’s cargo represents the “most distant LEGO launch” ever. The figurines will burn up in Jupiter’s atmosphere along with the spacecraft at the end of the mission in October 2017.

Apollo 15 Postal Covers Fiasco
Apollo 15 astronauts got in some hot water over a publicity scheme. The idea that stamp collector and dealer Hermann Sieger approached the astronauts with was simple: 400 commemorative postage stamp covers would be postmarked at point of departure from the Kennedy Space Center and again at the return point of arrival aboard the USS Okinawa after their circuitous journey via the Moon. NASA was less than happy with the whole affair, and Command Module Pilot Al Worden recounts the aftermath in his book, Falling to Earth.

Haiku for MAVEN
Last year’s MAVEN mission to Mars also carried haiku submitted by space fans. Over 12,530 valid entries were submitted and over 1,100 haiku received the necessary minimum of two votes to be included on a DVD disk affixed to the spacecraft. MAVEN reaches orbit around Mars in October 2014.
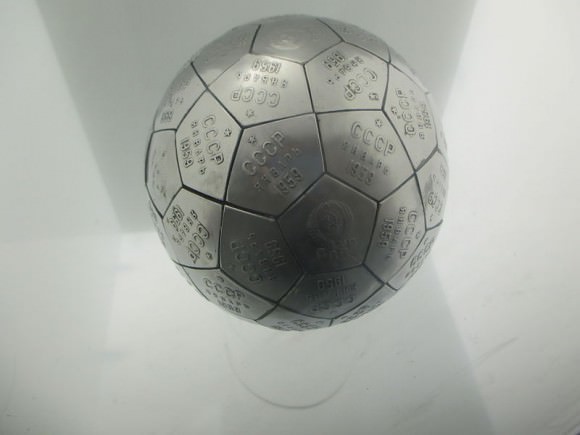

Luna 2: A Russian Pennant on Moon
On September 12th, 1959, the Soviet Union’s Luna 2 spacecraft became the first man-made object to impact the Moon. Luna 2 carried two spherical “pennants” composed of pentagon-shaped elements engraved with the USSR Coat of Arms and Cyrillic letters translating into “CCCP/USSR September 1959.” An identical pennant is now on display in the Kansas Cosmosphere.

A GeoSat Time Capsule Aboard EchoStar XVI
A disk entitled Last Pictures similar to the Voyager records was placed on a satellite headed to geosynchronous orbit in 2012. Launched aboard EchoStar XVI, Last Pictures is an ultra-archival disk containing 100 snapshots of modern life along with interviews with several 21st century artists and scientists. Geosynchronous satellites aren’t subject to atmospheric drag, and may be the last testament to the existence of humanity on Earth millions of years hence.

Lunar Prospector Carries An Astro-Geologist’s Ashes to the Moon
Though he never made the selection to become an astronaut, scientist Eugene Shoemaker did make a posthumous trip to the Moon. The Lunar Prospector spacecraft departed Earth with Shoemaker’s ashes on January 7th, 1998 in a capsule wrapped in brass foil. Lunar Prospector impacted the south pole of the Moon on July 31st, 1999.

SpaceX Takes Star Trek Actor to Space
The ashes actor James Doohan (AKA Scotty) were launched aboard a 2012 SpaceX flight to the International Space Station. The COTS Demo Flight, or COTS 2, was the first commercial spacecraft to berth at the ISS. SpaceX had flown a small amount of Doohan’s ashes on the 2008 unsuccessful test launch of the Falcon 1 rocket.

Cheese Wheel Makes a Suborbital Journey
All eyes were also on SpaceX during their December 8th 2010 maiden flight of the Dragon space capsule. And the hinted mystery cargo? None other than a wheel of cheese, a nod by SpaceX CEO Elon Musk to a classic Monty Python sketch.
The Apollo 12 “Moon Museum”
Did it really go into space? One of the legends surrounding the Apollo program is the existence of what’s been dubbed the “Moon Museum.” This was a postage stamp-sized “gallery” of art which included a sketch by Andy Warhol and other 1960s artists that was supposedly attached to descent stage of Apollo 12 and left on the Moon. It will be up to future lunar visitors to confirm or deny its existence!
…And lastly, I give you the “Space Hubcap”
Was the first man-made object propelled into space actually a 1 ton armor plate? On August 27th, 1957 — just two months prior to Sputnik 1 — the Pascal-B underground nuclear test was conducted in southern Nevada. During the explosion, a steel plate cap was blasted off of a test shaft. The plate could be seen in the initial high-speed video frames, and it was estimated to have reached a speed six times the sufficient escape velocity to depart Earth. To this day, no one knows if this strange artifact of early Space Age folklore still roams the void of space, or simply vaporized due to atmospheric compression at “launch”.