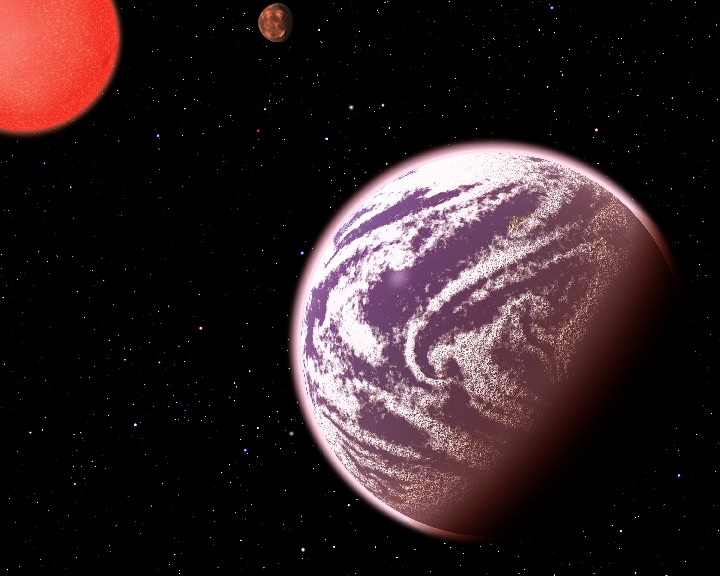
Gas planets aren’t always bloated, monstrous worlds the size of Jupiter or Saturn (or larger) they can also apparently be just barely bigger than Earth. This was the discovery announced earlier today during the 223rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Washington, DC, when findings regarding the gassy (but surprisingly small) exoplanet KOI-314c were presented.
“This planet might have the same mass as Earth, but it is certainly not Earth-like,” said David Kipping of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), lead author of the discovery. “It proves that there is no clear dividing line between rocky worlds like Earth and fluffier planets like water worlds or gas giants.”
Discovered by the Kepler space telescope — ironically, during a hunt for exomoons — KOI-314c was found transiting a red dwarf star only 200 light-years away — “a stone’s throw by Kepler’s standards,” according to Kipping. (Kepler’s observation depth is about 3000 light-years.)

Kipping used a technique called transit timing variations (TTV) to study two of three exoplanets found orbiting KOI-314. Both are about 60% larger than Earth in diameter but their respective masses are very different. KOI-314b is a dense, rocky world four times the mass of Earth, while KOI-314c’s lighter, Earthlike mass indicates a planet with a thick “puffy” atmosphere… similar to what’s found on Neptune or Uranus.
Unlike those chilly worlds, though, this newfound exoplanet turns up the heat. Orbiting its star every 23 days, temperatures on KOI-314c reach 220ºF (104ºC)… too hot for water to exist in liquid form and thus too hot for life as we know it.
In fact Kipping’s team found KOI-314c to only be 30 percent denser than water, suggesting that it has a “significant atmosphere hundreds of miles thick,” likely composed of hydrogen and helium.
It’s thought that KOI-314c may have originally been a “mini-Neptune” gas planet and has since lost some of its atmosphere, boiled off by the star’s intense radiation.
Not only is KOI-314c the lightest exoplanet to have both its mass and diameter measured but it’s also a testament to the success and sensitivity of the relatively new TTV method, which is particularly useful in multiple-planet systems where the tiniest gravitational wobbles reveal the presence and details of neighboring bodies.
(Watch the latest Kepler Orrery video here)
“We are bringing transit timing variations to maturity,” Kipping said. He added during the closing remarks of his presentation at AAS223: “It’s actually recycling the way Neptune was discovered by watching Uranus’ wobbles 150 years ago. I think it’s a method you’ll be hearing more about. We may be able to detect even the first Earth 2.0 Earth-mass/Earth-radius using this technique in the future.”