
Continue reading

Continue reading

Using isotope measurements of a supernova remnant, astronomers have calculated the core density of a white dwarf before it exploded.
Continue reading

A rocky world might not need a star to be habitable. It might just need to orbit a large gas planet.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

New research from the Australia National University shows that millions of lasers are the way to propel Breakthrough Starshot on its interstellar mission.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Blue Origin founder Jeff Bezos has announced that he and his brother will be on the New Shepard spacecraft as it makes it inaugural crewed flight to space.
Continue reading

At the 17th International Architecture Exhibition in Venice, an architectural firm showcasing the latest plans for the ESA's international lunar base!
Continue reading
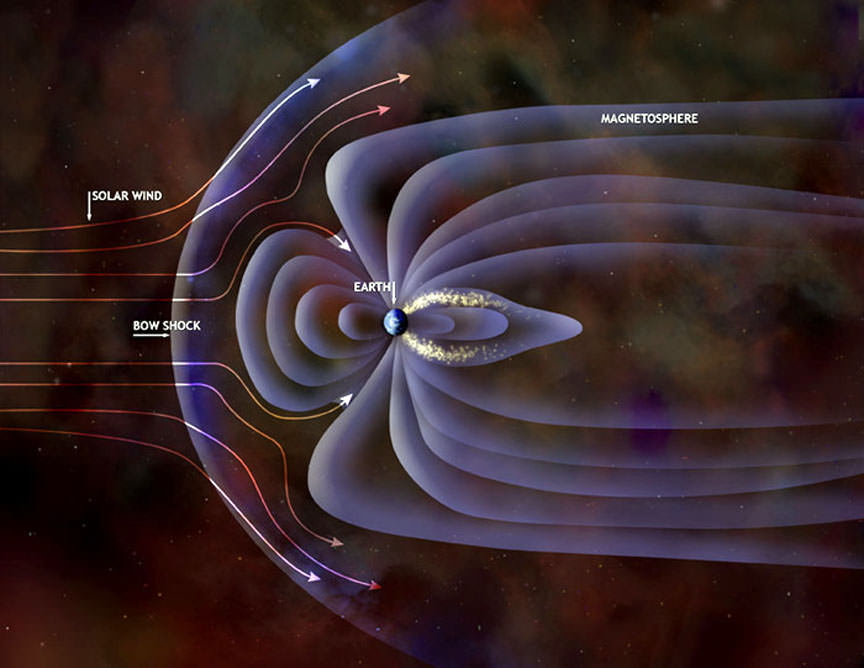
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

