The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. More specifically, it is a barred spiral galaxy, meaning that within its central region, there is a bar shape off of which the spirals emanate. About two-thirds of spiral galaxies are barred spirals, and astronomers have thought this difference is just a variance in how density waves cluster stars in a galaxy. But a new study suggests that the bar of the Milky Way may have been caused by an ancient collision with another galaxy.
Continue reading “Did the Last Great Galactic Merger Create the Milky Way's Bar?”A Star Near the Center of the Milky Way is a Visitor from Beyond
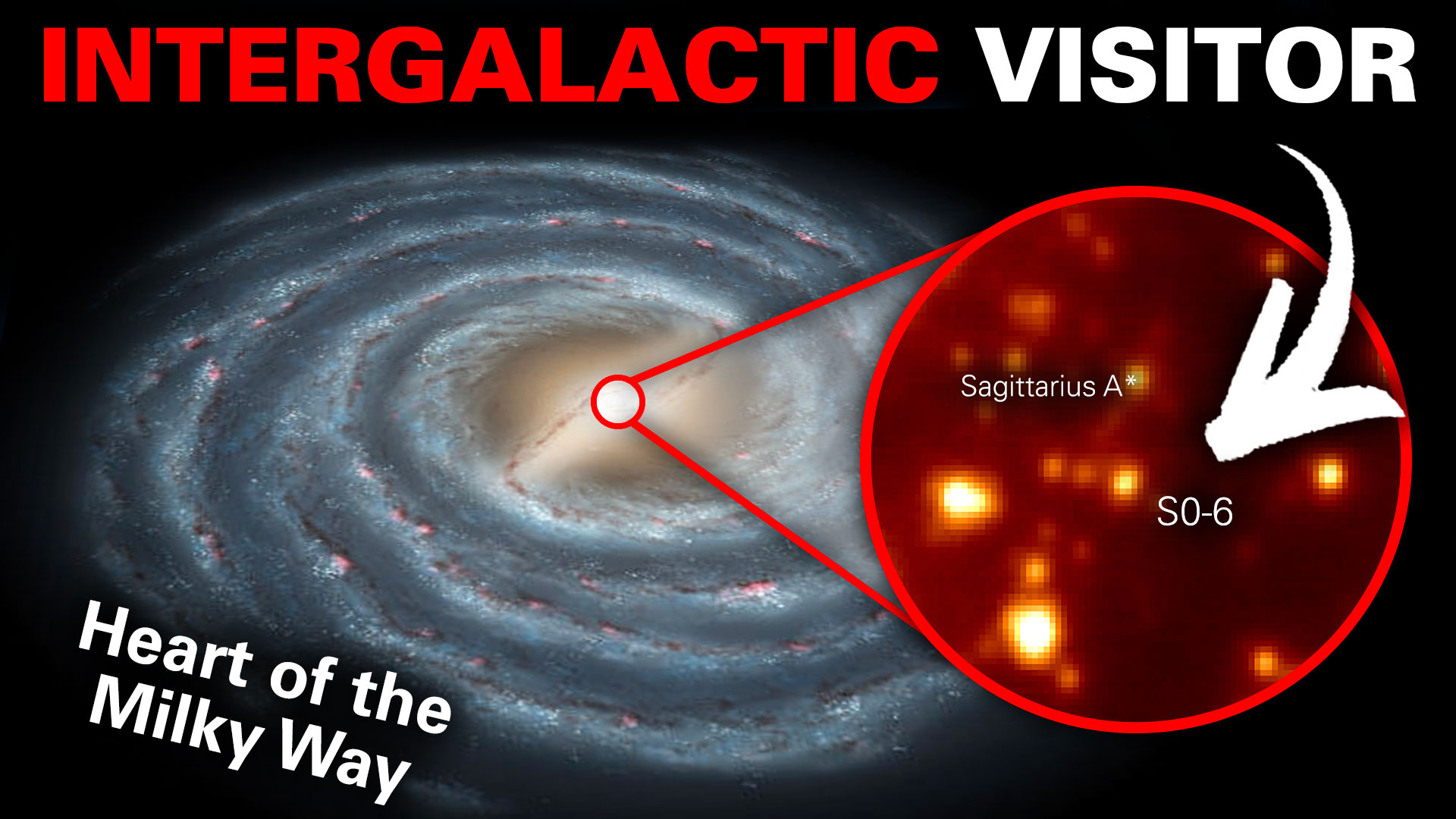
There’s an alien red giant star orbiting in the center of our galaxy. It’s called S0-6 and has chemical fingerprints from its birthplace far outside the Milky Way. This ancient star is spiraling slowly in toward the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*) at the heart of the Milky Way. Eventually, it could get drawn into the black hole and destroyed after traveling for tens of thousands of years to get there.
Continue reading “A Star Near the Center of the Milky Way is a Visitor from Beyond”The International Space Station Celebrates 25 Years in Space
NASA recently celebrated the 25th anniversary of the International Space Station (ISS) with a space-to-Earth call between the 7-person Expedition 70 crew and outgoing NASA Associate Administrator, Bob Cabana, and ISS Program Manager, Joel Montalbano. On December 6, 1998, the U.S.-built Unity module and the Russian-built Zarya module were mated in the Space Shuttle Endeavour cargo bay, as Endeavour was responsible for launching Unity into orbit that same day, with Zarya having waited in orbit after being launched on November 20 from Kazakhstan.
Continue reading “The International Space Station Celebrates 25 Years in Space”Fly Slowly Through Enceladus' Plumes to Detect Life
Enceladus is blasting water into space from the jets at its southern pole. This makes it the ideal place to send a dedicated mission, flying the spacecraft through the plumes with life-detection instruments s. A new study suggests that a spacecraft must proceed carefully through the plumes, keeping its speed below 4.2 km/second (2,236 miles per hour). Using a specialized, custom-built aerosol impact spectrometer at these speeds will allow fragile amino acids to be captured by the spacecraft’s sample collector. Any faster, they’ll shatter, providing inclusive results.
Continue reading “Fly Slowly Through Enceladus' Plumes to Detect Life”OSIRIS-REx Failed to Deploy its Drogue Chute Properly. Now NASA has Figured out Why

