Falcon 9 SpaceX CRS-2 launch of Dragon spacecraft on March 1, 2013 to the ISS from pad 40 at Cape Canaveral, Florida.- shot from the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building. During 2014, SpaceX plans two flight tests simulating human crewed Dragon emergency abort scenarios launching from right here at pad 40. Credit: Ken Kremer/www.kenkremer.com
Story updated[/caption]
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL – A trio of American companies – SpaceX, Boeing, and Sierra Nevada – are working diligently to restore America’s capability to launch humans into low Earth orbit from US soil, aided by seed money from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program in a public-private partnership.
We’ve been following the solid progress made by all three companies. Here we’ll focus on two crucial test flights planned by SpaceX in 2014 to human rate and launch the crewed version of their entry into the commercial crew ‘space taxi’ sweepstakes, namely the Dragon spacecraft.
Recently I had the opportunity to speak about the upcoming test flights with the head of SpaceX, Elon Musk.
So I asked Musk, the founder and CEO of SpaceX, about “what’s ahead in 2014”; specifically related to a pair of critical “abort tests” that he hopes to conduct with the human rated “version of our Dragon spacecraft.”
“Assuming all goes well, we expect to conduct [up to] two Dragon abort tests next year in 2014,” Musk told me.

The two abort flight tests in 2014 involve demonstrating the ability of the Dragon spacecraft abort system to lift an uncrewed spacecraft clear of a simulated launch emergency.
The crewed Dragon – also known as DragonRider – will be capable of lofting up to seven astronauts to the ISS and remaining docked for at least 180 days.
First a brief overview of the goals of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. It was started in the wake of the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle program which flew its final human crews to the International Space Station (ISS) in mid-2011.
“NASA has tasked SpaceX, Boeing, and Sierra Nevada to develop spacecraft capable of safely transporting humans to the space station, returning that capability to the United States where it belongs,’ says NASA Administrator Charles Bolden.
Since 2011, US astronauts have been 100% dependent on the Russians and their Soyuz capsules to hitch a ride to low Earth orbit and the ISS.
The abort tests are essential for demonstrating that the Dragon vehicle will activate thrusters and separate in a split second from a potentially deadly exploding rocket fireball to save astronauts lives in the event of a real life emergency – either directly on the launch pad or in flight.
“We are aiming to do at least the pad abort test next year [in 2014] with version 2 of our Dragon spacecraft that would carry astronauts,” Musk told me.

SpaceX plans to launch the crewed Dragon atop the human rated version of their own developed Falcon 9 next generation rocket, which is also being simultaneously developed to achieve all of NASA’s human rating requirements.
The initial pad abort test will test the ability of the full-size Dragon to safely push away and escape in case of a failure of its Falcon 9 booster rocket in the moments around launch, right at the launch pad.
“The purpose of the pad abort test is to demonstrate Dragon has enough total impulse (thrust) to safely abort,” SpaceX spokeswoman Emily Shanklin informed me.
For that test, Dragon will use its pusher escape abort thrusters to lift the Dragon safely away from the failing rocket. The vehicle will be positioned on a structural facsimile of the Dragon trunk in which the actual Falcon 9/Dragon interfaces will be represented by mockups.
This test will be conducted on SpaceX’s launch pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. It will not include an actual Falcon 9 booster.
The second Dragon flight test involves simulating an in flight emergency abort scenario during ascent at high altitude at maximum aerodynamic pressure at about T plus 1 minute, to save astronauts lives. The pusher abort thrusters would propel the capsule and crew safely away from a failing Falcon 9 booster for a parachute assisted landing into the Atlantic Ocean.
“Assuming all goes well we expect to launch the high altitude abort test towards the end of next year,” Musk explained.
The second test will use the upgraded next generation version of the Falcon 9 that was successfully launched just weeks ago on its maiden mission from Cape Canaveral on Dec. 3. Read my earlier reports – starting here.
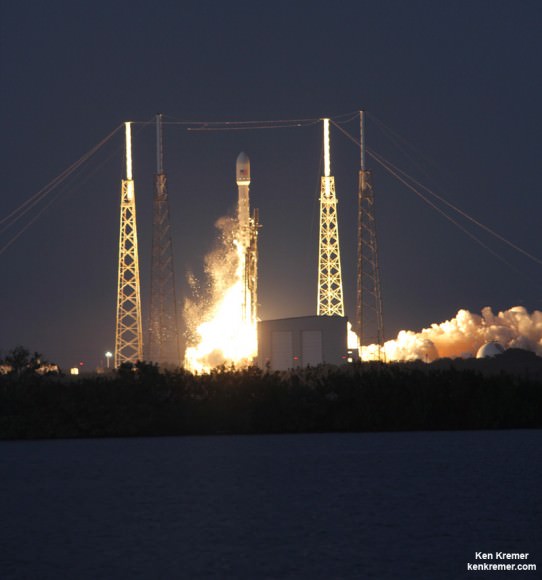

To date, SpaceX has already successfully launched the original cargo version of the Dragon a total of three times. And each one docked as planned at the ISS.
The last cargo Dragon blasted off on March 1, 2013. Read my prior articles starting – here.
The next cargo Dragon bound for the ISS is due to lift off on Feb. 22, 2014 from Cape Canaveral, FL.

Orbital Sciences – the commercial ISS cargo competitor to SpaceX – plans to launch its Cygnus cargo vehicle on the Orb-1 mission bound for the ISS on Jan. 7 atop the firms Antares rocket from NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Watch for my on site reports from NASA Wallops.
NASA’s Commercial Crew Program’s goal is launching American astronauts from U.S. soil within the next four years – by 2017 to the ISS.
The 2017 launch date is dependent on funding from the US federal government that will enable each of the firms to accomplish a specified series of milestones. NASA payments are only made after each companies milestones are successfully achieved.
SpaceX was awarded $440 million in the third round of funding in the Commercial Crew integrated Capability (CCiCAP) initiative which runs through the third quarter of 2014. As of November 2013, NASA said SpaceX had accomplished 9 of 15 milestones and was on track to complete all on time.
Musk hopes to launch an initial Dragon orbital test flight with a human crew of SpaceX test pilots perhaps as early as sometime in 2015 – if funding and all else goes well.
Either a US commercial ‘space taxi’ or the Orion exploration capsule could have blasted off with American astronauts much sooner – if not for the continuing year-by-year slashes to NASA’s overall budget forced by the so called ‘political leaders’ of all parties in Washington, DC.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars and more news.
…………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Orbital Sciences Antares Jan. 7 launch, Curiosity, Orion, MAVEN, MOM, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Jan 6-8: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia on Jan. 7”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, evening