That latest image from Hubble shows the NGC 691 spiral galaxy in all of it's glory!
Continue reading
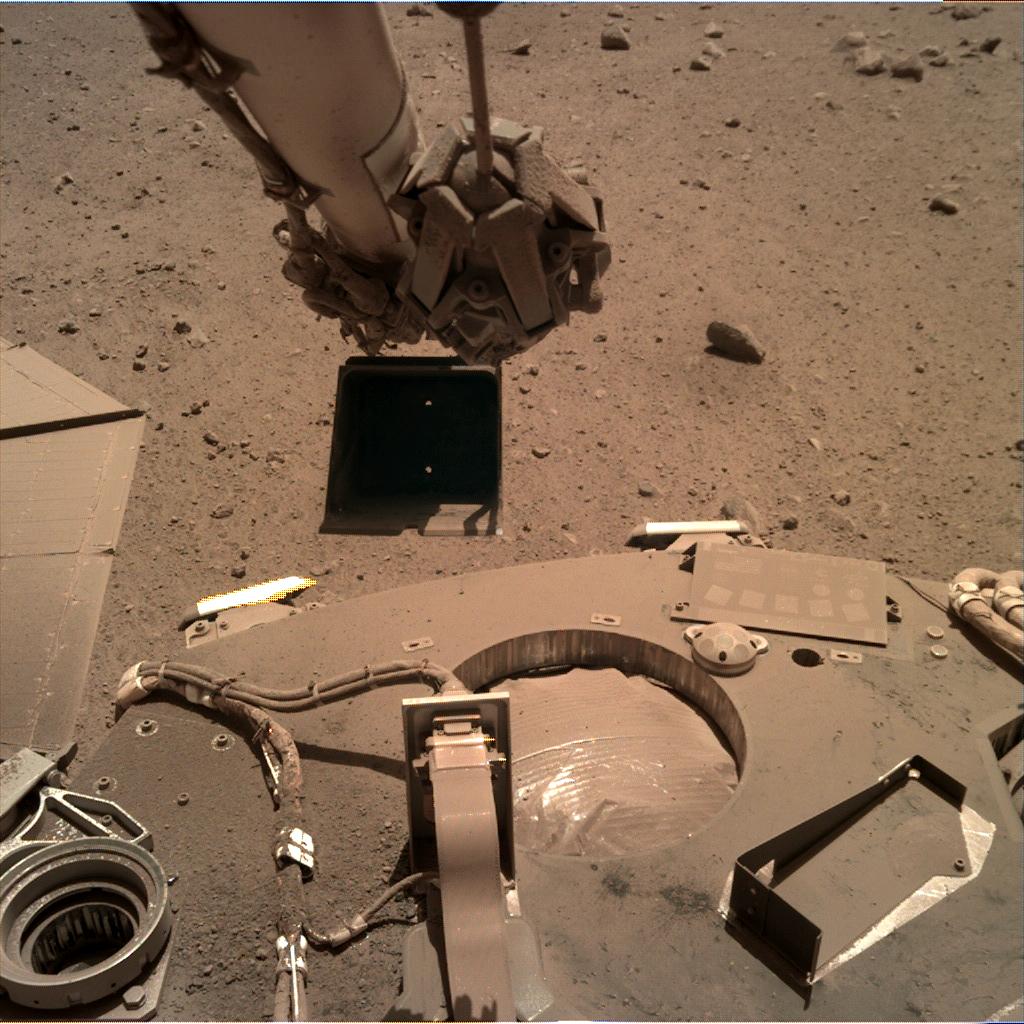
Continue reading

Continue reading

A new tool for measuring the complexity of molecules is able to identify those that must have formed in the presence of life, which will come in very handy for future astrobiology missions.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

NASA recently released a panoramic mosaic image that beautifully captures the mysterious and extremely energetic environment at the heart of our galaxy.
Continue reading

Continue reading

The Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope may reveal the dark edge of a black hole's event horizon.
Continue reading

On its sixth flight, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter suffered a bit of a glitch and was forced to land. But the helicopter has still been a killer mission!
Continue reading

The only annular eclipse of 2021 will produce a fine annular eclipse across most of North America and Europe.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Japan plans to send a robotic rover to explore the surface of the Moon. Here's the kicker, it transforms!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

JAXA and the Tiger Corporation have come together to develop next-generation cooling containers that will allow for regular sample-returns from the ISS
Continue reading

Continue reading

China's Zhurong rover has departed from its lander and commenced science operations, and has the pictures to prove it!
Continue reading

Continue reading

Tiny CubeSats could give us a detailed view of Earth in real time, thanks to folding adjustable mirrors.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

A new simulation by a team of astrophysicists has resulted in the most detailed 3D map of the cosmic web, revealing new Dark Matter structures.
Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

Continue reading

After a year of consultation, interviews, and intensive review, the Space Generation Advisory Council's EAGLE team has released a document on how humanity can live cooperatively and peacefully on the Moon - the Lunar Governance Report!
Continue reading