On September 24, 2023, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission returned a precious sample of rocky material from asteroid Bennu to Earth. The capsule landed safely under its main parachute, but it arrived more than a minute early. The cause: a small drogue parachute, designed to slow the spacecraft down prior to the main chute’s deployment, failed to open. After an investigation into the mishap, NASA believes they have determined the cause of the (happily non-catastrophic) failure.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Failed to Deploy its Drogue Chute Properly. Now NASA has Figured out Why”In 1872, a Solar Storm Hit the Earth Generating Auroras from the Tropics to the Poles

Imagine a solar storm generating auroral displays across the entire sky. No, we haven’t quite seen them that strong in the current solar cycle. But, back in February 1872, people around the world reported seeing brilliant northern and southern lights. The culprit? A medium-sized sunspot group that unleased a torrent of charged particles in a coronal mass ejection directed toward Earth.
Continue reading “In 1872, a Solar Storm Hit the Earth Generating Auroras from the Tropics to the Poles”For its Final Trick, Chandrayaan-3 Brings its Propulsion Module to Earth Orbit
On August 23, ISRO’s Vikram lander detached from its propulsion module and made a soft landing near the Moon’s south pole region. The lander then deployed its Pragyan rover, and for two weeks the endearing little solar-powered rover performed marvelously, detecting water ice and characterizing the makeup of the lunar regolith before succumbing to the darkness and cold of the lunar night.
But since the rover mission ended, the propulsion module that brought it to the Moon has made a detour, performing a series of complex maneuvers that took it from a tight lunar orbit back to Earth orbit. This was possible because the module still had more than 100 kg of fuel, allowing scientists to conduct additional maneuvers and experiments.
Continue reading “For its Final Trick, Chandrayaan-3 Brings its Propulsion Module to Earth Orbit”ESA’s Ariel Mission is Approved to Begin Construction

We’re about to learn a lot more about exoplanets. The ESA has just approved the construction of its Ariel mission, which will give us our first large survey of exoplanet atmospheres. The space telescope will help us answer fundamental questions about how planets form and evolve.
Continue reading “ESA’s Ariel Mission is Approved to Begin Construction”Communicating With a Relativistic Spacecraft Gets Pretty Weird

Someday, in the not-too-distant future, humans may send robotic probes to explore nearby star systems. These robot explorers will likely take the form of lightsails and wafercraft (a la Breakthrough Starshot) that will rely on directed energy (lasers) to accelerate to relativistic speeds – aka. a fraction of the speed of light. With that kind of velocity, lightsails and wafercraft could make the journey across interstellar space in a matter of decades instead of centuries (or longer!) Given time, these missions could serve as pathfinders for more ambitious exploration programs involving astronauts.
Of course, any talk of interstellar travel must consider the massive technical challenges this entails. In a recent paper, a team of engineers and astrophysicists considered the effects that relativistic space travel will have on communications. Their results showed that during the cruise phase of the mission (where a spacecraft is traveling close to the speed of light), communications become problematic for one-way and two-way transmissions. This will pose significant challenges for crewed missions but will leave robotic missions largely unaffected.
Continue reading “Communicating With a Relativistic Spacecraft Gets Pretty Weird”99% of Space Junk is Undetectable. That Could Change Soon
Private and military organizations are tracking some of the 170 million pieces of space junk orbiting the planet, but they’re limited to how small an object they can detect. Only chunks larger than a softball can be tracked with radar or optical systems, and that only accounts for less than 1% of the junk out there.
But a new technique is being developed to resolve space junk to pieces smaller than one millimeter in diameter.
Continue reading “99% of Space Junk is Undetectable. That Could Change Soon”