A new study by a team from Rice University has shown that where a planet forms in its star system could have a drastic effect on whether or not it can support life.
Continue reading
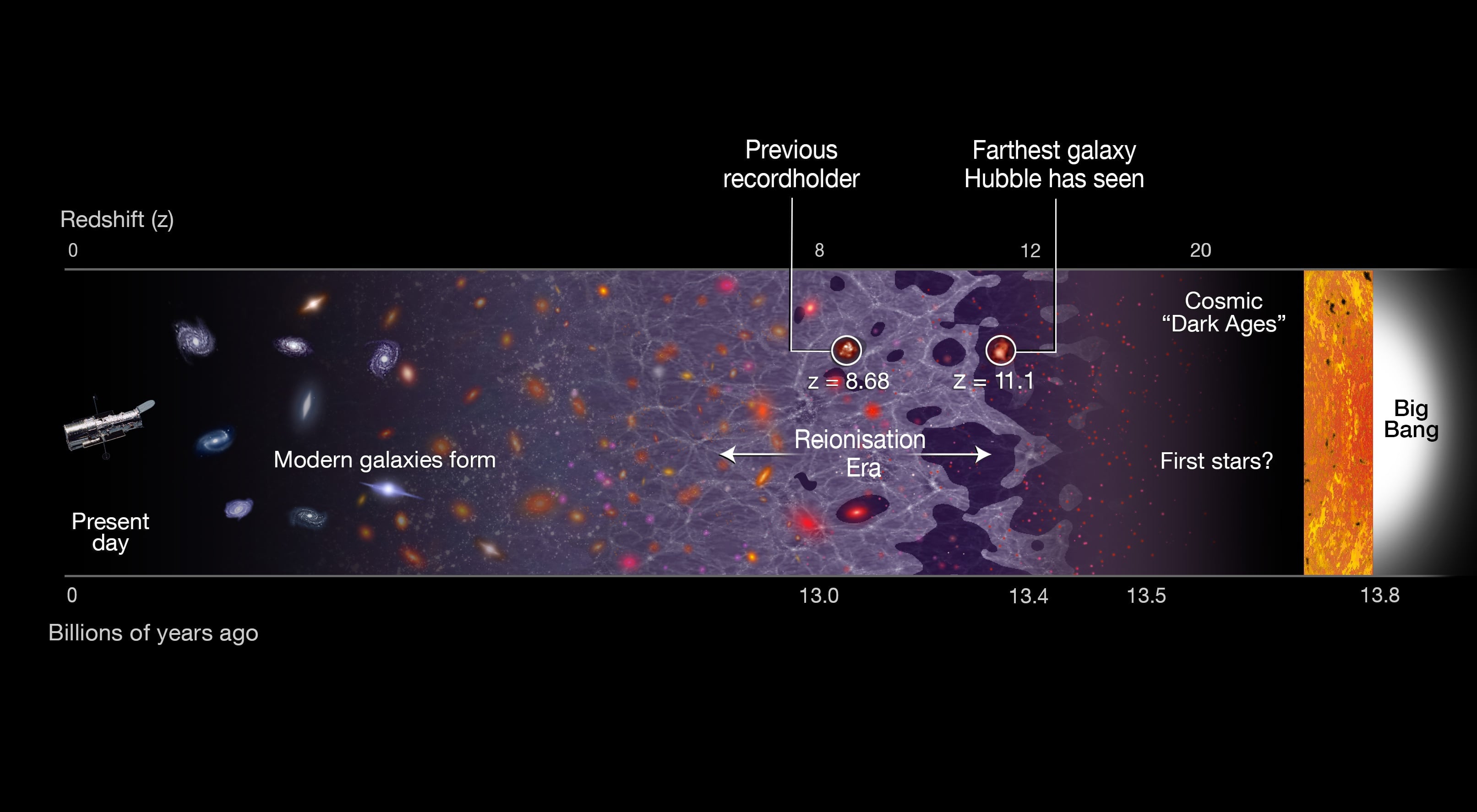
New experiments in particle physics yield surprising results about the earliest matter in the universe.
Continue reading

The Moon turned a ruddy hue during this morning's total lunar eclipse, in one of the top astronomical events of the year.
Continue reading


















































